Linux网络驱动学习
1.嵌入式网络硬件
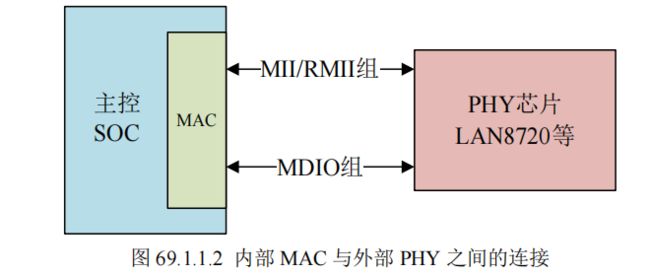
嵌入式网络硬件一般分为两部分,MAC和PHY。一般SOC会内置MAC,PHY一般外接。
1.SOC内部没有MAC
如果SOC没有内置MAC,还可以通过外接MAC+PHY芯片来上网,for example,三星的开发板都是通过外置的 DM9000 来完成有线网络功能的。有些外置的网络芯片更强大,内部甚至集成了硬件 TCP/IP 协议栈,对外提供一个 SPI 接口,比如 W5500。
2.SOC 内部集成网络 MAC 外设
1.内部MAC与网络的关系
我们一般说某个 SOC 支持网络,说的就是他内部集成网络 MAC 外设,此时我们还需要外接一个网络PHY 芯片。
一般常见的通用 SOC 都会集成网络 MAC 外设,比如 STM32F4/F7/H7 系列、NXP 的 I.MX系列.内部集成网络 MAC 的优点如下:
①、内部 MAC 外设会有专用的加速模块,比如专用的 DMA,加速网速数据的处理。
②、网速快,可以支持 10/100/1000M 网速。
③、外接 PHY 可选择性多,成本低
内部的 MAC 外设会通过 MII 或者 RMII 接口来连接外部的 PHY 芯片,MII/RMII 接口用来传输网络数据。另外主控需要配置或读取 PHY 芯片,也就是读写 PHY 的内部寄存器,所以还需要一个控制接口,叫做 MIDO,MDIO 很类似 IIC,也是两根线,一根数据线叫做 MDIO,一根时钟线叫做 MDC.
2.MAC读取外部数据(PHY)的接口
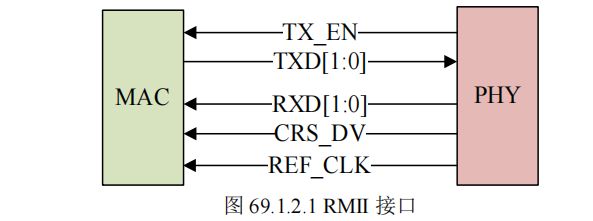
1. MII/RMII 接口
MII 全称是 Media Independent Interface,直译过来就是介质独立接口,它是 IEEE-802.3 定
义的以太网标准接口,MII 接口用于以太网 MAC 连接 PHY 芯片.
2.RMII 接口
RMII 全称是 Reduced Media Independent Interface,翻译过来就是精简的介质独立接口,也
就是 MII 接口的精简版本
dist:
REF_CLK:参考时钟,由外部时钟源提供, 频率为 50MHz。这里与 MII 不同,MII 的接
收和发送时钟是独立分开的,而且都是由 PHY 芯片提供的。
3.MDIO 接口
MDIO 全称是 Management Data Input/Output.是一个简单的两线串行接口,一根 MDIO 数据线,一根 MDC 时钟线。驱动程序可以通过 MDIO 和MDC 这两根线访问 PHY 芯片的任意一个寄存器。
MDIO 接口支持多达 32 个 PHY。同一时刻内只能对一个 PHY 进行操作,那么如何区分这 32 个 PHY 芯片呢?和 IIC 一样,使用器件地址即可。
同一 MDIO 接口下的所有 PHY 芯片,其器件地址不能冲突,必须保证唯一,具体器件地址值要查阅相应的 PHY 数据手册。
4.RJ45 接口
网络设备是通过网线连接起来的,插入网线的叫做 RJ45 座。如图所示。
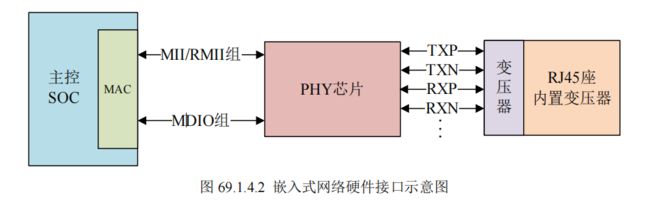
RJ45 座要与 PHY 芯片连接在一起,但是中间需要一个网络变压器,网络变压器用于隔离
以及滤波等,网络变压器也是一个芯片,如图
但是现在很多 RJ45 座子内部已经集成了网络变压器,比如正点原子 ALPHA 开发板所使HR911105A 就是内置网络变压器的 RJ45 座。内置网络变压器的 RJ45 座和不内置的引脚一样,但是一般不内置RJ45 座会短一点。
RJ45 座子上一般有两个灯,一个黄色(橙色),一个绿色,绿色亮的话表示网络连接正常,黄色闪烁的话说明当前正在进行网络通信。这两个灯由 PHY 芯片控制,PHY 芯片会有两个引脚来连接 RJ45 座上的这两个灯。内部 MAC+外部 PHY+RJ45 座(内置网络变压器)就组成了一个完整的嵌入式网络接口硬件。
3.PHY芯片
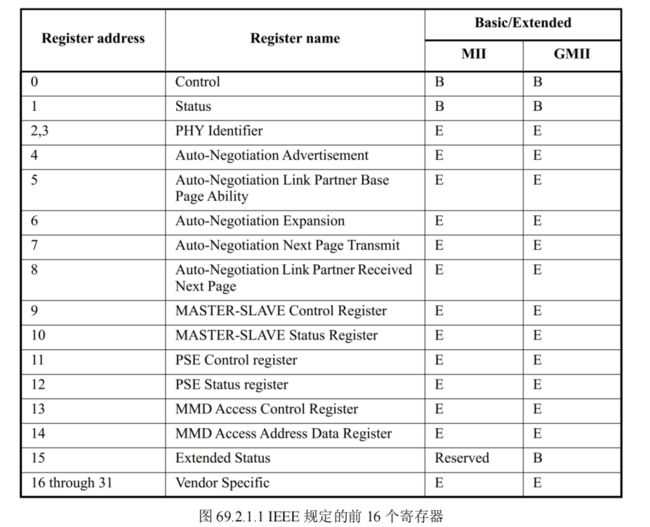
PHY 是 IEEE 802.3 规定的一个标准模块,SOC可以对PHY进行读取或配置相关状态。PHY 芯片寄存器地址空间为 5 位,地址 0~31 共 32 个寄存器,IEEE 定义了 0~15 这 16 个寄存器的功能,16~31 这 16 个寄存器由厂商自行实现。前16个寄存器是通用的。但是也有很多厂商采用分页技术来扩展寄存器地址空间,以求定义更多的寄存器。因此 Linux 内核的通用 PHY 驱动就无法驱动这些特色功能了,这个时候就需要 PHY 厂商提供相应的驱动源码。
1. LAN8720A 详解(PHY芯片)
开发板所使用的芯片,PHY芯片都符合 IEEE 802.3标准,所以相同的配置都一样。需要学习到是网络硬件配置相关的寄存器如何配置。
- LAN8720A 是低功耗的 10/100M 单以太网 PHY 层芯片,
- LAN8720A 支持通过 RMII 接口与以太网 MAC 层通信,内置 10-BASE-T/100BASE-TX 全双工传输模块,支持10Mbps 和 100Mbps。
- LAN8720A 可以通过自协商的方式选择与目的主机最佳的连接方式(速度和双工模式)。支持 HP Auto-MDIX 自动翻转功能,无需更换网线即可将连接更改为直连或交叉连接。
2.LAN8720A 中断管理
- LAN8720A 的器件管理接口支持非 IEEE 802.3 规范的中断功能。当一个中断事件发生并且相应事件的中断位使能,LAN8720A 就会在 nINT(14 脚)产生一个低电平有效的中断信号。
- LAN8720A 的中断系统提供两种中断模式:主中断模式和复用中断模式。主中断模式是默认中断模式,LAN8720A 上电或复位后就工作在主中断模式,当模式控制/状态寄存器(十进制地址为 17)的 ALTINT 位为 0 时 LAN8720A 工作在主模式,当 ALTINT 位为 1 时工作在复用中断模式。正点原子的 ALPHA 开发板虽然讲 LAN8720A 的中断引脚连接到了 I.MX6ULL 上,但是并没有使用中断功能,关于中断的具体用法可以参考 LAN8720A 数据手册的 29~30 页。
3.PHY 地址设置
- MAC 层通过 MDIO/MDC 总线对 PHY 进行读写操作,MDIO 最多可以控制 32 个 PHY 芯片,通过不同的 PHY 芯片地址来对不同的 PHY 操作。
- LAN8720A 通过设置 RXER/PHYAD0引脚来设置其 PHY 地址,默认情况下为 0(下拉),上拉为1.
- 正点原子 ALPHA 开发板的 ENET1 网络的 LAN8720A 上的 RXER/PHYAD0 引脚为默认状态(原理图上有个 10K 下拉,但是没有焊接),因此 ENET1 上的 LAN8720A 地址为 0。ENET2网络上的 LAN8720A 上的 RXER/PHYAD0 引脚接了个 10K 上拉电阻,因此 ENET2 上的LAN8720A 地址为 1。
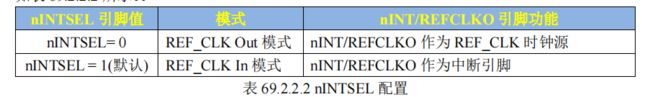
4.nINT/REFCLKO 配置
nINTSEL 引脚(2 号引脚)用于设置 nINT/REFCLKO 引脚(14 号引脚)的功能。有两种可选工作模式,
正点原子的 ALPHA 开发板工作在 REF_CLK In 模式下,因此需要外部 50MHz时钟信号,I.MX6ULL 有专用的网络时钟引脚,因此 ALPHA 开发板是通过 I.MX6ULL 的ENET1_REF_CLK 和 ENET2_REF_CLK 这两个网络时钟引脚来为 LAN8720A 提供 50MHz 的时钟。
5.LAN8720A 内部寄存器
需要配置的最基本的寄存器。
- BCR(Basic Control Rgsister)寄存器 配置 PHY 芯片,重点就是配置 BCR 寄存器,
- BSR(Basic Status Register)寄存器 通过读取 BSR寄存器的值我们可以得到当前的连接速度、双工状态和连接状态等。
- PHY ID 寄存器 1 和 ID 寄存器 2 IEEE 规定了一叫做 OUI 的 ID组成方式,全称是 Organizationally Unique Identifier,OUI 一共 32 位,分为三部分:22 位的 ID+6位厂商型号 ID+4 位厂商版本 ID
- 特殊控制/状态寄存器 我们关心的是 bit2~bit4 这三位,因为通过这 3 位来确定连接的状态和速度.
