GoBGP 中文入门指南
公众号关注 「奇妙的 Linux 世界」
设为「星标」,每天带你玩转 Linux !
GoBGP 是使用 Go 语言开发的,运行在 Linux 系统上的开源工具,可以提供 BGP 协议的控制平面功能。与 Quagga/FRRouting 相比,GoBGP 的性能更好,收敛时间更短,可以适用于更大规模的网络,比如充当 IXP 路由器。
可以使用 Python、C++ 等多种语言,通过 gRPC API 对 GoBGP 进行配置,当然也支持 CLI。GoBGP 还支持 OpenConfig,其 YANG 模型符合 draft-ietf-idr-bgp-model-03[1]。因为 GoBGP 可以很方便地人工干涉路由,参与感更强,是一个很好的实验工具。本文将介绍 gobgp 的主要功能与实践。
背景介绍
安装与组成
GoBGP 的安装非常简单,从 https://github.com/osrg/gobgp/releases 下载 tar.gz 文件,解压即可。此处选择的是 v2.27.0。
$ tar -xzf gobgp_2.27.0_linux_amd64.tar.gzgobgpd
Gobgp 的 daemon 程序,完整的实现了 BGP 协议
可以通过 gRPC API 与 gobgpd 交互
也可以通过配置文件来配置 bgp
gobgp
Full-featured CLI
可以查看 BGP 相关信息,也可以配置 BGP
配置文件:支持多种格式 toml/yaml/json 等等
支持特性
Full-featured CLI
Multiprotocol Support
IPv4/Pv6
Labeled IPv4/IPv6
Labeled IPv4/IPv6
EVPN
Flowspec IPv4/IPv6/L2
Flexible Policy
Graceful Restart
Both restarting/helper speak role
Route Reflector
Route Server
MRT Dumping
BMP
RPKI Validation
FIB manipulation
gRPC API
Standard configuration format
性能测试
与 Quagga/FRRouting 相比,GoBGP 的性能更好,收敛时间更短,可以适用于更大规模的网络,比如充当 IXP 路由器。更多关于 BGP 的性能测试,可以参考 Comparing Open Source BGP stacks with internet routes[2]
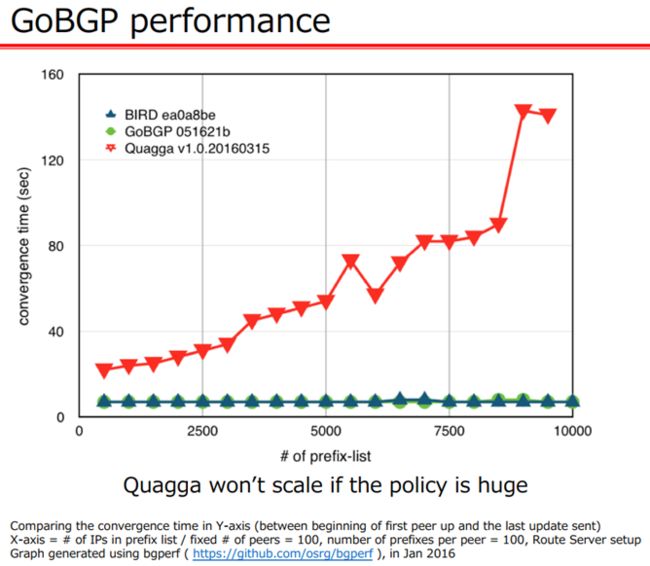
与 Quagga/Zebra 等集成
GoBGP 仅支持 BGP 这一种路由协议,但是它可以和 Zebra 集成,通过 API 的方式与 Quagga/FRR 协同工作,以支持多种路由协议。

GoBGP 可以集成到 Quagga/Zebra 体系中:
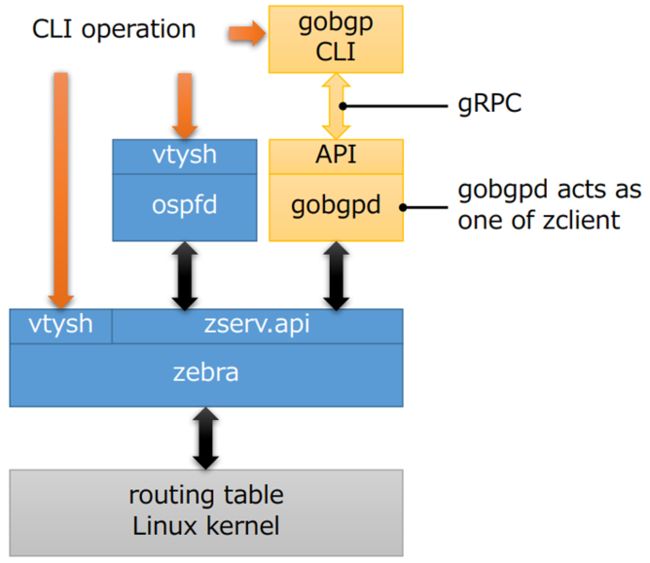
使用 GoBGP
Basic operation
我们可以启动 gobgpd 作为一个 bgp server,和交换机建立 BGP 连接。
此处有网络拓扑图
比如针对
[global.config]
as = 1002
router-id = "172.25.0.136"
[[neighbors]]
[neighbors.config]
peer-as = 1002
neighbor-address = "172.25.0.129"
auth-password: "xxxxx"启动 gobgpd:
/ # ./gobgpd -t yaml -f gobgpd.yaml
{"level":"info","msg":"gobgpd started","time":"2022-03-03T07:28:56Z"}
{"Topic":"Config","level":"info","msg":"Finished reading the config file","time":"2022-03-03T07:28:56Z"}
{"level":"info","msg":"Peer 172.25.0.129 is added","time":"2022-03-03T07:28:56Z"}
