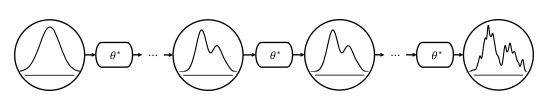
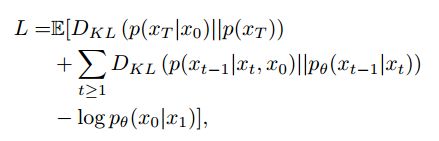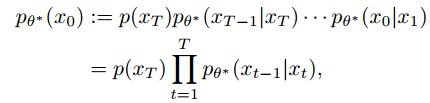On the Design Fundamentals ofDiffusion Models: A Survey
1 Title
On the Design Fundamentals of Diffusion Models: A Survey(Ziyi Chang, George A. Koulieris, and Hubert P. H. Shum)
2 Conclusion
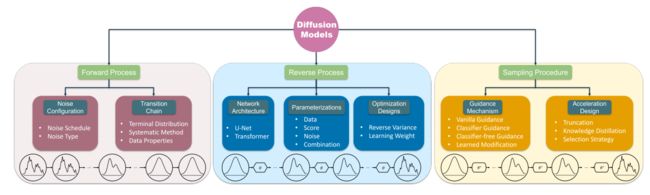
This study seeks to address this gap by providing a comprehensive and coherent review on component-wise design choices in diffusion models. Specifically, this paper organize this review according to their three key components, namely the forward process, the reverse process, and the sampling procedure. This allows us to provide a fine-grained perspective of diffusion models, benefiting future studies in the analysis of individual components, the applicability of design choices, and the implementation of diffusion models.
3 Good Sentences
1. Although these three components generally define the generic pipeline, they are currently lacking a comprehensive survey. Some existing survey papers focus on higher-level solutions to facilitate applications, and explore less on the design details of each component Some concentrate on specific domains or aspects of diffusion models, lacking insights on the holistic design fundamentals of the generic pipeline. Others focus on the application side, and thereby provide fewer observations on theoretical designs. Overall, a survey that concentrates specifically on designing the aforementioned components of diffusion models is lacking.(The existential significance of this learning)
2.This survey bridges the gap in the literature by offering a thorough and cohesive review of component-wise design fundamentals in diffusion models. In particular, we have organized design fundamentals of diffusion models into the forward process, the reverse process, and the sampling procedure(What has this paper done)
