Bugku:Snowfall
Bugku: Snowfall
-
- 1.知识点
-
-
-
- [1].WhiteSpace,是一种只用空白字符(空格,TAB和回车)编程的语言,==而其它可见字符统统为注释==。
- [2].栈的结构,==栈是先进后出==。
- [3].栈的结构图:
-
-
- 2.下载文件如下:
-
-
-
- [1].使用sublime text打开Ctrl + a全选查看,发现有很多的空格还有tab,所以我一开始也琢磨不明白,看了WP后明白了!
-
-
- 3.使用网站在线解析这段字符串。
-
-
-
- [1].打开[WhiteSpace在线解析网站](https://vii5ard.github.io/whitespace/)
- [2].复制step1.txt到网站的文本框,然后点击run,两个run随便那个都行。
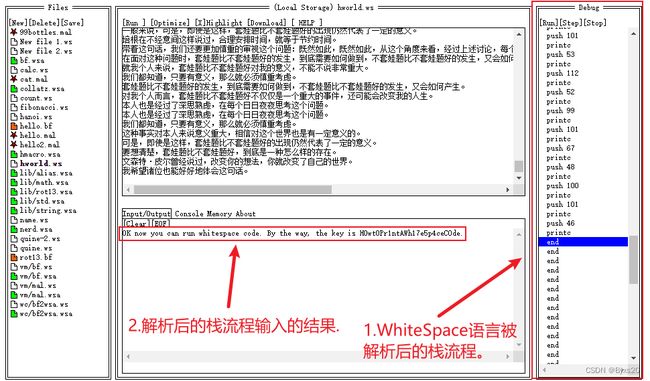
- [3].结果如图:
- [4].解析结果:
- [5].解析step2.txt
- [6].解析结果:
-
-
- 4.Python操作栈流程
-
-
-
- [1].首先复制栈流程保存到test.txt文件
- [2].分析里面的流程。
- [3].函数功能如下:
- [4].编写python代码.
-
-
- 5.解析flag.txt
-
-
-
- [1].解析flag.txt
- [2].分析栈流程
-
-
- 6.获取flag
-
-
-
- [1].稍加修改之前的脚本后,代码如下:
- [2].运行结果:
-
-
1.知识点
[1].WhiteSpace,是一种只用空白字符(空格,TAB和回车)编程的语言,而其它可见字符统统为注释。
它本身是个指令式、基于堆栈的语言。其程式运行在上的虚拟机器均有一个堆栈(Stack)和堆(Heap)。程式员可自由将整数推进堆栈中(只可以是整数,因为暂时并无浮点数或实数工具)。使用者亦可通过堆作为变量和数据结构的暂存区。
[2].栈的结构,栈是先进后出。
[3].栈的结构图:
2.下载文件如下:
[1].使用sublime text打开Ctrl + a全选查看,发现有很多的空格还有tab,所以我一开始也琢磨不明白,看了WP后明白了!
3.使用网站在线解析这段字符串。
[1].打开WhiteSpace在线解析网站
[2].复制step1.txt到网站的文本框,然后点击run,两个run随便那个都行。
[3].结果如图:
[4].解析结果:
OK now you can run whitespace code. By the way, the key is H0wt0Pr1ntAWh17e5p4ceC0de.
成功拿到key,显然现在不知道key有什么用处,我们现在解析step2.txt文件
[5].解析step2.txt
[6].解析结果:
根据7z和flag.txt很容易猜测到,这是一个7z格式的压缩包,里面的flag.txt就是我们需要的flag了。
由于我们直接复制解析结果,保存到为7z显示文件格式有误,所以只好在右边的栈流程进行操作了。
4.Python操作栈流程
[1].首先复制栈流程保存到test.txt文件
[2].分析里面的流程。
一共是有5个函数,分别是push, printc, dup, drop, add.
[3].函数功能如下:
push:将数字压入栈顶
printc:将栈顶元素弹出并以ASCII字符形式输出
dup:复制栈顶元素后压入栈顶drop:弹出栈顶元素
add:将堆栈最上方的两个元素弹出,二者做加法运算,得到的结果入栈
[4].编写python代码.
import re
from queue import LifoQueue
with open("test.txt", "r") as f:
data = f.read()
data = data.splitlines()
stack = LifoQueue()
ret = ""
for line in data:
if "push" in line:
num = int(re.findall("push (.*?)$", line)[0])
stack.put(num)
elif line == "add":
stack.put(stack.get() + stack.get())
elif line == "dup":
num = stack.get()
stack.put(num)
stack.put(num)
elif line == "drop":
stack.get()
elif line == "printc":
asc = chr(stack.get())
# print(asc, end="")
ret += asc
# save file
bin_data = ret.encode("latin1")
with open("1.7z", "wb") as f:
f.write(bin_data)
关于代码,不太懂的去学习一下吧,我这边也是现学现卖的。
运行python代码后,轻松拿到1.7z,解压密码为之前step1.txt解析出来的key,也就是H0wt0Pr1ntAWh17e5p4ceC0de
5.解析flag.txt
[1].解析flag.txt
由于这个也都是WhiteSpace,所以接着用网站解析,但是,这次解析结果居然为空白了:
[2].分析栈流程
我们把栈流程复制粘贴到test2.txt
仔细观察发现没有printc这个函数了,所以解析不出结果也很正常。我也是根据WP知道了,是要把drop这个函数换成printc.
6.获取flag
[1].稍加修改之前的脚本后,代码如下:
import re
from queue import LifoQueue
with open("test2.txt", "r") as f:
data = f.read()
data = data.splitlines()
stack = LifoQueue()
ret = ""
for line in data:
if "push" in line:
num = int(re.findall("push (.*?)$", line)[0])
stack.put(num)
elif line == "add":
stack.put(stack.get() + stack.get())
elif line == "dup":
num = stack.get()
stack.put(num)
stack.put(num)
elif line == "drop":
asc = chr(stack.get())
print(asc, end="")
[2].运行结果:
bugku{F1xAnE5olangPr0gr4mT0Cap7ureTh3F14g}
完结!~拜拜!