基于MATLAB代码DWA算法的移动车路径规划
基于MATLAB代码DWA算法的移动车路径规划,可实现动态避障和静态避障
DWA(Dynamic Window Approach)是一种常用于移动机器人路径规划的局部路径规划算法。它通过在速度空间中采样,结合机器人的运动学约束和环境信息,选择最优的速度组合来实现避障和目标点导航。
以下是一个基于DWA算法的MATLAB代码示例,用于实现移动车的路径规划:
% DWA (Dynamic Window Approach) Algorithm for Mobile Robot Path Planning
clc;
clear;
close all;
%% 参数设置
dt = 0.1; % 时间步长
max_speed = 1.0; % 最大线速度 (m/s)
min_speed = -0.5; % 最小线速度 (m/s)
max_yaw_rate = pi / 4.0; % 最大角速度 (rad/s)
max_accel = 0.2; % 最大加速度 (m/s^2)
max_dyaw_rate = pi / 4.0; % 最大角加速度 (rad/s^2)
v_resolution = 0.01; % 线速度分辨率 (m/s)
yaw_rate_resolution = 0.1 * pi / 180.0; % 角速度分辨率 (rad/s)
predict_time = 3.0; % 预测时间范围 (s)
to_goal_cost_gain = 0.15; % 到达目标点代价权重
speed_cost_gain = 1.0; % 速度代价权重
obstacle_cost_gain = 1.0; % 障碍物代价权重
robot_radius = 0.2; % 机器人半径 (m)
%% 初始化
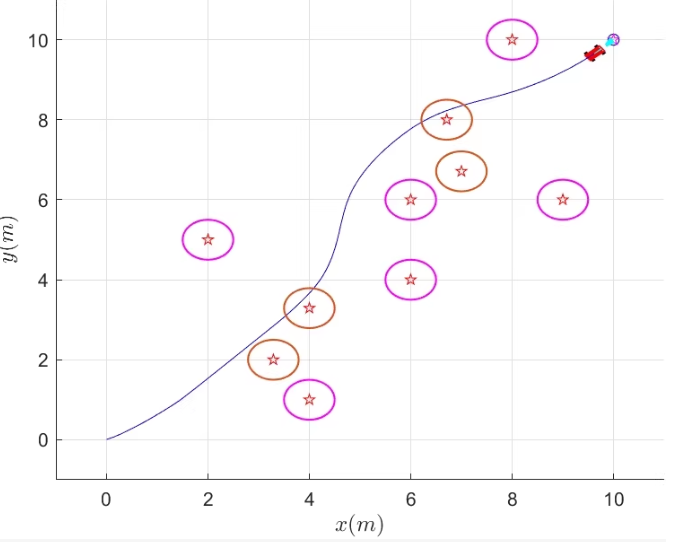
goal = [10, 10]; % 目标点位置 [x, y]
obstacles = [5, 5; 7, 7; 8, 8]; % 障碍物位置 [x, y]
pose = [0, 0, 0]; % 初始位置 [x, y, theta]
trajectory = pose;
%% 主循环
while true
% 动态窗口计算
[v_min, v_max, w_min, w_max] = calc_dynamic_window(pose, dt, max_speed, min_speed, ...
max_yaw_rate, max_accel, max_dyaw_rate);
% 轨迹评估
[best_v, best_w, trajectory] = dwa_control(pose, [v_min, v_max, w_min, w_max], ...
goal, obstacles, dt, predict_time, to_goal_cost_gain, speed_cost_gain, ...
obstacle_cost_gain, robot_radius);
% 更新机器人状态
pose = motion(pose, best_v, best_w, dt);
trajectory = [trajectory; pose];
% 绘图
clf;
plot_trajectory(trajectory);
hold on;
plot_obstacles(obstacles, robot_radius);
plot_robot(pose, robot_radius);
plot_goal(goal);
axis equal;
grid on;
xlim([-1, 11]);
ylim([-1, 11]);
drawnow;
% 检查是否到达目标点
if norm(pose(1:2) - goal) < 0.5
disp('Goal reached!');
break;
end
end
%% 函数定义
function [v_min, v_max, w_min, w_max] = calc_dynamic_window(pose, dt, max_speed, min_speed, ...
