多线程使用中的一些好习惯
本文主要介绍个人在多线程使用和调优中总结一些线程使用比较好的习惯,方便大家在线程出现问题时排查,好习惯是高效率的基础![]()
几个习惯分别为设置线程名,处理interrupt、使用ThreadLocal
其他下次再写吧
1、设置线程名
使用过VisualVM或其他java自带工具或是thread dump的朋友都能体会到如果线程没有设置名称,要进行性能问题排查和调优那是相当头大的一件事,下面先贴一张VisualVM的Threads运行图
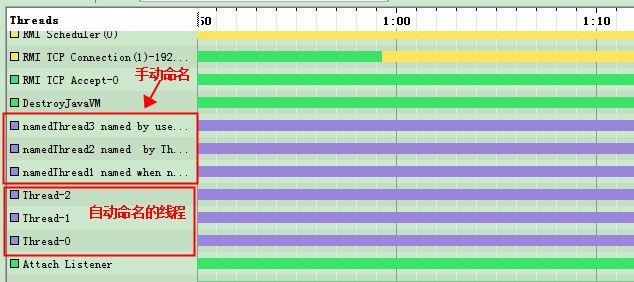
上图中几个紫色的线程是自定义线程,可以看出前三个线程被手动命名过,后三个线程为自动命令。在这个图中还不是很容易看出差别,因为它只是个简单的main函数,线程个数也有限。但如果对于一个较大的软件或是web程序,线程数成百上千,自动的命名方法你还能识别出哪个线程是你自己的吗???
下面介绍几种命名线程的方法,主要有三种:
(1) new Thread("threadName")
(2) thread.setName("threadName")
(3)子类的构造函数中super(threadName),其实跟第一种一样
具体代码可以查看本文最后源码,可以运行其中的setThreadNameExam()函数;
2、处理interrupt
通常将较耗时或较复杂操作单独放在线程中,所以线程中极有可能出现大循环或较耗时,如果这时候突然中断,默认线程退出是不会有其他响应的,对于线程中断有三种方法可以处理:
(1) 使用
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
doSomeThing();
}
处理
(2) 捕获异常
try {
doXXX();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
// handle Exception
} catch(Exception e) {
// handle Exception
}
(3) 抛出异常
public void foo() throws InterruptedException {
if(Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
具体使用可以查看本文最后的源码,可以运行其中的 threadInterruptExam();
3、使用ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal
本文示例代码如下
private static int count1InInterruptExam = 0, count2InInterruptExam = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// setThreadNameExam();
threadInterruptExam();
}
public static void setThreadNameExam() {
/** 未设置线程名 **/
nonNamedThread();
/** 在new thread时设置线程名,有多种构造函数,可以参考Thread java源代码中名为init的私有方法 **/
namedThread1();
/** 通过Thread的setName方法设置线程名 **/
namedThread2();
/** 继承自Thread的子类,可以在构造函数中使用super(name)设置线程名 **/
namedThread3();
}
public static void nonNamedThread() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Thread nonNamedThread = new Thread() {
public void run() {
threadLogic();
}
};
nonNamedThread.start();
}
}
public static void namedThread1() {
Thread namedThread1 = new Thread("namedThread1 named when new thread") {
public void run() {
threadLogic();
}
};
namedThread1.start();
}
public static void namedThread2() {
Thread namedThread2 = new Thread() {
public void run() {
threadLogic();
}
};
namedThread2.setName("namedThread2 named by Thread.setName");
namedThread2.start();
}
public static void namedThread3() {
class NamedThread extends Thread {
public NamedThread(){
super("namedThread");
}
public NamedThread(String threadName){
super(threadName);
}
public void run() {
threadLogic();
}
}
;
NamedThread namedThread3 = new NamedThread("namedThread3 named by use super in constructor");
namedThread3.start();
}
public static void threadLogic() {
try {
Thread.sleep(100000);
System.out.println("finished");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 线程interrupt举例
* 通常可用于循环中较长时间操作,对中断进行响应
*/
public static void threadInterruptExam() {
count1InInterruptExam = 0;
count2InInterruptExam = 0;
Thread threadHasHandedInterrupt = new Thread("thread has handed interrupt") {
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000000; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
count1InInterruptExam++;
} else if (i % 3 == 1) {
count1InInterruptExam--;
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
System.out.println("thread be interrupted, set count to 123456");
count1InInterruptExam = 123456;
}
}
}
};
threadHasHandedInterrupt.start();
Thread threadNotHandInterrupt = new Thread("thread does not handle interrupt") {
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000000; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
count2InInterruptExam++;
} else if (i % 3 == 1) {
count2InInterruptExam--;
}
}
}
};
threadNotHandInterrupt.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(1 * 1000);
threadHasHandedInterrupt.interrupt();
threadNotHandInterrupt.interrupt();
Thread.sleep(1 * 1000);
System.out.println("count in thread that has handed interrupt :" + count1InInterruptExam);
System.out.println("count in thread that does not hand interrupt :" + count2InInterruptExam);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
其中查看Thread的java源代码可以查看:http://trinea.iteye.com/blog/1351233