ETCD 七 gRPC 通信接口以及客户端
client/v3 client定义
// Client provides and manages an etcd v3 client session.
type Client struct {
Cluster // 向集群里增加 etcd 服务端节点之类,属于管理员操作。
KV //我们主要使用的功能,即操作 K-V。
Lease //租约相关操作,比如申请一个 TTL=10 秒的租约。
Watcher //观察订阅,从而监听最新的数据变化。
Auth //管理 etcd 的用户和权限,属于管理员操作。
Maintenance //维护 etcd,比如主动迁移 etcd 的 leader 节点,属于管理员操作。
conn *grpc.ClientConn
cfg Config
creds grpccredentials.TransportCredentials
resolver *resolver.EtcdManualResolver
mu *sync.RWMutex
ctx context.Context
cancel context.CancelFunc
// Username is a user name for authentication.
Username string
// Password is a password for authentication.
Password string
authTokenBundle credentials.Bundle
callOpts []grpc.CallOption
lgMu *sync.RWMutex
lg *zap.Logger
}gRPC 服务
etcd v3 的通信基于 gRPC,proto 文件是定义服务端和客户端通信接口的标准。包括:
-
客户端该传什么样的参数
-
服务端该返回什么参数
-
客户端该怎么调用
-
是阻塞还是非阻塞
-
是同步还是异步
gRPC 推荐使用 proto3 消息格式,在进行核心 API 的学习之前,我们需要对 proto3 的基本语法有初步的了解。proto3 是原有 Protocol Buffer 2(被称为 proto2)的升级版本,删除了一部分特性,优化了对移动设备的支持。
发送到 etcd 服务器的每个 API 请求都是一个 gRPC 远程过程调用。etcd 中的 RPC 接口定义根据功能分类到服务中。
处理 etcd 键值的重要服务包括:
-
KV Service,创建、更新、获取和删除键值对。
-
Watch Service,监视键的更改。
-
Lease Service,实现键值对过期,客户端用来续租、保持心跳。
-
Lock Service,etcd 提供分布式共享锁的支持。
-
Election Service,暴露客户端选举机制。
请求和响应
etcd3 中的所有 RPC 都遵循相同的格式。每个 RPC 都有一个函数名,该函数将 NameRequest 作为参数并返回 NameResponse 作为响应。例如,这是 Range RPC 描述:
service KV {
Range(RangeRequest) returns (RangeResponse)
...
}响应头
etcd API 的所有响应都有一个附加的响应标头,其中包括响应的集群元数据:
type ResponseHeader struct {
// cluster_id is the ID of the cluster which sent the response.
//产生响应的集群的 ID。
ClusterId uint64 `protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=cluster_id,json=clusterId,proto3" json:"cluster_id,omitempty"`
// member_id is the ID of the member which sent the response.
//产生响应的成员的 ID。
//应用服务可以通过 Cluster_ID 和 Member_ID 字段来确保,当前与之通信的正是预期的那个集群或者成
// 员。
MemberId uint64 `protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=member_id,json=memberId,proto3" json:"member_id,omitempty"`
// revision is the key-value store revision when the request was applied.
// For watch progress responses, the header.revision indicates progress. All future events
// recieved in this stream are guaranteed to have a higher revision number than the
// header.revision number.
//产生响应时键值存储的修订版本号。
//应用服务可以使用修订号字段来获得当前键值存储库最新的修订号。应用程序指定历史修订版以进行查询,如果希望在请求时知道最新修订版,此功能特别有用。
Revision int64 `protobuf:"varint,3,opt,name=revision,proto3" json:"revision,omitempty"`
// raft_term is the raft term when the request was applied.
