图形学中的噪声
1 value noise
四个点取随机数然后做插值。
float random (in vec2 st) {
return fract(sin(dot(st.xy,
vec2(12.9898,78.233)))
* 43758.5453123);
}
float noise (in vec2 st) {
vec2 i = floor(st);
vec2 f = fract(st);
float a = random(i);
float b = random(i + vec2(1.0, 0.0));
float c = random(i + vec2(0.0, 1.0));
float d = random(i + vec2(1.0, 1.0));
// Smooth Interpolation
// Cubic Hermine Curve. Same as SmoothStep()
vec2 u = f*f*(3.0-2.0*f);
// u = smoothstep(0.,1.,f);
// Mix 4 coorners percentages
return mix(a, b, u.x) +
(c - a)* u.y * (1.0 - u.x) +
(d - b) * u.x * u.y;
}
2 perlin noise
用小数部分与四个点连成向量,将向量点乘,再插值。
vec2 random2(vec2 st){
st = vec2( dot(st,vec2(127.1,311.7)),
dot(st,vec2(269.5,183.3)) );
return -1.0 + 2.0*fract(sin(st)*43758.5453123);
}
// Gradient Noise by Inigo Quilez - iq/2013
// https://www.shadertoy.com/view/XdXGW8
float noise(vec2 st) {
vec2 i = floor(st);
vec2 f = fract(st);
vec2 u = f*f*(3.0-2.0*f);
return mix( mix( dot( random2(i + vec2(0.0,0.0) ), f - vec2(0.0,0.0) ),
dot( random2(i + vec2(1.0,0.0) ), f - vec2(1.0,0.0) ), u.x),
mix( dot( random2(i + vec2(0.0,1.0) ), f - vec2(0.0,1.0) ),
dot( random2(i + vec2(1.0,1.0) ), f - vec2(1.0,1.0) ), u.x), u.y);
}
3 simplex noise
把采样从立方体换成四面体。
vec2 skew (vec2 st) {
vec2 r = vec2(0.0);
r.x = 1.1547*st.x;
r.y = st.y+0.5*r.x;
return r;
}
vec3 simplexGrid (vec2 st) {
vec3 xyz = vec3(0.0);
vec2 p = fract(skew(st));
if (p.x > p.y) {
xyz.xy = 1.0-vec2(p.x,p.y-p.x);
xyz.z = p.y;
} else {
xyz.yz = 1.0-vec2(p.x-p.y,p.y);
xyz.x = p.x;
}
return fract(xyz);
}
4 Cellular Noise
取距离所有采样点最近的距离。
void main() {
vec2 st = gl_FragCoord.xy/u_resolution.xy;
st.x *= u_resolution.x/u_resolution.y;
vec3 color = vec3(.0);
// Cell positions
vec2 point[5];
point[0] = vec2(0.83,0.75);
point[1] = vec2(0.60,0.07);
point[2] = vec2(0.28,0.64);
point[3] = vec2(0.31,0.26);
point[4] = u_mouse/u_resolution;
float m_dist = 1.; // minimum distance
// Iterate through the points positions
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
float dist = distance(st, point[i]);
// Keep the closer distance
m_dist = min(m_dist, dist);
}
// Draw the min distance (distance field)
color += m_dist;
// Show isolines
// color -= step(.7,abs(sin(50.0*m_dist)))*.3;
gl_FragColor = vec4(color,1.0);
}
优化:divide the space into tiles.划分格子,每个格子一个采样点,计算的时候只需计算相邻的点的距离。
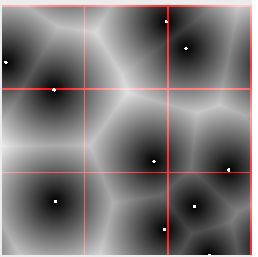
5 Voronoi Algorithm
除了距离外将最近的点保存,还可以保存一些特有的属性。
...
if( dist < m_dist ) {
m_dist = dist;
m_point = point;
}
...
6 Fractal Brownian Motion
一个八度一个八度的向上叠加。频率和振幅在每一次迭代中乘上一个值。
// Properties
const int octaves = 1;
float lacunarity = 2.0;
float gain = 0.5;
//
// Initial values
float amplitude = 0.5;
float frequency = 1.;
//
// Loop of octaves
for (int i = 0; i < octaves; i++) {
y += amplitude * noise(frequency*x);
frequency *= lacunarity;
amplitude *= gain;
}
