Java基础 LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap
- LinkedHashMap
-
- 定义
-
- LinkedHashMap的原理图
- LinkedHashMap和HashMap的Entry结构图
- LinkedHashMap在JDK中的定义
-
- LinkedHashMap继承关系:
- LinkedHashMap成员变量
- LinkedHashMap构造方法(5种)
- LinkedHashMap的init()方法
- LinkedHashMap基本数据结构(Entry:具体结构图在定义中)
- LinkedHashMap(Map m)
- LinkedHashMap的快速存取
-
- LinkedHashMap 的存储实现 : put(key, vlaue)
- LinkedHashMap 的读取实现 :get(Object key)
- LinkeList与LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法
-
- 使用LinkedList实现LRU算法
- LinkedList有序性原理分析
- 总结
LinkedHashMap
定义
LinkedHashMap是HashMap和双向链表的合二为一,即一个将所有Entry节点链入一个双向链表的HashMap(LinkedHashMap = HashMap + 双向链表)
- LinkedHashMap和HashMap是Java Collection Framework 的重要成员,也是Map族(如下图所示)
- LinkedHashMap是HashMap的子类(拥有HashMap的所有特性)
LinkedHashMap和HashMap最多只允许一条Entry的键为Null(多条会覆盖),但允许多条Entry的值为NullLinkedHashMap 也是 Map 的一个非同步的实现LinkedHashMap很好的支持LRU算法HashMap是无序的,LinkedHashMap通过维护一个额外的双向链表保证了迭代顺序迭代顺序可以是插入顺序,也可以是访问顺序(即根据链表中元素的顺序可以将LinkedHashMap分为:保持插入顺序的LinkedHashMap和保持访问顺序的LinkedHashMap,其中LinkedHashMap的默认实现是按插入顺序排序的)
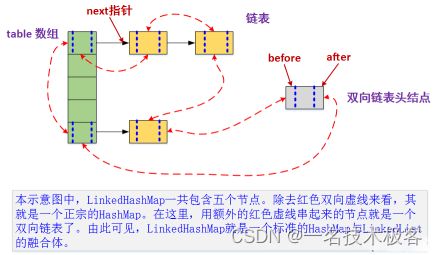
LinkedHashMap的原理图
LinkedHashMap和HashMap的Entry结构图
LinkedHashMap和HashMap都是Java中常用的数据结构,它们都实现了Map接口。
HashMap是一种基于哈希表实现的无序映射,它通过将键值对存储在哈希表中来实现快速查找和插入操作。HashMap使用哈希函数将键映射到哈希表中的一个位置,然后将键值对存储在该位置上。由于哈希表是无序的,因此HashMap不保证元素的顺序。
LinkedHashMap则是一种有序映射,它继承自HashMap并添加了一个双向链表来维护元素的插入顺序或访问顺序。当向LinkedHashMap中添加元素时,会将该元素添加到链表的末尾;当访问某个元素时,会将该元素移动到链表的末尾。这样,遍历LinkedHashMap时,就可以按照元素的插入顺序或访问顺序进行遍历。
总的来说,HashMap和LinkedHashMap的主要区别在于是否维护元素的顺序。HashMap是无序的,而LinkedHashMap是有序的。
LinkedHashMap在JDK中的定义
LinkedHashMap继承关系:
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
LinkedHashMap成员变量
- 相比于Hashmap,LinkedHashMap新增 双向链表头结点header和标志位accessOrder
accessOrder默认为false(即默认按照插入顺序迭代)为true时(按照访问顺序迭代,支持实现LRU算法时)
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3801124242820219131L;
private transient Entry<K,V> header;//双向链表头节点,也即哨兵节点,里面不存储任何信息
private final boolean accessOrder;//有序性标识
LinkedHashMap构造方法(5种)
- 相比于Hashmap,LinkedHashMap并没有增加构造方法
//传入的参数为初始容量,加载因子,调用了父类的构造方法,按照插入顺序
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}
//传入的参数的初始容量,调用父类的构造方法,取得键值对的顺序是插入顺序
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
//无参构造,调用父类的构造方法,取得键值对的顺序是插入顺序
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
//传入的参数是一个Map的集合,调用父类的构造方法,取得键值对的顺序是插入顺序
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super(m);
accessOrder = false;
}
//传入的参数为初始容量,加载因子,有序性标识(键值对保持顺序),调用了父类的构造方法
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
LinkedHashMap的init()方法
由 LinkedHashMap的五种构造方法可知
- 无论采用何种方式创建LinkedHashMap,其都会调用HashMap相应的构造函数
- 不管调用HashMap的哪个构造函数,HashMap的构造函数都会在最后调用一个init()方法进行初始化
- init()方法在HashMap中是一个空实现,而在LinkedHashMap中重写了它,用于初始化它所维护的双向链表
//Hashmap
/**
* Constructs an empty HashMap with the default initial capacity
* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
init();
}
//LinkedHashmap
@Override
void init() {
//header初始化
//hash为-1,其他的参数均为null
//也就是说这个header不在数组中
//只是用来标志开始元素和标志结束元素的