2.Linux网络驱动框架
1. net_device 结构体
Linux 内核使用 net_device 结构体表示一个具体的网络设备,net_device 是整个网络驱动的灵魂。网络驱动的核心就是初始化 net_device 结构体中的各个成员变量,然后将初始化完成以后net_device 注到Linux 内核中。net_device 结构体定义在 include/linux/netdevice.h 中。
其中一些关键的成员变量含义:
- name 是网络设备的名字。
- mem_end 是共享内存结束地址。
- mem_start 是共享内存起始地址。
- base_addr 是网络设备 I/O 地址。
- irq 是网络设备的中断号
- dev_list 是全局网络设备列表。
- napi_list 是 napi 网络设备的列表入口。
- unreg_list 是注销(unregister)的网络设备列表入口。
- close_list 是关闭的网络设备列表入口。
- netdev_ops 是网络设备的操作集函数,包含了一系列的网络设备操作回调函数,类似字符设备中的 file_operations
- ethtool_ops 是网络管理工具相关函数集,用户空间网络管理工具会调用此结构体中的相关函数获取网卡状态或者配置网卡
- header_ops 是头部的相关操作函数集,比如创建、解析、缓冲等
- flags 是网络接口标志,标志类型定义在 include/uapi/linux/if.h 文件中,为一个枚举类型
- if_port 指定接口的端口类型,如果设备支持多端口的话就通过 if_port 来指定所使用的端口类型。可选的端口类型定义在 include/uapi/linux/netdevice.h 中
- dma 是网络设备所使用的 DMA 通道,不是所有的设备都会用到 DMA。
- mtu 是网络最大传输单元,为 1500。
- type 用于指定 ARP 模块的类型,以太网的 ARP 接口为 ARPHRD_ETHER,Linux内核所支持的 ARP 协议定义在 include/uapi/linux/if_arp.h 中
- perm_addr 是永久的硬件地址,如果某个网卡设备有永久的硬件地址,那么就会填充 perm_addr。
- addr_len 是硬件地址长度。
- last_rx 是最后接收的数据包时间戳,记录的是 jiffies。
- dev_addr 也是硬件地址,是当前分配的 MAC 地址,可以通过软件修改
- _rx 是接收队列。
- num_rx_queues 是接收队列数量,在调用 register_netdev 注册网络设备的时候会分配指定数量的接收队列。
- real_num_rx_queues 是当前活动的队列数量
- _tx 是发送队列。
- num_tx_queues 是发送队列数量,通过 alloc_netdev_mq 函数分配指定数量的发送队列
- real_num_tx_queues 是当前有效的发送队列数量。
- trans_start 是最后的数据包发送的时间戳,记录的是 jiffies。
- phydev 是对应的 PHY 设备
2. 申请、删除、注册、注销net_device
2.1编写网络驱动的时候首先要申请 net_device,使用 alloc_netdev 函数
#define alloc_netdev(sizeof_priv, name, name_assign_type, setup) \
alloc_netdev_mqs(sizeof_priv, name, name_assign_type, setup, 1, 1)
struct net_device * alloc_netdev_mqs (
int sizeof_priv, //私有数据块大小
const char *name, //设备名称
void (*setup) (struct net_device *)) //回调函数
unsigned int txqs, //发送队列数量
unsigned int rxqs //接收队列数量
);事实上网络设备有多种,Linux 内核内核支持的网络接口有很多,比如光纤分布式数据接口(FDDI)、以太网设备(Ethernet)、红外数据接口(InDA)、高性能并行接口(HPPI)、CAN 网络等。内核针对不同的网络设备在 alloc_netdev 的基础上提供了一层封装,比如我们本章讲解的以太网,针对以太网封装的 net_device 申请函数是 alloc_etherdev和,这也是一个宏,内容如下
#define alloc_etherdev(sizeof_priv) alloc_etherdev_mq(sizeof_priv, 1)
#define alloc_etherdev_mq(sizeof_priv, count) alloc_etherdev_mqs(sizeof_priv, count, count)
struct net_device *alloc_etherdev_mqs(int sizeof_priv,unsigned int txqs,unsigned int rxqs){
return alloc_netdev_mqs(
sizeof_priv,
"eth%d", //网卡名称
NET_NAME_UNKNOWN,
ether_setup, //同样的,这里设置了以太网的 setup 函数为 ether_setup,不同的网络设备其 setup函数不同,比如 CAN 网络里面 setup 函数就是 can_setup。
txqs,
rxqs
);
}其中,ether_setup 函数会对 net_device 做初步的初始化
/**
* ether_setup - setup Ethernet network device
* @dev: network device
*
* Fill in the fields of the device structure with Ethernet-generic values.
*/
void ether_setup(struct net_device *dev)
{
dev->header_ops = ð_header_ops;
dev->type = ARPHRD_ETHER;
dev->hard_header_len = ETH_HLEN;
dev->mtu = ETH_DATA_LEN;
dev->addr_len = ETH_ALEN;
dev->tx_queue_len = 1000; /* Ethernet wants good queues */
dev->flags = IFF_BROADCAST|IFF_MULTICAST;
dev->priv_flags |= IFF_TX_SKB_SHARING;
eth_broadcast_addr(dev->broadcast);
}2.2删除net_device
void free_netdev(struct net_device *dev)2.3 注册net_device
net_device 申请并初始化完成以后就需要向内核注册 net_device,要用到函数 register_netdev
int register_netdev(struct net_device *dev)2.4注销net_device
void unregister_netdev(struct net_device *dev)3. net_device结构体中的成员net_device_ops结构体
3.1net_device_ops结构体
net_device 有个非常重要的成员变量:netdev_ops,为 net_device_ops 结构体指针类型,这就是网络设备的操作集。net_device_ops 结构体定义在 include/linux/netdevice.h 文件中
net_device_ops 结构体里面都是一些以“ndo_”开头的函数,这些函数就需要网络驱动编写人员去实现,不需要全部都实现,根据实际驱动情况实现其中一部分即可。
You can learn what they mean from their comments(annotation)!
* This structure defines the management hooks for network devices.
* The following hooks can be defined; unless noted otherwise, they are
* optional and can be filled with a null pointer.
*
* int (*ndo_init)(struct net_device *dev);
* This function is called once when network device is registered.
* The network device can use this to any late stage initializaton
* or semantic validattion. It can fail with an error code which will
* be propogated back to register_netdev
*
* void (*ndo_uninit)(struct net_device *dev);
* This function is called when device is unregistered or when registration
* fails. It is not called if init fails.
*
* int (*ndo_open)(struct net_device *dev);
* This function is called when network device transistions to the up
* state.
*
* int (*ndo_stop)(struct net_device *dev);
* This function is called when network device transistions to the down
* state.
* netdev_tx_t (*ndo_start_xmit)(struct sk_buff *skb,
* struct net_device *dev);
* Called when a packet needs to be transmitted.
* Returns NETDEV_TX_OK. Can return NETDEV_TX_BUSY, but you should stop
* the queue before that can happen; it's for obsolete devices and weird
* corner cases, but the stack really does a non-trivial amount
* of useless work if you return NETDEV_TX_BUSY.
* (can also return NETDEV_TX_LOCKED iff NETIF_F_LLTX)
* Required can not be NULL.
/*
ndo_start_xmit 函数:
当需要发送数据的时候此函数就会执行,此函数有一个参数
为 sk_buff 结构体指针,sk_buff 结构体在 Linux 的网络驱动中非常重要,sk_buff 保存了上层传
递给网络驱动层的数据。也就是说,要发送出去的数据都存在了 sk_buff 中,关于 sk_buff 稍后
会做详细的讲解。如果发送成功的话此函数返回 NETDEV_TX_OK,如果发送失败了就返回
NETDEV_TX_BUSY,如果发送失败了我们就需要停止队列
*/一些重要的设备操作函数:
- ndo_select_queue 函数,当设备支持多传输队列的时候选择使用哪个队列
- ndo_set_rx_mode 函数,此函数用于改变地址过滤列表,根据 net_device 的 flags成员变量来设置 SOC 的网络外设寄存器。比如 flags 可能为 IFF_PROMISC、IFF_ALLMULTI 或IFF_MULTICAST,分别表示混杂模式、单播模式或多播模式。
- ndo_set_mac_address 函数,此函数用于修改网卡的 MAC 地址,设置 net_device的 dev_addr 成员变量,并且将 MAC 地址写入到网络外设的硬件寄存器中
- ndo_validate_addr 函数,验证 MAC 地址是否合法,也即是验证 net_device 的dev_addr 中的 MAC 地址是否合法,直接调用 is_valid_ether_addr 函数。
- ndo_do_ioctl 函数,用户程序调用 ioctl 的时候此函数就会执行,比如 PHY 芯片相关的命令操作,一般会直接调用 phy_mii_ioctl 函数。
- ndo_change_mtu 函数,更改 MTU 大小。
- ndo_tx_timeout 函数,当发送超时的时候产生会执行,一般都是网络出问题了导致发送超时。一般可能会重启 MAC 和 PHY,重新开始数据发送等
- ndo_poll_controller 函数,使用查询方式来处理网卡数据的收发。
- ndo_set_features 函数,修改 net_device 的 features 属性,设置相应的硬件属性。
3.2 网络数据发送与接收机制
其中,一个非常重要的数据结构 sk_buff 结构体。
网络是分层的,对于应用层而言不用关系具体的底层是如何工作的,只需要按照协议将要发送或接收的数据打包好即可。打包好以后都通过 dev_queue_xmit 函数将数据发送出去,接收数据的话使用 netif_rx 函数即可,我们依次来看一下这两个函数。
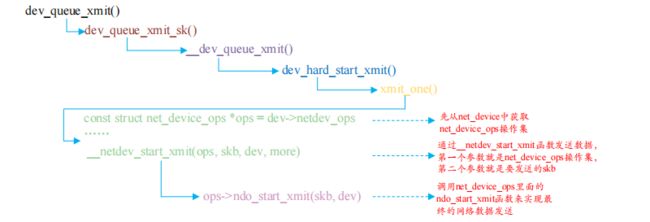
1.dev_queue_xmit 函数
此函数用于将网络数据发送出去,函数定义在 include/linux/netdevice.h 中
static inline int dev_queue_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb)skb:要发送的数据,这是一个 sk_buff 结构体指针,sk_buff 是 Linux 网络驱动中一个非常重要的结构体,网络数据就是以 sk_buff 保存的,各个协议层在 sk_buff 中添加自己的协议头,最终由底层驱动将 sk_buff 中的数据发送出去。网络数据的接收过程恰好相反,网络底层驱动将接收到的原始数据打包成 sk_buff,然后发送给上层协议,上层会取掉相应的头部,然后将最终的数据发送给用户。
dev_queue_xmit 函数最终是通过net_device_ops 操作集里面的 ndo_start_xmit 函数来完成最终发送了,ndo_start_xmit 就是网络驱动编写人员去实现的
dev_queue_xmit 执行流程
2.netif_rx函数
上层接收数据的话使用 netif_rx 函数,但是最原始的网络数据一般是通过轮询、中断或 NAPI
的方式来接收。netif_rx 函数定义在 net/core/dev.c 中
/*
* @return: NET_RX_SUCCESS 成功,NET_RX_DROP 数据包丢弃
*/
int netif_rx(struct sk_buff *skb)3.sk_buff结构体
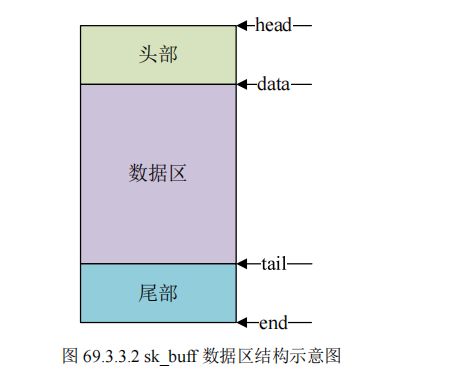
sk_buff 是 Linux 网络重要的数据结构,用于管理接收或发送数据包,sk_buff 结构体定义在 include/linux/skbuff.h 中
/**
* struct sk_buff - socket buffer
* @next: Next buffer in list
* @prev: Previous buffer in list