{"Topic":"Peer","level":"info","msg":"Add a peer configuration for:172.25.0.129","time":"2022-03-03T07:28:56Z"}
{"Key":"172.25.0.129","State":"BGP_FSM_OPENCONFIRM","Topic":"Peer","level":"info","msg":"Peer Up","time":"2022-03-03T07:29:01Z"}通过 gobgp 查看 peer 信息,这里 State 的 Establ 才表示连接已经建立,如果 State 是 Active 则需要查看交换机配置是否正确。
/ # ./gobgp neighbor
Peer AS Up/Down State |#Received Accepted
172.25.0.129 1002 00:01:29 Establ | 8 8
/ # ./gobgp neighbor 172.25.0.129
BGP neighbor is 172.25.0.129, remote AS 1002
BGP version 4, remote router ID 172.25.100.4
BGP state = ESTABLISHED, up for 00:01:34
BGP OutQ = 0, Flops = 0
Hold time is 90, keepalive interval is 30 seconds
Configured hold time is 90, keepalive interval is 30 seconds
Neighbor capabilities:
multiprotocol:
ipv4-unicast: advertised and received
route-refresh: advertised and received
extended-nexthop: advertised
Local: nlri: ipv4-unicast, nexthop: ipv6
4-octet-as: advertised and received
Message statistics:
Sent Rcvd
Opens: 1 1
Notifications: 0 0
Updates: 0 7
Keepalives: 4 4
Route Refresh: 0 0
Discarded: 0 0
Total: 5 12
Route statistics:
Advertised: 0
Received: 8
Accepted: 8查看 global table:
/ # ./gobgp global rib
Network Next Hop AS_PATH Age Attrs
*> 10.0.0.0/24 172.25.0.129 801 45090 45090 00:04:16 [{Origin: ?} {LocalPref: 100}]
*> 10.0.2.0/24 172.25.0.129 801 45090 45090 00:04:16 [{Origin: ?} {LocalPref: 100}]
*> 172.25.0.0/25 172.25.0.129 801 1001 00:04:16 [{Origin: i} {LocalPref: 100}]
*> 172.25.0.128/25 172.25.0.129 00:04:16 [{Origin: i} {Med: 0} {LocalPref: 100}]
*> 172.25.100.1/32 172.25.0.129 801 00:04:16 [{Origin: i} {Med: 0} {LocalPref: 100}]
*> 172.25.100.2/32 172.25.0.129 801 00:04:16 [{Origin: i} {Med: 0} {LocalPref: 100}]
*> 172.25.100.3/32 172.25.0.129 801 1001 00:04:16 [{Origin: i} {LocalPref: 100}]
*> 172.25.100.4/32 172.25.0.129 00:04:16 [{Origin: i} {Med: 0} {LocalPref: 100}]查看 adjacent rib-in and rib-out:
/ # ./gobgp neighbor 172.25.0.129 adj-in
ID Network Next Hop AS_PATH Age Attrs