header = new Entry<>(-1, null, null, null);
header.before = header.after = header;
}
LinkedHashMap基本数据结构(Entry:具体结构图在定义中)
- LinkedHashMap中的Entry增加了两个指针 before 和 after,用于维护双向链接列表
before、after用于维护Entry插入的先后顺序next用于维护HashMap各个桶中Entry的连接顺序
private static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Entry<K,V> {
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
LinkedHashMap(Map m)
- 构造一个与指定Map具有相同映射的 LinkedHashMap,其初始容量不小于16 (具体依赖于指定Map的大小),负载因子是 0.75,是 Java Collection Framework 规范推荐提供的,源码如下
/**
* Constructs an insertion-ordered LinkedHashMap instance with
* the same mappings as the specified map. The LinkedHashMap
* instance is created with a default load factor (0.75) and an initial
* capacity sufficient to hold the mappings in the specified map.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super(m); // 调用HashMap对应的构造函数
accessOrder = false; // 迭代顺序的默认值
}
LinkedHashMap的快速存取
LinkedHashMap 的存储实现 : put(key, vlaue)
- LinkedHashMap完全继承了HashMap的 put(Key,Value) 方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { //数组为null时
inflateTable(threshold); //给数组根据阈值分配内容空间
}
if (key == null) //key为null时
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key); //通过key计算hash
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); //计算在数组中的索引位置
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
//使用的是LinkedHashMap重写的方法
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
//addEntry调用的是LinkedHashMap重写了的方法
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
- 只是对put(Key,Value)方法所调用的recordAccess方法和addEntry方法进行了重写
- addEntry方法中还调用了removeEldestEntry方法,该方法是用来被重写的,一般如果用LinkedHashmap实现LRU算法,就要重写该方法
- 比如可以将该方法覆写为如果设定的内存已满,则返回true,这样当再次向LinkedHashMap中putEntry时,在调用的addEntry方法中便会将近期最少使用的节点删除掉(header后的那个节点)
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
//将传入的HashMap类型的m强制转换成LinkedHashMap类型的
LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m;
//accessOrder默认的是false,当accessOrder为true时进入
if (lm.accessOrder) {
lm.modCount++;
//移除当前节点
remove();
3
addBefore(lm.header);
}
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 重写了HashMap中的createEntry方法
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
// Remove eldest entry if instructed
Entry<K,V> eldest = header.after; //还是header自身
if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);
} else {
//扩容到原来的2倍
if (size >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
}
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}
- 在LinkedHashMap的addEntry方法中,它重写了HashMap中的createEntry方法
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 向哈希表中插入Entry,这点与HashMap中相同
//创建新的Entry并将其链入到数组对应桶的链表的头结点处,
HashMap.Entry<K,V> old = table[bucketIndex];
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, old);
table[bucketIndex] = e;
//在每次向哈希表插入Entry的同时,都会将其插入到双向链表的尾部,
//这样就按照Entry插入LinkedHashMap的先后顺序来迭代元素
//(LinkedHashMap根据双向链表重写了迭代器)
//同时,新put进来的Entry是最近访问的Entry,把其放在链表末尾 ,也符合LRU算法的实现
e.addBefore(header);
size++;
}
- 在LinkedHashMap中向哈希表中插入新Entry的同时,还会通过Entry的addBefore方法将其链入到双向链表中
- addBefore方法本质上是一个双向链表的插入操作