* @tstamp: Time we arrived/left
* @rbnode: RB tree node, alternative to next/prev for netem/tcp
* @sk: Socket we are owned by
* @dev: Device we arrived on/are leaving by
* @cb: Control buffer. Free for use by every layer. Put private vars here
* @_skb_refdst: destination entry (with norefcount bit)
* @sp: the security path, used for xfrm
* @len: Length of actual data
* @data_len: Data length
* @mac_len: Length of link layer header
* @hdr_len: writable header length of cloned skb
* @csum: Checksum (must include start/offset pair)
* @csum_start: Offset from skb->head where checksumming should start
* @csum_offset: Offset from csum_start where checksum should be stored
* @priority: Packet queueing priority
* @ignore_df: allow local fragmentation
* @cloned: Head may be cloned (check refcnt to be sure)
* @ip_summed: Driver fed us an IP checksum
* @nohdr: Payload reference only, must not modify header
* @nfctinfo: Relationship of this skb to the connection
* @pkt_type: Packet class
* @fclone: skbuff clone status
* @ipvs_property: skbuff is owned by ipvs
* @peeked: this packet has been seen already, so stats have been
* done for it, don't do them again
* @nf_trace: netfilter packet trace flag
* @protocol: Packet protocol from driver
* @destructor: Destruct function
* @nfct: Associated connection, if any
* @nf_bridge: Saved data about a bridged frame - see br_netfilter.c
* @skb_iif: ifindex of device we arrived on
* @tc_index: Traffic control index
* @tc_verd: traffic control verdict
* @hash: the packet hash
* @queue_mapping: Queue mapping for multiqueue devices
* @xmit_more: More SKBs are pending for this queue
* @ndisc_nodetype: router type (from link layer)
* @ooo_okay: allow the mapping of a socket to a queue to be changed
* @l4_hash: indicate hash is a canonical 4-tuple hash over transport
* ports.
* @sw_hash: indicates hash was computed in software stack
* @wifi_acked_valid: wifi_acked was set
* @wifi_acked: whether frame was acked on wifi or not
* @no_fcs: Request NIC to treat last 4 bytes as Ethernet FCS
* @napi_id: id of the NAPI struct this skb came from
* @secmark: security marking
* @mark: Generic packet mark
* @vlan_proto: vlan encapsulation protocol
* @vlan_tci: vlan tag control information
* @inner_protocol: Protocol (encapsulation)
* @inner_transport_header: Inner transport layer header (encapsulation)
* @inner_network_header: Network layer header (encapsulation)
* @inner_mac_header: Link layer header (encapsulation)
* @transport_header: Transport layer header
* @network_header: Network layer header
* @mac_header: Link layer header
* @tail: Tail pointer
* @end: End pointer
* @head: Head of buffer
* @data: Data head pointer
* @truesize: Buffer size
* @users: User count - see {datagram,tcp}.c
*/
struct sk_buff {
union {
struct {
/* These two members must be first. */
struct sk_buff *next;
struct sk_buff *prev;
union {
ktime_t tstamp;
struct skb_mstamp skb_mstamp;
};
};
struct rb_node rbnode; /* used in netem & tcp stack */
};
struct sock *sk;
struct net_device *dev;
/*
* This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every
* layer. Please put your private variables there. If you
* want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()
* first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.
*/
char cb[48] __aligned(8);
unsigned long _skb_refdst;
void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);
#ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
struct sec_path *sp;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE)
struct nf_conntrack *nfct;
#endif
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER)
struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge;
#endif
unsigned int len,
data_len;
__u16 mac_len,
hdr_len;
/* Following fields are _not_ copied in __copy_skb_header()
* Note that queue_mapping is here mostly to fill a hole.
*/
kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags1);
__u16 queue_mapping;
__u8 cloned:1,
nohdr:1,
fclone:2,
peeked:1,
head_frag:1,
xmit_more:1;
/* one bit hole */
kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags1);
/* fields enclosed in headers_start/headers_end are copied
* using a single memcpy() in __copy_skb_header()
*/
/* private: */
__u32 headers_start[0];
/* public: */
/* if you move pkt_type around you also must adapt those constants */
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD
#define PKT_TYPE_MAX (7 << 5)
#else
#define PKT_TYPE_MAX 7
#endif
#define PKT_TYPE_OFFSET() offsetof(struct sk_buff, __pkt_type_offset)
__u8 __pkt_type_offset[0];
__u8 pkt_type:3;
__u8 pfmemalloc:1;
__u8 ignore_df:1;
__u8 nfctinfo:3;
__u8 nf_trace:1;
__u8 ip_summed:2;
__u8 ooo_okay:1;
__u8 l4_hash:1;
__u8 sw_hash:1;
__u8 wifi_acked_valid:1;
__u8 wifi_acked:1;
__u8 no_fcs:1;
/* Indicates the inner headers are valid in the skbuff. */
__u8 encapsulation:1;
__u8 encap_hdr_csum:1;
__u8 csum_valid:1;
__u8 csum_complete_sw:1;
__u8 csum_level:2;
__u8 csum_bad:1;
#ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE
__u8 ndisc_nodetype:2;
#endif
__u8 ipvs_property:1;
__u8 inner_protocol_type:1;
__u8 remcsum_offload:1;
/* 3 or 5 bit hole */
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
__u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
__u16 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */
#endif
#endif
union {
__wsum csum;
struct {
__u16 csum_start;
__u16 csum_offset;
};
};
__u32 priority;
int skb_iif;
__u32 hash;
__be16 vlan_proto;
__u16 vlan_tci;
#if defined(CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL) || defined(CONFIG_XPS)
union {
unsigned int napi_id;
unsigned int sender_cpu;
};
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK
__u32 secmark;
#endif
union {
__u32 mark;
__u32 reserved_tailroom;
};
union {
__be16 inner_protocol;
__u8 inner_ipproto;
};
__u16 inner_transport_header;
__u16 inner_network_header;
__u16 inner_mac_header;
__be16 protocol;
__u16 transport_header;
__u16 network_header;
__u16 mac_header;
/* private: */
__u32 headers_end[0];
/* public: */
/* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */
sk_buff_data_t tail;
sk_buff_data_t end;
unsigned char *head,
*data;
unsigned int truesize;
atomic_t users;
};
内核针对sk_buff提供了一系列的API
3.1分配sk_buff
要使用 sk_buff 必须先分配,首先来看一下 alloc_skb 这个函数,此函数定义在include/linux/skbuff.h 中
/*
size:要分配的大小,也就是 skb 数据段大小
priority:为 GFP MASK 宏,比如 GFP_KERNEL、GFP_ATOMIC 等。
返回值:分配成功的话就返回申请到的 sk_buff 首地址,失败的话就返回 NULL。
*/
static inline struct sk_buff *alloc_skb(unsigned int size,gfp_t priority)在网络设备驱动中常常使用 netdev_alloc_skb 来为某个设备申请一个用于接收的 skb_buff,
此函数也定义在 include/linux/skbuff.h 中
/*
dev:要给哪个设备分配 sk_buff。
length:要分配的大小。
返回值:分配成功的话就返回申请到的 sk_buff 首地址,失败的话就返回 NULL。
*/
static inline struct sk_buff *netdev_alloc_skb(struct net_device *dev,
unsigned int length)3.2 释放sk_buff
当使用完成以后就要释放掉 sk_buff,释放函数可以使用 kfree_skb,函数定义include/linux/skbuff.c
void kfree_skb(struct sk_buff *skb)对于网络设备而言最好使用如下所示释放函数:
void dev_kfree_skb (struct sk_buff *skb)3.3 skb_put、skb_push、sbk_pull 和 skb_reserve
这四个函数用于变更 sk_buff.