0 10.0.0.0/24 172.25.0.129 801 45090 45090 00:07:18 [{Origin: ?} {LocalPref: 100}]
0 10.0.2.0/24 172.25.0.129 801 45090 45090 00:07:18 [{Origin: ?} {LocalPref: 100}]
0 172.25.0.0/25 172.25.0.129 801 1001 00:07:18 [{Origin: i} {LocalPref: 100}]
0 172.25.0.128/25 172.25.0.129 00:07:18 [{Origin: i} {Med: 0} {LocalPref: 100}]
0 172.25.100.1/32 172.25.0.129 801 00:07:18 [{Origin: i} {Med: 0} {LocalPref: 100}]
0 172.25.100.2/32 172.25.0.129 801 00:07:18 [{Origin: i} {Med: 0} {LocalPref: 100}]
0 172.25.100.3/32 172.25.0.129 801 1001 00:07:18 [{Origin: i} {LocalPref: 100}]
0 172.25.100.4/32 172.25.0.129 00:07:18 [{Origin: i} {Med: 0} {LocalPref: 100}]
/ # ./gobgp neighbor 172.25.0.129 adj-out
Network not in table可以通过以下命令 宣告路由
gobgp global rib -a ipv4 add 192.168.1.0/24Route Reflector
为保证 iBGP 对等体之间的连通性,需要在 IBGP 对等体之间建立全连接关系。随着集群规模扩大,Full Mesh 模式效率将急剧降低,Route Reflection[3] 模式是一种成熟的替代方案。RR 方案下允许一个 BGP Speaker (也即是 Route Reflector)向其他 BGP Peer 广播学习到的路由信息,大大减少了 BGP Peer 连接数量。
对于 gobgpd,可以通过修改配置文件,添加 RouteReflector.RouteReflectorConfig 配置来支持 BGP Server 作为 Route Reflector。如下所示:
节点 172.25.0.7 作为 RR 节点,与交换机
172.25.0.1建立 bgp peer节点 172.25.0.6 作为 RR client 节点,与 RR 节点 172.25.0.7 建立 bgp peer
节点 172.25.0.8 作为 RR client 节点,与 RR 节点 172.25.0.7 建立 bgp peer
[global.config]
as = 1001
router-id = "172.25.0.7"
[[neighbors]]
[neighbors.config]
neighbor-address = "172.25.0.1"
peer-as = 1001
auth-password = "xxxxxx"
[[neighbors]]
[neighbors.config]
neighbor-address = "172.25.0.6"
peer-as = 1001
auth-password = "xxxxxx"
[neighbors.route-reflector.config]
route-reflector-client = true
route-reflector-cluster-id = "172.25.0.137"
[[neighbors]]
[neighbors.config]
neighbor-address = "172.25.0.8"
peer-as = 1001
auth-password = "xxxxxx"
[neighbors.route-reflector.config]
route-reflector-client = true
route-reflector-cluster-id = "172.25.0.137"Route Server
