hdu 1401
Solitaire
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3077 Accepted Submission(s): 954
Problem Description
Solitaire is a game played on a chessboard 8x8. The rows and columns of the chessboard are numbered from 1 to 8, from the top to the bottom and from left to right respectively.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).
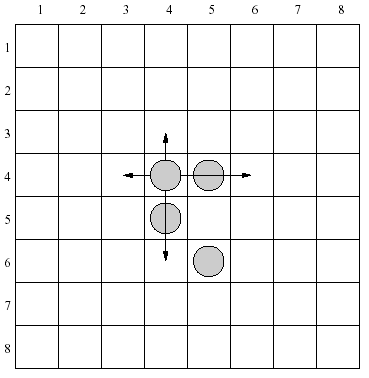
There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).

There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
Input
Each of two input lines contains 8 integers a1, a2, ..., a8 separated by single spaces and describes one configuration of pieces on the chessboard. Integers a2j-1 and a2j (1 <= j <= 4) describe the position of one piece - the row number and the column number respectively. Process to the end of file.
Output
The output should contain one word for each test case - YES if a configuration described in the second input line is reachable from the configuration described in the first input line in at most 8 moves, or one word NO otherwise.
Sample Input
4 4 4 5 5 4 6 5
2 4 3 3 3 6 4 6
Sample Output
YES
Source
Recommend
四个点的哈希,由于这四个点没有什么区分,哈希的时候注意一下。
由于的用set哈希,用*10的方法。所以要先排序。很容易理解的。
bfs的代码,有点意思。
1 /** 2 4 4 4 5 5 4 6 5 3 2 4 3 3 3 6 4 6 4 5 **/ 6 7 #include<iostream> 8 #include<stdio.h> 9 #include<cstring> 10 #include<cstdlib> 11 #include<queue> 12 #include<algorithm> 13 #include<set> 14 using namespace std; 15 16 struct node 17 { 18 int x[4]; 19 int y[4]; 20 }; 21 struct node start,end1; 22 23 queue<node>Q[2]; 24 set<int>hxl[2]; 25 bool flag; 26 int map1[4][2]={{1,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1}}; 27 28 bool fun(node &t,int i) 29 { 30 int j; 31 if(t.x[i]>=1&&t.x[i]<=8 && t.y[i]>=1&&t.y[i]<=8) 32 { 33 for(j=0;j<4;j++) 34 { 35 if(j==i)continue; 36 if(t.x[i]==t.x[j] && t.y[i]==t.y[j]) return true; 37 } 38 return false; 39 } 40 return true; 41 } 42 void pai(node &t) 43 { 44 int i,j,x; 45 for(i=0;i<4; i++) 46 { 47 x=i; 48 for(j=i+1;j<4; j++) 49 if(t.x[x]>t.x[j]) 50 x=j; 51 else if(t.x[x]==t.x[j] && t.y[x]>t.y[j]) 52 x=j; 53 swap(t.x[i],t.x[x]); 54 swap(t.y[i],t.y[x]); 55 } 56 57 } 58 int serch(node &t) 59 { 60 int i,sum=0; 61 for(i=0;i<4;i++) 62 sum=sum*100+t.x[i]*10+t.y[i]; 63 return sum; 64 } 65 void bfs(int x) 66 { 67 int i,j,size1,k; 68 node cur,t; 69 size1=Q[x].size(); 70 while(size1--) 71 { 72 cur=Q[x].front(); 73 Q[x].pop(); 74 for(i=0;i<4;i++)/** every four point **/ 75 { 76 for(j=0;j<4;j++) /** n s w e**/ 77 { 78 t=cur; 79 t.x[i]=t.x[i]+map1[j][0]; 80 t.y[i]=t.y[i]+map1[j][1]; 81 if(fun(t,i)==true) 82 { 83 t.x[i]=t.x[i]+map1[j][0]; 84 t.y[i]=t.y[i]+map1[j][1]; 85 if(fun(t,i)==true) continue; 86 } 87 pai(t); 88 k=serch(t); 89 if(hxl[x].count(k)>0)continue; 90 if(hxl[x^1].count(k)>0) 91 { 92 flag=true; 93 return; 94 } 95 hxl[x].insert(k); 96 Q[x].push(t); 97 } 98 } 99 } 100 } 101 void dbfs() 102 { 103 int ans=0,k; 104 pai(start); 105 k=serch(start); 106 hxl[0].insert(k); 107 Q[0].push(start); 108 109 pai(end1); 110 Q[1].push(end1); 111 k=serch(end1); 112 hxl[1].insert(k); 113 while(true) 114 { 115 if(Q[0].size()<Q[1].size()) 116 bfs(0); 117 else bfs(1); 118 ans++; 119 if(ans==8)break; 120 if(flag==true) return; 121 } 122 } 123 int main() 124 { 125 int i; 126 while(scanf("%d%d",&start.x[0],&start.y[0])>0) 127 { 128 for(i=1;i<4;i++) 129 scanf("%d%d",&start.x[i],&start.y[i]); 130 for(i=0;i<4;i++) 131 scanf("%d%d",&end1.x[i],&end1.y[i]); 132 while(!Q[0].empty()){ 133 Q[0].pop(); 134 } 135 while(!Q[1].empty()){ 136 Q[1].pop(); 137 } 138 hxl[0].clear(); 139 hxl[1].clear(); 140 flag=false; 141 dbfs(); 142 if(flag==true) printf("YES\n"); 143 else printf("NO\n"); 144 } 145 return 0; 146 }