Spring 中的 bean 生命周期(代码实现)
Bean的生命周期
为了更好理解,可以重构成实例化、属性注入、初始化、销毁四个主要部分,其余部分相当于使用AOP技术,如果实现了相关接口,才会有这些过程。

也可以按这下面理解:
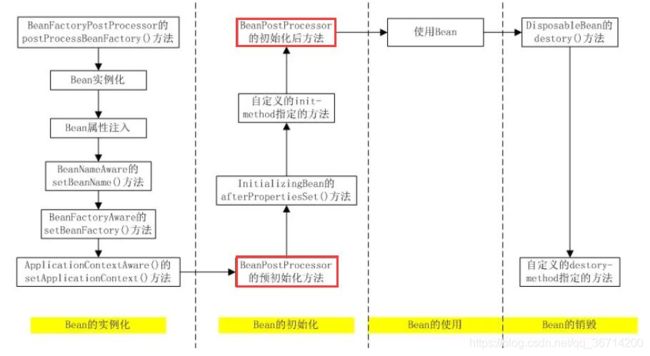
从代码看Bean的生命周期
Person :自定义Bean
public class Person implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean, BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware {
private String name;
private String sex;
Person(){
System.out.println("Person 实例化");
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
System.out.println("Person 注入{sex}属性");
this.sex = sex;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("Person 注入{name}属性");
this.name = name;
}
public void myInit(){
System.out.println("Person 的初始化myInit()方法");
}
public void myDestory(){
System.out.println("Person 的初始化myDestory()方法");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String s) {
System.out.println("【BeanNameAware接口】调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()");
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("【BeanFactoryAware】调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("【ApplicationContextAware】调用ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext()");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("【InitializingBean】调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("【DisposableBean】调用DisposableBean.destroy()");
}
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor : 其实BeanFactoryPostProcessor其实不属于Bean的生命周期,而是容器的生命周期。
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用【BeanFactoryPostProcessor】的【postProcessBeanFactory】方法");
}
}
BeanPostProcessor
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用【BeanPostProcessor】的【postProcessBeforeInitialization】方法");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用【BeanPostProcessor】的【postProcessAfterInitialization】方法");
return bean;
}
}
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor】的【postProcessBeforeInstantiation】方法");
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor】的【postProcessAfterInstantiation】方法");
return true;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor】的【postProcessProperties】方法");
return pvs;
}
}
application-context.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="person" class="org.whu.mya.Person" scope="singleton"
init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestory">
<property name="name" value="张三">property>
<property name="sex" value="男">property>
bean>
<bean class="org.whu.mya.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor">bean>
<bean class="org.whu.mya.MyBeanPostProcessor" >bean>
<bean class="org.whu.mya.MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor">bean>
beans>
入口程序SpringLifeCycleApplication
public interface SpringLifeCycleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("现在开始初始化容器!!!");
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application-context.xml");
System.out.println("容器初始化成功!!!");
System.out.println("现在开始关闭容器!!!");
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)context).registerShutdownHook();
}
}
结果展示:
现在开始初始化容器!!!
调用【BeanFactoryPostProcessor】的【postProcessBeanFactory】方法
调用【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor】的【postProcessBeforeInstantiation】方法
Person 实例化
调用【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor】的【postProcessAfterInstantiation】方法
调用【InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor】的【postProcessProperties】方法
Person 注入{name}属性
Person 注入{sex}属性
【BeanNameAware接口】调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()
【BeanFactoryAware】调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()
【ApplicationContextAware】调用ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext()
调用【BeanPostProcessor】的【postProcessBeforeInitialization】方法
【InitializingBean】InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()
Person 的初始化myInit()方法
调用【BeanPostProcessor】的【postProcessAfterInitialization】方法
容器初始化成功!!!
现在开始关闭容器!!!
【DisposableBean】调用DisposableBean.destroy()
Person 的初始化myDestory()方法
Bean生命周期中的一些钩子函数
按Bean生命周期的顺序介绍一下各钩子函数的作用
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口是 Spring 初始化 BeanFactory 时对外暴露的扩展点,Spring IoC 容器允许 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 在容器实例化任何 bean 之前读取 bean 的定义,并可以修改它。
说通俗一些就是可以管理我们的bean工厂内所有的beandefinition(未实例化)数据,可以随心所欲的修改属性。
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor与 BeanPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口是BeanPostProcessor的子接口,通过接口字面意思翻译该接口的作用是感知Bean实例化(Bean构造方法)的处理器。
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口有三个可重写的方法,
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException;
boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
从源码中我们可以获知的信息是该接口除了具有父接口中的两个方法以外还自己额外定义了三个方法。所以该接口一共定义了5个方法,这5个方法的作用分别是:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| postProcessBeforeInstantiation | InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 自身方法,是最先执行的方法,它在目标对象实例化之前调用,该方法的返回值类型是Object,我们可以返回任何类型的值。由于这个时候目标对象还未实例化,所以这个返回值可以用来代替原本该生成的目标对象的实例(比如代理对象)。如果该方法的返回值代替原本该生成的目标对象,后续只有postProcessAfterInitialization方法会调用,其它方法不再调用;否则按照正常的流程走 |
| postProcessAfterInstantiation | InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 自身方法,在目标对象实例化之后调用,这个时候对象已经被实例化,但是该实例的属性还未被设置,都是null。因为它的返回值是决定要不要调用postProcessPropertyValues方法的其中一个因素(因为还有一个因素是mbd.getDependencyCheck());如果该方法返回false,并且不需要check,那么postProcessPropertyValues就会被忽略不执行;如果返回true,postProcessPropertyValues就会被执行 |
| postProcessPropertyValues | InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 自身方法,对属性值进行修改,如果postProcessAfterInstantiation方法返回false,该方法可能不会被调用。可以在该方法内对属性值进行修改 |
| postProcessBeforeInitialization | BeanPostProcessor接口中的方法,在Bean的自定义初始化方法之前执行 |
| postProcessAfterInitialization | BeanPostProcessor接口中的方法,在Bean的自定义初始化方法执行完成之后执行,可以对Bean对象的属性进行修改替换 |