现网中存在一些场景,为了达到网络流量互通的目的,通常需要通过 eBGP 方式进行全连接。边界设备之间的全连接,对于经费消耗、设备性能要求都是比较高的,并且不利于网络拓扑和设备数量的扩张。Route Server 类似于 IBGP 全连接使用路由反射器,是一台(或多台)用于进行路由服务的设备,其主要的功能是,向各个客户端(边界设备)传播路由,且向客户端发布的路由不修改 AS_PATH、Nexthop、MED 等路径属性,从而减轻边界路由器全连接的消耗。
如下图所示,一个 IX (Internet eXchange) 中,包含多个独立的 SP (service provider),这些网络想要实现流量互通。每个 SP 都有一个边界路由器连接到公共的交换网络。每个 SP 都有自己的 AS 号,BGP Router 的地址从 10.0.0.1 到 10.0.0.8。
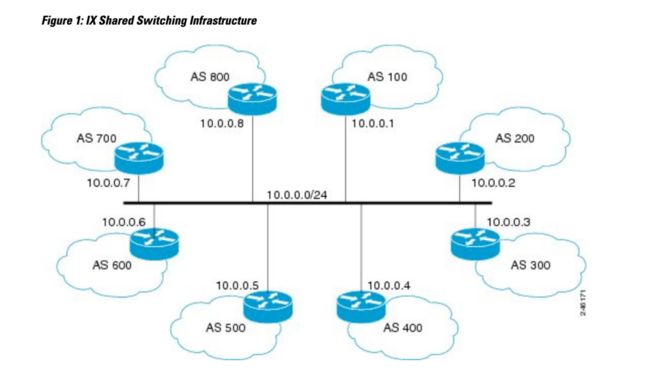
这种情况下,要求这 8 个 BGP Peer 建立全连接,和 iBGP 一样,这种 full mesh 连接对于经费消耗、设备性能要求都是比较高的,并且不利于网络拓扑和设备数量的扩张。

BGP Route Server 可以简化 SP 的连接,如下所示:
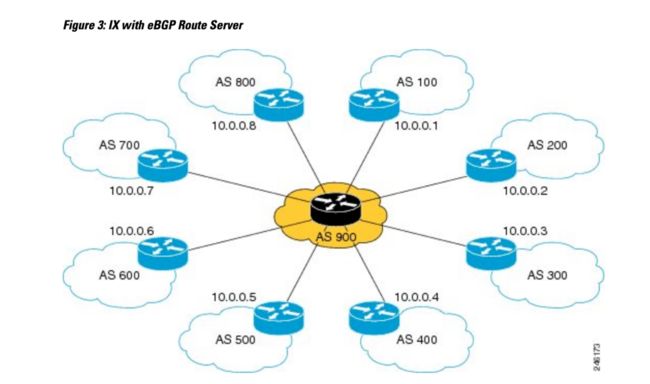
下图展示了 route server 实现的透明路由传播:

更多关于 route server 的信息,可以参考 Route Server[4]。
对于 GoBGP 同样支持 Route Server:
[global.config]
as = 64512
router-id = "192.168.255.1"
[[neighbors]]
[neighbors.config]
neighbor-address = "10.0.255.1"
peer-as = 65001
auth-password = "hoge1"
[neighbors.transport.config]
passive-mode = true
[neighbors.route-server.config]
route-server-client = true
[[neighbors]]
[neighbors.config]
neighbor-address = "10.0.255.2"
peer-as = 65002
auth-password = "hoge2"
[neighbors.transport.config]
passive-mode = true
[neighbors.route-server.config]
route-server-client = trueBGP Policy
Policy 是一种控制 BGP 路由如何插入到 RIB 或者广播给 BGP Peer 的方法,分为两个部分 Condition 和 Action。当 Policy 配置完成后,触发 Condition 条件后,会执行 Action 操作来修改路由。
Condition 包括
prefix,neighbor(source/destination of the route) 和aspath等Action 包括
accept,reject,MED/aspath/community manipulation等
Policy Model
Policy model 包括有 Import Policy 和 Export Policy:
Import policy is invoked before best path calculation and pushing routes to RIB.
Export policy is invoked after that.
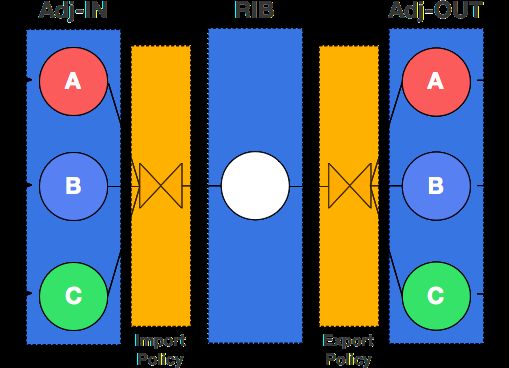
可以通过以下命令查看 policy
$ gobgp global policy import
$ gobgp global policy exportRoute Server Policy Model
对于 Route Server 模式,Import and Export policies 都是针对于一个 Peer 而言的:
The Import policy defines what routes will be imported into the master RIB.
The Export policy defines what routes will be exported from the master RIB.

