deeplearning.ai——构建循环神经网络
目录
1 - Forward propagation for the basic Recurrent Neural Network
1.1 - RNN cell
1.2 - RNN forward pass
2 - Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network
2.1 - LSTM cell
2.2 - Forward pass for LSTM
3 - Backpropagation in recurrent neural networks (OPTIONAL / UNGRADED)
3.1 - Basic RNN backward pass
本文中的符号:
- 上标[l]表示与第l层相关的对象,例如:
![a^{[4]}](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/6a0f661b034b4a75ab4b9bc85fd51acc.gif) 是第4层的激活值,
是第4层的激活值,![W^{[5]}](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/edd817aa7e9a4061bcb9b50df331aa30.gif) 和
和![b^{[5]}](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/b462d20f136f4670a30d46dbb8477c7a.gif) 是第5层的参数。
是第5层的参数。 - 上标(i)表示与第i个样本相关的对象,例如:
 是第i个训练样本输入。
是第i个训练样本输入。 - 上标
表示在第t个时间步的对象,例如:  是第t个时间步的输入x,
是第t个时间步的输入x,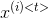 是样本i在第t个时间步的输入。
是样本i在第t个时间步的输入。 - 下标i表示向量的第i个输入,例如:
![a_{i}^{[l]}](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/93be4029946f41e6a2cfb6208c9077d9.gif) 表示在l层的激活值的第i个输入。
表示在l层的激活值的第i个输入。
1 - Forward propagation for the basic Recurrent Neural Network
在这个例子中,![]()
如何实现一个RNN:
- 实现RNN一个时间步所需要的计算过程
- 在
 时间步上实现一个循环使得能够一次处理所有输入
时间步上实现一个循环使得能够一次处理所有输入
1.1 - RNN cell
下图描述了一个RNN单元单个时间步的操作:
练习:实现上图中的RNN单元
说明:
- 使用tanh激活函数计算隐藏状态:

- 使用新的隐藏状态
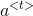 计算预测值
计算预测值
- 将
 储存在缓存cache中
储存在缓存cache中 - 返回
 和cache
和cache
已在m个样本上向量化,因此![]() 的维度为
的维度为![]() ,
,![]() 的维度为
的维度为![]()
# compute next activation state using the formula given above (n_a, m)
a_next = np.tanh(np.dot(Wax, xt) + np.dot(Waa, a_prev) + ba)
# compute output of the current cell using the formula given above
yt_pred = softmax(np.dot(Wya, a_next) + by)1.2 - RNN forward pass
练习:实现RNN的前向传播
说明:
- 创建一个零向量a,能够存储由RNN计算得到的所有隐藏状态
- 初始化“next”隐藏状态为

- 开始在每一个时间步上循环:更新“next”隐藏状态和缓存值,在a中存储“next”隐藏状态,在y中存储预测值,在cache列表中增加缓存值
- 返回a,y和cache
# initialize "a" and "y" with zeros (≈2 lines)
a = np.zeros((n_a, m, T_x))
y_pred = np.zeros((n_y, m, T_x))
# Initialize a_next (≈1 line)
a_next = a0
# loop over all time-steps
for t in range(T_x):
# Update next hidden state, compute the prediction, get the cache (≈1 line)
a_next, yt_pred, cache = rnn_cell_forward(x[:,:,t], a_next, parameters)
# 这里a_prev不能用a[:,:,t-1],因为t从0开始遍历,第一个a_prev为a[:,:,-1],无效值,只能用a_next自身遍历
# Save the value of the new "next" hidden state in a (≈1 line)
a[:,:,t] = a_next
# Save the value of the prediction in y (≈1 line)
y_pred[:,:,t] = yt_pred
# Append "cache" to "caches" (≈1 line)
caches.append(cache)
2 - Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network
2.1 - LSTM cell
练习:实现上图中的LSTM单元
说明:
# Concatenate a_prev and xt (≈3 lines)
concat = np.zeros((n_a+n_x, m))
concat[: n_a, :] = a_prev
concat[n_a :, :] = xt
# Compute values for ft, it, cct, c_next, ot, a_next using the formulas given figure (4) (≈6 lines)
ft = sigmoid(np.dot(Wf, concat) + bf)
it = sigmoid(np.dot(Wi, concat) + bi)
cct = np.tanh(np.dot(Wc, concat) + bc)
c_next = ft * c_prev + it * cct
ot = sigmoid(np.dot(Wo, concat) + bo)
a_next = ot * np.tanh(c_next)
# Compute prediction of the LSTM cell (≈1 line)
yt_pred = softmax(np.dot(Wy, a_next) + by)2.2 - Forward pass for LSTM
练习:实现lstm_forward()在![]() 时间步上运行LSTM
时间步上运行LSTM
提示:![]() 被初始化为全零
被初始化为全零
# Retrieve dimensions from shapes of xt and Wy (≈2 lines)
n_x, m, T_x = x.shape
n_y, n_a = parameters['Wy'].shape
# initialize "a", "c" and "y" with zeros (≈3 lines)
a = np.zeros((n_a, m, T_x))
c = np.zeros((n_a, m, T_x))
y = np.zeros((n_y, m, T_x))
# Initialize a_next and c_next (≈2 lines)
a_next = a0
c_next = np.zeros((n_a, m))
# loop over all time-steps
for t in range(T_x):
# Update next hidden state, next memory state, compute the prediction, get the cache (≈1 line)
a_next, c_next, yt, cache = lstm_cell_forward(x[:,:,t], a_next, c_next, parameters)
# Save the value of the new "next" hidden state in a (≈1 line)
a[:,:,t] = a_next
# Save the value of the prediction in y (≈1 line)
y[:,:,t] = yt
# Save the value of the next cell state (≈1 line)
c[:,:,t] = c_next
# Append the cache into caches (≈1 line)
caches.append(cache)
3 - Backpropagation in recurrent neural networks (OPTIONAL / UNGRADED)
3.1 - Basic RNN backward pass