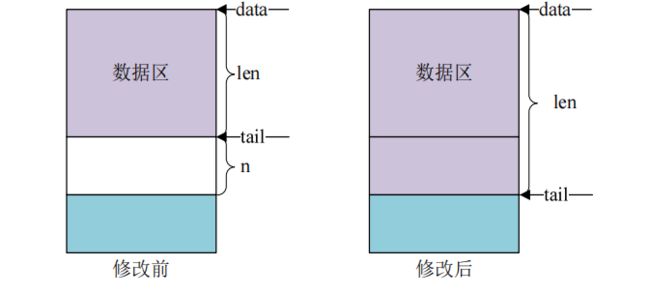
- skb_put 函数,此函数用于在尾部扩展 skb_buff的数据区,也就将 skb_buff 的 tail 后移 n 个字节,从而导致 skb_buff 的 len 增加 n 个字节
/*
skb:要操作的 sk_buff。
len:要增加多少个字节。
返回值:扩展出来的那一段数据区首地址。
*/
unsigned char *skb_put(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len)skb_put 操作之前和操作之后的数据区
- skb_push 函数用于在头部扩展 skb_buff 的数据区
/*
skb:要操作的 sk_buff。
len:要增加多少个字节。
返回值:扩展完成以后新的数据区首地址。
*/
unsigned char *skb_push(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len)skb_push 函数操作前后对比
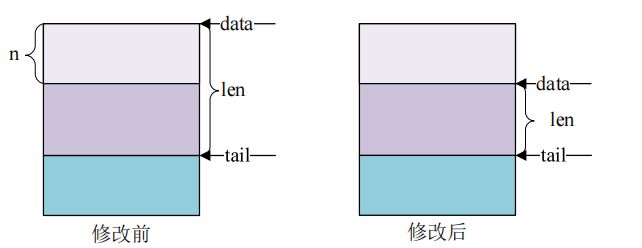
- sbk_pull 函数用于从 sk_buff 的数据区起始位置删除数据
/*
skb:要操作的 sk_buff。
len:要删除的字节数。
返回值:删除以后新的数据区首地址
*/
unsigned char *skb_pull(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len)skb_pull 函数操作前后对比
- sbk_reserve 函数用于调整缓冲区的头部大小,方法很简单将 skb_buff 的 data 和 tail 同时后移 n 个字节即可
/*
skb:要操作的 sk_buff。
len:要增加的缓冲区头部大小。
*/
static inline void skb_reserve(struct sk_buff *skb, int len)4. 网络 NAPI 处理机制
- Linux 里面的网络数据接收也有轮询和中断两种,中断的好处就是响应快,数据量小的时候处理及时,速度快,但是一旦当数据量大,而且都是短帧的时候会导致中断频繁发生,消耗大量的 CPU 处理时间在中断自身处理上。轮询恰好相反,响应没有中断及时,但是在处理大量数据的时候不需要消耗过多的 CPU 处理时间。
- Linux 在这两个处理方式的基础上提出了另外一种网络数据接收的处理方法:NAPI(New API),NAPI 是一种高效的网络处理技术。
- NAPI 的核心思想就是不全部采用中断来读取网络数据,而是采用中断来唤醒数据接收服务程序,在接收服务程序中采用 POLL 的方法来轮询处理数据。
- 这种方法的好处就是可以提高短数据包的接收效率,减少中断处理的时间。
如何在驱动中使用NAIP?
Linux 内核使用结构体 napi_struct 表示 NAPI,在使用 NAPI 之前要先初始化一个 napi_struct 实例。
/*
* Structure for NAPI scheduling similar to tasklet but with weighting
*/
struct napi_struct {
/* The poll_list must only be managed by the entity which
* changes the state of the NAPI_STATE_SCHED bit. This means
* whoever atomically sets that bit can add this napi_struct
* to the per-cpu poll_list, and whoever clears that bit
* can remove from the list right before clearing the bit.
*/
struct list_head poll_list;
unsigned long state;
int weight;
unsigned int gro_count;
int (*poll)(struct napi_struct *, int);
#ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL
spinlock_t poll_lock;
int poll_owner;
#endif
struct net_device *dev;
struct sk_buff *gro_list;
struct sk_buff *skb;
struct hrtimer timer;
struct list_head dev_list;
struct hlist_node napi_hash_node;
unsigned int napi_id;
};
1.初始化NAPI
/*
dev:每个 NAPI 必须关联一个网络设备,此参数指定 NAPI 要关联的网络设备。
napi:要初始化的 NAPI 实例。
poll:NAPI 所使用的轮询函数,非常重要,一般在此轮询函数中完成网络数据接收的工作。
weight:NAPI 默认权重(weight),一般为 NAPI_POLL_WEIGHT。/*
*/
void netif_napi_add(struct net_device *dev, struct napi_struct *napi,
int (*poll)(struct napi_struct *, int), int weight)
{
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&napi->poll_list);
hrtimer_init(&napi->timer, CLOCK_MONOTONIC, HRTIMER_MODE_REL_PINNED);
napi->timer.function = napi_watchdog;
napi->gro_count = 0;
napi->gro_list = NULL;
napi->skb = NULL;
napi->poll = poll;
if (weight > NAPI_POLL_WEIGHT)
pr_err_once("netif_napi_add() called with weight %d on device %s\n",
weight, dev->name);
napi->weight = weight;
list_add(&napi->dev_list, &dev->napi_list);
napi->dev = dev;
#ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL
spin_lock_init(&napi->poll_lock);
napi->poll_owner = -1;
#endif
set_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &napi->state);
}2.删除NAPI
void netif_napi_del(struct napi_struct *napi)
{
list_del_init(&napi->dev_list);
napi_free_frags(napi);
kfree_skb_list(napi->gro_list);
napi->gro_list = NULL;
napi->gro_count = 0;
}3.使能 NAPI
/**
* napi_enable - enable NAPI scheduling
* @n: napi context
*
* Resume NAPI from being scheduled on this context.
* Must be paired with napi_disable.
*/
static inline void napi_enable(struct napi_struct *n)
{
BUG_ON(!test_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state));
smp_mb__before_atomic();
clear_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state);
}4.关闭 NAPI
void napi_disable(struct napi_struct *n)
{
might_sleep();
set_bit(NAPI_STATE_DISABLE, &n->state);
while (test_and_set_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state))
msleep(1);
hrtimer_cancel(&n->timer);
clear_bit(NAPI_STATE_DISABLE, &n->state);
}5.检查 NAPI 是否可以进行调度
/**
* napi_schedule_prep - check if napi can be scheduled
* @n: napi context
*
* Test if NAPI routine is already running, and if not mark
* it as running. This is used as a condition variable
* insure only one NAPI poll instance runs. We also make
* sure there is no pending NAPI disable.
*/
static inline bool napi_schedule_prep(struct napi_struct *n)
{
return !napi_disable_pending(n) &&
!test_and_set_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state);
}6.NAPI 调度
/**
* __napi_schedule - schedule for receive
* @n: entry to schedule
*
* The entry's receive function will be scheduled to run.
* Consider using __napi_schedule_irqoff() if hard irqs are masked.
*/
void __napi_schedule(struct napi_struct *n)
{
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags);
____napi_schedule(this_cpu_ptr(&softnet_data), n);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}我们也可以使用 napi_schedule 函数来一次完成 napi_schedule_prep 和__napi_schedule 这两
个函数的工作(5、6)
/**
* napi_schedule - schedule NAPI poll
* @n: napi context
*
* Schedule NAPI poll routine to be called if it is not already
* running.
*/
static inline void napi_schedule(struct napi_struct *n)
{
if (napi_schedule_prep(n))
__napi_schedule(n);
}7.NAPI 处理完成
NAPI 处理完成以后需要调用 napi_complete 函数来标记 NAPI 处理完成
/**
* napi_complete - NAPI processing complete
* @n: napi context
*
* Mark NAPI processing as complete.
* Consider using napi_complete_done() instead.
*/
static inline void napi_complete(struct napi_struct *n)
{
return napi_complete_done(n, 0);
}
void napi_complete_done(struct napi_struct *n, int work_done)
{
unsigned long flags;
/*
* don't let napi dequeue from the cpu poll list
* just in case its running on a different cpu
*/
if (unlikely(test_bit(NAPI_STATE_NPSVC, &n->state)))
return;
if (n->gro_list) {
unsigned long timeout = 0;
if (work_done)
timeout = n->dev->gro_flush_timeout;
if (timeout)
hrtimer_start(&n->timer, ns_to_ktime(timeout),
HRTIMER_MODE_REL_PINNED);
else
napi_gro_flush(n, false);
}
if (likely(list_empty(&n->poll_list))) {
WARN_ON_ONCE(!test_and_clear_bit(NAPI_STATE_SCHED, &n->state));
} else {
/* If n->poll_list is not empty, we need to mask irqs */
local_irq_save(flags);
__napi_complete(n);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
}4. I.MX6ULL 网络驱动简介
1.修改设备树
根据I.MX6ULL 网络硬件设置相关的属性。NXP 的 I.MX 系 列 SOC 网 络 绑 定 文 档 为
Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/fsl-fec.txt,此绑定文档描述了 I.MX 系列 SOC 网络设备树
节点的要求。
①、必要属性
- compatible:这个肯定是必须的,一般是“fsl,
-fec”,比如 I.MX6ULL 的 compatible 属性就是"fsl,imx6ul-fec",和"fsl,imx6q-fec"。 - reg:SOC 网络外设寄存器地址范围。
- interrupts:网络中断。
- phy-mode:网络所使用的 PHY 接口模式,是 MII 还是 RMII。
②、可选属性
- phy-reset-gpios:PHY 芯片的复位引脚。
- phy-reset-duration:PHY 复位引脚复位持续时间,单位为毫秒。只有当设置了 phy-resetgpios 属性此属性才会有效,如果不设置此属性的话 PHY 芯片复位引脚的复位持续时间默认为1 毫秒,数值不能大于 1000 毫秒,大于 1000 毫秒的话就会强制设置为 1 毫秒。
- phy-supply:PHY 芯片的电源调节。
- phy-handle:连接到此网络设备的 PHY 芯片句柄。
- fsl,num-tx-queues:此属性指定发送队列的数量,如果不指定的话默认为 1。
- fsl,num-rx-queues:此属性指定接收队列的数量,如果不指定的话默认为 2。
- fsl,magic-packet:此属性不用设置具体的值,直接将此属性名字写到设备树里面即可,表示支持硬件魔术帧唤醒。
- fsl,wakeup_irq:此属性设置唤醒中断索引。
- stop-mode:如果此属性存在的话表明 SOC 需要设置 GPR 位来请求停止模式。
③、可选子节点
- mdio:可以设置名为“mdio”的子节点,此子节点用于指定网络外设所使用的 MDIO 总线,主要做为 PHY 节点的容器,也就是在 mdio 子节点下指定 PHY 相关的属性信息,具体信息可以参考 PHY 的绑定文档 Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/phy.txt。
PHY 节点相关属性内容如下:
interrupts:中断属性,可以不需要。
interrupt-parent:中断控制器句柄,可以不需要。
reg:PHY 芯片地址,必须的!