$ gobgp neighbor policy import
$ gobgp neighbor policy export Policy Structure
一个 Policy 包含多个 Statement,每个 Statement 都有自己的 Condtions 和 Actions
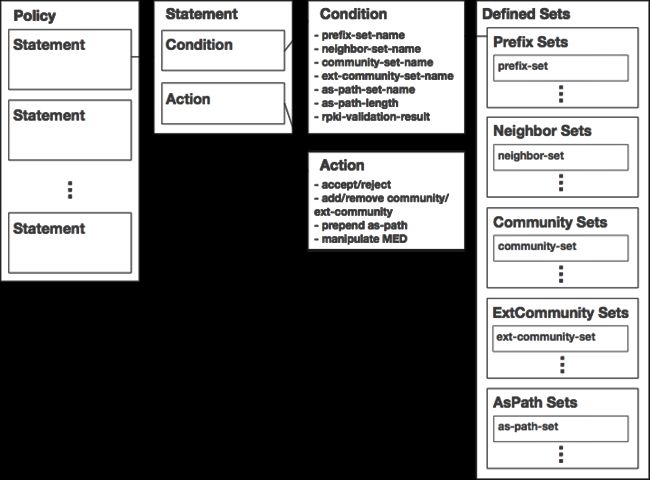
Conditions 包括:
prefix
neighbor
aspath
aspath length
community
extended community
rpki validation result
route type (internal/external/local)
large community
afi-safi in
Actions 包括:
accept or reject
add/replace/remove community or remove all communities
add/subtract or replace MED value
set next-hop (specific address/own local address/don’t modify)
set local-pref
prepend AS number in the AS_PATH attribute
可以通过以下命令查看 Policy 配置
$ gobgp policy
$ gobgp policy statement
$ gobgp policy prefix
$ gobgp policy neighbor
$ gobgp policy as-path
$ gobgp policy community
$ gobgp policy ext-community
$ gobgp policy large-communityPolicy Configuration
Policy 配置比较复杂,以下是配置的步骤,具体可以参考 这里[5]:
define defined-sets
define prefix-sets
define neighbor-sets
define bgp-defined-sets
define community-sets
define ext-community-sets
define as-path-setList
define large-community-sets
define policy-definitions
attach policies to global rib (or neighbor local rib when neighbor is route-server-client[6]).
Graceful Restart
[global.config]
as = 64512
router-id = "192.168.255.1"
[[neighbors]]
[neighbors.config]
neighbor-address = "10.0.255.1"
peer-as = 65001
[neighbors.graceful-restart.config]
enabled = trueBMP
GoBGP 支持 BGP Monitoring Protocol (RFC 7854)[7] 对 BGP 会话的运行状态进行实时监控,包括对等体关系的建立与关闭、路由信息等。
[global.config]
as = 64512
router-id = "192.168.255.1"
[[bmp-servers]]
[bmp-servers.config]
address = "127.0.0.1"
port=11019Dynamic Neighbors
在 BGP 网络中,当多个对等体经常发生变动时,如果采用静态配置对等体的方式,则需频繁地在本端进行增加或删除对等体的配置,维护工作量很大。此时可以配置 BGP 动态对等体功能,使 BGP 侦听指定网段的 BGP 连接请求并动态建立 BGP 对等体,同时将这些对等体加入到同一个对等体组中。这样当对等体发生变动时,无需在本端进行增加或删除 BGP 对等体的配置,减少网络维护的工作量。
交换机都一般都支持配置 Dynamic Neighbors,比如 这里是华为交换机配置 Dynamic Neighbors 方法[8],对于 gobgp 同样也支持 Dynamic Neighbors。
如下所示,主要需要配置两个部分:
创建一个 peer group,描述这个 peer group 的基本信息
配置 peer group 监听在
172.40.0.0/16网段
[global.config]
as = 65001
router-id = "172.40.1.2"
[[peer-groups]]
[peer-groups.config]
peer-group-name = "sample-group"
peer-as = 65002
[[peer-groups.afi-safis]]
[peer-groups.afi-safis.config]
afi-safi-name = "ipv4-unicast"
[[peer-groups.afi-safis]]
[peer-groups.afi-safis.config]
afi-safi-name = "ipv4-flowspec"
[[dynamic-neighbors]]
[dynamic-neighbors.config]
prefix = "172.40.0.0/16"
peer-group = "sample-group"Others
在 GitHub 中还有很多其他关于 MRT/BMP/EVPN 等特性的说明,此处不再赘述,如有需要可以直接查看文档。
GoBGP 编程
Basic Server
参考 gobgp 库 提供的文档[9],我们可以实现一个简单的 go bgp server,如下所示:
package main
import (
"context"
"time"
"github.com/sirupsen/logrus"
apb "google.golang.org/protobuf/types/known/anypb"
api "github.com/osrg/gobgp/v3/api"
"github.com/osrg/gobgp/v3/pkg/log"
"github.com/osrg/gobgp/v3/pkg/server"
)
func main() {
log := logrus.New()
// 创建 BGP Server 实例
s := server.NewBgpServer(server.LoggerOption(&myLogger{logger: log}))
go s.Serve()
// global configuration
if err := s.StartBgp(context.Background(), &api.StartBgpRequest{
Global: &api.Global{
Asn: 65003,
RouterId: "10.0.255.254",