max_yaw_rate, max_accel, max_dyaw_rate)
% 动态窗口计算
v_min = max(min_speed, pose(3) - max_accel * dt);
v_max = min(max_speed, pose(3) + max_accel * dt);
w_min = max(-max_yaw_rate, pose(4) - max_dyaw_rate * dt);
w_max = min(max_yaw_rate, pose(4) + max_dyaw_rate * dt);
end
function [best_v, best_w, trajectory] = dwa_control(pose, dw, goal, obstacles, dt, ...
predict_time, to_goal_cost_gain, speed_cost_gain, obstacle_cost_gain, robot_radius)
% DWA控制
best_cost = inf;
best_v = 0;
best_w = 0;
trajectory = [];
for v = dw(1):v_resolution:dw(2)
for w = dw(3):yaw_rate_resolution:dw(4)
% 预测轨迹
traj = predict_trajectory(pose, v, w, dt, predict_time);
% 计算代价
to_goal_cost = calc_to_goal_cost(traj, goal);
speed_cost = calc_speed_cost(v, max_speed);
ob_cost = calc_obstacle_cost(traj, obstacles, robot_radius);
if isnan(ob_cost)
continue;
end
final_cost = to_goal_cost_gain * to_goal_cost + ...
speed_cost_gain * speed_cost + ...
obstacle_cost_gain * ob_cost;
% 更新最佳速度组合
if final_cost < best_cost
best_cost = final_cost;
best_v = v;
best_w = w;
trajectory = traj;
end
end
end
end
function traj = predict_trajectory(pose, v, w, dt, predict_time)
% 预测轨迹
traj = pose;
time = 0;
while time <= predict_time
pose = motion(pose, v, w, dt);
traj = [traj; pose];
time = time + dt;
end
end
function cost = calc_to_goal_cost(traj, goal)
% 到达目标点代价
dx = goal(1) - traj(end, 1);
dy = goal(2) - traj(end, 2);
cost = sqrt(dx^2 + dy^2);
end
function cost = calc_speed_cost(v, max_speed)
% 速度代价
cost = max_speed - abs(v);
end
function cost = calc_obstacle_cost(traj, obstacles, robot_radius)
% 障碍物代价
min_dist = inf;
for i = 1:size(obstacles, 1)
dx = obstacles(i, 1) - traj(:, 1);
dy = obstacles(i, 2) - traj(:, 2);
dist = sqrt(dx.^2 + dy.^2) - robot_radius;
min_dist = min(min_dist, min(dist));
end
if min_dist < 0
cost = NaN; % 发生碰撞
else
cost = 1.0 / min_dist; % 距离越小,代价越大
end
end
function pose = motion(pose, v, w, dt)
% 运动模型
x = pose(1) + v * cos(pose(3)) * dt;
y = pose(2) + v * sin(pose(3)) * dt;
theta = pose(3) + w * dt;
pose = [x, y, theta];
end
function plot_trajectory(trajectory)
% 绘制轨迹
plot(trajectory(:, 1), trajectory(:, 2), '-b');
end
function plot_obstacles(obstacles, robot_radius)
% 绘制障碍物
theta = linspace(0, 2*pi, 50);
for i = 1:size(obstacles, 1)
x = obstacles(i, 1) + robot_radius * cos(theta);
y = obstacles(i, 2) + robot_radius * sin(theta);
fill(x, y, 'r', 'FaceAlpha', 0.5);
end
end
function plot_robot(pose, robot_radius)
% 绘制机器人
theta = linspace(0, 2*pi, 50);
x = pose(1) + robot_radius * cos(theta);
y = pose(2) + robot_radius * sin(theta);
fill(x, y, 'g', 'FaceAlpha', 0.5);
end
function plot_goal(goal)
% 绘制目标点
plot(goal(1), goal(2), '*c', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'LineWidth', 2);
end
```
### 说明:
1. **参数设置**:可以根据实际需求调整参数,例如最大速度、加速度、预测时间等。
2. **动态窗口计算**:根据当前状态和约束条件计算可行的速度范围。
3. **轨迹评估**:通过采样速度组合,生成预测轨迹,并计算代价函数。
4. **运动模型**:使用简单的差分驱动模型更新机器人状态。
5. **可视化**:实时绘制机器人轨迹、障碍物和目标点。
