二叉树OJ题目(2)
目录
1.二叉树的深度
2.单值二叉树
3.二叉树的前序遍历
4.二叉树的中序遍历
5.二叉树的后序遍
- 题目目代码
- 思路整体分析&注意事项
- 易错点
- 画图递归分析
1.二叉树的深度
LCR 175. 计算二叉树的深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/er-cha-shu-de-shen-du-lcof/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/er-cha-shu-de-shen-du-lcof/description/
int calculateDepth(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int left=calculateDepth(root->left);
int right=calculateDepth(root->right);
return left>right?left+1:right+1;
}
//❌
int calculateDepth(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return calculateDepth(root->left)>calculateDepth(root->right)?
calculateDepth(root->left)+1:calculateDepth(root->right)+1;
}
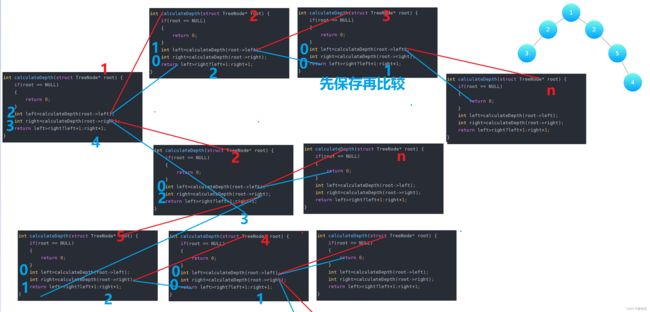
- 分治思想:根的高度(1)+左右子树高的一棵
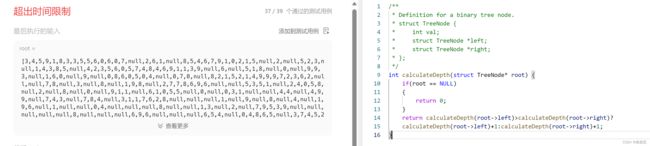
易错点
- 需要保存之后再比较。不然会多次调用,超出时间限制❗❗
2.单值二叉树
965. 单值二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/univalued-binary-tree/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/univalued-binary-tree/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(root->left != NULL )
{
if(root->val != root->left->val)
{
return false;
}
}
if(root->right != NULL )
{
if(root->val != root->right->val)
{
return false;
}
}
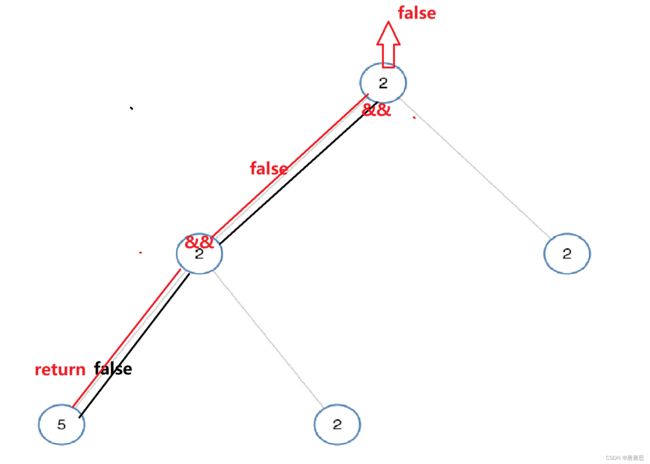
return isUnivalTree(root->left)&&isUnivalTree(root->right);
//相等往下走且返回
}一棵树的所有节点都有相同的值,当且仅当对于树上的每一条边的两个端点,它们都有相同的值(这样根据传递性,所有节点都有相同的值)。因此,我们可以对树进行一次深度优先搜索。当搜索到节点 xxx 时,我们检查 xxx 与 xxx 的每一个子节点之间的边是否满足要求。
例如对于左子节点而言,如果其存在并且值与 xxx 相同,那么我们继续向下搜索该左子节点;如果值与 xxx 不同,那么我们直接返回 False
- 分治的思想:检查每个节点和他的左右孩子
若为空树就返回true
若左孩子不为空,比较值不一样就返回false
若右子树不为空,比较值不一样就返回false
比较完根和左右孩子,递归下去左右子树走上诉相同的逻辑
若两边树所有值遍历完都一样,才返回true
易错点
&& 都为true才返回true
!= 是因为只要一个节点元素值不一样就返回false,不能通过确定一个节点元素值一样就返回true(逻辑思维)
if(root->val != root->right->val) { return false; } if(root->val == root->right->val) { return true;//❌ } //比较
3.二叉树的前序遍历
144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/description/
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return TreeSize(root->left)+TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
int *preorder(struct TreeNode* root,int*a,int* pi)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;//
preorder(root->left,a,pi);//
preorder(root->right,a,pi);
return a;
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {
int treesize=TreeSize(root);
*returnSize=treesize;
int*a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)*treesize);
int i=0;
a=preorder(root,a,&i);
i=0;
return a;
}
- 题目要求:开辟数组,把遍历树的顺序放入数组即可。
- 计算树的节点个数
- malloc节点个数的空间
- 前序:根左右
- 把根的val放入数组第一个元素
- 接着放入左右(递归下去)
易错点
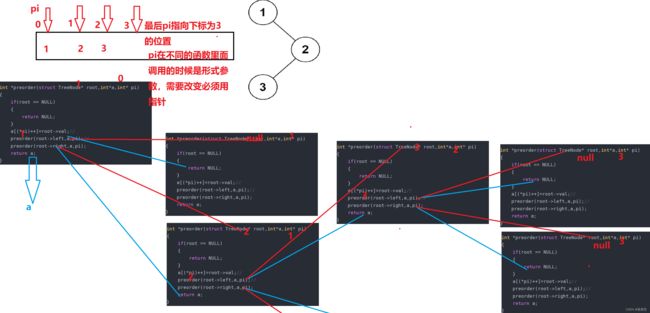
改变形式参数必须要用指针!!!(&i)
形参是实参的一份临时拷贝
int* returnSize 这个是返回数组的元素个数(*代表leetcode后台有一份returnsize的实际参数需要改变用的指针&returnsize,这里才用指针接收)
4.二叉树的中序遍历
94. 二叉树的中序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/description/
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return TreeSize(root->left)+TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
int *inorder(struct TreeNode* root,int*a,int* pi)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
inorder(root->left,a,pi);//
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;//
inorder(root->right,a,pi);
return a;
}
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {
int treesize=TreeSize(root);
*returnSize=treesize;
int*a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)*treesize);
int i=0;
a=inorder(root,a,&i);
i=0;
return a;
}5.二叉树的后序遍
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/description/
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return TreeSize(root->left)+TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
int *postorder(struct TreeNode* root,int*a,int* pi)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
postorder(root->left,a,pi);//
postorder(root->right,a,pi);
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;//
return a;
}
int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {
int treesize=TreeSize(root);
*returnSize=treesize;
int*a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)*treesize);
int i=0;
a=postorder(root,a,&i);
i=0;
return a;
}6.二叉树的构建及其遍历
二叉树遍历_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
感谢大家的阅读,若有错误和不足,欢迎指正