05-读写锁、阻塞队列及四组API、同步队列
读写锁
ReadWriteLocks维护一对关联的ocks,一个用于只读操作,一个用于写入,Read lock可由多个阅读器同时进行操作(多线程同时进行),而write lock是独家的。
示例:
/**
* @author
* @Date 2022/7/25
* @apiNote
*/
public class ReadWriteDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCache myCache=new MyCache();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(()->{
myCache.read(finalI);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();//多线程读取
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(()->{
myCache.write(finalI,finalI);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();//多线程写入
}
}
static class MyCache{
private volatile Map<Integer,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
private void write(Integer key,Object value){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"准备插入"+key);
map.put(key, value);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"插入完毕"+key);
}
private void read(Integer key){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读"+key);
map.get(key);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读完毕"+key);
}
}
}
结果:
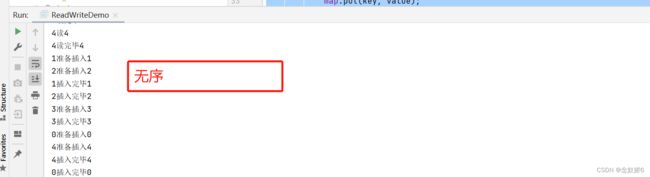
分析:在写入操作的时候,前一个未写入完毕,中间就会有其他数据插入进来,很容易造成脏数据。
解决办法
- 加入sychronized
- 加入Lock锁
- 加入readWriteLock锁(更细粒度的划分)
readWriteLock
/**
* @author
* @Date 2022/7/25
* @apiNote
*/
public class ReadWriteDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyCache myCache=new MyCache();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int finalI=i;
new Thread(()->{
myCache.read(finalI);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int finalI=i;
new Thread(()->{
myCache.write(finalI,finalI);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
static class MyCache{
private volatile Map<Integer,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
//读写锁
private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock= new ReadWriteLock() {
@Override
public Lock readLock() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Lock writeLock() {
return null;
}
};
private void write(Integer key,Object value){
readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();//写锁
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"准备插入"+key);
map.put(key, value);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"插入完毕"+key);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();//解锁
}
}
private void read(Integer key){
readWriteLock.readLock().lock();//读锁
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读"+key);
Object o = map.get(key);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读完毕"+key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();//解锁
}
}
}
}
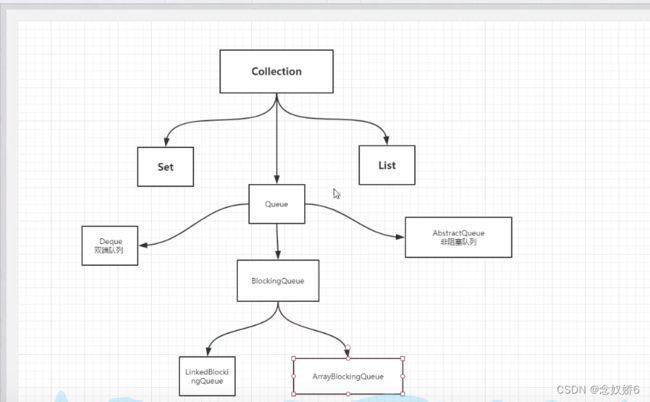
阻塞队列
四组API
抛出异常版本:
添加
add();
/**
* @author
* @Date 2022/7/25
* @apiNote