ListenPort: -1, // gobgp won't listen on tcp:179
},
}); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// monitor the change of the peer state
if err := s.MonitorPeer(ctx, &api.MonitorPeerRequest{}, func(p *api.Peer) { log.Print(p) }); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// neighbor configuration
n := &api.Peer{
Conf: &api.PeerConf{
NeighborAddress: "172.17.0.2",
PeerAsn: 65002,
},
}
if err := s.AddPeer(context.Background(), &api.AddPeerRequest{
Peer: n,
}); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// add routes
nlri, _ := apb.New(&api.IPAddressPrefix{
Prefix: "10.0.0.0",
PrefixLen: 24,
})
a1, _ := apb.New(&api.OriginAttribute{
Origin: 0,
})
a2, _ := apb.New(&api.NextHopAttribute{
NextHop: "10.0.0.1",
})
a3, _ := apb.New(&api.AsPathAttribute{
Segments: []*api.AsSegment{
{
Type: 2,
Numbers: []uint32{6762, 39919, 65000, 35753, 65000},
},
},
})
attrs := []*apb.Any{a1, a2, a3}
_, err := s.AddPath(context.Background(), &api.AddPathRequest{
Path: &api.Path{
Family: &api.Family{Afi: api.Family_AFI_IP, Safi: api.Family_SAFI_UNICAST},
Nlri: nlri,
Pattrs: attrs,
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
v6Family := &api.Family{
Afi: api.Family_AFI_IP6,
Safi: api.Family_SAFI_UNICAST,
}
// add v6 route
nlri, _ = apb.New(&api.IPAddressPrefix{
PrefixLen: 64,
Prefix: "2001:db8:1::",
})
v6Attrs, _ := apb.New(&api.MpReachNLRIAttribute{
Family: v6Family,
NextHops: []string{"2001:db8::1"},
Nlris: []*apb.Any{nlri},
})
c, _ := apb.New(&api.CommunitiesAttribute{
Communities: []uint32{100, 200},
})
_, err = s.AddPath(context.Background(), &api.AddPathRequest{
Path: &api.Path{
Family: v6Family,
Nlri: nlri,
Pattrs: []*apb.Any{a1, v6Attrs, c},
},
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
s.ListPath(context.Background(), &api.ListPathRequest{Family: v6Family}, func(p *api.Destination) {
log.Info(p)
})
// do something useful here instead of exiting
time.Sleep(time.Minute * 3)
}
// ...可以看到,示例代码相对比较简单,主要使用了以下的 API:
// 创建 BGP Server 实例
func NewBgpServer(opt ...ServerOption) *BgpServer
// 启动 BGP Server
func (s *BgpServer) Serve()
// global 配置
// BGP Server 的 AS 是 65003,RouterId 是 10.0.255.254
api.Global{
Asn: 65003,
RouterId: "10.0.255.254",
ListenPort: -1, // gobgp won't listen on tcp:179
}
// 根据传入 global 配置,开启 BGP Server 的 BGP 协商
func (s *BgpServer) StartBgp(ctx context.Context, r *api.StartBgpRequest) error
// 观察 BGP Peer 状态变化
func (s *BgpServer) MonitorPeer(ctx context.Context, r *api.MonitorPeerRequest, fn func(*api.Peer)) error
// Peer 信息
api.Peer{
Conf: &api.PeerConf{
NeighborAddress: "172.17.0.2",
PeerAsn: 65002,
},
}
// 建立 BGP Peer 连接
func (s *BgpServer) AddPeer(ctx context.Context, r *api.AddPeerRequest) error
// 传递 BGP 路由信息
func (s *BgpServer) AddPath(ctx context.Context, r *api.AddPathRequest) (*api.AddPathResponse, error)Route Reflector
可以通过对 api.Peer 这个结构进行更详细的配置,使得加入的 BGP Peer 是作为 RR client:
n := &api.Peer{
Conf: &api.PeerConf{
NeighborAddress: "172.25.0.6",
PeerAsn: 1001,
},
RouteReflector: &api.RouteReflector{
RouteReflectorClient: true,
RouteReflectorClusterId: "172.25.0.7",
}
}BMP
