Java Notes-10
Summay: The Map Interface, Collection implementations
-Maps store and retrieve elements with key values
e.g:
Map dateMap = new HashMap();
dateMap.put( "today", new Date() );
Date today = dateMap.get( "today" ); -Functions:
public V put( K key , V value )//This method adds the specified key/value pair to the map.
public V get( K key )//This method retrieves the value corresponding to key from the map.
public V remove( K key )//This method removes the value corresponding to key from the map
public int size()//Use this method to find the number of key/value pairs in this map
public Set keySet()//This method returns a Set that contains all the keys in this map.
public Collection values()//Use this method to retrieve all the values in this map-Map has one child interface, SortedMap . A SortedMap maintains its key/value pairs sorted
in a particular order according to the key values.
-All of the methods of the Collection interface would appear to make sense for Map ,
except for iterator() . A Map , again, has two sets of objects: keys and values, and separate
iterators for each. This is why a Map does not implement Collection
-ConcurrentMap, It extends the base Map interface and adds atomic put, remove, and replace functionality that is
useful for concurrent programming
public V putIfAbsent( K key, V value )//This method associates the value with the key only if the key was not already in use.
public boolean remove( Object key, Object value )//This method removes the mapping (key and value) only if the current value asso‐
ciated with the key equals the supplied value
public boolean replace( K key, V existingValue, V newValue)//This method replaces the value associated with the key only if the existing value
equals the existingValue argument.
public boolean replace( K key, V value )//This method replaces the value associated with the key only if a mapping already
exists for the key-Arrays are described as consuming constant time for retrieval, but linear time for insertion into or deletion from the body of the array.
-Arrays are useful when you are mostly reading or exclusively appending to the end of the collection.
-Link List holds its elements in a chain of nodes, each referencing the node before and after it (if any).
-Unlike the magic of an array, however, to retrieve an element from a linked list, you must traverse the list from either the head or
tail to reach the correct spot. As you might have guessed, this is a linear-time operation that gets more expensive as the number of elements grows.
-Linked lists are useful when you are doing a lot of insertions or deletions on a collection
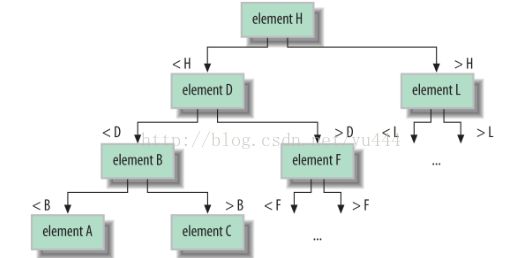
-Trees are useful for maintaining and searching large collections of sorted elements.
-A hash map (or hash table, as it is also called) uses a mathematical hash algorithm applied to its key value to distribute its element
-Java Collections implementations
| Interface | Implementation |
| Set | HashSet LinkedHashSet CopyOnWriteArraySet EnumSet CopyOnWriteArraySet |
| SortedSet | TreeSet ConcurrentSkipListSet |
| List | ArrayList LinkedList Vector a Stack CopyOnWriteArrayList |
| Map | HashMap EnumMap LinkedHashMap IdentityHashMap Hashtable a |
| ConcurrentMap | ConcurrentHashMap ConcurrentSkipListMap |
| SortedMap | TreeMap |
| Queue / Dequeue | LinkedList ArrayDeque PriorityQueue DelayQueue SynchronousQueue ConcurrentLinkedQueue ConcurrentLinkedDequeue |
| BlockingQueue | ArrayBlockingQueue LinkedBlockingQueue PriorityBlockingQueue |
Next Synchronized and Unsynchronized Collections...