3.Transformer is increasingly adapted as an alternative architecture for the denoising network. In principle, a transformer can directly substitute U-Nets because it can also maintain the data dimensions. Nevertheless, direct substitution empirically does not yield better quality because transformers are known to model global relations and may suffer from losing short-range dependency. Therefore, some U-Net structures are usually added to transformers to retain the benefits of U-Net as much as possible.(Why Transformer can't be completely replaced U-net)
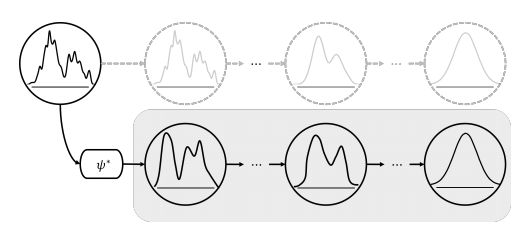
如图,本文将扩散模型的训练分成三个过程:前向过程、逆向过程和采样过程,分别复杂添加噪声,训练模型以及生成样本。
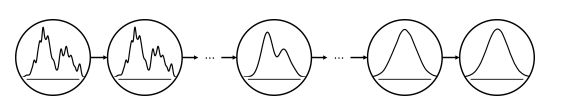
前向过程如上图所示,通过具有多个时间步长的分布过渡链,逐渐向给定的数据样本集添加噪声,从而扰动原始未知分布。链的每个时间步长都用一个圆圈表示。,由于仅通过链向样本中添加噪声,所以前向过程不需要训练任何参数。
前向过程的公式如下:
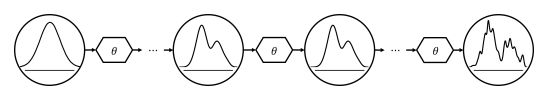
而反向过程则如图所示,![]() 通过优化去噪网络中的可训练参数θ来近似,用神经网络通过递归的方式来去除前向过程添加的噪声,而并不像GAN那样在一个时间步中消除所有噪声,公式如下
通过优化去噪网络中的可训练参数θ来近似,用神经网络通过递归的方式来去除前向过程添加的噪声,而并不像GAN那样在一个时间步中消除所有噪声,公式如下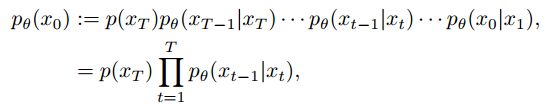
其中θ是去噪网络的参数,pθ(xt−1| xt)是逆向跃迁分布。逆向过程通常被参数化为![]() 右边这个是一个正态分布,可以通过重参数化技巧把均值和方差的相关性绑定在一个标准正态分布的上。
右边这个是一个正态分布,可以通过重参数化技巧把均值和方差的相关性绑定在一个标准正态分布的上。
这个D代表KL散度,最小化L的目的是使得![]() 的差异也最小化。
的差异也最小化。
如图所示,采样过程与逆向过程类似,但是是利用优化的去噪网络θ*生成新的数据x*0,它首先从最终的分布p(xT)中获得样本xT,然后使用经过训练的网络通过采样过渡pθ*(xT−1|xT)迭代去除噪声。通过一系列这样的转换,它最终生成新的数据![]()
扩散模型可以用两种不同的方式来表示,即离散和连续,它们的差异是在时间步的定义上是否是连续的。
离散式的典型是DDPM。
连续式在时间步长之间以无穷小的间隔添加噪声。因此,在这种公式化的扩散模型中采用了随机微分方程(SDE)来描述连续时间步长的变化
正向过程:正向过程通过配置噪声和指定过渡链来定义数据被扰动的方式。噪声配置包括时间表和要添加的噪声类型。转换链指定了如何转换数据分布。
噪声时间表可以通过网络学习,或者使用数学公式进行经验设计。为了学习噪声调度,现有方法将其识别为要与其他参数联合学习的参数,这些参数通常通过最大化对数似然的变分下界来优化。由于噪声调度是由网络学习的,因此训练和采样可能会有所不同,以获得最佳结果。相比之下,手动设计的噪声调度是用各种各样的数学启发式方法制定的
噪声类型的选择导致了改进的分布近似和更大的自由度,强调了其对扩散模型表现力的重要性。具体而言,选择适当的噪声类型可以增强模型容量,因为它更准确地拟合不同时间步长的扰动分布
转换链控制扰动给定数据分布的方式。在正向过程中改变最终的分布有助于在反向过程中有效地训练去噪网络。原始分布p(x0)和终端分布p(xT)之间的较大差异可能导致扩散模型的次优学习结果。p(xT)通过在T个时间步后将噪声添加到原始分布p(x0)中来确定。它们的差异通常很大,因为xT充满了噪声,几乎没有原始结构保留,这样逆向过程就需要更多的时间步来客服差异。
如图所示。尽管使用简单,但DDPM使用的各向同性高斯分布没有关于给定数据样本的信息,其改进方法通常考虑训练数据集的统计数据,如均值和方差,以指示数据结构
The Systematic Method,系统方法在通用流水线中涉及多个转换链
不同的数据类型(语音、文本、图片)需要调整转换链。本质上,不同的数据类型具有不同的特征
潜在表示是转换的另一种可行选择,如图所示,在低维空间中计算更加方便,并学习更抽象的语义表示。
逆向过程的重点在于训练去噪网络以去除噪
U-Net和Transformer是去噪网络的两种常用架构。U-Net是一种通用的U形编码器/解码器架构。Transformer也是一种编码器-解码器架构。其编码器和解码器都具有自注意功能。