这里列出了几种常见的 BMP Message:
type BMPMessage struct {
Header BMPHeader
PeerHeader BMPPeerHeader
Body BMPBody
}
type BMPRouteMonitoring struct {
BGPUpdate *bgp.BGPMessage
BGPUpdatePayload []byte
}
type BMPPeerDownNotification struct {
Reason uint8
BGPNotification *bgp.BGPMessage
Data []byte
}
type BMPPeerUpNotification struct {
LocalAddress net.IP
LocalPort uint16
RemotePort uint16
SentOpenMsg *bgp.BGPMessage
ReceivedOpenMsg *bgp.BGPMessage
}
// ...参考资料
GoBGP 配置[10]
GoBPG 命令行工具使用[11]
IETF: Internet Exchange BGP Route Server[12]
Tutorial: Using GoBGP as an IXP connecting router[13]
GoBGP library[14]
GoBGP slides[15]
Comparing Open Source BGP stacks with internet routes[16]
draft-ietf-idr-bgp-model-03[17]
bgp perf[18]
Route Server[19]
https://www.twblogs.net/a/5db3af42bd9eee310da061d0
引用链接
[1]
draft-ietf-idr-bgp-model-03: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/draft-ietf-idr-bgp-model-03
[2]Comparing Open Source BGP stacks with internet routes: https://elegantnetwork.github.io/posts/comparing-open-source-bgp-internet-routes
[3]Route Reflection: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc2796
[4]Route Server: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_bgp/configuration/xe-3s/irg-xe-3s-book/irg-route-server.pdf
[5]这里: https://github.com/osrg/gobgp/blob/master/docs/sources/policy.md#examples
[6]route-server-client: https://github.com/osrg/gobgp/blob/master/docs/sources/route-server.md
[7]BGP Monitoring Protocol (RFC 7854): https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7854
[8]这里是华为交换机配置 Dynamic Neighbors 方法: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/zh/doc/EDOC1100034251/f1ac6afd
[9]提供的文档: https://github.com/osrg/gobgp/blob/master/docs/sources/lib.md
[10]GoBGP 配置: https://github.com/osrg/gobgp/blob/master/docs/sources/configuration.md
[11]GoBPG 命令行工具使用: https://github.com/osrg/gobgp/blob/master/docs/sources/cli-command-syntax.md
[12]IETF: Internet Exchange BGP Route Server: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7947
[13]Tutorial: Using GoBGP as an IXP connecting router: http://www.slideshare.net/shusugimoto1986/tutorial-using-gobgp-as-an-ixp-connecting-router
[14]GoBGP library: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/keshonok/[email protected]
[15]GoBGP slides: https://ripe71.ripe.net/presentations/135-RIPE71_GoBGP.pdf
[16]Comparing Open Source BGP stacks with internet routes: https://elegantnetwork.github.io/posts/comparing-open-source-bgp-internet-routes/
[17]draft-ietf-idr-bgp-model-03: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/draft-ietf-idr-bgp-model-03
[18]bgp perf: https://github.com/osrg/bgperf
[19]Route Server: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_bgp/configuration/xe-3s/irg-xe-3s-book/irg-route-server.pdf
原文链接:https://houmin.cc/posts/23fb5364/
本文转载自:「云原生实验室」,原文:https://tinyurl.com/2p8f42uw,版权归原作者所有。欢迎投稿,投稿邮箱: [email protected]。
最近,我们建立了一个技术交流微信群。目前群里已加入了不少行业内的大神,有兴趣的同学可以加入和我们一起交流技术,在 「奇妙的 Linux 世界」 公众号直接回复 「加群」 邀请你入群。
![]()
你可能还喜欢
点击下方图片即可阅读
Fig : 一款超高颜值和功能强大的终端自动补全工具
点击上方图片,『美团|饿了么』外卖红包天天免费领
更多有趣的互联网新鲜事,关注「奇妙的互联网」视频号全了解!