别瞎写工具类了,Spring自带的不香吗?
前言
最近有些小伙伴,希望我分享一些好用的工具类,帮他们提升开发效率。
今天这篇文章专门跟大家一起总结一下,Spring框架本身自带的一些好用的工具类,希望对你会有所帮助。
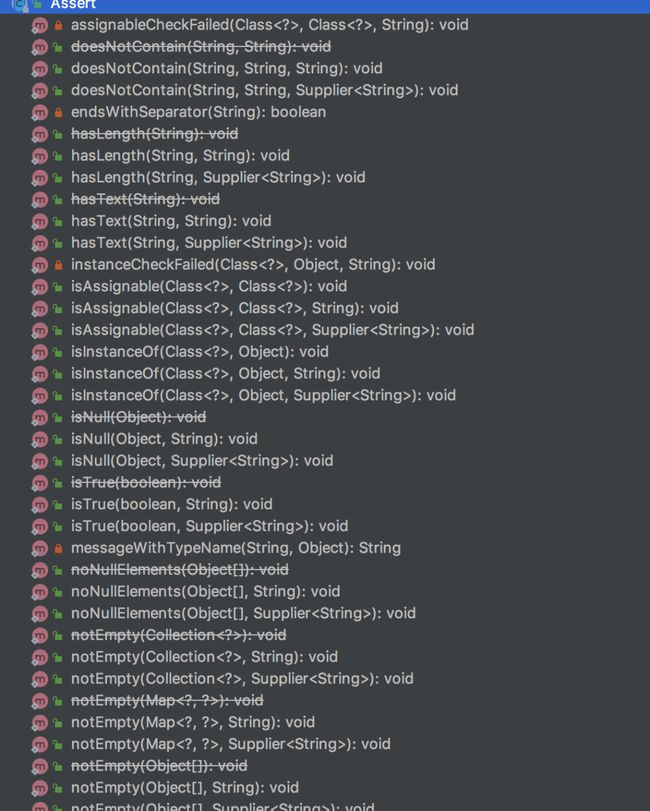
1 Assert
很多时候,我们需要在代码中做判断:如果不满足条件,则抛异常。
有没有统一的封装呢?
其实Spring给我们提供了Assert类,它表示断言。
1.1 断言参数是否为空
断言参数是否空,如果不满足条件,则直接抛异常。
String str = null; Assert.isNull(str, "str必须为空"); Assert.isNull(str, () -> "str必须为空"); Assert.notNull(str, "str不能为空");
如果不满足条件就会抛出IllegalArgumentException异常。
1.2 断言集合是否为空
断言集合是否空,如果不满足条件,则直接抛异常。
List
如果不满足条件就会抛出IllegalArgumentException异常。
1.3 断言条件是否为空
断言是否满足某个条件,如果不满足条件,则直接抛异常。
List
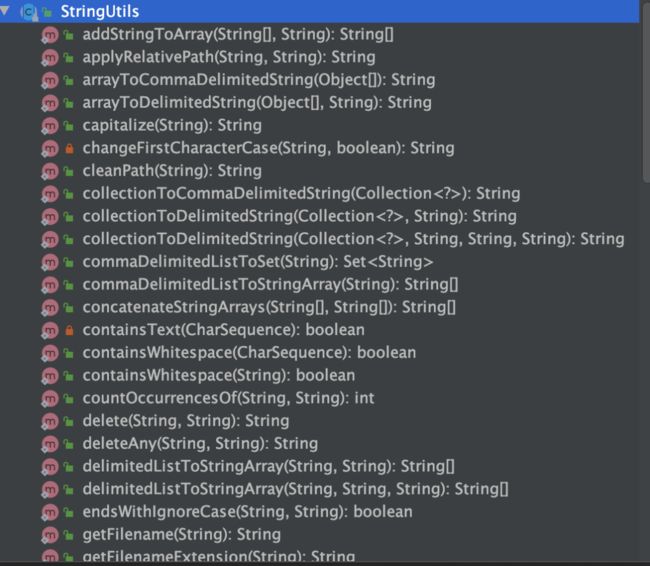
2 StringUtils
在我们日常开发过程中,对字符串的操作是非常频繁的,但JDK提供的对于字符串操作的方法,过于简单,无法满足我们开发中的需求。
其实Spring提供了工具类StringUtils,对JDK中一些字符串的操作进行了扩展。
2.1 判空
StringUtils类其实有个isEmpty()方法判断,不过已经被废弃了。
我们可以改成使用hasLength()方法判断,例如:
if (!StringUtils.hasLength("")) { System.out.println("字符串为空"); }
2.2 去掉空格
对于后端的很多接口,经常需要去掉前后空格,我们可以使用String类的trim(),但是如果要同时去掉中间的空格呢?