//插入有序不做处理,在访问有序做相应处理:addBefore(将当前节点插到header的前面)
private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry; //existingEntry即为header
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this; //this即为要插入的节点
after.before = this;
}
- LinkedHashMap完全继承了HashMap的resize()方法,只是对它所调用的transfer方法进行了重写
- Map扩容操作的核心在于重哈希
- 重哈希是指重新计算原HashMap中的元素在新table数组中的位置并进行复制处理的过程,鉴于性能和LinkedHashMap自身特点的考量,LinkedHashMap对重哈希过程(transfer方法)进行了重写
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
// 若 oldCapacity 已达到最大值,直接将 threshold 设为 Integer.MAX_VALUE
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return; // 直接返回
}
// 否则,创建一个更大的数组
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
//将每条Entry重新哈希到新的数组中
transfer(newTable); //LinkedHashMap对它所调用的transfer方法进行了重写
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor); // 重新设定 threshold
}
void transfer(HashMap.Entry[] newTable) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
// 与HashMap相比,借助于双向链表的特点进行重哈希使得代码更加简洁
for (Entry<K,V> e = header.after; e != header; e = e.after) {
int index = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); // 计算每个Entry所在的桶
// 将其链入桶中的链表
e.next = newTable[index];
newTable[index] = e;
}
}
LinkedHashMap 的读取实现 :get(Object key)
public V get(Object key) {
//调用父类HashMap的getEntry()方法,取得要查找的元素
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)getEntry(key);
if (e == null)
return null;
// 记录访问顺序
e.recordAccess(this);
return e.value;
}
private static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Entry<K,V> {
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
//在HashMap的put和get方法中,会调用该方法,在HashMap中该方法为空;
//在LinkedHashMap中,
//当按访问顺序排序时,该方法会将当前节点插入到链表尾部(头结点的前一个节点),
//否则不做任何事
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m;
if (lm.accessOrder) {
lm.modCount++;
//移除当前节点
remove();
//将当前节点插入到头结点前面
addBefore(lm.header);
}
}
private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}
recordAccess方法:如果链表中元素的排序规则是按照插入的先后顺序排序的话(accessOrder=false),该方法什么也不做如果链表中元素的排序规则是按照访问的先后顺序排序的话(accessOrder=true),则将e移到链表的末尾处
调用LinkedHashMap的get(Object key)方法,返回值是 NULL,有如下两种可能:该 key 对应的值就是 nullHashMap 中不存在该 key
LinkeList与LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法
当accessOrder标志位为true时,表示双向链表中的元素按照访问的先后顺序排列,可以看到,虽然Entry插入链表的顺序依然是按照其put到LinkedHashMap中的顺序,但put和get方法均有调用recordAccess方法(put方法在key相同时会调用)
recordAccess方法判断accessOrder是否为true,如果是,则将当前访问的Entry(put进来的Entry或get出来的Entry)移到双向链表的尾部(key不相同时,put新Entry时,会调用addEntry,它会调用createEntry,该方法同样将新插入的元素放入到双向链表的尾部,既符合插入的先后顺序,又符合访问的先后顺序,因为这时该Entry也被访问了)
当标志位accessOrder的值为false时,表示双向链表中的元素按照Entry插入LinkedHashMap到中的先后顺序排序,即每次put到LinkedHashMap中的Entry都放在双向链表的尾部,这样遍历双向链表时,Entry的输出顺序便和插入的顺序一致,这也是默认的双向链表的存储顺序
当标志位accessOrder的值为false时,虽然也会调用recordAccess方法,但不做任何操作
使用LinkedList实现LRU算法
public class LRU<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> implements Map<K, V>{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public LRU(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor, accessOrder);
}
/**
* @description 重写LinkedHashMap中的removeEldestEntry方法,当LRU中元素多余6个时,
