基于python中的mysql管理,多线程和soecket
pyhton中的mysql
MySQL是一个关系型数据库管理系统,由瑞典MySQL AB 公司开发,目前属于 Oracle 旗下产品。MySQL 是最流行的关系型数据库管理系统之一,在 WEB 应用方面,MySQL是最好的 RDBMS (Relational Database Management System,关系数据库管理系统) 应用软件。
MySQL是一种关系数据库管理系统,关系数据库将数据保存在不同的表中,而不是将所有数据放在一个大仓库内,这样就增加了速度并提高了灵活性。
MySQL所使用的 SQL 语言是用于访问数据库的最常用标准化语言。MySQL 软件采用了双授权政策,分为社区版和商业版,由于其体积小、速度快、总体拥有成本低,尤其是开放源码这一特点,一般中小型网站的开发都选择 MySQL 作为网站数据库。
由于其社区版的性能卓越,搭配 PHP 和 Apache 可组成良好的开发环境
管理数据库分以下几步走:
在进行数据库管理之前需要把python中的MYSQLdb数据包导入python中
具体操作如下:
yum install mariadb-server -y 安装
systemctl start mariadb
systemctl stop firewalld
mysql_secure_installation #安装设置,只允许本机超级用户加密登陆
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Reloading privilege tables..
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
mysql -uroot -predhat #用root登陆,密码为redhat,不安全,其他用户可以看到超级用户密码
mysql -uroot -p #超级用户加密后登录
yum search MySQL-python
yum install MySQL-python.x86_64 -y 安装服务
pip install Mysql-Python 建立连接在网上下载三方软件网页管理数据库
yum install php httpd -y
systemctl start httpd
systemctl stop firewalld
cd /var/www/html/
ls
get phpMyAdmin-3.4.0-all-languages.tar.bz2
ls
tar jxf phpMyAdmin-3.4.0-all-languages.tar.bz2
ls
rm -f phpMyAdmin-3.4.0-all-languages.tar.bz2
ls
mv phpMyAdmin-3.4.0-all-languages/ mysqladmin
ls
cd mysqladmin/
ls
cp config.sample.inc.php config.inc.php
cd ..
yum install php-mysql.x86_64 -y #该安装包是为了在php中添加mysql功能
systemctl restart httpdimport MySQLdb
# 打开门
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user = 'root',passwd='redhat',db='python')
# 伸出手
cur = conn.cursor()
# 拿东西
recont = cur.execute('select * from userInfo')
# 把手伸回来
cur.close()
# 把门关上
conn.close()
# 打印返回结果
print recont1 >查看并输出数据库指定表中的数据:
import MySQLdb
# 打开门
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user = 'root',passwd='redhat',db='python')
# 伸出手
# 创建了一只手
cur = conn.cursor()
# 拿东西
# 这个操作影响了多少行数(有多少行被操作了) execute 执行
recont = cur.execute('select * from userInfo')
# 看东西 fetchall 取物
data = cur.fetchall()
# 把手伸回来
cur.close()
# 把门关上
conn.close()
print recont
print data1.1>以字典的方式查看并输出数据库中的内容:
# 打开门
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user = 'root',passwd='redhat',db='python')
# 伸出手
# 创建了一只手 cursor 指针
# cur = conn.cursor()
**cur = conn.cursor(cursorclass=MySQLdb.cursors.DictCursor)**
# 拿东西
# 这个操作影响了多少行数(有多少行被操作了) execute 执行
recont = cur.execute('select * from userInfo')
# 看东西 fetchall 取物
data = cur.fetchall()
# 把手伸回来
cur.close()
# 把门关上
conn.close()
print recont
print data2>python中的mysql增
import MySQLdb
# 打开门
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='redhat',db='python')
# 伸出手
cur = conn.cursor()
# 操作数据
sql = 'insert into new_table (name,age,Feature)values(%s,%s,%s)'
