Vuex由入门到深入
入门
Vuex是什么?
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
什么是“状态管理模式 ”
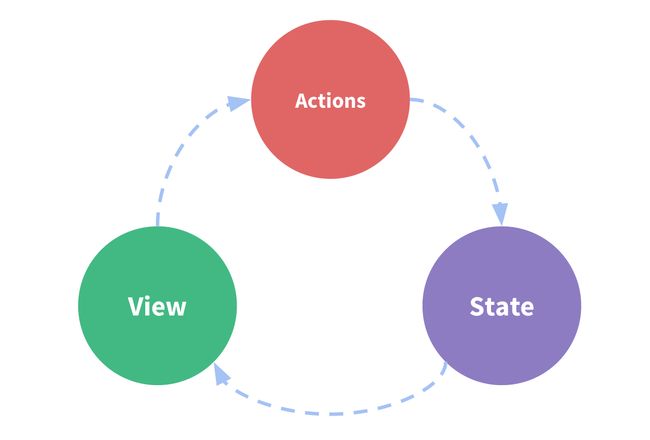
让我们从一个简单的计数器开始
new Vue({
// state
data () {
return {
count: 0
}
},
// view
template: `
{
{ count }}
`,
// actions
methods: {
increment () {
this.count++
}
}
})
这个状态包含一下几个部分
但是当我们遇到多个组件共享状态是,单项数据的简洁性很容易被破坏
- 多个视图依赖同一个状态
- 来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态
对于问题一,传参的方法对于多层嵌套的组件将会非常繁琐,并且对于兄弟组件间的状态传递无能为力。
对于问题二,我们经常会采用父子组件直接引用或者通过事件来变更和同步状态的多份拷贝。以上的这些模式非常脆弱,通常会导致无法维护的代码。
适合场景
Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,并附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要的对短期和长期效益进行权衡
如果你不打算开发大型单页面应用使用Vuex可能是繁琐冗余的,如果构建中大型单页面应用,Vuex将会成为自然而然的选择
安装
使用脚手架创建vue项目后下载vuex
npm install vuex --save
创建store文件夹并在其创建index.js文件,引入vue和vuex
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
特点
每一个Vuex应用的核心就是一个store(仓库)。它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态。Vuex和单纯的全局对象有以下两点不同
- Vuex和状态存储是响应式的。当Vue组件从store中读取状态时,若store中的状态发生改变,那么响应的组件也会得到高效的更新
- 你不能直接改变store中的状态。改变store中的状态的唯一途径就是显式的提交mutation。
使用store的计数器
安装Vuex后,我们需要创建你一个store。仅需要提供一个初始state对象和一些mutation
stored
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:10
},
mutations:{
add(state){
state.count++
},
sub(state){
state.count--
}
}
})
export default store
为了在 Vue 组件中访问 this.$store property,你需要为 Vue 实例提供创建好的 store。Vuex 提供了一个从根组件向所有子组件,以 store 选项的方式“注入”该 store 的机制:
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store: store,
})
可以通过store.state来获取状态对象,以及通过store.commit方法触发状态的改变
子组件
{
{ $store.state.count }}
父组件
{
{ $store.state.count }}

深入
1、state
单一状态树
在Vue组件中获得Vuex的状态
由于Vuex的状态是响应式的,从store实例中读取状态最简单的方法就是在计算属性中返回某个状态
姓名:{
{ name }}
性别:{
{ gender }}
作品:{
{ works }}
mapState辅助函数
当一个组件需要获得多个状态的时候,将这些状态都声明为计算属性会有些重复和冗余。为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用mapState辅助函数帮助我们生成计算属性
import {
mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: mapState({
name (state) {
return state.name
},
gender (state) {
return state.gender
},
works (state) {
return state.works
}
})
改为以上代码后还是显得有些冗余,所以让我们使用箭头函数来改造一下
import {
mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: mapState({
name: state => state.name,
gender: state => state.gender,
works: state => state.works,
})
}
当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时,我们也可以给 mapState 传一个字符串数组。
computed: mapState([
'name',
'gender',
'works'
])
对象展开运算符
mapState 函数返回的是一个对象。我们如何将它与局部计算属性混合使用呢?通常,我们需要使用一个工具函数将多个对象合并为一个,以使我们可以将最终对象传给 computed 属性。但是自从有了对象展开运算符 ,我们可以极大地简化写法:
export default {
computed: {
localComputed(){
//........