* 删除最不经常使用的元素
* @author rico
* @created 2017年5月12日 上午11:32:51
* @param eldest
* @return
* @see java.util.LinkedHashMap#removeEldestEntry(java.util.Map.Entry)
*/
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(java.util.Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(size() > 6){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRU<Character, Integer> lru = new LRU<Character, Integer>(
16, 0.75f, true);
String s = "abcdefghijkl";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
lru.put(s.charAt(i), i);
}
System.out.println("LRU中key为h的Entry的值为: " + lru.get('h'));
System.out.println("LRU的大小 :" + lru.size());
System.out.println("LRU :" + lru);
}
}
LinkedList有序性原理分析
LinkedHashMap 增加了双向链表头结点header 和 标志位accessOrder两个属性用于保证迭代顺序。但是要想真正实现其有序性,还差临门一脚,那就是重写HashMap 的迭代器,其源码实现如下:
private abstract class LinkedHashIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
Entry<K,V> nextEntry = header.after;
Entry<K,V> lastReturned = null;
/**
* The modCount value that the iterator believes that the backing
* List should have. If this expectation is violated, the iterator
* has detected concurrent modification.
*/
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() { // 根据双向列表判断
return nextEntry != header;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
LinkedHashMap.this.remove(lastReturned.key);
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
Entry<K,V> nextEntry() { // 迭代输出双向链表各节点
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (nextEntry == header)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Entry<K,V> e = lastReturned = nextEntry;
nextEntry = e.after;
return e;
}
}
// Key 迭代器,KeySet
private class KeyIterator extends LinkedHashIterator<K> {
public K next() { return nextEntry().getKey(); }
}
// Value 迭代器,Values(Collection)
private class ValueIterator extends LinkedHashIterator<V> {
public V next() { return nextEntry().value; }
}
// Entry 迭代器,EntrySet
private class EntryIterator extends LinkedHashIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextEntry(); }
}
总结
上文是基于JDK1.6的实现,实际上JDK1.8对其进行了改动linkedhashmap在hashmap的数组加链表结构的基础上,将所有节点连成了一个双向链表当主动传入的accessOrder参数为false时, 使用put方法时,新加入元素不仅加入哈希桶中,还被加入双向链表末尾,get方法使用时不会把元素放到双向链表尾部当主动传入的accessOrder参数为true时,使用put方法新加入的元素,如果遇到了哈希冲突,并且对key值相同的元素进行了替换,就会被放在双向链表的尾部,当元素超过上限且removeEldestEntry方法返回true时,直接删除最早元素以便新元素插入。如果没有冲突直接放入,同样加入到链表尾部。使用get方法时会把get到的元素放入双向链表尾部inkedhashmap的扩容比hashmap来的方便,因为hashmap需要将原来的每个链表的元素分别在新数组进行反向插入链化,而linkedhashmap的元素都连在一个链表上,可以直接迭代然后插入linkedhashmap的removeEldestEntry方法默认返回false,要实现LRU很重要的一点就是集合满时要将最久未访问的元素删除,在linkedhashmap中这个元素就是头指针指向的元素。实现LRU可以直接实现继承linkedhashmap并重写removeEldestEntry方法来设置缓存大小。jdk中实现了LRUCache也可以直接使用在put操作上,虽然LinkedHashMap完全继承了HashMap的put操作,但是在细节上还是做了一定的调整,比如,在LinkedHashMap中向哈希表中插入新Entry的同时,还会通过Entry的addBefore方法将其链入到双向链表中在扩容操作上,虽然LinkedHashMap完全继承了HashMap的resize操作,但是鉴于性能和LinkedHashMap自身特点的考量,LinkedHashMap对其中的重哈希过程(transfer方法)进行了重写在读取操作上,LinkedHashMap中重写了HashMap中的get方法(加入recordAccess方法,重写transfer方法),通过HashMap中的getEntry方法获取Entry对象