Linux巩固篇008-Linux 防火墙
前言
身为一个三年的运维工程师,从开发转测开再转运维,都是不断学习的过程,未必开发才是最优秀的,找到适合自己的职业不断深耕,你也会在自己的行业大放光彩,本系列依照《Linux就该这么学》系列随书学习练习操作,将一些课本上不顺畅的地方,全部以最简方式免费开源展示给大家,资源大家可以自行百度,也希望大家多关注刘遄老师的第二版关于centos8的丛书,学习最前沿的Linux相关技术。
常用命令汇总
防火墙是公网与内网之间的保护屏障,iptables、firewall-cmd、firewall-config 和TCP Wrappers,RHEL 7 新增firewalld 防火墙
防火墙管理工具
防火墙策略可以基于流量的源目地址、端口号、协议、应用等信息来定制,使用预先定制的策略规则监控出入的流量,在 RHEL 7 系统中,firewalld 防火墙取代了iptables 防火墙,这些都是定义防火墙策略的防火墙管理工具,iptables交由内核层面的netfilter 网络过滤器来处理,firewalld交由内核层面的nftables 包过滤框架来处理
iptables 命令
iptables 服务把用于处理或过滤流量的策略条目称之为规则,多条规则可以组成一个规则链,而规则链则依据数据包处理位置的不同进行分类
在进行路由选择前处理数据包(PREROUTING)
处理流入的数据包(INPUT)
处理流出的数据包(OUTPUT)
处理转发的数据包(FORWARD)
在进行路由选择后处理数据包(POSTROUTING)
iptables 服务
ACCEPT(允许流量通过)
REJECT(拒绝流量通过)流量发送方会看到端口不可达
LOG(记录日志信息)
DROP(拒绝流量通过)响应超时

在 iptables 命令后添加-L 参数查看已有的防火墙规则链
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
ACCEPT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:domain
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:domain
ACCEPT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:bootps
ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:bootps
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
ACCEPT all -- anywhere 192.168.122.0/24 ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
ACCEPT all -- 192.168.122.0/24 anywhere
ACCEPT all -- anywhere anywhere
REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
REJECT all -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
ACCEPT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:bootpc
在iptables 命令后添加-F 参数清空已有的防火墙规则链:
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -F
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -L
INPUT 规则链的默认策略设置为拒绝:
规则链的默认拒绝动作只能是DROP,而不能是REJECT
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -P INPUT DROP
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy DROP)
target prot opt source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
向 INPUT 链中添加允许ICMP 流量进入的策略规则:
-I 参数代表规则链头部加入新规则
-p 参数代表匹配协议,以下匹配的是icmp协议
-j 参数代表跳转目标jump,以下是允许访问
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
[root@localhost ~]# ping -c 4 192.168.10.10
PING 192.168.10.10 (192.168.10.10) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.10.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=1.18 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.10.10: icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=0.575 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.10.10: icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=0.455 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.10.10: icmp_seq=4 ttl=128 time=0.638 ms
--- 192.168.10.10 ping statistics ---
4 packets transmitted, 4 received, 0% packet loss, time 3003ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.455/0.712/1.181/0.279 ms
删除INPUT 规则链中刚刚加入的那条策略(允许ICMP 流量),并把默认策略设置为允许:
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -D INPUT 1
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
INPUT 规则链设置为只允许指定网段的主机访问本机的22 端口,拒绝来自其他所有主机的流量:
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.10.0/24 -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j REJECT
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
ACCEPT tcp -- 192.168.10.0/24 anywhere tcp dpt:ssh
REJECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ssh reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
防火墙策略规则是按照从上到下的顺序匹配的,一定要把允许动作放到拒绝动作前面,否则所有的流量就将被拒绝掉,从而导致任何主机都无法访问内网服务,22 号端口是ssh 服务
[root@localhost ~]# ssh 192.168.10.10
The authenticity of host '192.168.10.10 (192.168.10.10)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:nxSiZLJhB8ddUuwbWmegzhOU8xzmni6NSJ3X40HMTc0.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:d3:ff:a2:64:b0:ad:65:80:84:7a:25:44:e3:d3:69:6c.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.10.10' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
[email protected]'s password:
[root@localhost ~]# ssh 192.168.11.10
ssh: connect to host 192.168.11.10 port 22: Connection refused
INPUT 规则链中添加拒绝所有人访问本机12345 端口的策略规则:
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 12345 -j REJECT
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p udp --dport 12345 -j REJECT
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
REJECT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:italk reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
REJECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:italk reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
ACCEPT tcp -- 192.168.10.0/24 anywhere tcp dpt:ssh
REJECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ssh reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
INPUT 规则链中添加拒绝192.168.10.5 主机访问本机80 端口(Web 服务)的策略规则:
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -s 192.168.10.5 --dport 80 -j REJECT
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
REJECT tcp -- 192.168.10.5 anywhere tcp dpt:http reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
REJECT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:italk reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
REJECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:italk reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
ACCEPT tcp -- 192.168.10.0/24 anywhere tcp dpt:ssh
REJECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ssh reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
INPUT 规则链中添加拒绝所有主机访问本机1000~1024 端口的策略规则:
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 1000:1024 -j REJECT
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 1000:1024 -j REJECT
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -L
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
REJECT tcp -- 192.168.10.5 anywhere tcp dpt:http reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
REJECT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpt:italk reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
REJECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:italk reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
ACCEPT tcp -- 192.168.10.0/24 anywhere tcp dpt:ssh
REJECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ssh reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
REJECT tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpts:cadlock2:1024 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
REJECT udp -- anywhere anywhere udp dpts:cadlock2:1024 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
使用iptables 命令配置的防火墙规则默认会在系统下一次重启时失效,让配置的防火墙策略永久生效,还要执行保存命令:
[root@localhost ~]# service iptables save
iptables: Saving firewall rules to /etc/sysconfig/iptables: [ OK ]
firewalld 命令
firewalld(Dynamic Firewall Manager of Linuxsystems,Linux 系统的动态防火墙管理器)服务是默认的防火墙配置管理工具,firewalld 中常见的区域名称(默认为public)以及相应的策略规则
 终端管理工具
终端管理工具
firewalld-cmd 是firewalld 防火墙配置管理工具的CLI(命令行界面)版本