params = ('Tom','12','westos')
recount = cur.execute(sql,params)
recont = cur.execute('select * from new_table')
# 看东西 fetchall 取物
data = cur.fetchall()
# 提交
conn.commit()
# 把手伸回来
cur.close()
# 把门关上
conn.close()
print recount
print data3>python中的mysql改
import MySQLdb
# 打开门
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='redhat',db='python')
# 伸出手
cur = conn.cursor()
# 操作数据
sql = 'update new_table set age= %s where name=%s'
# 元组中如果第一个数字后面不加','会被看作int整形,在元组中所有数据都是字符串
params = (1,'Tom',) # ('更改后的内容',where,)
recount = cur.execute(sql,params)
# 拿东西
recont = cur.execute('select * from new_table')
# 看东西 fetchall 取物
data = cur.fetchall()
# 提交
conn.commit()
# 把手伸回来
cur.close()
# 把门关上
conn.close()
print recount
print data4>python中的mysql删
import MySQLdb
# 打开门
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='redhat',db='python')
# 伸出手
cur = conn.cursor()
# 操作数据
sql = 'delete from new_table where name = %s '
# 元组中如果第一个数字后面不加','会被看作int整形,在元组中所有数据都是字符串
params = ('Tom',)
recount = cur.execute(sql,params)
# 提交
conn.commit()
# 把手伸回来
cur.close()
# 把门关上
conn.close()
print recount5>python中的提交和回滚
在数据库里提交事物操作
如果没有提交,那么系统不会接收到用户操作,结果也不会改变
交互式假设A给B转账,那么A的户头就会减少,B的户头会增加
如何实现:
import MySQLdb
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='redhat',db='python')
cur = conn.cursor()
sql = 'update count set money = %s where id = 1'
params = ('100',)
recount = cur.execute(sql,params)
conn.commit()
sql = 'update count set money = %s where id = 2'
params = ('0',)
recount = cur.execute(sql,params)
conn.commit()6>在mysql中插入多条数据
import MySQLdb
# 打开门
conn = MySQLdb.connect(host='127.0.0.1',user='root',passwd='redhat',db='python')
# 伸出手
cur = conn.cursor()
# 操作数据
sql = 'insert into new_table (name,age,Feature)values(%s,%s,%s)'
params = [('Lily',2,'Teacher'),
('Oldlee',3,'Pang'),
('Yuhan',4,'Mei')]
# cur.executemany 多行执行
recount = cur.executemany(sql, params)
# 测试查看修改是否成功
recont = cur.execute('select * from new_table')
data = cur.fetchall()
# 提交
conn.commit()
# 把手伸回来
cur.close()
# 把门关上
conn.close()
print recount
print data线程和进程的区别:
1.进程:是执行中一段程序,即一旦程序被载入到内存中并准备执行,它就是一个进程。进程是表示资源分配的的基本概念,又是调度运行的基本单位,是系统中的并发执行的单位。
线程:单个进程中执行中每个任务就是一个线程。线程是进程中执行运算的最小单位。
2.一个线程只能属于一个进程,但是一个进程可以拥有多个线程。多线程处理就是允许一个进程中在同一时刻执行多个任务。
3.线程是一种轻量级的进程,与进程相比,线程给操作系统带来侧创建、维护、和管理的负担要轻,意味着线程的代价或开销比较小。
4.线程没有地址空间,线程包含在进程的地址空间中。线程上下文只包含一个堆栈、一个寄存器、一个优先权,线程文本包含在他的进程 的文本片段中,进程拥有的所有资源都属于线程。所有的线程共享进程的内存和资源。
线程是操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位(程序执行流的最小单位)
它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位.一个进程中可以并发多个线程
每条西那成并行执行不同的任务
(线程是进程中的一个实体,是被系统独立调度和分派的基本单元)
每一个进程启动时都会最先产生一个线程,即主线程
然后主线程会再创建其他的子线程
多线程能干什么?