},
...mapState(['name', 'gender', 'works'])
}
}
效果:
2、getter
有时候我们需要从 store 中的 state 中派生出一些状态,例如对列表进行过滤并计数:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
starData: [
{
id: 1, name: '周杰伦',gender:'男' },
{
id: 2, name: '林俊杰',gender:'男' },
{
id: 3, name: '王力宏',gender:'男' },
{
id: 4, name: '范冰冰',gender:'女' },
{
id: 6, name: '林青霞',gender:'女' },
]
},
getters: {
starCount: state => {
return state.starData.length
}
}
一共有{
{ $store.getters.starCount }}位明星
mapGetters 辅助函数
mapGetters 辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性:
import {
mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
localComputed () {
//........
},
...mapGetters(['starCount'])
}
}
筛选案例
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
starData: [
{
id: 1, name: '周杰伦',gender:'男' },
{
id: 2, name: '林俊杰',gender:'男' },
{
id: 3, name: '王力宏',gender:'男' },
{
id: 4, name: '范冰冰',gender:'女' },
{
id: 6, name: '林青霞',gender:'女' },
]
},
getters: {
starCount: state => {
return state.starData.length
},
actress:state=> state.starData.filter(item=>item.gender=='女')
}
})
一共有{
{ starCount }}位明星
女演员有:
- {
{ item.name }}
3、mutations
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
starData: [
{
id: 1, name: '周杰伦',gender:'男' },
{
id: 2, name: '林俊杰',gender:'男' },
{
id: 3, name: '王力宏',gender:'男' },
{
id: 4, name: '范冰冰',gender:'女' },
{
id: 6, name: '林青霞',gender:'女' },
]
},
getters: {
starCount: state => {
return state.starData.length
},
actress:state=> state.starData.filter(item=>item.gender=='女'),
stars:state =>state.starData
},
mutations:{
addStar(state,star){
state.starData.push(star)
}
}
})
export default store
import {
mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
localComputed () {
//........
},
...mapGetters(['starCount', 'actress', 'stars'])
},
methods: {
addStar () {
var star = {
id: 6, name: '郭老师', denger: '女' }
this.$store.commit('addStar', star)
}
}
}
mapMutations辅助函数
mapMutations 辅助函数将组件中的 methods 映射为 store.commit 调用(需要在根节点注入 store)。
methods: {
...mapMutations(['addStar']),
add () {
var star = {
id: 6, name: '郭老师', gender: '女' }
this.addStar(star)
}
}
4、Action
Action类似于mutation
active提交的是mutation。而不是直接变更状态action可以包含任意异步操作
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:0
},
mutations:{
updateCount(state){
state.count++
}
},
actions:{
add(context){
context.commit('updateCount')
}
}
})
分发Action
action通过store.dispatch()方法触发
this.$store.dispatch('add')
看似和mutations一样,但是mutation只支持同步执行,而actions不受约束,可以在其内部执行异步操作
actions: {
add ({
commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('updateCount')
}, 1000)
}
}
5、Module
如果我们把所有转台都存储到了store中,后期会变得非常难以维护,store也就变得非常臃肿,为了解决这问题,vuex允许我们将store分割成模块。每个模块都有自己的state、mutation、getter、action。
首先在src/store下创建module文件夹用于创建模块的内容。
先创建一个shop模块
export default {
state: {
products: [
{
id: 1, title: 'iPhone11', price: 8000 },
{
id: 2, title: 'iPhone12', price: 10000 }
]
},
mutations: {
setProducts (state, payload) {
state.products = payload }
}
}
在index.js中导入shop模块
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import shop from './module/shop'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
shop
},
getters: {
products (state) {
return state.shop.products
}
},
state: {
count: 0,
},
mutations: {
increate (state, played) {
state.count += played
}
}
})
export default store
在组件中写入
{
{ item.title }}
mutations: {
increate (state, played) {
state.count += played
}
}
})
export default store
在组件中写入
```vue
{
{ item.title }}
当我们点击时发现shop模块中的products被清空了