运行时(Runtime)模式
永久(Permanent)模式
firewall-cmd 命令正常设置防火墙策略时添加–permanent 参数永久生效
查看 firewalld 服务当前所使用的区域:
[root@localhost /]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
public
查询 eno16777728 网卡在firewalld 服务中的区域:
[root@localhost /]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=ens33
public
把 firewalld 服务网卡的默认区域修改为external,并在系统重启后生效。查看当前与永久模式下的区域名称:
[root@localhost /]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=external --change-interface=ens33
The interface is under control of NetworkManager, setting zone to 'external'.
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=ens33
external
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --get-zone-of-interface=ens33
no zone
firewalld 服务的当前默认区域设置为public:
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=public
Warning: ZONE_ALREADY_SET: public
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
public
启动/关闭firewalld 防火墙服务的应急状况模式,阻断一切网络连接
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --panic-on
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --panic-off
success
查询 public 区域是否允许请求SSH 和HTTPS 协议的流量:
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --query-service=ssh
yes
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --query-service=https
no
firewalld 服务中请求HTTPS 协议的流量设置为永久允许,并立即生效:
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=https
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
firewalld 服务中请求HTTP 协议的流量设置为永久拒绝,并立即生效:
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --remove-service=http
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
firewalld 服务中访问8080 和8081 端口的流量策略设置为允许,仅当前生效:
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080-8081/tcp
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
8080-8081/tcp
888 端口的流量转发到22 端口,要且求当前和长期均有效:
流量转发命令格式为 firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=<区域> --add-forward-port=port=<源端口号>:proto=<协议>:toport=<目标端口号>:toaddr=<目标IP 地址>
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-forward-port=port=888:proto=tcp:toport=22:toaddr=192.168.10.10
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
使用 ssh 命令尝试访问192.168.10.10 主机的888 端口:
[root@localhost ~]# ssh -p 888 192.168.10.10
ssh: connect to host 192.168.10.10 port 888: Connection refused
这条是失败的,但是生成了对应的转发配置信息,查了很多资料并没有解决,如有大佬请赐教
public
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces:
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client https
ports:
protocols:
masquerade: no
forward-ports: port=888:proto=tcp:toport=22:toaddr=192.168.10.10
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
在firewalld 服务中配置一条富规则,使其拒绝192.168.10.0/24 网段的所有用户访问本机的ssh 服务(22 端口):
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.10.0/24" service name="ssh" reject"
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
此条命令也没有起到作用,仍能访问到192.168.10.10端口,但是规则里已经写入进去了,暂时没发现相关问题原因
public
target: default
icmp-block-inversion: no
interfaces:
sources:
services: ssh dhcpv6-client https
ports:
protocols:
masquerade: yes
forward-ports: port=888:proto=tcp:toport=22:toaddr=192.168.10.10
source-ports:
icmp-blocks:
rich rules:
rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.10.0/24" service name="ssh" reject
图形管理工具
firewall-config 的界面
1:选择运行时(Runtime)模式或永久(Permanent)模式的配置。
2:可选的策略集合区域列表。
3:常用的系统服务列表。
4:当前正在使用的区域。
5:管理当前被选中区域中的服务。
6:管理当前被选中区域中的端口。
7:开启或关闭SNAT(源地址转换协议)技术。
8:设置端口转发策略。
9:控制请求icmp 服务的流量。
10:管理防火墙的富规则。
11:管理网卡设备。
12:被选中区域的服务,若勾选了相应服务前面的复选框,则表示允许与之相关的流量。
13:firewall-config 工具的运行状态。