- compatible:兼容性列表,一般为“ethernet-phy-ieee802.3-c22”或“ethernet-phy-ieee802.3-c45”,分别对应 IEEE802.3 的 22 簇和 45 簇,默认是 22 簇。也可以设置为其他值,如果 PHY的 ID 不知道的话可以 compatible 属性可以设置为“ethernet-phy-idAAAA.BBBB”,AAAA 和BBBB 的含义如下:
- AAAA:PHY 的 16 位 ID 寄存器 1 值,也就是 OUI 的 bit3~18,16 进制格式。
- BBBB:PHY 的 16 位 ID 寄存器 2 值,也就是 OUI 的 bit19~24,16 进制格式。
- max-speed:PHY 支持的最高速度,比如 10、100 或 1000。
&fec1 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_enet1
&pinctrl_enet1_reset>;
phy-mode = "rmii";
phy-handle = <ðphy0>;
phy-reset-gpios = <&gpio5 7 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
phy-reset-duration = <200>;
status = "okay";
};
&fec2 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_enet2
&pinctrl_enet2_reset>;
phy-mode = "rmii";
phy-handle = <ðphy1>;
phy-reset-gpios = <&gpio5 8 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>;
phy-reset-duration = <200>;
status = "okay";
mdio {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
ethphy0: ethernet-phy@0 {
compatible = "ethernet-phy-ieee802.3-c22";
reg = <0>;
};
ethphy1: ethernet-phy@1 {
compatible = "ethernet-phy-ieee802.3-c22";
reg = <1>;
};
};
}设备树中网络相关引脚的描述
pinctrl_enet1: enet1grp {
fsl,pins = <
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_RX_EN__ENET1_RX_EN 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_RX_ER__ENET1_RX_ER 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_RX_DATA0__ENET1_RDATA00 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_RX_DATA1__ENET1_RDATA01 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_TX_EN__ENET1_TX_EN 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_TX_DATA0__ENET1_TDATA00 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_TX_DATA1__ENET1_TDATA01 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET1_TX_CLK__ENET1_REF_CLK1 0x4001b009
>;
};
pinctrl_enet2: enet2grp {
fsl,pins = <
MX6UL_PAD_GPIO1_IO07__ENET2_MDC 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_GPIO1_IO06__ENET2_MDIO 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET2_RX_EN__ENET2_RX_EN 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET2_RX_ER__ENET2_RX_ER 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET2_RX_DATA0__ENET2_RDATA00 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET2_RX_DATA1__ENET2_RDATA01 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET2_TX_EN__ENET2_TX_EN 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET2_TX_DATA0__ENET2_TDATA00 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET2_TX_DATA1__ENET2_TDATA01 0x1b0b0
MX6UL_PAD_ENET2_TX_CLK__ENET2_REF_CLK2 0x4001b009
>;
};
/*enet1 reset zuozhongkai*/
pinctrl_enet1_reset: enet1resetgrp {
fsl,pins = <
/* used for enet1 reset */
MX6ULL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER7__GPIO5_IO07 0x10B0
>;
};
/*enet2 reset zuozhongkai*/
pinctrl_enet2_reset: enet2resetgrp {
fsl,pins = <
/* used for enet2 reset */
MX6ULL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER8__GPIO5_IO08 0x10B0
>;
};2.驱动源码简析
对于 I.MX6ULL 而言网络驱动主要分两部分:I.MX6ULL 网络外设驱动以及 PHY 芯片驱动,网络外设驱动是 NXP 编写的,PHY 芯片有通用驱动文件,有些 PHY 芯片厂商还会针对自己的芯片编写对应的 PHY 驱动。总体来说,SOC 内置网络 MAC+外置 PHY 芯片这种方案我们是不需要编写什么驱动的,基本可以直接使用。
2.1 NXP的I.IMX6ULL网络外设驱动核心
驱动文件为 drivers/net/ethernet/freescale/fec_main.c
匹配表包含“fsl,imx6ul-fec”,因此设备树和驱动匹配上之后操作函数就会执行
static const struct of_device_id fec_dt_ids[] = {
{ .compatible = "fsl,imx25-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX25_FEC], },
{ .compatible = "fsl,imx27-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX27_FEC], },
{ .compatible = "fsl,imx28-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX28_FEC], },
{ .compatible = "fsl,imx6q-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX6Q_FEC], },
{ .compatible = "fsl,mvf600-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[MVF600_FEC], },
{ .compatible = "fsl,imx6sx-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX6SX_FEC], },
{ .compatible = "fsl,imx6ul-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX6UL_FEC], },
{ /* sentinel */ }
};static struct platform_driver fec_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = DRIVER_NAME,
.pm = &fec_pm_ops,
.of_match_table = fec_dt_ids,
},
.id_table = fec_devtype,
.probe = fec_probe,
.remove = fec_drv_remove,
};fec_probe函数会完成net_device设备驱动注册,整个过程代码如下
static int
fec_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct fec_enet_private *fep;
struct fec_platform_data *pdata;
struct net_device *ndev;
int i, irq, ret = 0;
struct resource *r;
const struct of_device_id *of_id;
static int dev_id;
struct device_node *np = pdev->dev.of_node, *phy_node;
int num_tx_qs;
int num_rx_qs;
void __iomem *IMX6U_ENET1_TX_CLK;
void __iomem *IMX6U_ENET2_TX_CLK;
IMX6U_ENET1_TX_CLK = ioremap(0x020E00DC, 4);
writel(0x14, IMX6U_ENET1_TX_CLK);
IMX6U_ENET2_TX_CLK = ioremap(0x020E00FC, 4);
writel(0x14, IMX6U_ENET2_TX_CLK);
/*获取设备树中的“fsl,num-tx-queues”和
“fsl,num-rx-queues”这两个属性值,也就是发送队列和接收队列的大小,设备树中这两个属性
都设置为 1。*/
fec_enet_get_queue_num(pdev, &num_tx_qs, &num_rx_qs);
/* Init network device 使用 alloc_etherdev_mqs 函数申请 net_device。*/
ndev = alloc_etherdev_mqs(sizeof(struct fec_enet_private),
num_tx_qs, num_rx_qs);
if (!ndev)
return -ENOMEM;
SET_NETDEV_DEV(ndev, &pdev->dev);
/* setup board info structure 获取 net_device 中私有数据内存首地址*/
fep = netdev_priv(ndev);
of_id = of_match_device(fec_dt_ids, &pdev->dev);
if (of_id)
pdev->id_entry = of_id->data;
/*初始化网络设备结构体各个成员变量*/
fep->quirks = pdev->id_entry->driver_data;
fep->netdev = ndev;
fep->num_rx_queues = num_rx_qs;
fep->num_tx_queues = num_tx_qs;
#if !defined(CONFIG_M5272)
/* default enable pause frame auto negotiation */
if (fep->quirks & FEC_QUIRK_HAS_GBIT)
fep->pause_flag |= FEC_PAUSE_FLAG_AUTONEG;
#endif
/* Select default pin state */
pinctrl_pm_select_default_state(&pdev->dev);
/*获取设备树中 I.MX6ULL 网络外设(ENET)相关寄存器起始地址,ENET1 的寄存
器起始地址 0X02188000,ENET2 的寄存器起始地址 0X20B4000。*/
r = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
/*行获取到的地址做虚拟地址转换,转换后的 ENET 虚拟寄存器起始地址
保存在 fep 的 hwp 成员中。*/
fep->hwp = devm_ioremap_resource(&pdev->dev, r);
if (IS_ERR(fep->hwp)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(fep->hwp);
goto failed_ioremap;
}
fep->pdev = pdev;
fep->dev_id = dev_id++;
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, ndev);
/*解析设备树中关于 ENET 的停止模式属性值*/
fec_enet_of_parse_stop_mode(pdev);
/*从设备树查找“fsl,magic-packet”属性是否存在,如果存在的话就说明有魔术包,
有魔术包的话就将 fep 的 wol_flag 成员与 FEC_WOL_HAS_MAGIC_PACKET 进行或运算,也
就是在 wol_flag 中做登记,登记支持魔术包。*/
if (of_get_property(np, "fsl,magic-packet", NULL))
fep->wol_flag |= FEC_WOL_HAS_MAGIC_PACKET;
/*获取“phy-handle”属性的值,phy-handle 属性指定了 I.MX6ULL 网络外设所对
应获取 PHY 的设备节点。在前面设备树中我们已经设置了,在MDIO节点下,
如果需要添加其它PHY设备,则在MDIO下添加该设备就好了*/
phy_node = of_parse_phandle(np, "phy-handle", 0);
if (!phy_node && of_phy_is_fixed_link(np)) {
ret = of_phy_register_fixed_link(np);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev,
"broken fixed-link specification\n");
goto failed_phy;
}
phy_node = of_node_get(np);
}
fep->phy_node = phy_node;
/*获取 PHY 工作模式,函数 of_get_phy_mode 会读取属性 phy-mode 的值,”
phymode”中保存了 PHY 的工作方式,即 PHY 是 RMII 还是 MII,IMX6ULL 中的 PHY 工作在RMII 模式*/
ret = of_get_phy_mode(pdev->dev.of_node);
if (ret < 0) {
pdata = dev_get_platdata(&pdev->dev);
if (pdata)
fep->phy_interface = pdata->phy;
else
fep->phy_interface = PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_MII;
} else {
fep->phy_interface = ret;
}
/*分别获取时钟 ipg、ahb、enet_out、enet_clk_ref 和 ptp*/
fep->clk_ipg = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "ipg");
if (IS_ERR(fep->clk_ipg)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(fep->clk_ipg);
goto failed_clk;
}
fep->clk_ahb = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "ahb");
if (IS_ERR(fep->clk_ahb)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(fep->clk_ahb);
goto failed_clk;
}
fep->itr_clk_rate = clk_get_rate(fep->clk_ahb);
/* enet_out is optional, depends on board */
fep->clk_enet_out = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "enet_out");
if (IS_ERR(fep->clk_enet_out))
fep->clk_enet_out = NULL;
fep->ptp_clk_on = false;
mutex_init(&fep->ptp_clk_mutex);
/* clk_ref is optional, depends on board */
fep->clk_ref = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "enet_clk_ref");
if (IS_ERR(fep->clk_ref))
fep->clk_ref = NULL;
fep->bufdesc_ex = fep->quirks & FEC_QUIRK_HAS_BUFDESC_EX;
fep->clk_ptp = devm_clk_get(&pdev->dev, "ptp");
if (IS_ERR(fep->clk_ptp)) {
fep->clk_ptp = NULL;
fep->bufdesc_ex = false;
}
pm_runtime_enable(&pdev->dev);
/*使能时钟*/
ret = fec_enet_clk_enable(ndev, true);
if (ret)
goto failed_clk;
fep->reg_phy = devm_regulator_get(&pdev->dev, "phy");
if (!IS_ERR(fep->reg_phy)) {
ret = regulator_enable(fep->reg_phy);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev,
"Failed to enable phy regulator: %d\n", ret);
goto failed_regulator;
}
} else {
fep->reg_phy = NULL;
}
fec_reset_phy(pdev);
if (fep->bufdesc_ex)
fec_ptp_init(pdev);
/*初始化 enet,此函数会分配队列、申请 dma、设置 MAC
地址,初始化 net_device 的 netdev_ops 和 ethtool_ops 成员*/
ret = fec_enet_init(ndev);
if (ret)
goto failed_init;
/*从设备树中获取中断号。*/
for (i = 0; i < FEC_IRQ_NUM; i++) {
irq = platform_get_irq(pdev, i);
if (irq < 0) {
if (i)
break;
ret = irq;
goto failed_irq;
}
/*申请中断,中断处理函数为 fec_enet_interrupt,重点!*/
ret = devm_request_irq(&pdev->dev, irq, fec_enet_interrupt,
0, pdev->name, ndev);
if (ret)
goto failed_irq;
fep->irq[i] = irq;
}
ret = of_property_read_u32(np, "fsl,wakeup_irq", &irq);
if (!ret && irq < FEC_IRQ_NUM)
fep->wake_irq = fep->irq[irq];
else
fep->wake_irq = fep->irq[0];
/*初始化完成量 completion,用于一个执行单元等待另一个执行单元执行完某事*/
init_completion(&fep->mdio_done);
/* MII/RMII 接口的初始化 来向内核注册 MDIO 总线*/
ret = fec_enet_mii_init(pdev);
if (ret)
goto failed_mii_init;
/* Carrier starts down, phylib will bring it up */
netif_carrier_off(ndev);
/*使能网络相关时钟*/
fec_enet_clk_enable(ndev, false);
pinctrl_pm_select_sleep_state(&pdev->dev);
/*注册 net_device*/
ret = register_netdev(ndev);
if (ret)