*/
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
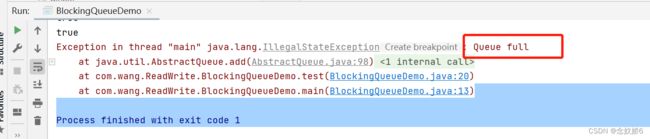
public static void test(){
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);//容量
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("A"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("B"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("C"));
}
}
结果:
则会抛出queue满的异常。
移除
remove(),遵循先进先出的原则,先添加的元素先被移除,后添加的元素后移除。
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
结果:
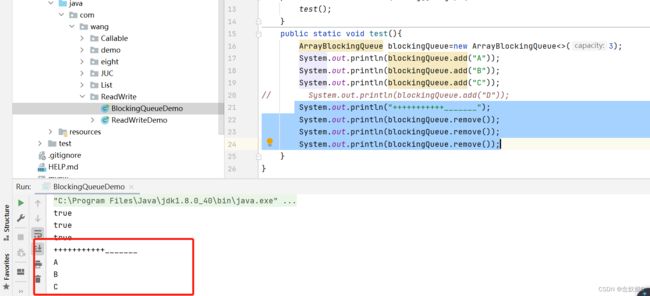
执行成功会打印被移除的元素。
若再次移除一次:
则会抛出找不到元素的异常

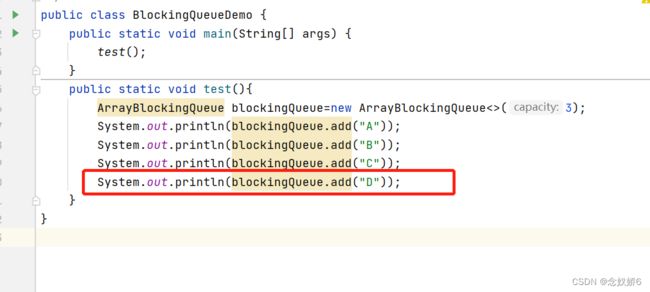
不抛出异常版本:
添加
offer()
public static void test1(){
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("A"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("B"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("C"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("D"));
}
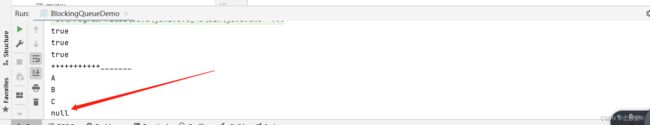
结果:

超过队列容量后再插入元素,不会抛出异常,插入元素打印后false代替。
删除:
poll();
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
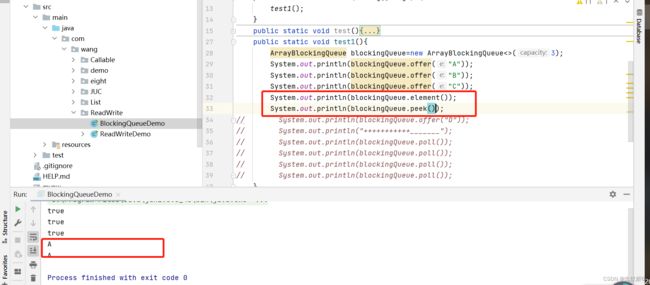
查看对首元素:
等待阻塞(一直等待)
put();
take();
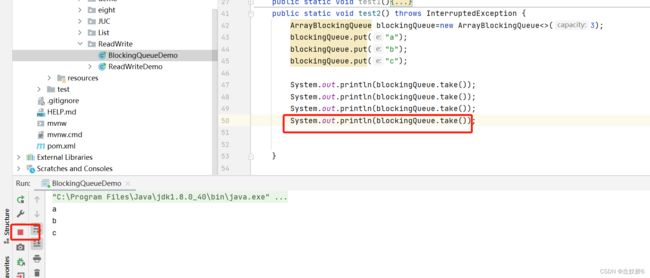
public static void test2() throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
blockingQueue.put("a");
blockingQueue.put("b");
blockingQueue.put("c");
}
结果:
执行成功
当超过最大容量再次添加元素后,程序会一直等待,形成阻塞:
获取元素
若超过最大容量的获取元素,也会形成一直阻塞的状态,程序会一直等待。
等待超时
public static void test3() throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("A"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("B"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("C"));
System.out.println("+++++++++++++++++++");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("D",2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}
结果:
再超过容量大小的元素时,会等待两秒后程序结束。
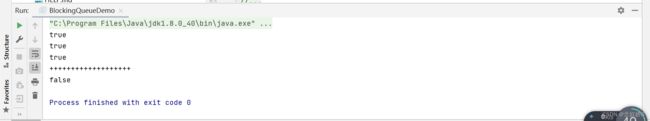
poll()等待超时方法相同。
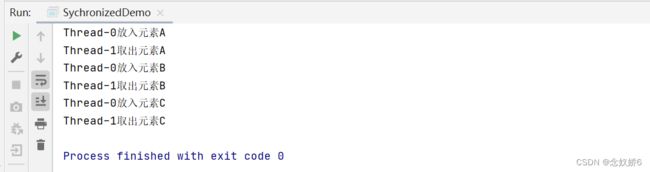
同步队列
sychronized队列不存储元素,put一个元素后。必须取出元素才能再次put,否则无法put元素。
示例:
/**
* @author
* @Date 2022/7/26
* @apiNote
*/
public class SychronizedDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> queue=new SynchronousQueue();
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"放入元素A");
queue.put("A");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"放入元素B");
queue.put("B");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"放入元素C");
queue.put("C");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);//每次取出元素之前休眠三秒,以便更好地观察。
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"取出元素A");
queue.take();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"取出元素B");
queue.take();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"取出元素C");
queue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}