可以使用StringUtils类的trimAllWhitespace方法。
例如:
@Test public void testEmpty() { System.out.println("1" + StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(" 苏三说技术 测试 ") + "1"); }
这个方法执行接口:1苏三说技术测试1,会把中间的空格也去掉了。
2.3 判断开头或结尾字符串
要判断一个字符串,是不是以某个固定字符串开头或者结尾,是非常常见的需求。
我们可以使用StringUtils类的startsWithIgnoreCase和endsWithIgnoreCase,可以忽略大小写比较字符串。
例如:
@Test public void testEmpty() { System.out.println(StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase("苏三说技术", "苏三")); System.out.println(StringUtils.endsWithIgnoreCase("苏三说技术", "技术")); }
该方法的执行结果会返回两个true。
2.4 集合拼接字符串
有时候我们需要将某个字符串集合的所有元素,拼接成一个字符串,用逗号隔开。
这种场景可以使用StringUtils类的collectionToCommaDelimitedString方法。
例如:
@Test public void testEmpty() { List
该方法的执行结果:a,b,c
3. CollectionUtils
在我们日常开发当中,经常会遇到集合,比如:list判空的情况。
其实Spring专门为我们提供了,给集合判空的工具类:CollectionUtils,它位于org.springframework.util包下。
对于一些简单的集合判断,集合中是否包含某个元素,集合转数组,用这个工具还是非常方便的。
3.1 集合判空
通过CollectionUtils工具类的isEmpty方法可以轻松判断集合是否为空。
例如:
`List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(2);
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)) {
System.out.println(“集合为空”);
}
`
3.2 判断元素是否存在
通过CollectionUtils工具类的contains方法,可以判断元素在集合中是否存在。
例如:
`List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(2);
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
if (CollectionUtils.contains(list.iterator(), 3)) {
System.out.println(“元素存在”);
}
`
在判断时需要先调用集合的iterator()方法。
4 ObjectUtils
Spring为我们专门提供了一个对象操作工具:ObjectUtils,也在org.springframework.util包下。
里面有很多非常有用的方法。
4.1 判空
之前已经介绍过字符串判空工具类StringUtils,和集合的判空工具类CollectionUtils。
而ObjectUtils工具的判空更强大,支持:对象、字符串、集合、数组、Optional、Map的判断。
例如:
@Test public void testEmpty() { String a = "123"; Integer b = new Integer(1); List
这6种对象的判空都支持,非常强大。
4.2 判断两个对象相等
之前我们用Objects.equals方法,判断两个对象是否相等,经常会出现空指针问题。
而ObjectUtils类提供了安全的判断两个对象相等的方法:nullSafeEquals。
例如:
@Test public void testEquals() { String a = "123"; String b = null; System.out.println(ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(a, b)); }
这个例子返回的是false,不会出现空指针的问题。
甚至可以判断两个数组是否相等。
例如:
@Test public void testArrayEquals() { String[] a = new String[]{"123"}; String[] b = new String[]{"123"}; System.out.println(ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(a, b)); }