goto failed_register;
device_init_wakeup(&ndev->dev, fep->wol_flag &
FEC_WOL_HAS_MAGIC_PACKET);
if (fep->bufdesc_ex && fep->ptp_clock)
netdev_info(ndev, "registered PHC device %d\n", fep->dev_id);
fep->rx_copybreak = COPYBREAK_DEFAULT;
INIT_WORK(&fep->tx_timeout_work, fec_enet_timeout_work);
return 0;
failed_register:
fec_enet_mii_remove(fep);
failed_mii_init:
failed_irq:
failed_init:
if (fep->reg_phy)
regulator_disable(fep->reg_phy);
failed_regulator:
fec_enet_clk_enable(ndev, false);
failed_clk:
failed_phy:
of_node_put(phy_node);
failed_ioremap:
free_netdev(ndev);
return ret;
}2.2 MDIO总线注册
MDIO 就是用来管理 PHY 芯片的,分为 MDIO 和 MDC 两根线,Linux内核专门为 MDIO 准备一个总线,叫做 MDIO 总线,采用 mii_bus 结构体表示,定义在include/linux/phy.h 文件中
/*
* The Bus class for PHYs. Devices which provide access to
* PHYs should register using this structure
*/
struct mii_bus {
const char *name;
char id[MII_BUS_ID_SIZE];
void *priv;
/*读/些 PHY 芯片的操作函数,最终会被前面的fec_probe函数初始化并注册到内核(194行)*/
int (*read)(struct mii_bus *bus, int phy_id, int regnum);
int (*write)(struct mii_bus *bus, int phy_id, int regnum, u16 val);
int (*reset)(struct mii_bus *bus);
/*
* A lock to ensure that only one thing can read/write
* the MDIO bus at a time
*/
struct mutex mdio_lock;
struct device *parent;
enum {
MDIOBUS_ALLOCATED = 1,
MDIOBUS_REGISTERED,
MDIOBUS_UNREGISTERED,
MDIOBUS_RELEASED,
} state;
struct device dev;
/* list of all PHYs on bus */
struct phy_device *phy_map[PHY_MAX_ADDR];
/* PHY addresses to be ignored when probing */
u32 phy_mask;
/*
* Pointer to an array of interrupts, each PHY's
* interrupt at the index matching its address
*/
int *irq;
};读/些 PHY 芯片的操作函数,最终会被前面的fec_probe函数的ffec_enet_mii_init函数初始化并注册到内核。fec_enet_mii_init函数如下
static int fec_enet_mii_init(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
static struct mii_bus *fec0_mii_bus;
static int *fec_mii_bus_share;
struct net_device *ndev = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
struct fec_enet_private *fep = netdev_priv(ndev);
struct device_node *node;
int err = -ENXIO, i;
u32 mii_speed, holdtime;
/*
* The i.MX28 dual fec interfaces are not equal.
* Here are the differences:
*
* - fec0 supports MII & RMII modes while fec1 only supports RMII
* - fec0 acts as the 1588 time master while fec1 is slave
* - external phys can only be configured by fec0
*
* That is to say fec1 can not work independently. It only works
* when fec0 is working. The reason behind this design is that the
* second interface is added primarily for Switch mode.
*
* Because of the last point above, both phys are attached on fec0
* mdio interface in board design, and need to be configured by
* fec0 mii_bus.
*/
if ((fep->quirks & FEC_QUIRK_ENET_MAC) && fep->dev_id > 0) {
/* fec1 uses fec0 mii_bus */
if (mii_cnt && fec0_mii_bus) {
fep->mii_bus = fec0_mii_bus;
*fec_mii_bus_share = FEC0_MII_BUS_SHARE_TRUE;
mii_cnt++;
return 0;
}
return -ENOENT;
}
fep->mii_timeout = 0;
/*
* Set MII speed to 2.5 MHz (= clk_get_rate() / 2 * phy_speed)
*
* The formula for FEC MDC is 'ref_freq / (MII_SPEED x 2)' while
* for ENET-MAC is 'ref_freq / ((MII_SPEED + 1) x 2)'. The i.MX28
* Reference Manual has an error on this, and gets fixed on i.MX6Q
* document.
*/
mii_speed = DIV_ROUND_UP(clk_get_rate(fep->clk_ipg), 5000000);
if (fep->quirks & FEC_QUIRK_ENET_MAC)
mii_speed--;
if (mii_speed > 63) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev,
"fec clock (%lu) to fast to get right mii speed\n",
clk_get_rate(fep->clk_ipg));
err = -EINVAL;
goto err_out;
}
/*
* The i.MX28 and i.MX6 types have another filed in the MSCR (aka
* MII_SPEED) register that defines the MDIO output hold time. Earlier
* versions are RAZ there, so just ignore the difference and write the
* register always.
* The minimal hold time according to IEE802.3 (clause 22) is 10 ns.
* HOLDTIME + 1 is the number of clk cycles the fec is holding the
* output.
* The HOLDTIME bitfield takes values between 0 and 7 (inclusive).
* Given that ceil(clkrate / 5000000) <= 64, the calculation for
* holdtime cannot result in a value greater than 3.
*/
holdtime = DIV_ROUND_UP(clk_get_rate(fep->clk_ipg), 100000000) - 1;
fep->phy_speed = mii_speed << 1 | holdtime << 8;
writel(fep->phy_speed, fep->hwp + FEC_MII_SPEED);
fep->mii_bus = mdiobus_alloc();
if (fep->mii_bus == NULL) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto err_out;
}
fep->mii_bus->name = "fec_enet_mii_bus";
fep->mii_bus->read = fec_enet_mdio_read;
fep->mii_bus->write = fec_enet_mdio_write;
snprintf(fep->mii_bus->id, MII_BUS_ID_SIZE, "%s-%x",
pdev->name, fep->dev_id + 1);
fep->mii_bus->priv = fep;
fep->mii_bus->parent = &pdev->dev;
fep->mii_bus->irq = kmalloc(sizeof(int) * PHY_MAX_ADDR, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!fep->mii_bus->irq) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto err_out_free_mdiobus;
}
for (i = 0; i < PHY_MAX_ADDR; i++)
fep->mii_bus->irq[i] = PHY_POLL;
node = of_get_child_by_name(pdev->dev.of_node, "mdio");
if (node) {
err = of_mdiobus_register(fep->mii_bus, node);
of_node_put(node);
} else {
err = mdiobus_register(fep->mii_bus);
}
if (err)
goto err_out_free_mdio_irq;
mii_cnt++;
/* save fec0 mii_bus */
if (fep->quirks & FEC_QUIRK_ENET_MAC) {
fec0_mii_bus = fep->mii_bus;
fec_mii_bus_share = &fep->mii_bus_share;
}
return 0;
err_out_free_mdio_irq:
kfree(fep->mii_bus->irq);
err_out_free_mdiobus:
mdiobus_free(fep->mii_bus);
err_out:
return err;
}从中可以看出,通过 of_mdiobus_register或者 mdiobus_register 函数将初始化以后的 mii_bus 注册到 Linux 内核,此外该函数还调用of_mdiobus_register_phy 函数完成向内核注册 PHY设备。
of_mdiobus_register函数如下
/**
* of_mdiobus_register - Register mii_bus and create PHYs from the device tree
* @mdio: pointer to mii_bus structure
* @np: pointer to device_node of MDIO bus.
*
* This function registers the mii_bus structure and registers a phy_device
* for each child node of @np.
*/
int of_mdiobus_register(struct mii_bus *mdio, struct device_node *np)
{
struct device_node *child;
const __be32 *paddr;
bool scanphys = false;
int addr, rc, i;
/* Mask out all PHYs from auto probing. Instead the PHYs listed in
* the device tree are populated after the bus has been registered */
mdio->phy_mask = ~0;
/* Clear all the IRQ properties */
if (mdio->irq)
for (i=0; iirq[i] = PHY_POLL;
mdio->dev.of_node = np;
/* Register the MDIO bus */
rc = mdiobus_register(mdio);
if (rc)
return rc;
/* Loop over the child nodes and register a phy_device for each one */
for_each_available_child_of_node(np, child) {
addr = of_mdio_parse_addr(&mdio->dev, child);
if (addr < 0) {
scanphys = true;
continue;
}
rc = of_mdiobus_register_phy(mdio, child, addr);
if (rc)
continue;
}
if (!scanphys)
return 0;
/* auto scan for PHYs with empty reg property */
for_each_available_child_of_node(np, child) {
/* Skip PHYs with reg property set */
paddr = of_get_property(child, "reg", NULL);
if (paddr)
continue;
for (addr = 0; addr < PHY_MAX_ADDR; addr++) {
/* skip already registered PHYs */
if (mdio->phy_map[addr])
continue;
/* be noisy to encourage people to set reg property */
dev_info(&mdio->dev, "scan phy %s at address %i\n",
child->name, addr);
rc = of_mdiobus_register_phy(mdio, child, addr);
if (rc)
continue;
}
}
return 0;
} 注册PHY驱动函数如下:
static int of_mdiobus_register_phy(struct mii_bus *mdio, struct device_node *child,
u32 addr)
{
struct phy_device *phy;
bool is_c45;
int rc;
u32 phy_id;
/*检查 PHY 节点的 compatible 属性是否为“ethernetphy-ieee802.3-c45*/
is_c45 = of_device_is_compatible(child,
"ethernet-phy-ieee802.3-c45");
if (!is_c45 && !of_get_phy_id(child, &phy_id))
phy = phy_device_create(mdio, addr, phy_id, 0, NULL);
else
phy = get_phy_device(mdio, addr, is_c45);
if (!phy || IS_ERR(phy))
return 1;
/*获取 PHY 芯片的中断信息*/
rc = irq_of_parse_and_map(child, 0);
if (rc > 0) {
phy->irq = rc;
if (mdio->irq)
mdio->irq[addr] = rc;
} else {
if (mdio->irq)
phy->irq = mdio->irq[addr];
}
/* Associate the OF node with the device structure so it
* can be looked up later */
of_node_get(child);
phy->dev.of_node = child;
/* All data is now stored in the phy struct;
* register it */
/*向 Linux 内核注册 PHY 设备。*/
rc = phy_device_register(phy);
if (rc) {
phy_device_free(phy);
of_node_put(child);
return 1;
}
dev_dbg(&mdio->dev, "registered phy %s at address %i\n",
child->name, addr);
return 0;
}总结一下整个流程如下:
2.3 fec_drv_remove 函数简析
卸载 I.MX6ULL 网络驱动的时候 fec_drv_remove 函数就会执行
static int fec_drv_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct net_device *ndev = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
struct fec_enet_private *fep = netdev_priv(ndev);
cancel_delayed_work_sync(&fep->time_keep);
cancel_work_sync(&fep->tx_timeout_work);
unregister_netdev(ndev);
fec_enet_mii_remove(fep);
if (fep->reg_phy)
regulator_disable(fep->reg_phy);
if (fep->ptp_clock)
ptp_clock_unregister(fep->ptp_clock);
of_node_put(fep->phy_node);
free_netdev(ndev);
return 0;
}
3. fec_netdev_ops 操作集
fec_probe 函数设置了网卡驱动的 net_dev_ops 操作集为 fec_netdev_ops
static const struct net_device_ops fec_netdev_ops = {
.ndo_open = fec_enet_open,
.ndo_stop = fec_enet_close,
.ndo_start_xmit = fec_enet_start_xmit,
.ndo_select_queue = fec_enet_select_queue,
.ndo_set_rx_mode = set_multicast_list,
.ndo_change_mtu = eth_change_mtu,
.ndo_validate_addr = eth_validate_addr,
.ndo_tx_timeout = fec_timeout,
.ndo_set_mac_address = fec_set_mac_address,
.ndo_do_ioctl = fec_enet_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_POLL_CONTROLLER
.ndo_poll_controller = fec_poll_controller,
#endif
.ndo_set_features = fec_set_features,
};3.1 fec_enet_open 函数简析
static int fec_enet_open(struct net_device *ndev)
{
struct fec_enet_private *fep = netdev_priv(ndev);
const struct platform_device_id *id_entry =
platform_get_device_id(fep->pdev);
int ret;
pinctrl_pm_select_default_state(&fep->pdev->dev);
ret = fec_enet_clk_enable(ndev, true);
if (ret)
return ret;
/* I should reset the ring buffers here, but I don't yet know
* a simple way to do that.
