二叉树
package foo; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.util.Queue; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Stack; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; /** * 创建树的文件内容,例如树<pre> * A * B C * D E * </pre> * 就是其先序序列:A B D # # # C E # # # * 其中第1、2个#是D的左右子节点(空),滴3个#是B的右子节点(空),第4、5个#是 * E的左右子节点(空),第6个#是C的右子节点(空) * */ /** * 仅作演示使用 * */ class Tree { // 在eclipse 中创建的普通java项目,所以路径是这么写的 private static final String filePath = "bin/foo/input.txt"; private Node<String> root; public Tree() { } public Tree(Node<String> root) { this.root = root; } //创建二叉树 public void buildTree() { Scanner scn = null; try { scn = new Scanner(new File(filePath)); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); return; } root = createTree(root,scn); } // 先序遍历创建二叉树(递归) private Node<String> createTree(Node<String> node,Scanner scn) { String temp = scn.next(); if (temp.trim().equals("#")) { return null; } else { node = new Node<String>(temp); node.setLeft(createTree(node.getLeft(), scn)); node.setRight(createTree(node.getRight(), scn)); return node; } } //中序遍历(递归) public void inOrderTraverse() { inOrderTraverse(root); } public void inOrderTraverse(Node<String> node) { if (node != null) { inOrderTraverse(node.getLeft()); System.out.println(node.getValue()); inOrderTraverse(node.getRight()); } } //中序遍历(非递归) public void nrInOrderTraverse() { Stack<Node<String>> stack = new Stack<Node<String>>(); Node<String> node = root; while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { while (node != null) { stack.push(node); node = node.getLeft(); } node = stack.pop(); System.out.println(node.getValue()); node = node.getRight(); } } //先序遍历(递归) public void preOrderTraverse() { preOrderTraverse(root); } public void preOrderTraverse(Node<String> node) { if (node != null) { System.out.println(node.getValue()); preOrderTraverse(node.getLeft()); preOrderTraverse(node.getRight()); } } //先序遍历(非递归) public void nrPreOrderTraverse() { Stack<Node<String>> stack = new Stack<Node<String>>(); Node<String> node = root; while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { while (node != null) { System.out.println(node.getValue()); stack.push(node); node = node.getLeft(); } node = stack.pop(); node = node.getRight(); } } //后序遍历(递归) public void postOrderTraverse() { postOrderTraverse(root); } public void postOrderTraverse(Node<String> node) { if (node != null) { postOrderTraverse(node.getLeft()); postOrderTraverse(node.getRight()); System.out.println(node.getValue()); } } //后续遍历(非递归) public void nrPostOrderTraverse() { Stack<Node<String>> stack = new Stack<Node<String>>(); Node<String> node = root; Node<String> preNode = null;//表示最近一次访问的节点 while (node != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { while (node != null) { stack.push(node); node = node.getLeft(); } node = stack.peek(); if (node.getRight() == null || node.getRight() == preNode) { System.out.println(node.getValue()); node = stack.pop(); preNode = node; node = null; } else { node = node.getRight(); } } } //按层次遍历 public void levelTraverse() { levelTraverse(root); } public void