Servlet的作用
Servlet 是一些遵从Java Servlet API的Java类,这些Java类可以响应请求。尽管Servlet可以响应任意类型的请求,但是它们使用最广泛的是响应web方面的请求。 Servlet必须部署在Java servlet容器才能使用。
一、:Servlet的生命周期
在你的应用加载并使用一个Servlet时,从初始化到销毁这个Servlet期间会发生一系列的事件。这些事件叫做Servlet的生命周期事件(或方法)。让我们一起来进一步了解它们。(1) 在Servlet生命周期的初始化阶段,web容器通过调用init()方法来初始化Servlet实例,并且可以传递一个实现 javax.servlet.ServletConfig 接口的对象给它。这个配置对象(configuration object)使Servlet能够读取在web应用的web.xml文件里定义的名值(name-value)初始参数。这个方法在Servlet实例的生命周期里只调用一次。
<span style="font-size:14px;">public void init() throws ServletException {
//custom initialization code
}</span>
(2)初始化后,Servlet实例就可以处理客户端请求了。web容器调用Servlet的service()方法来处理每一个请求。service() 方法定义了能够处理的请求类型并且调用适当方法来处理这些请求。编写Servlet的开发者必须为这些方法提供实现。如果发出一个Servlet没实现的请求,那么父类的方法就会被调用并且通常会给请求方(requester)返回一个错误信息。
<span style="font-size:14px;">protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}</span>
(3)最后,web容器调用destroy()方法来终结Servlet。如果你想在Servlet的生命周期内关闭或者销毁一些文件系统或者网络资源,你可以调用这个方法来实现。destroy() 方法和init()方法一样,在Servlet的生命周期里只能调用一次。
<span style="font-size:14px;"><span style="font-family:Microsoft YaHei;">public void destroy() {
//
}</span></span>
二、:Servlet的接口实现
Servlet接口SUN公司定义了两个默认实现类,分别为:GenericServlet、HttpServlet。
HttpServlet指能够处理HTTP请求的servlet,它在原有Servlet接口上添加了一些与HTTP协议处理方法,它比Servlet接口的功能更为强大。因此开发人员在编写Servlet时,通常应继承这个类,而避免直接去实现Servlet接口。
HttpServlet在实现Servlet接口时,覆写了service方法,该方法体内的代码会自动判断用户的请求方式,如为GET请求,则调用HttpServlet的doGet方法,如为Post请求,则调用doPost方法。因此,开发人员在编写Servlet时,通常只需要覆写doGet或doPost方法,而不要去覆写service方法。
下图是eclipse中web项目的目录解析:
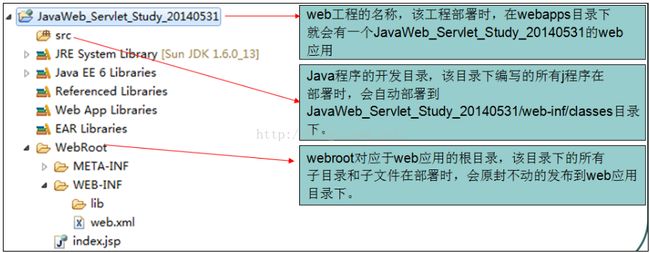
三、:在Eclipse中开发Servlet实例
(1)新建一个Web工程(2)工程目录如上图所示,我们可以在src目录下New一个Servlet文件,创建过程中勾选doGet()和doPost()方法
(3)工程建立之后会自动在WEB-INF目录下的web.xml文件中生成Servlet的配置信息
(4)打开Tomcat部署工程,在浏览器中输入对应的URL访问Servlet
如下是生成的Servlet文件代码:
package servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class ServletDemo extends HttpServlet {
/**
* The doGet method of the servlet. <br>
*
* This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to get.
*
* @param request the request send by the client to the server
* @param response the response send by the server to the client
* @throws ServletException if an error occurred
* @throws IOException if an error occurred
*/
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\">");
out.println("<HTML>");
out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");
out.println(" <BODY>");
out.print(" This is ");
out.print(this.getClass());
out.println(", using the GET method");
out.println(" </BODY>");
out.println("</HTML>");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
/**
* The doPost method of the servlet. <br>
*
* This method is called when a form has its tag value method equals to post.
*
* @param request the request send by the client to the server
* @param response the response send by the server to the client
* @throws ServletException if an error occurred
* @throws IOException if an error occurred
*/
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\">");
out.println("<HTML>");
out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");
out.println(" <BODY>");
out.print(" This is ");
out.print(this.getClass());
out.println(", using the POST method");
out.println(" </BODY>");
out.println("</HTML>");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
如下是web.xml的代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.0"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<servlet>
<description>This is the description of my J2EE component</description>
<display-name>This is the display name of my J2EE component</display-name>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>servlet.ServletDemo</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet/ServletDemo</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
如下是访问URL(http://localhost:8080/day07-Servlet/servlet/ServletDemo)后的效果
This is class servlet.ServletDemo, using the GET method
四、:Http中的get和post区别
Http定义了与服务器交互的不同方法,最基本的方法有4种,分别是GET,POST,PUT,DELETE。URL全称是资源描述符,我们可以这样认为:一个URL地址,它用于描述一个网络上的资源,而HTTP中的GET,POST,PUT,DELETE就对应着对这个资源的查,改,增,删4个操作。到这里,大家应该有个大概的了解了,GET一般用于获取/查询资源信息,而POST一般用于更新资源信息。GET请求一般不应产生副作用。就是说,它仅仅是获取资源信息,就像数据库查询一样,不会修改,增加数据,不会影响资源的状态。比如,新闻站点的头版不断更新。虽然第二次请求会返回不同的一批新闻,该操作仍然被认为是安全的和幂等的,因为它总是返回当前的新闻。从根本上说,如果目标是当用户打开一个链接时,他可以确信从自身的角度来看没有改变资源即可。
POST表示可能修改变服务器上的资源的请求。继续引用上面的例子:还是新闻以网站为例,读者对新闻发表自己的评论应该通过POST实现,因为在评论提交后站点的资源已经不同了,或者说资源被修改了。
总结一下,Get是向服务器发索取数据的一种请求,而Post是向服务器提交数据的一种请求,在FORM(表单)中,Method默认为"GET",实质上,GET和POST只是发送机制不同,并不是一个取一个发!
参考文献:http://www.cnblogs.com/xdp-gacl/p/3760336.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/hyddd/archive/2009/03/31/1426026.html