void func()函数和void func(void)函数的区别
例子1:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> void show1(int age) { printf("Age: %d\n", age); } void show2(char* str) { printf("Name: %s\n", str); } void show3(int age, int number, char* str) { printf("Age: %d\n", age); printf("Number: %d\n", number); printf("Name: %s\n", str); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { typedef void (*ptr_fun)(); ptr_fun pfunc; pfunc = show1; pfunc(23); printf("\n"); pfunc = show2; pfunc("Jack"); printf("\n"); pfunc = show3; pfunc(23, 202, "Jack"); return 0; }
可以看到当我们定义了typedef void (*ptr_fun)();此类型的函数指针,表示它可以指向任意个数参数的函数。
例子2:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> void show() { printf("Argument count is variable!\n"); } struct Student { int age; int number; }; int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { struct Student Mike = {12, 56}; show(23); show(3, "Jack"); show(Mike); return 0; }
程序输出:
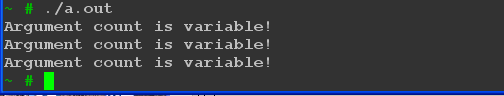
可以看到输出各种类型,任意的参数都是可以的。
例子3:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> void show(void) { printf("No argument!\n"); } struct Student { int age; int number; }; int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { struct Student Mike = {12, 56}; show(23); show(Mike); show(); return 0; }
程序输出:
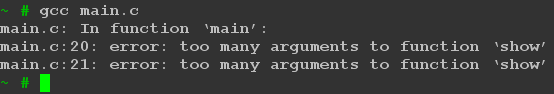
这里我们可看到void show(void)不接受任何参数,调用时只能写成show()。