Decorator Pattern
装饰模式是以对客户端透明的方式扩展对象的功能。是继承的替代方案。
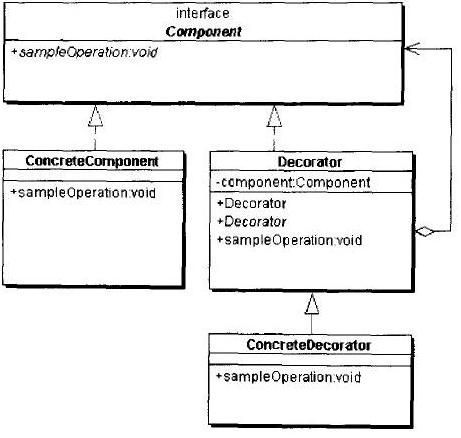
UML图
参照夏昕的hibernate书中的连接池例子,来了解装饰模式如何应用。
先新建一个连接池接口。
ConnectionPool.java
新建一个连接池
DBConnectionPool.java
DBConnectionPool是一个简陋的连接池,它有一个问题,当客户端调用Connection.close()关闭连接,而不是调用DBConnectionPool.releaseConncetion(Connection conn)返还Connection.这样会导致连接池彻底失效。
新建一个Dectorator
新建一个Concrete Decorator
修改DBConnectionPool
当有多个Concrete Decorator类动态组合时,更能体现装饰模式的威力。当然,这里用动态代理代码会更简洁一些。
UML图

参照夏昕的hibernate书中的连接池例子,来了解装饰模式如何应用。
先新建一个连接池接口。
ConnectionPool.java
package com.javapatterns.decorator.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
public interface ConnectionPool {
public Connection getConnection();
public void releaseConncetion(Connection conn) ;
}
新建一个连接池
DBConnectionPool.java
package com.javapatterns.decorator.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Vector;
public class DBConnectionPool implements ConnectionPool{
private Vector pool;
private Map stmtPool = new HashMap();
private static final int POOL_MAX_SIZE = 30;
public synchronized Connection getConnection() {
if(pool == null)
pool = new Vector();
Connection conn;
if (pool.isEmpty())
conn = createConnection();
else {
int last_idx = pool.size() - 1;
conn = (Connection)pool.get(last_idx);
pool.remove(last_idx);
}
return conn;
}
private Connection createConnection(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
Class.forName("org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("dbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test","root","root");
return conn;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public void releaseConncetion(Connection conn) {
if (pool.size() > POOL_MAX_SIZE) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
else {
pool.add(conn);
}
}
}
DBConnectionPool是一个简陋的连接池,它有一个问题,当客户端调用Connection.close()关闭连接,而不是调用DBConnectionPool.releaseConncetion(Connection conn)返还Connection.这样会导致连接池彻底失效。
新建一个Dectorator
package com.javapatterns.decorator.jdbc;
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DatabaseMetaData;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLWarning;
import java.sql.Savepoint;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Map;
public class ConnectionDectorator implements Connection {
Connection conn;
public ConnectionDectorator(Connection conn) {
this.conn = conn;
}
public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {
this.conn.clearWarnings();
}
public void close() throws SQLException {
this.conn.close();
}
public void commit() throws SQLException {
this.conn.commit();
}
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.createStatement();
}
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency)
throws SQLException {
return this.conn.createStatement(resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);
}
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType,
int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability)
throws SQLException {
return this.conn.createStatement(resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, resultSetHoldability);
}
public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.getAutoCommit();
}
public String getCatalog() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.getCatalog();
}
public int getHoldability() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.getHoldability();
}
public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.getMetaData();
}
public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.getTransactionIsolation();
}
public Map getTypeMap() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.getTypeMap();
}
public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.getWarnings();
}
public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.isClosed();
}
public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.isReadOnly();
}
public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {
return this.conn.nativeSQL(sql);
}
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {
return this.conn.prepareCall(sql);
}
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType,
int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return this.conn.prepareCall(sql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);
}
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType,
int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability)
throws SQLException {
return this.conn.prepareCall(sql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, resultSetHoldability);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
return this.conn.prepareStatement(sql);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys)
throws SQLException {
return this.conn.prepareStatement(sql, autoGeneratedKeys);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes)
throws SQLException {
return this.conn.prepareStatement(sql, columnIndexes);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames)
throws SQLException {
return this.conn.prepareStatement(sql, columnNames);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType,
int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return this.conn.prepareStatement(sql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);
}
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType,
int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability)
throws SQLException {
return this.conn.prepareStatement(sql, resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);
}
public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
this.conn.releaseSavepoint(savepoint);
}
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
this.conn.rollback();
}
public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
this.conn.rollback(savepoint);
}
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
this.conn.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);
}
public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {
this.conn.setCatalog(catalog);
}
public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {
this.conn.setHoldability(holdability);
}
public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {
this.conn.setReadOnly(readOnly);
}
public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {
return this.conn.setSavepoint();
}
public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {
return this.conn.setSavepoint(name);
}
public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {
this.conn.setTransactionIsolation(level);
}
public void setTypeMap(Map arg0) throws SQLException {
this.conn.setTypeMap(arg0);
}
}
新建一个Concrete Decorator
package com.javapatterns.decorator.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class PooledConnection extends ConnectionDectorator {
private ConnectionPool pool;
public PooledConnection(ConnectionPool pool, Connection conn) {
super(conn);
this.pool = pool;
}
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
pool.releaseConncetion(conn);
}
}
修改DBConnectionPool
package com.javapatterns.decorator.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Vector;
public class DBConnectionPool implements ConnectionPool{
private Vector pool;
private Map stmtPool = new HashMap();
private static final int POOL_MAX_SIZE = 30;
public synchronized Connection getConnection() {
if(pool == null)
pool = new Vector();
Connection conn;
if (pool.isEmpty())
conn = createConnection();
else {
int last_idx = pool.size() - 1;
conn = (Connection)pool.get(last_idx);
pool.remove(last_idx);
}
//decorator implementation
return new PooledConnection(this, conn);
}
...
}
当有多个Concrete Decorator类动态组合时,更能体现装饰模式的威力。当然,这里用动态代理代码会更简洁一些。