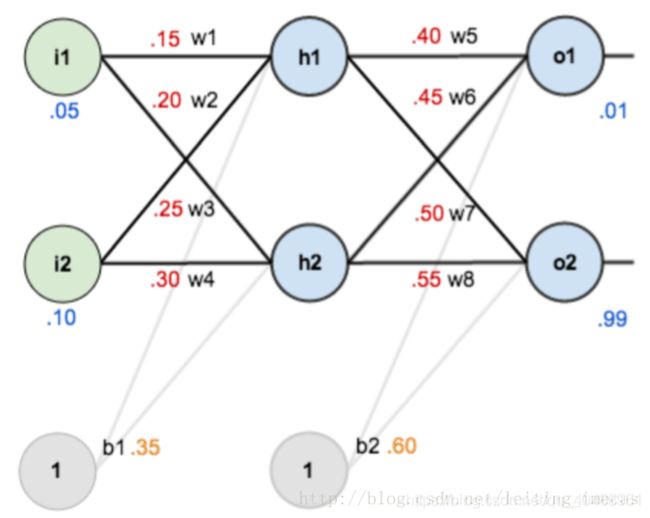
1)前向计算误差:
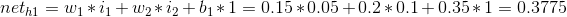
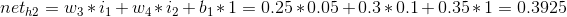
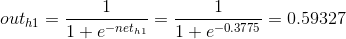
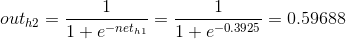
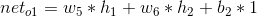
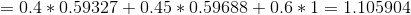
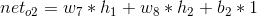
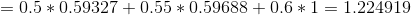
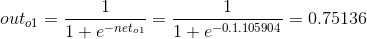
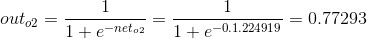
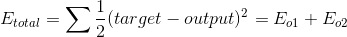
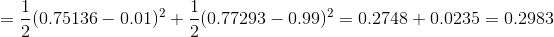
2)向后传播
1、更新W5参数
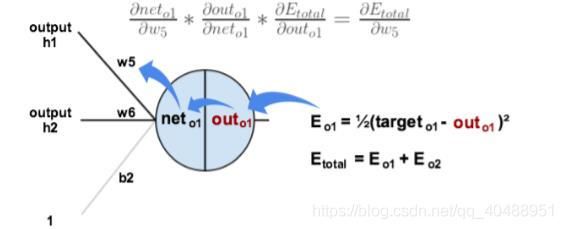
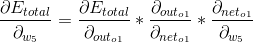
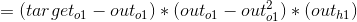
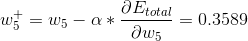
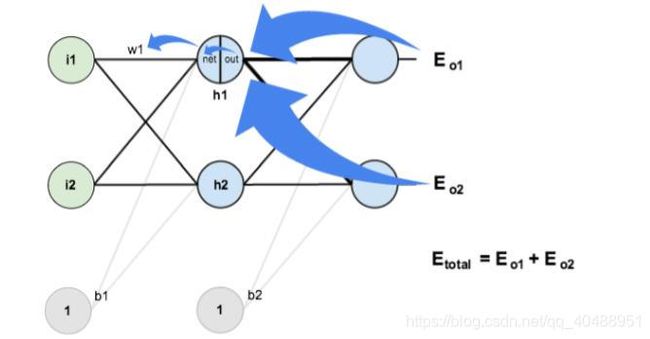
2、更新W1参数

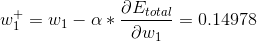
import numpy as np
import h5py
def load_dataset():
train_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/train_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels
test_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/test_catvnoncat.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes
def predict(w, b, X):
Y_prediction = np.zeros((1, X.shape[1]))
w = w.reshape(X.shape[0], 1) #(12288, 1)
# 计算结果
A = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-(np.dot(w.T, X) + b)))
for i in range(A.shape[1]):
if A[0, i] <= 0.5:
Y_prediction[0, i] = 0
else:
Y_prediction[0, i] = 1
return Y_prediction
# 1、读取样本数据
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, classes = load_dataset()
# print("训练集的样本数: ", train_x.shape[0]) #209
# print("测试集的样本数: ", test_x.shape[0]) #50
# print("train_x形状: ", train_x.shape) #(209, 64, 64, 3)
# print("train_y形状: ", train_y.shape) #(1, 209)
# print("test_x形状: ", test_x.shape) #(50, 64, 64, 3)
# print("test_x形状: ", test_y.shape) #(1, 50)
# 输入数据的形状修改以及归一化
train_x = train_x.reshape(train_x.shape[0], -1).T #将图像拉成一维,转置后每列代表一副图,每个元素为灰度值
# print(train_x.shape) #(12288, 209)
test_x = test_x.reshape(test_x.shape[0], -1).T
# print(test_x.shape) #(12288, 50)
train_x = train_x / 255.
test_x = test_x / 255.
# 2、模型训练以及预测
# 初始化参数
w = np.zeros((train_x.shape[0], 1)) #(12288, 1)
b = 0
num_iterations = 2000
learning_rate = 0.005
# 梯度下降
for i in range(num_iterations):
# 梯度更新计算函数
m = train_x.shape[1] #209
# 前向传播
A = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-(np.dot(w.T, train_x) + b))) #(1, 209)
# 计算损失
cost = -1 / m * np.sum(train_y * np.log(A) + (1 - train_y) * np.log(1 - A))
# 反向传播
dz = A - train_y
dw = 1 / m * np.dot(train_x, dz.T) #(12288, 1)
db = 1 / m * np.sum(dz)
# 按照梯度下降公式去计算
w = w - learning_rate * dw #(12288, 1)
b = b - learning_rate * db
if i % 200 == 0:
print("损失结果 %i: %f" % (i, cost))
print(b)
Y_prediction_train = predict(w, b, train_x)
Y_prediction_test = predict(w, b, test_x)
# 打印准确率
print("训练集准确率: {} ".format(100 - np.mean(np.abs(Y_prediction_train - train_y)) * 100))
print("测试集准确率: {} ".format(100 - np.mean(np.abs(Y_prediction_test - test_y)) * 100))
------------------------------------------
损失结果 1600: 0.159305
-0.01619503271238927
。。。。。。
损失结果 1800: 0.146542
-0.016079553977362767
训练集准确率: 99.04306220095694
测试集准确率: 70.0
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()


