STL——STL中string的写时拷贝机制
string的写时拷贝机制是为了提高效率。STL中许多类都采用了该机制(Copy-on-Write),该技术确实使STL的程序有着比较高的效率。
string类中有一个私有成员变量char *ch,该变量指向该类从堆上分配的内存,其在构造的时候分配内存,在析构的时候释放内存。
输出:
string类中有一个私有成员变量char *ch,该变量指向该类从堆上分配的内存,其在构造的时候分配内存,在析构的时候释放内存。
写时拷贝的意思是:在例子中string str1 = "linux_ever"; string str2 = str1;可以看到str1和str2中的指针变量指向相同的内存地址。当改变str的内容的时候才拷贝该对象。
从程序的输出结果中看出:
string str1 = "linux_ever";执行完之后,str1对象的内容就是"linux_ever",会调用复制构造函数。
string str2 = str1;//执行完之后,会调用str2的复制构造函数,str2中的指针成员变量指向刚才str1中指向成员变量指向的内存单元。
当修改了str1的时候,就将str1的内存单元重新分配,将之前指向的内存单元中的内存拷贝过来,并修改相应的值。理所应当地,刚才的内存空间被str2单独占用了。所以接下来即使修改了str2的值,它的地址也没有发生改变。
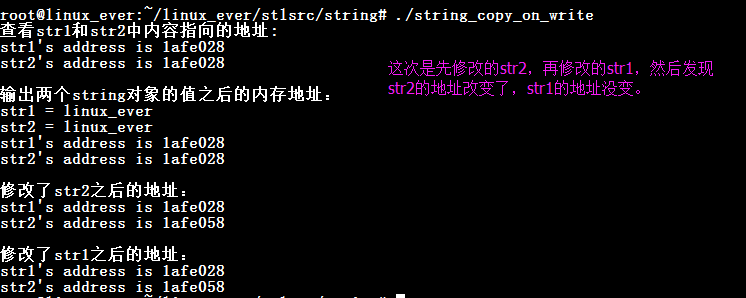
在第二个程序中,先修改了str2,所以就将str2的内存单元重新分配,将之前指向的内存单元中的内存拷贝过来,并修改相应的值。理所应当地,刚才的内存空间被str1单独占用了。所以接下来即使修改了str1的值,它的地址也没有发生改变。
先修改str1,再修改str2:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: string_copy_on_write.cpp
> Author:
> Mail:
> Created Time: 2016年03月25日 星期五 20时22分39秒
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1 = "linux_ever";
string str2 = str1;
cout << "查看str1和str2中内容指向的地址: " << endl;
printf("str1's address is %x\n", str1.c_str());
printf("str2's address is %x\n", str2.c_str());
cout << "\n输出两个string对象的值之后的内存地址:" << endl;
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
printf("str1's address is %x\n", str1.c_str());
printf("str2's address is %x\n", str2.c_str());
cout << "\n修改了str1之后的地址:" << endl;
str1[0] = 'u';
printf("str1's address is %x\n", str1.c_str());
printf("str2's address is %x\n", str2.c_str());
cout << "\n修改了str2之后的地址:" << endl;
str2[0] = 'w';
printf("str1's address is %x\n", str1.c_str());
printf("str2's address is %x\n", str2.c_str());
return 0;
}
输出:
先修改str2,再修改str1:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: string_copy_on_write.cpp
> Author:
> Mail:
> Created Time: 2016年03月25日 星期五 20时22分39秒
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1 = "linux_ever";
string str2 = str1;
cout << "查看str1和str2中内容指向的地址: " << endl;
printf("str1's address is %x\n", str1.c_str());
printf("str2's address is %x\n", str2.c_str());
cout << "\n输出两个string对象的值之后的内存地址:" << endl;
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
printf("str1's address is %x\n", str1.c_str());
printf("str2's address is %x\n", str2.c_str());
cout << "\n修改了str2之后的地址:" << endl;
str2[1] = 'u';
printf("str1's address is %x\n", str1.c_str());
printf("str2's address is %x\n", str2.c_str());
cout << "\n修改了str1之后的地址:" << endl;
str1[1] = 'w';
printf("str1's address is %x\n", str1.c_str());
printf("str2's address is %x\n", str2.c_str());
return 0;
}
输出结果: