在JBoss AS7中使用WS-AT
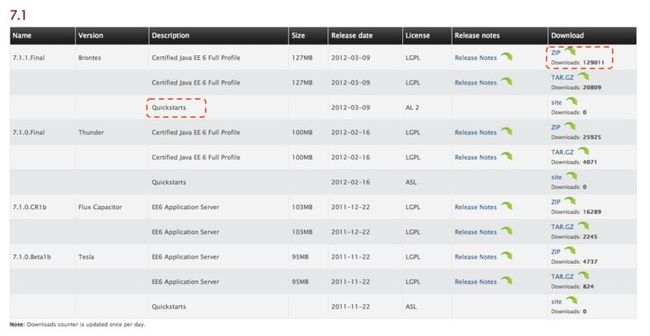
WS-AT全称Web Services Atomic Transaction,是基于SOAP的事务解决方案。JBoss AS7默认支持WS-AT,本文介绍使用方法。首先从JBoss AS的网站下载JBoss AS7和quickstart:
在quickstart当中,有一个wsat-simple项目,我们要使用这个项目做为demo。下面是对这个项目的简单讲解。这个项目实现了一个饭店的订位服务:
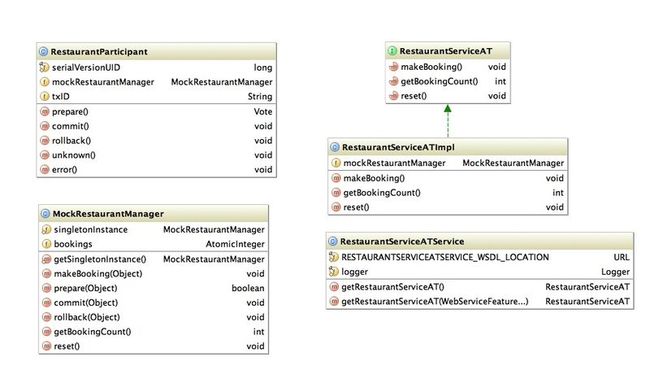
可以看到包含业务包含makeBooking,getBookingCount和reset,都很好理解,即订位,获得已订位数,重置订位数。以下是整个项目的设计:
接下来我们要部署并运行这个例子,我们要使用standalone-xts.xml来启动AS7,在这套配置里面,包含了对WS-AT的支持。这个配置文件位于AS7的example目录当中:
为了正确启动,我们要将这个配置copy到standalone的配置目录中:
在这个配置文件中,增加了对xts模块的配置:
以及xts模块的配置:
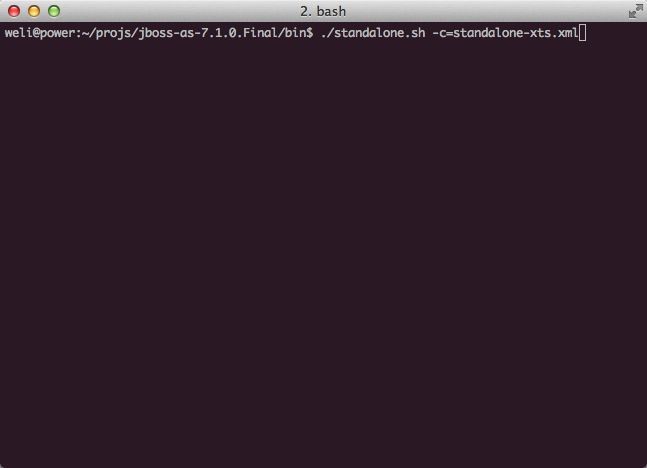
接下来我们用standalone-xts.xml这个配置来启动AS7:
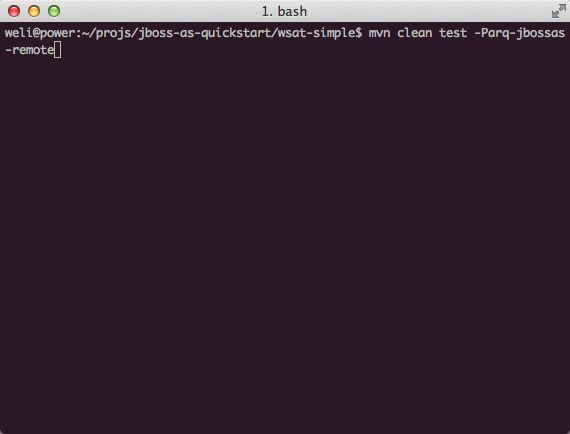
启动成功后,进到wsat-simple项目中,执行maven命令进行编译,部署,测试:
可以看到,通过使用JBoss Arquillian的Maven插件,项目的编译、部署、打包是一次完成的。如果你成功执行了上面的命令,那么从AS7的目录里面会看到项目部署,运行过程,卸载的全部日志。下面对提取出来的日志进行分段讲解。
首先是xts模块的启动过程:
从日志中,你可以看到xts模块会默认注册多个WebService,用于支持WS-AT事务流。在WS-AT标准定义的事务中,包括Participant,Client,Coordinator这几个角色。
项目的执行过程分为testCommit()和testRollback()两部分。我们先从testCommit看起:
我将上面的过程,做成时序图,程序的执行过程如下:
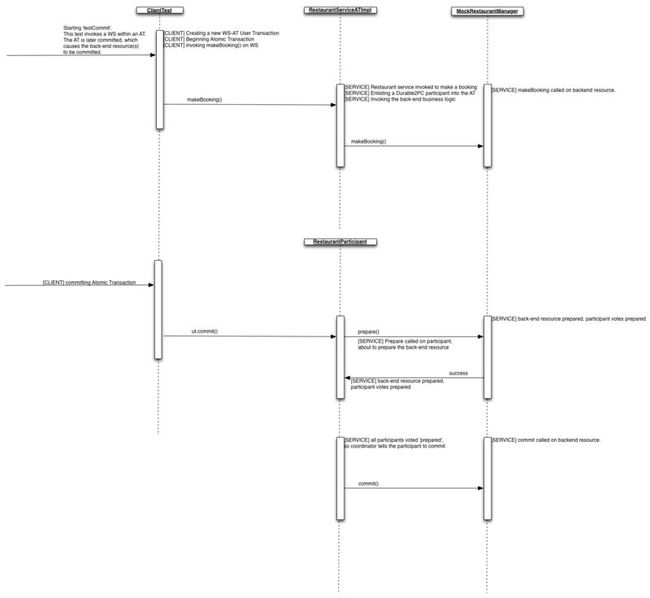
我们可以看到WS-AT定义的事务是一个2-Phase-Commit,事务先由Participant进入Prepare阶段,如果准备就绪,则Commit事务。
以下是rollback的日志输出:
注意到rollback测试最终的结果是事务回滚了:
通过上面的流程,我们可以看到,WS-AT的特色就是客户端和服务端共同参与事务。事务的开始,提交,回滚,都是由客户端发起的:
而事务的参与,执行,则在服务端完成。这是WS-AT的真正Power所在。如果你对WS-AT的实现感兴趣,可以参考具体协议标准:
Web Services Atomic Transaction (WS-AtomicTransaction) Version 1.2

在quickstart当中,有一个wsat-simple项目,我们要使用这个项目做为demo。下面是对这个项目的简单讲解。这个项目实现了一个饭店的订位服务:
public interface RestaurantServiceAT {
/**
* Create a new booking
*/
@WebMethod
public void makeBooking() throws RestaurantException;
/**
* obtain the number of existing bookings
*
* @return the number of current bookings
*/
@WebMethod
public int getBookingCount();
/**
* Reset the booking count to zero
*/
@WebMethod
public void reset();
}
可以看到包含业务包含makeBooking,getBookingCount和reset,都很好理解,即订位,获得已订位数,重置订位数。以下是整个项目的设计:

接下来我们要部署并运行这个例子,我们要使用standalone-xts.xml来启动AS7,在这套配置里面,包含了对WS-AT的支持。这个配置文件位于AS7的example目录当中:
为了正确启动,我们要将这个配置copy到standalone的配置目录中:
weli@power:~/projs/jboss-as-7.1.1.Final$ find . | grep xts ./docs/examples/configs/standalone-xts.xml
weli@power:~/projs/jboss-as-7.1.1.Final$ cp docs/examples/configs/standalone-xts.xml standalone/configuration/
在这个配置文件中,增加了对xts模块的配置:
<extension module="org.jboss.as.xts"/>
以及xts模块的配置:
<subsystem xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:xts:1.0">
<xts-environment url="http://${jboss.bind.address:127.0.0.1}:8080/ws-c11/ActivationService"/>
</subsystem>
接下来我们用standalone-xts.xml这个配置来启动AS7:

启动成功后,进到wsat-simple项目中,执行maven命令进行编译,部署,测试:

可以看到,通过使用JBoss Arquillian的Maven插件,项目的编译、部署、打包是一次完成的。如果你成功执行了上面的命令,那么从AS7的目录里面会看到项目部署,运行过程,卸载的全部日志。下面对提取出来的日志进行分段讲解。
首先是xts模块的启动过程:
11:02:55,303 INFO [org.jboss.as.webservices] (MSC service thread 1-14) JBAS015539: Starting service jboss.ws.endpoint-publish.ws-t11-participant 11:02:55,304 INFO [org.jboss.as.webservices] (MSC service thread 1-7) JBAS015539: Starting service jboss.ws.endpoint-publish.ws-t11-client 11:02:55,303 INFO [org.jboss.as.webservices] (MSC service thread 1-13) JBAS015539: Starting service jboss.ws.endpoint-publish.ws-t11-coordinator 11:02:55,304 INFO [org.jboss.as.webservices] (MSC service thread 1-16) JBAS015539: Starting service jboss.ws.endpoint-publish.ws-c11
从日志中,你可以看到xts模块会默认注册多个WebService,用于支持WS-AT事务流。在WS-AT标准定义的事务中,包括Participant,Client,Coordinator这几个角色。
项目的执行过程分为testCommit()和testRollback()两部分。我们先从testCommit看起:
Starting 'testCommit'. This test invokes a WS within an AT. The AT is later committed, which causes the back-end resource(s) to be committed. [CLIENT] Creating a new WS-AT User Transaction [CLIENT] Beginning Atomic Transaction (All calls to Web services that support WS-AT wil be included in this transaction) [CLIENT] invoking makeBooking() on WS [SERVICE] Restaurant service invoked to make a booking [SERVICE] Enlisting a Durable2PC participant into the AT [SERVICE] Invoking the back-end business logic [SERVICE] makeBooking called on backend resource. [CLIENT] committing Atomic Transaction (This will cause the AT to complete successfully) Prepare called on participant, about to prepare the back-end resource prepare called on backend resource. back-end resource prepared, participant votes prepared all participants voted 'prepared', so coordinator tells the participant to commit commit called on backend resource.
我将上面的过程,做成时序图,程序的执行过程如下:

我们可以看到WS-AT定义的事务是一个2-Phase-Commit,事务先由Participant进入Prepare阶段,如果准备就绪,则Commit事务。
以下是rollback的日志输出:
Starting 'testRollback'. This test invokes a WS within an AT. The AT is later rolled back, which causes the back-end resource(s) to be rolled back. [CLIENT] Creating a new WS-AT User Transaction [CLIENT] Beginning Atomic Transaction (All calls to Web services that support WS-AT wil be included in this transaction) [CLIENT] invoking makeBooking() on WS [SERVICE] Restaurant service invoked to make a booking [SERVICE] Enlisting a Durable2PC participant into the AT [SERVICE] Invoking the back-end business logic [SERVICE] makeBooking called on backend resource. [CLIENT] rolling back Atomic Transaction (This will cause the AT and thus the enlisted back-end resources to rollback) one or more participants voted 'aborted' or a failure occurred, so coordinator tells the participant to rollback rollback called on backend resource.
注意到rollback测试最终的结果是事务回滚了:
[SERVICE] one or more participants voted 'aborted' or a failure occurred, so coordinator tells the participant to rollback
通过上面的流程,我们可以看到,WS-AT的特色就是客户端和服务端共同参与事务。事务的开始,提交,回滚,都是由客户端发起的:
public class ClientTest {
/**
* Test the simple scenario where a booking is made and then committed.
*
* @throws Exception if something goes wrong.
*/
@Test
public void testCommit() throws Exception {
UserTransaction ut = UserTransactionFactory.userTransaction();
try {
ut.begin();
} finally {
rollbackIfActive(ut);
client.reset();
}
}
/**
* Tests the scenario where a booking is made and the transaction is later rolledback.
*
* @throws Exception if something goes wrong
*/
@Test
public void testRollback() throws Exception {
UserTransaction ut = UserTransactionFactory.userTransaction();
try {
ut.begin();
} finally {
rollbackIfActive(ut);
client.reset();
}
}
/**
* Utility method for rolling back a transaction if it is currently active.
*
* @param ut The User Business Activity to cancel.
*/
private void rollbackIfActive(UserTransaction ut) {
try {
ut.rollback();
} catch (Throwable th2) {
// do nothing, not active
}
}
}
而事务的参与,执行,则在服务端完成。这是WS-AT的真正Power所在。如果你对WS-AT的实现感兴趣,可以参考具体协议标准:
Web Services Atomic Transaction (WS-AtomicTransaction) Version 1.2