import threading
from time import ctime, sleep
def music(a):
for i in range(2):
print 'I was listening to %s. %s \n' % (a, ctime())
sleep(1)
def movie(b):
for i in range(2):
print 'I was watching to %s. %s \n' % (b, ctime())
sleep(5)
# music('故乡')
# movie('我不是药神')
t1 = threading.Thread(target=music,args=('故乡',))
t1.start()
t2 = threading.Thread(target=movie,args=('我不是药神',))
t2.start()
print 'all over %s' %ctime()可以看到music和movie是同时进行的,他们是两个互不干扰的线程,主线程不等待分线程的执行
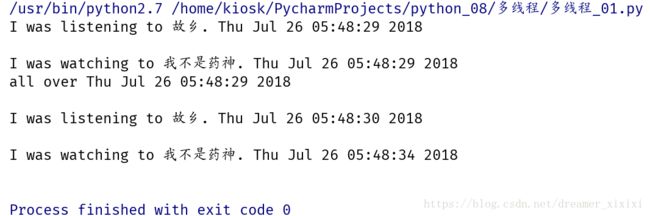
线程之间建立关系
from threading import Thread
def Foo(arg):
print arg
print 'before'
# 线程之间建立关系
t1 = Thread(target=Foo,args=(1,))
t1.start()
print 'after'getName 获取分线程名称
这个程序中主线程等待分线程执行完毕才执行
from threading import Thread
def Foo(arg):
print arg
print 'before'
# 线程之间建立关系
t1 = Thread(target=Foo,args=(1,))
t1.start()
print t1.getName()
t2 = Thread(target=Foo,args=(2,))
t2.start()
print t2.getName()
print 'after'主线程不等待分线程执行结束
from threading import Thread
import time
def Foo():
for item in range(8):
print item
time.sleep(1)
print 'before'
# 线程之间建立关系
t1 = Thread(target=Foo)
t1.setDaemon(True)
t1.start()
print 'after'
time.sleep(100)import threading
import time
def Foo():
for item in range(10):
print item
time.sleep(1)
print 'before'
t1 = threading.Thread(target=Foo)
t1.start()
# 主线程到join()就不往下走了,直到子线程执行完毕
t1.join(5)
print 'after'
# 主线程只等分线程5秒,然后就执行自己的程序
买包子事件,消费者购买包子时间短,生产者生产包子时间长,当包子不能满足消费者时,
就会提醒生产者没有包子了,生产者就会制作包子满足消费者,这样程序就不会中断,用异常来处理
import threading
import Queue
import time
import random
def Producer(name,que):
while True:
que.put('baozi')
print '%s:Made a baobzi..======' % name
time.sleep(random.randrange(5))
def Consumer(name,que):
while True:
try:
que.get_nowait()
print '%s:Got a baobao..' % name
except Exception:
print '没有包子了'
time.sleep(random.randrange(3))
# 创建队列
q = Queue.Queue()
p1 = threading.Thread(target=Producer,args=['chef1',q] )
p2 = threading.Thread(target=Producer,args=['chef2',q] )
p1.start()
p2.start()
c1 = threading.Thread(target=Consumer,args=['tom',q] )
c2 = threading.Thread(target=Consumer,args=['harry',q] )
c1.start()
c2.start()def Producer(name, que):
while True:
if que.qsize() < 3:
que.put('baozi')
print '%s:Made a baobzi..======' % name
else:
print '还有三个包子'
time.sleep(random.randrange(5))
def Consumer(name, que):
while True:
try:
que.get_nowait()
print '%s:Got a baobao..' % name
except Exception:
print '没有包子了'
time.sleep(random.randrange(3))
# 创建队列
q = Queue.Queue()
p1 = threading.Thread(target=Producer, args=['chef1', q])
p2 = threading.Thread(target=Producer, args=['chef2', q])
p1.start()
p2.start()
c1 = threading.Thread(target=Consumer, args=['tom', q])
c2 = threading.Thread(target=Consumer, args=['harry', q])
c1.start()
c2.start()import time
import threading
num = 0
def run(n):
time.sleep(1)
global num
# 线程锁
lock.acquire()
num += 1
print '%s\n' %num
lock.release()