//产生响应时,成员的 Raft 称谓。
//应用服务可以使用 Raft_Term 来检测集群何时完成一个新的 leader 选举。
RaftTerm uint64 `protobuf:"varint,4,opt,name=raft_term,json=raftTerm,proto3" json:"raft_term,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}etcd clientv3 客户端
etcd 客户端 clientv3 接入的示例将会以 Go 客户端为主,你需要准备好基本的开发环境。
首先是 etcd clientv3 的初始化,我们根据指定的 etcd 节点,建立客户端与 etcd 集群的连接:
client/v3/doc.go
// expect dial time-out on ipv4 blackhole
_, err := clientv3.New(clientv3.Config{
Endpoints: []string{"http://254.0.0.1:12345"},
DialTimeout: 2 * time.Second,
})如上的代码实例化了一个 client,这里需要传入两个参数。
-
Endpoints:etcd 的多个节点服务地址,因为我是单点本机测试,所以只传 1 个。
-
DialTimeout:创建 client 的首次连接超时,这里传了 5 秒,如果 5 秒都没有连接成功就会返回 err。需要注意的是,一旦 client 创建成功,我们就不用再关心后续底层连接的状态了,client 内部会重连。
etcd 客户端初始化
// 使用client v3 测试连接到etcd集群
func TestClient(t *testing.T) {
var (
config Config
client *Client
err error
)
// 客户端配置
config = Config{
// 节点配置
Endpoints: []string{"192.168.70.100:22379"},
DialTimeout: 5 * time.Second,
}
// 建立连接
if client, err = New(config); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
} else {
// 输出集群信息
fmt.Println(client.Cluster.MemberList(context.TODO()))
}
client.Close()
}etcd 中几个重要的服务和接口:
KV 存储
KV 对象的实例获取通过如下的方式:
kv := clientev3.NewKV(client)KV 接口的具体定义:
type KV interface {
// Put puts a key-value pair into etcd.
// Note that key,value can be plain bytes array and string is
// an immutable representation of that bytes array.
// To get a string of bytes, do string([]byte{0x10, 0x20}).
Put(ctx context.Context, key, val string, opts ...OpOption) (*PutResponse, error)
// Get retrieves keys.
// By default, Get will return the value for "key", if any.
// When passed WithRange(end), Get will return the keys in the range [key, end).
// When passed WithFromKey(), Get returns keys greater than or equal to key.
// When passed WithRev(rev) with rev > 0, Get retrieves keys at the given revision;
// if the required revision is compacted, the request will fail with ErrCompacted .
// When passed WithLimit(limit), the number of returned keys is bounded by limit.
// When passed WithSort(), the keys will be sorted.
Get(ctx context.Context, key string, opts ...OpOption) (*GetResponse, error)
// Delete deletes a key, or optionally using WithRange(end), [key, end).
Delete(ctx context.Context, key string, opts ...OpOption) (*DeleteResponse, error)
// Compact compacts etcd KV history before the given rev.
Compact(ctx context.Context, rev int64, opts ...CompactOption) (*CompactResponse, error)
// Do applies a single Op on KV without a transaction.
// Do is useful when creating arbitrary operations to be issued at a
// later time; the user can range over the operations, calling Do to
// execute them. Get/Put/Delete, on the other hand, are best suited
// for when the operation should be issued at the time of declaration.
Do(ctx context.Context, op Op) (OpResponse, error)
// Txn creates a transaction.
Txn(ctx context.Context) Txn
}从 KV 对象的定义我们可知,它就是一个接口对象,包含以下几个主要的 KV 操作方法。
KV 存储 Put
Put 的定义如下:
Put(ctx context.Context, key, val string, opts ...OpOption) (*PutResponse, error)
其中的参数
-
ctx:Context 包对象,用来跟踪上下文,比如超时控制。
-
key:存储对象的 key。
-
val:存储对象的 value。
-
opts:可变参数,额外选项。
Put 将一个键值对放入 etcd 中。请注意,键值可以是纯字节数组,字符串是该字节数组的不可变表示形式。要获取字节字符串,请执行string([] byte {0x10,0x20})。
Put 的使用方法如下所示:
putResp, err := kv.Put(context.TODO(),"aa", "hello-world!")KV 查询 Get
现在可以对存储的数据进行取值了。默认情况下,Get 将返回“key”对应的值:
Get(ctx context.Context, key string, opts ...OpOption) (*GetResponse, error)
OpOption 为可选的函数传参,传参为WithRange(end)时,Get 将返回 [key,end) 范围内的键;传参为 WithFromKey() 时,Get 返回大于或等于 key 的键;当通过 rev> 0 传递 WithRev(rev) 时,Get 查询给定修订版本的键;如果压缩了所查找的修订版本,则返回请求失败,并显示 ErrCompacted。 传递 WithLimit(limit) 时,返回的 key 数量受 limit 限制;传参为 WithSort 时,将对键进行排序。
对应的使用方法如下:
getResp, err := kv.Get(context.TODO(), "aa")从以上数据的存储和取值,我们知道:Put 返回 PutResponse,Get 返回 GetResponse。注意:不同的 KV 操作对应不同的 Response 结构,定义如下:
type (
CompactResponse pb.CompactionResponse
PutResponse pb.PutResponse
GetResponse pb.RangeResponse
DeleteResponse pb.DeleteRangeResponse
TxnResponse pb.TxnResponse
)下面我们分别来看一看 PutResponse 和 GetResponse 映射的 RangeResponse 结构的定义:
type PutResponse struct {
Header *ResponseHeader `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=header,proto3" json:"header,omitempty"`
// if prev_kv is set in the request, the previous key-value pair will be returned.