这个例子的执行结果返回的是true。
4.3 获取对象的hashCode
如果想要快速获取某个对象十六进制的hashCode,则可以调用getIdentityHexString方法。
例如:
@Test public void testIdentityHex() { String a = "123"; System.out.println(ObjectUtils.getIdentityHexString(a)); }
执行结果:2925bf5b
5 ClassUtils
Spring的org.springframework.util包下的ClassUtils类,它里面有很多让我们惊喜的功能。
它里面包含了类和对象相关的很多非常实用的方法。
5.1 获取对象的所有接口
如果你想获取某个对象的所有接口,可以使用ClassUtils的getAllInterfaces方法。例如:
Class[] allInterfaces = ClassUtils.getAllInterfaces(new User());
5.2 获取某个类的包名
如果你想获取某个类的包名,可以使用ClassUtils的getPackageName方法。例如:
String packageName = ClassUtils.getPackageName(User.class); System.out.println(packageName);
5.3 判断某个类是否内部类
如果你想判断某个类是否内部类,可以使用ClassUtils的isInnerClass方法。例如:
System.out.println(ClassUtils.isInnerClass(User.class));
5.4 判断对象是否代理对象
如果你想判断对象是否代理对象,可以使用ClassUtils的isCglibProxy方法。例如:
System.out.println(ClassUtils.isCglibProxy(new User()));
ClassUtils还有很多有用的方法,等待着你去发掘。感兴趣的朋友,可以看看下面内容: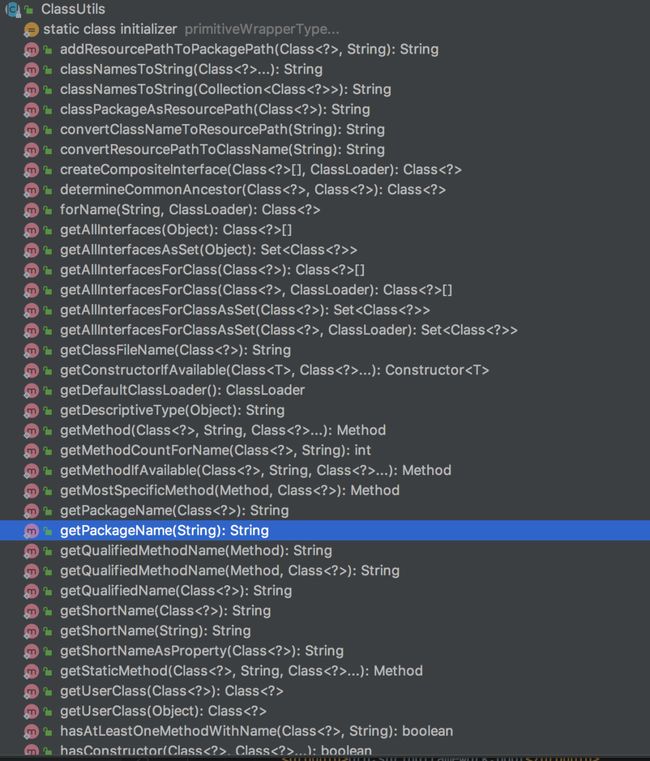
6 BeanUtils
Spring给我们提供了一个JavaBean的工具类,它在org.springframework.beans包下面,它的名字叫做:BeanUtils。
让我们一起看看这个工具可以带给我们哪些惊喜。
6.1 拷贝对象的属性
曾几何时,你有没有这样的需求:把某个对象中的所有属性,都拷贝到另外一个对象中。这时就能使用BeanUtils的copyProperties方法。例如:
`User user1 = new User();
user1.setId(1L);
user1.setName(“苏三说技术”);
user1.setAddress(“成都”);
User user2 = new User();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(user1, user2);
System.out.println(user2);
`
6.2 实例化某个类
如果你想通过反射实例化一个类的对象,可以使用BeanUtils的instantiateClass方法。例如:
User user = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(User.class); System.out.println(user);
6.3 获取指定类的指定方法
如果你想获取某个类的指定方法,可以使用BeanUtils的findDeclaredMethod方法。例如:
Method declaredMethod = BeanUtils.findDeclaredMethod(User.class, "getId"); System.out.println(declaredMethod.getName());
6.4 获取指定方法的参数
如果你想获取某个方法的参数,可以使用BeanUtils的findPropertyForMethod方法。例如:
Method declaredMethod = BeanUtils.findDeclaredMethod(User.class, "getId"); PropertyDescriptor propertyForMethod = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(declaredMethod); System.out.println(propertyForMethod.getName());
7 ReflectionUtils
有时候,我们需要在项目中使用反射功能,如果使用最原始的方法来开发,代码量会非常多,而且很麻烦,它需要处理一大堆异常以及访问权限等问题。
好消息是Spring给我们提供了一个ReflectionUtils工具,它在org.springframework.util包下面。