lock = threading.Lock()
for i in range(500):
t = threading.Thread(target=run,args=(i,))
t.start() 事物驱动:
import threading
import time
def Producer():
print 'chef:等人来买包子'
#收到了消费者的event.set 也就是把这个flag改为了true,但是我们的包子并没有做好
event.wait()
#此时应该将flag的值改回去
event.clear()
print 'chef:someone is coming for 包子'
print 'chef:making a 包子 for someone'
time.sleep(5)
# 告诉人家包子做好了
print '你的包子好了~'
event.set()
def Consumer():
print 'tom:去买包子'
# 告诉人家我来了
event.set()
time.sleep(2)
print 'tom:waiting for 包子 to be ready'
event.wait()
print '哎呀~真好吃'
event = threading.Event()
p1 = threading.Thread(target=Producer)
c1 = threading.Thread(target=Consumer)
p1.start()
c1.start()异步:
import threading
import time
def Producer():
print 'chef:等人来买包子'
# 收到了消费者的event.set 也就是把这个flag改为了true,但是我们的包子并没有做好
event.wait()
# 此时应该将flag的值改回去
event.clear()
print 'chef:someone is coming for 包子'
print 'chef:making a 包子 for someone'
time.sleep(5)
# 告诉人家包子做好了
print '你的包子好了~'
event.set()
def Consumer():
print 'tom:去买包子'
# 告诉人家我来了
event.set()
time.sleep(2)
print 'tom:waiting for 包子 to be ready'
# 我在不断检测,但我已经不阻塞了
while True:
if event.is_set():
print 'Thanks~'
break
else:
print '怎么还没好呀~'
# 模拟正在做自己的事情
time.sleep(1)
event = threading.Event()
p1 = threading.Thread(target=Producer)
c1 = threading.Thread(target=Consumer)
p1.start()
c1.start()Socket
什么是socket?
网络上的两个程序通过一个双向的通信连接实现数据的交换,这个连接的一端称为一个socket
所谓socket通常也称作“套接字”,用于描述IP地址和端口,是一个通信链的句柄,应用程序通常通过“套接字”向网络发出请求或应答网络请求
socket起源于Uinx,而Unix/Linux基本哲学之一就是“一切皆文件”,都可以用“打开open–>读写write/read–>关闭close”模式来操作,socket就是该模式的一个实现,socket即是一种特殊的文件,一些socket函数就是对其进行的操作(读/写 IO,打开,关闭)
Socket的英文原义是“孔”或“插座”。作为BSD UNIX的进程通信机制,取后一种意思。通常也称作”套接字”,用于描述IP地址和端口,是一个通信链的句柄,可以用来实现不同虚拟机或不同计算机之间的通信。在Internet上的主机一般运行了多个服务软件,同时提供几种服务。每种服务都打开一个Socket,并绑定到一个端口上,不同的端口对应于不同的服务。Socket正如其英文原义那样,像一个多孔插座。一台主机犹如布满各种插座的房间,每个插座有一个编号,有的插座提供220伏交流电,有的提供110伏交流电,有的则提供有线电视节目。 客户软件将插头插到不同编号的插座,就可以得到不同的服务
例如:中国移动客服
对于移动来说:一直监听一个号码10086,当有电话进来后,就分配一个客服和客户去沟通并处理请求
对于用户:需要知道10086这个号码,并需要打电话
建了一个服务端一个客户端:
客户端:
import socket
# 创建一个socket对象
client = socket.socket()
# 创建连接
ip_port = ('127.0.0.1', 2387)
client.connect(ip_port)
# 获取数据
while True:
data = client.recv(1024)
print data
# 发送数据
inp = raw_input('client:')
client.send(inp)
if inp == 'exit':
breakimport socket
# 1.创建socket对象
sk = socket.socket()
# 2.绑定端口和ip
ip_port = ('127.0.0.1',2387)
sk.bind(ip_port)
# 3.最大连接数
sk.listen(5)
while True:
# 获取客户端的ip和端口号
conn,address = sk.accept()
# conn = result[0]
# address = result[1]
# print result
# print type(result) 元组型
conn.send('hello')
flag = True
while flag:
data = conn.recv(1024)
print data
if data == 'exit':
flag = False
conn.send('ouhayou')
conn.close()在服务端运行的过程中:在客户端发出请求:
[kiosk@foundation30 socket]$ python client.py
hello
client:nihao
ouhayou
client:exit
[kiosk@foundation30 socket]$ pwd
/home/kiosk/PycharmProjects/python_08/socket




