//请求中如有 prev_kv,响应时也会携带 prev_kv
PrevKv *mvccpb.KeyValue `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=prev_kv,json=prevKv,proto3" json:"prev_kv,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
type RangeResponse struct {
Header *ResponseHeader `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=header,proto3" json:"header,omitempty"`
// kvs is the list of key-value pairs matched by the range request.
// kvs is empty when count is requested.
kvs 是一个匹配 range 请求的键值对列表
Kvs []*mvccpb.KeyValue `protobuf:"bytes,2,rep,name=kvs,proto3" json:"kvs,omitempty"`
// more indicates if there are more keys to return in the requested range.
More bool `protobuf:"varint,3,opt,name=more,proto3" json:"more,omitempty"`
// count is set to the number of keys within the range when requested.
Count int64 `protobuf:"varint,4,opt,name=count,proto3" json:"count,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}KVS 字段,保存了本次 Get 查询到的所有 KV 对,我们继续看一下 mvccpb.KeyValue 对象的定义:
type KeyValue struct {
// key is the key in bytes. An empty key is not allowed.
Key []byte `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=key,proto3" json:"key,omitempty"`
// create_revision is the revision of last creation on this key.
// create_revision 是当前 key 的最后创建版本
CreateRevision int64 `protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=create_revision,json=createRevision,proto3" json:"create_revision,omitempty"`
// mod_revision is the revision of last modification on this key.
// mod_revision 是指当前 key 的最新修订版本
ModRevision int64 `protobuf:"varint,3,opt,name=mod_revision,json=modRevision,proto3" json:"mod_revision,omitempty"`
// version is the version of the key. A deletion resets
// the version to zero and any modification of the key
// increases its version.
// key 的版本,每次更新都会增加版本号
Version int64 `protobuf:"varint,4,opt,name=version,proto3" json:"version,omitempty"`
// value is the value held by the key, in bytes.
Value []byte `protobuf:"bytes,5,opt,name=value,proto3" json:"value,omitempty"`
// lease is the ID of the lease that attached to key.
// When the attached lease expires, the key will be deleted.
// If lease is 0, then no lease is attached to the key.
// 绑定了 key 的租期 Id,当 lease 为 0 ,则表明没有绑定 key;租期过期,则会删除 key
Lease int64 `protobuf:"varint,6,opt,name=lease,proto3" json:"lease,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}至于 RangeResponse.More 和 Count,当我们使用 withLimit() 选项进行 Get 时会发挥作用,相当于分页查询。
接下来,我们通过一个特别的 Get 选项,获取 aa 目录下的所有子目录:
rangeResp, err := kv.Get(context.TODO(), "/aa", clientv3.WithPrefix())
WithPrefix()用于查找以/aa为前缀的所有 key,因此可以模拟出查找子目录的效果。我们知道 etcd 是一个有序的 KV 存储,因此/aa为前缀的 key 总是顺序排列在一起。
WithPrefix 实际上会转化为范围查询,它根据前缀/aa生成了一个 key range,[“/aa/”, “/aa0”),这是因为比 / 大的字符是 0,所以以 /aa0 作为范围的末尾,就可以扫描到所有的 /aa/ 打头的 key 了。
KV 操作实践
// 使用client v3 测试连接到etcd集群
func TestClient(t *testing.T) {