levelTraverse(Node<String> node) { Queue<Node<String>> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Node<String>>(); queue.add(node); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node<String> temp = queue.poll(); if (temp != null) { System.out.println(temp.getValue()); queue.add(temp.getLeft()); queue.add(temp.getRight()); } } } } //树的节点 class Node<T> { private Node<T> left; private Node<T> right; private T value; public Node() { } public Node(Node<T> left,Node<T> right,T value) { this.left = left; this.right = right; this.value = value; } public Node(T value) { this(null,null,value); } public Node<T> getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(Node<T> left) { this.left = left; } public Node<T> getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(Node<T> right) { this.right = right; } public T getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(T value) { this.value = value; } } public class Main { /** * 二分查找 * @param key 搜索的目标 * */ private static int binarySearch(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, int key) { int low = fromIndex; int high = toIndex - 1; int mid, midVal; while (low <= high) { mid = (low + high) >>> 1; midVal = a[mid]; if (midVal < key) low = mid + 1; else if (midVal > key) high = mid - 1; else return mid; // key found } return -(low + 1); // key not found. } public static void swap(int[] a, int index1, int index2) { int temp = a[index1]; a[index1] = a[index2]; a[index2] = temp; } public static void main(String[] args) { Tree tree = new Tree(); tree.buildTree(); System.out.println("中序遍历(递归)"); tree.inOrderTraverse(); System.out.println("中序遍历(非递归)"); tree.nrInOrderTraverse(); System.out.println("后续遍历(递归)"); tree.postOrderTraverse(); System.out.println("后续遍历(非递归)"); tree.nrPostOrderTraverse(); System.out.println("先序遍历(递归)"); tree.preOrderTraverse(); System.out.println("先序遍历(非递归)"); tree.nrPreOrderTraverse(); } }
二叉树的遍历有三种方式,如下:
(1)前序遍历(DLR),首先访问根结点,然后遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树。简记根-左-右。
(2)中序遍历(LDR),首先遍历左子树,然后访问根结点,最后遍历右子树。简记左-根-右。
(3)后序遍历(LRD),首先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根结点。简记左-右-根。

例1:如上图所示的二叉树,若按前序遍历,则其输出序列为 。若按中序遍历,则其输出序列为 。若按后序遍历,则其输出序列为 。
前序:根A,A的左子树B,B的左子树没有,看右子树,为D,所以A-B-D。再来看A的右子树,根C,左子树E,E的左子树F,E的右子树G,G的左子树为H,没有了结束。连起来为C-E-F-G-H,最后结果为ABDCEFGH
中序:先访问根的左子树,B没有左子树,其有右子树D,D无左子树,下面访问树的根A,连起来是BDA。
再访问根的右子树,C的左子树的左子树是F,F的根E,E的右子树有左子树是H,再从H出发找到G,到此C的左子树结束,找到根C,无右子树,结束。连起来是FEHGC, 中序结果连起来是BDAFEHGC
后序:B无左子树,有右子树D,再到根B。再看右子树,最下面的左子树是F,其根的右子树的左子树是H,再到H的根G,再到G的根E,E的根C无右子树了,直接到C,这时再和B找它们其有的根A,所以连起来是DBFHGECA
例2:有下列二叉树,对此二叉树前序遍历的结果为( )。
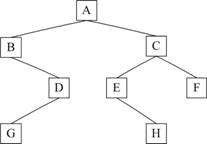
A)ACBEDGFH B)ABDGCEHF
C)HGFEDCBA D)ABCDEFGH
解析:先根A,左子树先根B,B无左子树,其右子树,先根D,在左子树G,连起来是ABDG。 A的右子树,先根C,C左子树E,E无左子树,有右子树为H,C的右子树只有F,连起来是CEHF。整个连起来是B答案 ABDGCEHF。
例3:已知二叉树后序遍历是DABEC,中序遍历序列是DEBAC,它的前序遍历序列是( ) 。
A)CEDBA B)ACBED C)DECAB D)DEABC
解析:由后序遍历可知,C为根结点,由中序遍历可知,C左边的是左子树含DEBA,C右边无结点,知根结点无右子树。先序遍历先访问根C,答案中只有A以C开头,为正确答案。
例4: 如下二叉树中序遍历的结果是( )。
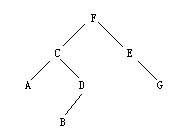
A). ACBDFEG B). ACBDFGE C).ABDCGEF D).FCADBEG
解析:首先中序遍历根F会把左右子树分开,F不会在答案的开头和结尾,排除C和D。在看F的右子树,G是E的右子树,中序遍历先访问E,再访问G,E在G前面,排除B。答案为A。
例5:如下二叉树后序遍历的结果是( )。
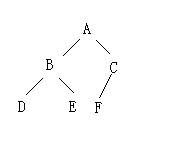
A) ABCDEF B) DBEAFC C)ABDECF D)DEBFCA
解析:后序的最后一个必须是二叉树的根,快速判断答案为D。