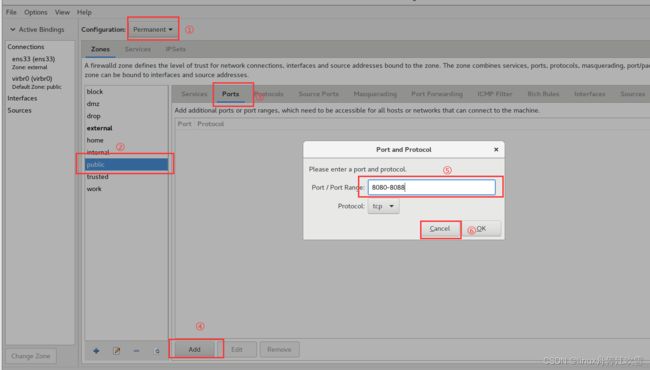
尝试添加一条防火墙策略规则,使其放行访问8080~8088 端口(TCP 协议)的流量,8.3 firewalld并将其设置为永久生效,以达到系统重启后防火墙策略依然生效的目的,在Options 菜单中单击Reload Firewalld 命令,让配置的防火墙策略立即生效


网络中不使用SNAT 技术,无法在网络中找到这个私有网络的IP 地址
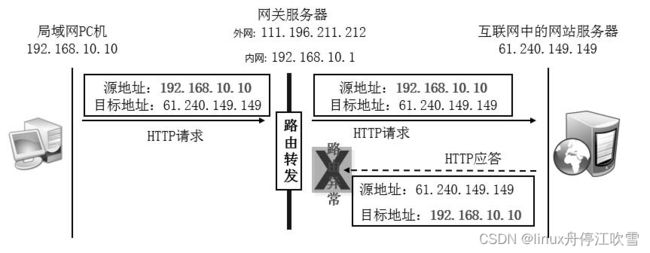
网络中使用SNAT 技术,互联网中的网站服务器会将响应数据包发给网关服务器,再由后者转发给局域网中的PC

firewall-config配置SNAT 技术,选中Masquerade zone 复选框,就自动开启了SNAT 技术


配置富规则,让 192.168.10.20 主机访问到本机的1234 端口号


网卡与防火墙策略区域进行绑定

访问控制列表
TCP Wrappers 是RHEL 7 系统中默认启用的一款流量监控程序,它能够根据来访主机的地址与本机的目标服务程序作出允许或拒绝的操作
Linux 系统中两层防火墙基于TCP/IP 协议的流量过滤工具,TCP Wrappers 服务允许或禁止Linux 系统提供服务的防火墙
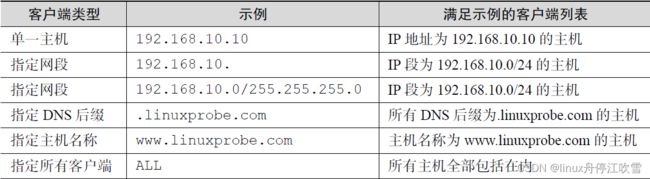
TCP Wrappers 服务遵循两个原则:
编写拒绝策略规则时,填写的是服务名称,而非协议名称
先编写拒绝策略规则,再编写允许策略规则
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/hosts.deny
#
# hosts.deny This file contains access rules which are used to
# deny connections to network services that either use
# the tcp_wrappers library or that have been
# started through a tcp_wrappers-enabled xinetd.
#
# The rules in this file can also be set up in
# /etc/hosts.allow with a 'deny' option instead.
#
# See 'man 5 hosts_options' and 'man 5 hosts_access'
# for information on rule syntax.
# See 'man tcpd' for information on tcp_wrappers
#
sshd:*
xshell连接
[C:\~]$ ssh 192.168.227.129
Connecting to 192.168.227.129:22...
Connection established.
#
# hosts.allow This file contains access rules which are used to
# allow or deny connections to network services that
# either use the tcp_wrappers library or that have been
# started through a tcp_wrappers-enabled xinetd.
#
# See 'man 5 hosts_options' and 'man 5 hosts_access'
# for information on rule syntax.
# See 'man tcpd' for information on tcp_wrappers
#
sshd:192.168.227.
xshell连接
[C:\~]$ ssh 192.168.227.129
Connecting to 192.168.227.129:22...
Connection established.
To escape to local shell, press 'Ctrl+Alt+]'.
Last login: Wed Oct 26 08:53:27 2022
结语
简问简答
请简述防火墙策略规则中DROP 和REJECT 的不同之处
答:DROP 的动作是丢包,不响应;REJECT 是拒绝请求,同时向发送方回送拒绝信息
如何把iptables 服务的INPUT 规则链默认策略设置为DROP
答:执行命令iptables -P INPUT DROP
禁止源自192.168.10.0/24 网段的流量访问本机的sshd 服务(22 端口)
答:执行命令iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.10.0/24 -p tcp --dport 22 -j REJECT
如何让firewalld 中以永久(Permanent)模式配置的防火墙策略规则立即生效
答:执行命令firewall-cmd --reload
如何让firewalld 中以永久(Permanent)模式配置的防火墙策略规则立即生效?
答:执行命令firewall-cmd --reload