rootContext := context.Background()
var (
config Config
client *Client
err error
)
// 客户端配置
config = Config{
// 节点配置
Endpoints: []string{"192.168.70.100:22379"},
DialTimeout: 5 * time.Second,
}
// 建立连接
if client, err = New(config); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
} else {
// 输出集群信息
fmt.Println(client.Cluster.MemberList(context.TODO()))
}
defer client.Close()
kv := NewKV(client)
//设置值
str := time.Now().String()
fmt.Println("key aa new value is:", str)
ctx1, _ := context.WithTimeout(rootContext, 2*time.Second)
_, err = kv.Put(ctx1, "aa", str)
if err!=nil{
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
//获取值
ctx, _ := context.WithTimeout(rootContext, 2*time.Second)
resp, err := kv.Get(ctx, "aa")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
kvs := resp.Kvs
if len(kvs) > 0 {
fmt.Println("key aa last value is:", string(kvs[0].Value))
} else {
fmt.Println("key aa value is empty")
}
//删除值
delResp,err:=kv.Delete(ctx,"aa")
if err!=nil{
fmt.Println(err)
}
fmt.Println("delete key:cc:",delResp.Deleted>0)
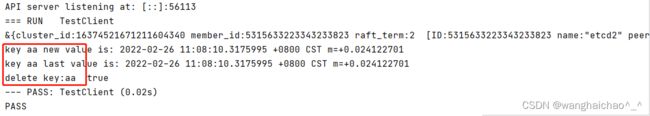
}输出结果:
其他通信接口
其他常用的接口还有 Txn、Compact、Watch、Lease、Lock 等。我们依次看看这些接口的定义。
事务 Txn
Txn 方法在单个事务中处理多个请求。Txn 请求增加键值存储的修订版本,并为每个完成的请求生成带有相同修订版本的事件,etcd 不容许在一个 Txn 中多次修改同一个 key。Txn 接口定义如下:
rpc Txn(TxnRequest) returns (TxnResponse) {}
Compact
Compact 方法压缩 etcd 键值对存储中的事件历史。键值对存储应该定期压缩,否则事件历史会无限制地持续增长。Compact 接口定义如下:
rpc Compact(CompactionRequest) returns (CompactionResponse) {}
请求的消息体是 CompactionRequest, CompactionRequest 压缩键值对存储到给定修订版本,所有修订版本比压缩修订版本小的键都将被删除。
Watch
Watch API 提供了一个基于事件的接口,用于异步监视键的更改。etcd 监视程序通过给定的修订版本(当前版本或历史版本)持续监视 key 更改,并将 key 更新流回客户端。
在 rpc.proto 中 Watch Service 定义如下:
service Watch {
rpc Watch(stream WatchRequest) returns (stream WatchResponse) {}
}
Watch 观察将要发生或者已经发生的事件。输入和输出都是流,输入流用于创建和取消观察,而输出流发送事件。一个观察 RPC 可以一次性在多个 key 范围上观察,并为多个观察流化事件。整个事件历史可以从最后压缩修订版本开始观察。Watch Service 只有一个 Watch 方法。
Lease Service
Lease Service 提供租约的支持。Lease 是一种检测客户端存活状况的机制。集群授予客户端具有生存时间的租约。如果 etcd 集群在给定的 TTL 时间内未收到 keepAlive,则租约到期。
为了将租约绑定到键值存储中,每个 key 最多可以附加一个租约。当租约到期或被撤销时,该租约依附的所有 key 都将被删除,每个过期的密钥都会在事件历史记录中生成一个删除事件。
在 rpc.proto 中 Lease Service 定义的接口如下:
service Lease {
rpc LeaseGrant(LeaseGrantRequest) returns (LeaseGrantResponse) {}
rpc LeaseRevoke(LeaseRevokeRequest) returns (LeaseRevokeResponse) {}
rpc LeaseKeepAlive(stream LeaseKeepAliveRequest) returns (stream LeaseKeepAliveResponse) {}
rpc LeaseTimeToLive(LeaseTimeToLiveRequest) returns (LeaseTimeToLiveResponse) {}
}
其中:
-
LeaseGrant,创建一个租约;
-
LeaseRevoke,撤销一个租约;
-
LeaseKeepAlive,用于维持租约;
-
LeaseTimeToLive,获取租约信息。
Lock Service
Lock Service 提供分布式共享锁的支持。Lock Service 以 gRPC 接口的方式暴露客户端锁机制。在 v3lock.proto 中 Lock Service 定义如下:
service Lock {
rpc Lock(LockRequest) returns (LockResponse) {}
rpc Unlock(UnlockRequest) returns (UnlockResponse) {}
}
其中:
-
Lock 方法,在给定命令锁上获得分布式共享锁;
-
Unlock 使用 Lock 返回的 key 并释放对锁的持有。