Core Data
Core Data
一、Core Data简介
Core Data是iOS5之后才出现的一个框架,它提供了对象-关系映射(ORM)的功能,即能够将OC对象转化成数据,保存在SQLite数据库文件中,也能够将保存在数据库中的数据还原成OC对象。在此数据操作期间,我们不需要编写任何SQL语句。另外,这里不介绍Core Data和SQLite、FMDB的区别,如若需要请另行google。
二、Core Data使用步骤
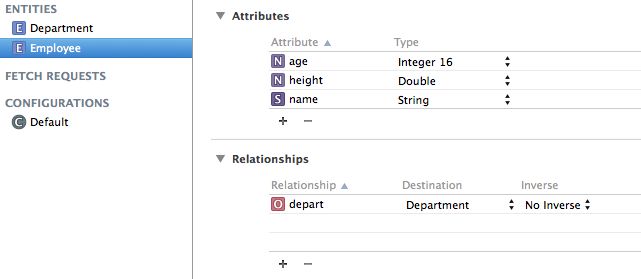
- 创建模型文件(相当于数据库)
- 添加实体(相当表)
- 创建实体类(相当于模型类)
- 生成上下文,关联模型文件,生成数据库
- 数据操作
三、代码编写
创建模型文件、添加实体、创建实体类等步骤非常简单,这里不作介绍。
3.1 生成上下文
-(void)setupContext{
// 1.生成上下文,关联模型文件
NSManagedObjectContext *context = [[NSManagedObjectContext alloc] init];
// 2.创建一个模型对象
// 如果只有一个数据库,使用下面这条注释的语句即可
//NSManagedObjectModel *model = [NSManagedObjectModel mergedModelFromBundles:nil];
//Company是你生成的模型文件的名字,
NSURL *url = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"Company" withExtension:@"momd"];
NSManagedObjectModel *model = [[NSManagedObjectModel alloc] initWithContentsOfURL:url];
// 3.持久化存储调度器
NSPersistentStoreCoordinator *store = [[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator alloc] initWithManagedObjectModel:model];
// 4.数据库保存的路径
NSString *doc = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) lastObject];
//company.sqlite是在手机中创建的数据库文件的名字
NSString *sqlitePath = [doc stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Company.sqlite"];
NSError *error = nil;
[store addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType configuration:nil URL:[NSURL fileURLWithPath:sqlitePath] options:nil error:&error];
context.persistentStoreCoordinator = store;
self.context = context;
}3.2 插入数据
#pragma mark 添加员工信息
- (IBAction)addEmployee:(id)sender {
// 创建员工,Employee是数据库Company中的一个表的名字,也是需要添加的实体类
Employee *emp1 = [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@"Employee" inManagedObjectContext:self.context];
// 设置员工属性
emp1.name = @"lisi";
emp1.age = @28;
emp1.height = @2.10;
//保存
NSError *error = nil;
[self.context save:&error];
if (!error) {
NSLog(@"success");
}else{
NSLog(@"%@",error);
}
}3.3 查询数据
#pragma mark 查找某个员工
-(NSArray *)findEmployeeWithName:(NSString *)name{
// 1.查找员工
NSFetchRequest *request = [NSFetchRequest fetchRequestWithEntityName:@"Employee"];
// 2.过滤条件
NSPredicate *pre = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"name=%@",name];
request.predicate = pre;
return [self.context executeFetchRequest:request error:nil];
}
#pragma mark 读取员工信息
- (IBAction)readEmployee:(id)sender {
//创建一个请求对象 (填入要查询的表名-实体类)
NSFetchRequest *request = [NSFetchRequest fetchRequestWithEntityName:@"Employee"];
// 过滤查询
// 查找名为张三且身高大于1.8的Employee对象
NSPredicate *pre = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"name=%@ AND height > %@",@"zhangsan",@(1.8)];
request.predicate = pre;
//以身高进行升序排序
NSSortDescriptor *sort = [NSSortDescriptor sortDescriptorWithKey:@"height" ascending:NO];
request.sortDescriptors = @[sort];
// 分页查询 假设总共13条数据 每页显示5条数据(fetchLimit),从第几条数据开始查找(fetchOffset)
// 第一页的数据
request.fetchLimit = 5;
request.fetchOffset = 0;
//读取信息
NSError *error = nil;
NSArray *emps = [self.context executeFetchRequest:request error:&error];
