一,什么是 json
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。它基于JavaScript的一个子集。 JSON采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,但是也使用了类似于C语言家族的习惯(包括C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, Python等)。这些特性使JSON成为理想的数据交换语言。易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成。
二,json 的语法
json 语法是 JavaScript 对象表示法语法的子集。
- 数据在名称/值对中
- 数据由逗号分隔
- 花括号保存对象
- 方括号保存数组
json 的值可以是:

三,json 举例
{
"person":
{
"name": "peter",
"age": 20,
"fruits": "apple",
"color": "RED",
"hobby": [666 , "EAT" , "dadooudou" , "睡觉"]
}
}
四, 操作测试
int main()
{
ifstream fin("test.txt");
stringstream ss;
ss << fin.rdbuf();
Json x = parser(ss.str());
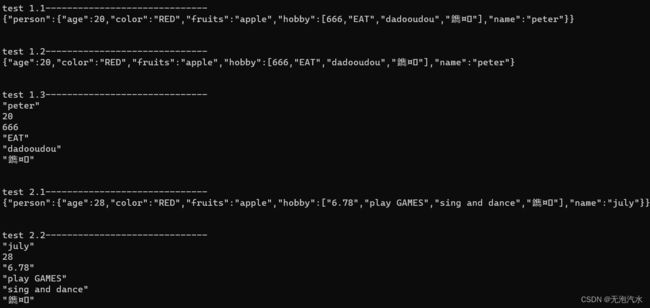
cout << "test 1.1------------------------------" << endl;
cout << x << endl;
cout << "\n\ntest 1.2------------------------------" << endl;
cout << x["person"] << endl;
cout << "\n\ntest 1.3------------------------------" << endl;
cout << x["person"]["name"] << endl;
cout << x["person"]["age"] << endl;
cout << x["person"]["hobby"][0] << endl;
cout << x["person"]["hobby"][1] << endl;
cout << x["person"]["hobby"][2] << endl;
cout << x["person"]["hobby"][3] << endl;
//修改内容
Json y = parser(x.str());
y["person"]["name"] = "july";
y["person"]["age"] = 28;
y["person"]["hobby"][0] = "6.78";
y["person"]["hobby"][1] = "play GAMES";
y["person"]["hobby"][2] = "sing and dance";
x = parser(y.str());
cout << "\n\ntest 2.1------------------------------" << endl;
cout << x << endl;
cout << "\n\ntest 2.2------------------------------" << endl;
cout << x["person"]["name"] << endl;
cout << x["person"]["age"] << endl;
cout << x["person"]["hobby"][0] << endl;
cout << x["person"]["hobby"][1] << endl;
cout << x["person"]["hobby"][2] << endl;
cout << x["person"]["hobby"][3] << endl;
return 0;
}
五,源代码
#include
#include
#include //存储数组
#include
六,参考链接
常用文件类型 -- JSON文件介绍_json文件是什么样的
用C++编写一个简易的JSON解析器(2)parser 完成
用C++编写一个简易的JSON解析器(1) 写一个动态类型