*/
/*申请环形缓冲区 buffer,此函数里面会调用
fec_enet_alloc_rxq_buffers 和 fec_enet_alloc_txq_buffers
这两个函数分别实现发送队列和接收队列缓冲区的申请。*/
ret = fec_enet_alloc_buffers(ndev);
if (ret)
goto err_enet_alloc;
/* Init MAC prior to mii bus probe */
/*重启网络,一般连接状态改变、传输超时或者配置网络的时候都会调用 fec_restart函数*/
fec_restart(ndev);
/* Probe and connect to PHY when open the interface */
/*打开网卡的时候调用 fec_enet_mii_probe 函数来探测并连接对应的 PHY 设备。*/
ret = fec_enet_mii_probe(ndev);
if (ret)
goto err_enet_mii_probe;
/*使能 NAPI 调度*/
napi_enable(&fep->napi);
/*开启 PHY 设备*/
phy_start(fep->phy_dev);
/*激活发送队列。*/
netif_tx_start_all_queues(ndev);
pm_runtime_get_sync(ndev->dev.parent);
if ((id_entry->driver_data & FEC_QUIRK_BUG_WAITMODE) &&
!fec_enet_irq_workaround(fep))
pm_qos_add_request(&fep->pm_qos_req,
PM_QOS_CPU_DMA_LATENCY,
0);
else
pm_qos_add_request(&fep->pm_qos_req,
PM_QOS_CPU_DMA_LATENCY,
PM_QOS_DEFAULT_VALUE);
device_set_wakeup_enable(&ndev->dev, fep->wol_flag &
FEC_WOL_FLAG_ENABLE);
fep->miibus_up_failed = false;
return 0;
err_enet_mii_probe:
fec_enet_free_buffers(ndev);
err_enet_alloc:
fep->miibus_up_failed = true;
if (!fep->mii_bus_share)
pinctrl_pm_select_sleep_state(&fep->pdev->dev);
return ret;
}2. fec_enet_close 函数简析
static int
fec_enet_close(struct net_device *ndev)
{
struct fec_enet_private *fep = netdev_priv(ndev);
phy_stop(fep->phy_dev);
if (netif_device_present(ndev)) {
napi_disable(&fep->napi);
netif_tx_disable(ndev);
fec_stop(ndev);
}
phy_disconnect(fep->phy_dev);
fep->phy_dev = NULL;
fec_enet_clk_enable(ndev, false);
pm_qos_remove_request(&fep->pm_qos_req);
pinctrl_pm_select_sleep_state(&fep->pdev->dev);
pm_runtime_put_sync_suspend(ndev->dev.parent);
fec_enet_free_buffers(ndev);
return 0;
}3. fec_enet_start_xmit 函数简析
static netdev_tx_t fec_enet_start_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *ndev)
{
struct fec_enet_private *fep = netdev_priv(ndev);
int entries_free;
unsigned short queue;
struct fec_enet_priv_tx_q *txq;
struct netdev_queue *nq;
int ret;
queue = skb_get_queue_mapping(skb);
txq = fep->tx_queue[queue];
nq = netdev_get_tx_queue(ndev, queue);
if (skb_is_gso(skb))
ret = fec_enet_txq_submit_tso(txq, skb, ndev);
else
ret = fec_enet_txq_submit_skb(txq, skb, ndev);
if (ret)
return ret;
entries_free = fec_enet_get_free_txdesc_num(fep, txq);
if (entries_free <= txq->tx_stop_threshold)
netif_tx_stop_queue(nq);//通过暂停发送来通知应用层停止向网络发送 skb
return NETDEV_TX_OK;
}此函数的参数第一个参数 skb 就是上层应用传递下来的要发送的网络数据,第二个参数
ndev 就是要发送数据的设备。
TSO:全称是 TCP Segmentation Offload,利用网卡对大数据包进行自动分段处理,降低 CPU
负载。
GSO:全称是 Generic Segmentation Offload,在发送数据之前先检查一下网卡是否支持 TSO,
如果支持的话就让网卡分段,不过不支持的话就由协议栈进行分段处理,分段处理完成以后再
交给网卡去发送。
4. fec_enet_interrupt 中断服务函数简析
了 I.MX6ULL 的网络数据接收采用 NAPI 框架,所以肯定要用到中断。fec_probe 函数会初始化网络中断,中断服务函数为 fec_enet_interrupt.
static irqreturn_t fec_enet_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct net_device *ndev = dev_id;
struct fec_enet_private *fep = netdev_priv(ndev);
uint int_events;
irqreturn_t ret = IRQ_NONE;
int_events = readl(fep->hwp + FEC_IEVENT);
writel(int_events, fep->hwp + FEC_IEVENT);
fec_enet_collect_events(fep, int_events);
if ((fep->work_tx || fep->work_rx) && fep->link) {
ret = IRQ_HANDLED;
if (napi_schedule_prep(&fep->napi)) {
/* Disable the NAPI interrupts */
writel(FEC_ENET_MII, fep->hwp + FEC_IMASK);
__napi_schedule(&fep->napi);
}
}
if (int_events & FEC_ENET_MII) {
ret = IRQ_HANDLED;
complete(&fep->mdio_done);
}
if (fep->ptp_clock)
fec_ptp_check_pps_event(fep);
return ret;
}
可以看出中断服务函数非常短! 具体的网络数据收发是在 NAPI 的 poll 函数中完成的,中断里面只需要进行 napi 调度即可,这个就是中断的上半部和下半部处理机制.(复习中断)
fec_enet_init 函数初始化网络的时候会调用 netif_napi_add 来设置 NAPI 的 poll 函数为
fec_enet_rx_napi
5. Linux 内核 PHY 子系统与 MDIO 总线简析
注册 MDIO 总线的时候也会向内核注册 PHY 设备,PHY 子系统就是用于 PHY 设备相关内容的,分
为 PHY 设备和 PHY 驱动,和 platform 总线一样,PHY 子系统也是一个设备、总线和驱动模型。
5.1PHY设备
Linux 内核使用 phy_device 结构体来表示 PHY 设备,结构体定义在 include/linux/phy.h,结构体内容如下:
/* phy_device: An instance of a PHY
*
* drv: Pointer to the driver for this PHY instance
* bus: Pointer to the bus this PHY is on
* dev: driver model device structure for this PHY
* phy_id: UID for this device found during discovery
* c45_ids: 802.3-c45 Device Identifers if is_c45.
* is_c45: Set to true if this phy uses clause 45 addressing.
* is_internal: Set to true if this phy is internal to a MAC.
* has_fixups: Set to true if this phy has fixups/quirks.
* suspended: Set to true if this phy has been suspended successfully.
* state: state of the PHY for management purposes
* dev_flags: Device-specific flags used by the PHY driver.
* addr: Bus address of PHY
* link_timeout: The number of timer firings to wait before the
* giving up on the current attempt at acquiring a link
* irq: IRQ number of the PHY's interrupt (-1 if none)
* phy_timer: The timer for handling the state machine
* phy_queue: A work_queue for the interrupt
* attached_dev: The attached enet driver's device instance ptr
* adjust_link: Callback for the enet controller to respond to
* changes in the link state.
*
* speed, duplex, pause, supported, advertising, lp_advertising,
* and autoneg are used like in mii_if_info
*
* interrupts currently only supports enabled or disabled,
* but could be changed in the future to support enabling
* and disabling specific interrupts
*
* Contains some infrastructure for polling and interrupt
* handling, as well as handling shifts in PHY hardware state
*/
struct phy_device {
/* Information about the PHY type */
/* And management functions */
struct phy_driver *drv;
struct mii_bus *bus;
struct device dev;
u32 phy_id;
struct phy_c45_device_ids c45_ids;
bool is_c45;
bool is_internal;
bool has_fixups;
bool suspended;
enum phy_state state;
u32 dev_flags;
phy_interface_t interface;
/* Bus address of the PHY (0-31) */
int addr;
/*
* forced speed & duplex (no autoneg)
* partner speed & duplex & pause (autoneg)
*/
int speed;
int duplex;
int pause;
int asym_pause;
/* The most recently read link state */
int link;
/* Enabled Interrupts */
u32 interrupts;
/* Union of PHY and Attached devices' supported modes */
/* See mii.h for more info */
u32 supported;
u32 advertising;
u32 lp_advertising;
int autoneg;
int link_timeout;
/*
* Interrupt number for this PHY
* -1 means no interrupt
*/
int irq;
/* private data pointer */
/* For use by PHYs to maintain extra state */
void *priv;
/* Interrupt and Polling infrastructure */
struct work_struct phy_queue;
struct delayed_work state_queue;
atomic_t irq_disable;
struct mutex lock;
struct net_device *attached_dev;
void (*adjust_link)(struct net_device *dev);
};一个 PHY 设备对应一个 phy_device 实例,然后需要向 Linux 内核注册这个实例。
注册PHY设备
1先获取PHY设备
/**
* get_phy_device - reads the specified PHY device and returns its @phy_device
* struct
* @bus: the target MII bus
* @addr: PHY address on the MII bus
* @is_c45: If true the PHY uses the 802.3 clause 45 protocol
*
* Description: Reads the ID registers of the PHY at @addr on the
* @bus, then allocates and returns the phy_device to represent it.