if (!error) {
NSLog(@"emps: %@",emps);
for (Employee *emp in emps) {
NSLog(@"%@ %@ %@",emp.name,emp.age,emp.height);
}
}else{
NSLog(@"%@",error);
}
}3.4 更新数据
#pragma mark 更新员工信息
- (IBAction)updateEmployee:(id)sender {
// 把wangwu的身高更改成 1.7
// 1.查找wangwu
NSArray *emps = [self findEmployeeWithName:@"wangwu"];
// 2.更新身高
if (emps.count == 1) {
Employee *emp = emps[0];
emp.height = @1.7;
}
// 3.同步(保存)到数据
[self.context save:nil];
}3.5 删除数据
#pragma mark 删除员工
- (IBAction)deleteEmployee:(id)sender {
[self deleteEmployeeWithName:@"lisi"];
}
-(void)deleteEmployeeWithName:(NSString *)name{
// 删除lisi
// 1.查找到lisi
NSFetchRequest *request = [NSFetchRequest fetchRequestWithEntityName:@"Employee"];
NSPredicate *pre = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"name=%@",name];
request.predicate = pre;
// 2.删除lisi
NSArray *emps = [self.context executeFetchRequest:request error:nil];
for (Employee *emp in emps) {
NSLog(@"删除员工 %@",emp.name);
[self.context deleteObject:emp];
}
// 3.用context同步下数据库
//所有的操作暂时都是在内存里,调用save 同步数据库
[self.context save:nil];
}3.6 模糊查询
#pragma mark 模糊查询
- (IBAction)likeSearcher:(id)sender {
// 查询
NSFetchRequest *request = [NSFetchRequest fetchRequestWithEntityName:@"Employee"];
// 过滤
// 1.查询以wang开头员工
NSPredicate *pre1 = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"name BEGINSWITH %@",@"wang"];
// 2.以si 结尾
NSPredicate *pre2 = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"name ENDSWITH %@",@"si"];
// 3.名字包含 g
NSPredicate *pre3 = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"name CONTAINS %@",@"g"];
// 4.like,以li开头
NSPredicate *pre4 = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"name like %@",@"li*"];
request.predicate = pre1;
//读取信息
NSError *error = nil;
NSArray *emps = [self.context executeFetchRequest:request error:&error];
if (!error) {
NSLog(@"emps: %@",emps);
for (Employee *emp in emps) {
NSLog(@"%@ %@ %@",emp.name,emp.age,emp.height);
}
}else{
NSLog(@"%@",error);
}
}3.7 多表关联
则插入操作:
#pragma mark 添加员工信息
- (IBAction)addEmployee:(id)sender {
// 创建员工
// 1.添加zhangsan 属于ios部门
Employee *emp1 = [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@"Employee" inManagedObjectContext:self.context];
emp1.name = @"zhangsan";
emp1.height = @1.7;
emp1.age = @27;
// 创建ios部门
Department *dep1 = [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@"Department" inManagedObjectContext:self.context];
dep1.name = @"ios";
dep1.createDate = [NSDate date];
dep1.departNo = @"D001";
//关联
emp1.depart = dep1;
//一次保存
[self.context save:nil];
}查询操作:
#pragma mark 读取员工信息
- (IBAction)readEmployee:(id)sender {
NSFetchRequest *request = [NSFetchRequest fetchRequestWithEntityName:@"Employee"];
// 过滤查询,查找ios部门的员工
NSPredicate *pre = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"depart.name = %@",@"ios"];
request.predicate = pre;其他功能同理,这里不再详述。值得一提的是,即使一个数据库里有多个表,代码的编写还是没什么区别的,唯一不同的是数据表的管理变得麻烦了。比如两个关联的表,一个表更新了数据,另一个表是跟着更新还是插入新的数据,或者在已有的数据中选择另一个与之相关联,这些才是真正要考虑的。