Spring Bean生命周期-阶段汇总,面试必备(十二)
以后面试问到Bean的生命周期再也不怕了!
看了这么久的Spring源码,想必对Spring的生命周期已经有了一定的了解,这次将之前零散的生命周期处理的事情贯穿起来,看过之后,一定对bean的生命周期有更深入的理解
简介
- 实例化
- 设置bean的Aware
- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
- InitializingBean.afterPorpertiesSet
- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
- SmartInitializingSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated
- SmartLifecycle.start
- bean已经在spring容器的管理下,可以做我们想做的事
- SmartLifecycle.stop(Runnable callback)
- DisposableBean.destroy()
细节部分
- 实例化对应代码,使用合适的初始化方案来创建一个新的bean实例,factory-method,或者构造器注入,或者简单的直接实例化
实例化策略类:
InstantiationStrategy
实例化具体方法:
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args)
- 设置bean的Aware。InitializingBean.afterPorpertiesSet,BeanPostProcessor对bean的加工处理基本上在一块出现。
设置Aware方法顺序:
- BeanNameAware
- BeanClassLoaderAware
- BeanFactoryAware
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor也会设置Aware:
- EnvironmentAware
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware
- ResourceLoaderAware
- ApplicationEventPublisherAware
- MessageSourceAware
- ApplicationContextAware
调用afterpropertiesSet方法:位于AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd)方法中
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 设置Aware
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction- SmartInitializingSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated的调用位置
DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons方法,其在所有的bean都实例化完成之后调用
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List beanNames = new ArrayList(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
// 触发实例化所有的非懒加载的单例
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
...
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
// 触发应用bean的post-initialization回调,也就是afterSingletonsInstantiated方法
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction - SmartLifecycle.start在ApplicationContext结束刷新finishRefresh时,getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
判断bean是否为SmartLifecycle并且autoStartup。
位于:
DefaultLifecycleProcessor.onRefresh
- stop方法在Application.close的时候,调用getLifecycleProcessor().stop()方法仍然在DefaultLifecycleProcessor内部
- DisposableBean.destroy方法,doCreateBean方法中会判断bean是否有销毁相关操作,实现了DisposableBean方法或定义了销毁方法。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)
代码演示
public class HelloWorld implements SmartInitializingSingleton,SmartLifecycle,InitializingBean,
DisposableBean,MyInterface,BeanNameAware,ApplicationContextAware
{
private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private boolean isRunning;
public HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("实例化");
}
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello World");
}
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
System.out.println("SmartInitializingSingleton afterSingletonsInstantiated");
}
public void start() {
isRunning = true;
System.out.println("LifeCycle start");
}
public void stop() {
System.out.println("LifeCycle stop");
}
public boolean isRunning() {
return isRunning;
}
public boolean isAutoStartup() {
return true;
}
public void stop(Runnable callback) {
System.out.println("LifeScycle stop");
callback.run();
}
public int getPhase() {
return 0;
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("afterproperties set");
}
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("destroy");
}
public void my(String str) {
System.out.println(str);
}
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("set bean Name aware");
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("set Application Aware");
}
}
//MyInterface接口
public interface MyInterface {
void my(String str);
}
//app.xml
//SpringApp
public class SpringApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("app.xml");
HelloWorld hello = (HelloWorld) applicationContext.getBean("hello");
hello.sayHello();
applicationContext.close();
}
}
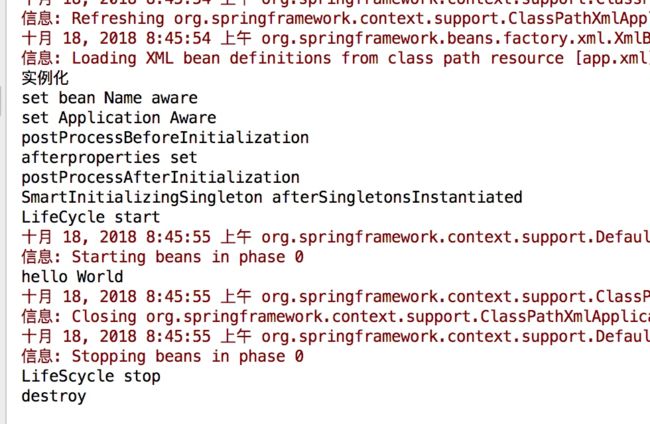
运行结果:
最后
可对照源代码自行验证生命周期。