*/
struct phy_device *get_phy_device(struct mii_bus *bus, int addr, bool is_c45)
{
struct phy_c45_device_ids c45_ids = {0};
u32 phy_id = 0;
int r;
r = get_phy_id(bus, addr, &phy_id, is_c45, &c45_ids);
if (r)
return ERR_PTR(r);
/* If the phy_id is mostly Fs, there is no device there */
if ((phy_id & 0x1fffffff) == 0x1fffffff)
return NULL;
return phy_device_create(bus, addr, phy_id, is_c45, &c45_ids);
}2.使用phy_device_register 函数完成 PHY 设备的注册。
/**
* phy_device_register - Register the phy device on the MDIO bus
* @phydev: phy_device structure to be added to the MDIO bus
*/
int phy_device_register(struct phy_device *phydev)
{
int err;
/* Don't register a phy if one is already registered at this address */
if (phydev->bus->phy_map[phydev->addr])
return -EINVAL;
phydev->bus->phy_map[phydev->addr] = phydev;
/* Run all of the fixups for this PHY */
err = phy_scan_fixups(phydev);
if (err) {
pr_err("PHY %d failed to initialize\n", phydev->addr);
goto out;
}
err = device_add(&phydev->dev);
if (err) {
pr_err("PHY %d failed to add\n", phydev->addr);
goto out;
}
return 0;
out:
phydev->bus->phy_map[phydev->addr] = NULL;
return err;
}5.2 PHY驱动
PHY 驱动使用结构体 phy_driver 表示,结构体也定义在 include/linux/phy.h 文件中,结构体
内容如下
/* struct phy_driver: Driver structure for a particular PHY type
*
* phy_id: The result of reading the UID registers of this PHY
* type, and ANDing them with the phy_id_mask. This driver
* only works for PHYs with IDs which match this field
* name: The friendly name of this PHY type
* phy_id_mask: Defines the important bits of the phy_id
* features: A list of features (speed, duplex, etc) supported
* by this PHY
* flags: A bitfield defining certain other features this PHY
* supports (like interrupts)
* driver_data: static driver data
*
* The drivers must implement config_aneg and read_status. All
* other functions are optional. Note that none of these
* functions should be called from interrupt time. The goal is
* for the bus read/write functions to be able to block when the
* bus transaction is happening, and be freed up by an interrupt
* (The MPC85xx has this ability, though it is not currently
* supported in the driver).
*/
struct phy_driver {
u32 phy_id;
char *name;
unsigned int phy_id_mask;
u32 features;
u32 flags;
const void *driver_data;
/*
* Called to issue a PHY software reset
*/
int (*soft_reset)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/*
* Called to initialize the PHY,
* including after a reset
*/
int (*config_init)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/*
* Called during discovery. Used to set
* up device-specific structures, if any
*/
int (*probe)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/* PHY Power Management */
int (*suspend)(struct phy_device *phydev);
int (*resume)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/*
* Configures the advertisement and resets
* autonegotiation if phydev->autoneg is on,
* forces the speed to the current settings in phydev
* if phydev->autoneg is off
*/
int (*config_aneg)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/* Determines the auto negotiation result */
int (*aneg_done)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/* Determines the negotiated speed and duplex */
int (*read_status)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/* Clears any pending interrupts */
int (*ack_interrupt)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/* Enables or disables interrupts */
int (*config_intr)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/*
* Checks if the PHY generated an interrupt.
* For multi-PHY devices with shared PHY interrupt pin
*/
int (*did_interrupt)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/* Clears up any memory if needed */
void (*remove)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/* Returns true if this is a suitable driver for the given
* phydev. If NULL, matching is based on phy_id and
* phy_id_mask.
*/
int (*match_phy_device)(struct phy_device *phydev);
/* Handles ethtool queries for hardware time stamping. */
int (*ts_info)(struct phy_device *phydev, struct ethtool_ts_info *ti);
/* Handles SIOCSHWTSTAMP ioctl for hardware time stamping. */
int (*hwtstamp)(struct phy_device *phydev, struct ifreq *ifr);
/*
* Requests a Rx timestamp for 'skb'. If the skb is accepted,
* the phy driver promises to deliver it using netif_rx() as
* soon as a timestamp becomes available. One of the
* PTP_CLASS_ values is passed in 'type'. The function must
* return true if the skb is accepted for delivery.
*/
bool (*rxtstamp)(struct phy_device *dev, struct sk_buff *skb, int type);
/*
* Requests a Tx timestamp for 'skb'. The phy driver promises
* to deliver it using skb_complete_tx_timestamp() as soon as a
* timestamp becomes available. One of the PTP_CLASS_ values
* is passed in 'type'.
*/
void (*txtstamp)(struct phy_device *dev, struct sk_buff *skb, int type);
/* Some devices (e.g. qnap TS-119P II) require PHY register changes to
* enable Wake on LAN, so set_wol is provided to be called in the
* ethernet driver's set_wol function. */
int (*set_wol)(struct phy_device *dev, struct ethtool_wolinfo *wol);
/* See set_wol, but for checking whether Wake on LAN is enabled. */
void (*get_wol)(struct phy_device *dev, struct ethtool_wolinfo *wol);
/*
* Called to inform a PHY device driver when the core is about to
* change the link state. This callback is supposed to be used as
* fixup hook for drivers that need to take action when the link
* state changes. Drivers are by no means allowed to mess with the
* PHY device structure in their implementations.
*/
void (*link_change_notify)(struct phy_device *dev);
/* A function provided by a phy specific driver to override the
* the PHY driver framework support for reading a MMD register
* from the PHY. If not supported, return -1. This function is
* optional for PHY specific drivers, if not provided then the
* default MMD read function is used by the PHY framework.
*/
int (*read_mmd_indirect)(struct phy_device *dev, int ptrad,
int devnum, int regnum);
/* A function provided by a phy specific driver to override the
* the PHY driver framework support for writing a MMD register
* from the PHY. This function is optional for PHY specific drivers,
* if not provided then the default MMD read function is used by
* the PHY framework.
*/
void (*write_mmd_indirect)(struct phy_device *dev, int ptrad,
int devnum, int regnum, u32 val);
/* Get the size and type of the eeprom contained within a plug-in
* module */
int (*module_info)(struct phy_device *dev,
struct ethtool_modinfo *modinfo);
/* Get the eeprom information from the plug-in module */
int (*module_eeprom)(struct phy_device *dev,
struct ethtool_eeprom *ee, u8 *data);
struct device_driver driver;
};可以看出,phy_driver 重点是大量的函数,编写 PHY 驱动的主要工作就是实现这些函数,但是不一定全部实现。
- 注册PHY驱动
int phy_driver_register(struct phy_driver *new_driver);- 连续注册多个PHY驱动
int phy_drivers_register(struct phy_driver *new_driver, int n);- 卸载PHY驱动
void phy_driver_unregister(struct phy_driver *drv);
void phy_drivers_unregister(struct phy_driver *drv, int n);5.3 MDIO总线
PHY 子系统也是遵循设备、总线、驱动模型的,设备和驱动就是 phy_device 和phy_driver。总线就是 MDIO 总线,因为 PHY 芯片是通过 MIDO 接口来管理的,MDIO 总线最主要的工作就是匹配 PHY 设备和 PHY 驱动。
在文件 drivers/net/phy/mdio_bus.c 中有如下定义
struct bus_type mdio_bus_type = {
.name = "mdio_bus",
.match = mdio_bus_match,
.pm = MDIO_BUS_PM_OPS,
.dev_groups = mdio_dev_groups,
};其中,匹配函数mdio_bus_match
/**
* mdio_bus_match - determine if given PHY driver supports the given PHY device
* @dev: target PHY device
* @drv: given PHY driver
*
* Description: Given a PHY device, and a PHY driver, return 1 if
* the driver supports the device. Otherwise, return 0.
*/
static int mdio_bus_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct phy_device *phydev = to_phy_device(dev);
struct phy_driver *phydrv = to_phy_driver(drv);
/*三种匹配方式*/
/*设备树查找*/
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/*驱动匹配函数*/
if (phydrv->match_phy_device)
return phydrv->match_phy_device(phydev);
/*设备id和驱动id*/
return (phydrv->phy_id & phydrv->phy_id_mask) ==
(phydev->phy_id & phydrv->phy_id_mask);
}5.4 通用PHY驱动
如果前面的匹配失败,则使用内核通用PHY驱动。通用PHY驱动名字为“Generic PHY”。
static int __init phy_init(void)
{
int rc;
rc = mdio_bus_init();
if (rc)
return rc;
rc = phy_drivers_register(genphy_driver,
ARRAY_SIZE(genphy_driver));
if (rc)
mdio_bus_exit();
return rc;
}static struct phy_driver genphy_driver[] = {
{
.phy_id = 0xffffffff,
.phy_id_mask = 0xffffffff,
.name = "Generic PHY",
.soft_reset = genphy_soft_reset,
.config_init = genphy_config_init,
.features = PHY_GBIT_FEATURES | SUPPORTED_MII |
SUPPORTED_AUI | SUPPORTED_FIBRE |
SUPPORTED_BNC,
.config_aneg = genphy_config_aneg,
.aneg_done = genphy_aneg_done,
.read_status = genphy_read_status,
.suspend = genphy_suspend,
.resume = genphy_resume,
.driver = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, },
}, {
.phy_id = 0xffffffff,
.phy_id_mask = 0xffffffff,
.name = "Generic 10G PHY",
.soft_reset = gen10g_soft_reset,
.config_init = gen10g_config_init,
.features = 0,
.config_aneg = gen10g_config_aneg,
.read_status = gen10g_read_status,
.suspend = gen10g_suspend,
.resume = gen10g_resume,
.driver = {.owner = THIS_MODULE, },
} };5.5 LAN8720A 驱动
正点原子 ALPHA 开发板所用的 LAN8720A 是 SMSC 公司的产品,此公司针对自家的所有 PHY 芯片编写了一个驱动文件smsc.c,这驱动文件里面用到了大量的通用 PHY 驱动相关函数.
只需要配置内核修改使用驱动重新编译内核即可。
5.6 DHCP 功能配置
通过 udhcpc 命令来实现从路由器动态申请 IP 地址,udhcpc 命令已经集成到了 busybox 中,所以不需要我们另外移植。