7.1 获取方法
如果你想获取某个类的某个方法,可以使用ReflectionUtils类的findMethod方法。例如:
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(User.class, "getId");
7.2 获取字段
如果你想获取某个类的某个字段,可以使用ReflectionUtils类的findField方法。例如:
Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(User.class, "id");
7.3 执行方法
如果你想通过反射调用某个方法,传递参数,可以使用ReflectionUtils类的invokeMethod方法。例如:
ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(method, springContextsUtil.getBean(beanName), param);
7.4 判断字段是否常量
如果你想判断某个字段是否常量,可以使用ReflectionUtils类的isPublicStaticFinal方法。例如:
Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(User.class, "id"); System.out.println(ReflectionUtils.isPublicStaticFinal(field));
7.5 判断是否equals方法
如果你想判断某个方法是否equals方法,可以使用ReflectionUtils类的isEqualsMethod方法。例如:
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(User.class, "getId"); System.out.println(ReflectionUtils.isEqualsMethod(method));
当然这个类还有不少有趣的方法,感兴趣的朋友,可以看看下面内容: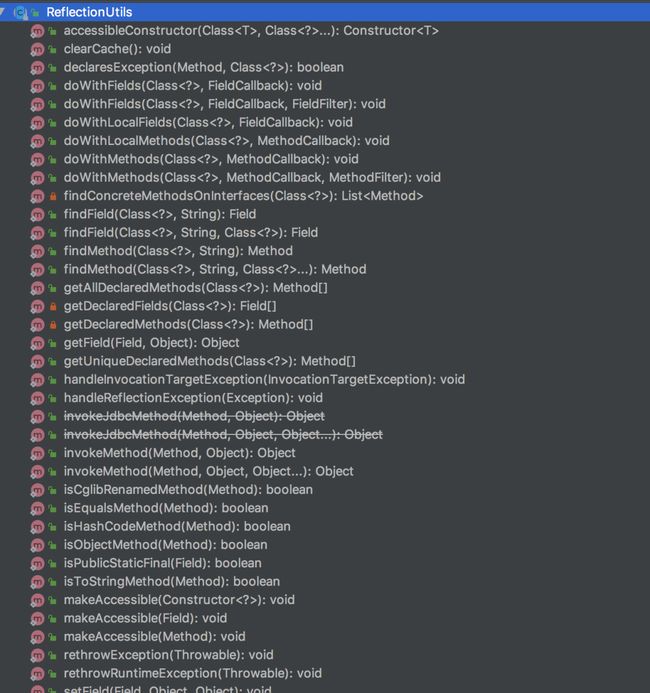
8 Base64Utils
有时候,为了安全考虑,需要将参数只用base64编码。
这时就能直接使用org.springframework.util包下的Base64Utils工具类。
它里面包含:encode和decode方法,用于对数据进行编码和解码。
例如:
String str = "abc"; String encode = new String(Base64Utils.encode(str.getBytes())); System.out.println("编码后:" + encode); try { String decode = new String(Base64Utils.decode(encode.getBytes()), "utf8"); System.out.println("解码:" + decode); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
执行结果:
编码后:YWJj 解码后:abc
9 SerializationUtils
有时候,我们需要把数据进行序列化和反序列化处理。
传统的做法是某个类实现Serializable接口,然后重新它的writeObject和readObject方法。
但如果使用org.springframework.util包下的SerializationUtils工具类,能更轻松实现序列化和反序列化功能。
例如:
Map
10 HttpStatus
很多时候,我们会在代码中定义http的返回码,比如:接口正常返回200,异常返回500,接口找不到返回404,接口不可用返回502等。
private int SUCCESS_CODE = 200; private int ERROR_CODE = 500; private int NOT_FOUND_CODE = 404;
其实org.springframework.http包下的HttpStatus枚举,或者org.apache.http包下的HttpStatus接口,已经把常用的http返回码给我们定义好了,直接拿来用就可以了,真的不用再重复定义了。
11 HtmlUtils
有时候,用户输入的内容中包含了一些特殊的标签,比如<,如果不错处理程序可能会报错。
而且为了安全性,对用户输入的特色字符,也需要做转义,防止一些SQL注入,或者XSS攻击等。
其实Spring给我们提供了一个专门处理html的工具:HtmlUtils,我们可以直接用它来做转义,使用起来非常方便。
例如:
@Test public void testHtml() { String specialStr = "
执行结果:<div id="testDiv">test1;test2</div>;