《Thinking in java》第18章--Java BIO
BIO(阻塞式IO)
1、File类:
①File可以根据路径访问到文件或是文件目录,并将文件或是文件目录以java对象的方式存储。如 File file = new File("d:/IO/hello.txt");
②File可以创建、删除、重命名文件以及文件目录
③但是File不能访问到文件的内容,此时,必须将file作为对象传递给输入输出流才行。
访问文件名相关:
---|getName()
---|getPath()
---|getAbsoluteFile()
---|getAbsolutePath()
---|getParent()
---|renameTo(File newname)
文件操作相关:
---|exists()
---|canWrite()
---|canRead()
---|isFile()
---|isDirectory()
---|createNewFile()
---|delete()
目录操作相关:
---|mkDir()
---|mkDirs()
---|list()
---|listFile()
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2、IO流(用来处理设备之间的数据传输|输入input|输出output)
2.0 常识
一个英文字母和一个数字占一个字节(8bit)
一个汉字占一个字符,等于两个字节(16bit)
byte 8bit/1byte 负2的7次方,至2的7次方-1
short 16bit/2byte 负2的15次方 至 2的15次方-1
int 32bit/4byte 负2的31次方 至 2的31次方-1
long 64bit/8byte 负2的63次方 至 2的63次方-1
float 32bit/4byte 2的128次方-1
double 64bit/8byte 2的1024次方-1
char 16bit/2byte \u0000~\uFFFF,unicode编码
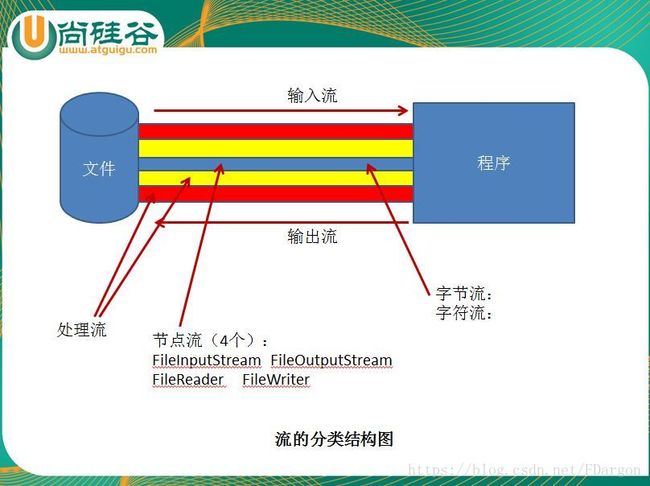
2.1 流的分类
1)按操作数据单位不同:字节流(8bit)、字符流(16bit),字节流和字符流的区别还体现在,字节流直接操作文件,字符流先放到缓存中
抽象基类--|
字节流--|
输入字节流--|InputStream
输出字节流--|OutputStream
字符流--|
输入字节流--|Reader
输出字节流--|Writer
2) 按数据的流向不同: 输入流、输出流
3)按流的角色不同:节点流(直接作用在数据上)、处理流(对流做处理)
2.2 字节流的使用
/**
* 测试字节输入输出流(适用于图片等)
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void TestStram() throws Exception{
File file = new File("C:/Users/huzangyi/Desktop/hello.txt");
File file2 = new File("C:/Users/huzangyi/Desktop/hello2.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
byte[] b = new byte[20];
int len;//每次读入到byte数组中的字节的长度
while((len = fis.read(b))!=-1){
fos.write(b, 0, len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
2.3 字符流的使用
/**
* 测试字符输入输出流(适用于文字)
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void TestReaderWriter() throws Exception{
File file = new File("C:/Users/huzangyi/Desktop/hello.txt");
File file2 = new File("C:/Users/huzangyi/Desktop/hello2.txt");
FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file2);
char[] cbuf = new char[10];
int len;
while((len = reader.read(cbuf))!=-1){
writer.write(cbuf, 0, len);
}
//若不关闭输出流,无法完成数据传递,因为先放到缓存里,缓存没有刷新给文件
writer.close();
reader.close();
}
2.4 处理流的使用(提升文件操作效率)
/**
* 测试处理流,如缓冲流BufferInputStream/BufferOutputStream,BufferReader/BufferWriter
* 将流包起来,提升文件操作的效率
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void TestBuffer() throws Exception{
File file = new File("C:/Users/huzangyi/Desktop/hello.txt");
File file2 = new File("C:/Users/huzangyi/Desktop/hello2.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
byte[] b = new byte[10];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(b))!=-1){
bos.write(b, 0, len);
bos.flush();
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
2.4 转换流的使用InputStreamReader(InputStream-->Reader)/OutputStreamWriter(Writer-->OutputStream)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------