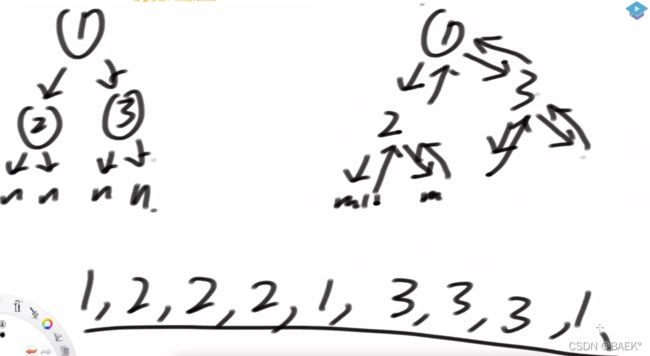数据结构与算法XS班-左程云第六节课笔记(比较器、优先级队列、二叉树)
第6节 比较器、优先级队列、二叉树
##这是数据结构与算法新手班-左程云第六节课的笔记##
视频顺序就按照文件夹顺序来看,体系学习班的内容不会大于基础班(基础上半部分)和进阶班(基础下半部分+刷题),只是揉进去一些比较新的题目。之后额外开了一门大厂刷题班,这个是进阶班和新题集成的班。

比较器
类似于最近学习的算法笔记:C++里面的cmp函数。
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
class Test{
public static class Student{
private String name;
private int ID;
private int age;
public Student(){}
public Student(String name,int ID,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.ID = ID;
}
public String toString(){
return name + "," + ID + "," + age;
}
}
public static class IDComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
// 返回负数,认为第一个参数应该排在前面。
// 返回正数,认为第二个参数应该排在前面。
// 如果返回0,认为谁放在前面都无所谓。
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
if(o1.ID < o2.ID){
return -1;
}else if (o1.ID > o2.ID){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}
public static void printStudents(Student[] stu){
for(Student s:stu){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Student s1 = new Student("panlichao",22,26);
Student s2 = new Student("panlichao2",123,26);
Student s3 = new Student("panlichao3",234,26);
Student s4 = new Student("panlichao4",33,26);
Student s5 = new Student("panlichao5",21,26);
Student[] stu = {s1,s2,s3,s4,s5};
Arrays.sort(stu,new IDComparator());
printStudents(stu);
}
}
优先级队列(时间代价:logN)
之前讲过,有印象的打个1,没印象的打个2。现在重新讲一下。
- 小根堆设计
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
heap.add(1);
heap.add(3);
heap.add(2);
heap.add(3);
heap.add(1);
System.out.println("=========");
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
int s = heap.poll();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
- 大根堆设计
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Test {
public static class MyComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
// 要实现大根堆的话,在这里动手脚
// 负,第一个参数在前
// 正,第二个参数在前
// 0, 谁放前都行
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
if (o1 < o2) {
return 1;
} else if (o1 > o2) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
public static class Student {
public String name;
public int id;
public int age;
public Student(String name, int id, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
}
}
// 谁id大,谁放前!
public static class IdComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
// 如果返回负数,认为第一个参数应该排在前面
// 如果返回正数,认为第二个参数应该排在前面
// 如果返回0,认为谁放前面无所谓
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
if (o1.id < o2.id) {
return 1;
} else if (o2.id < o1.id) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "b";
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));
// out:-1,按照字典序比较
PriorityQueue<Student> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(new IdComparator());
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 5, 27);
Student s2 = new Student("李四", 1, 17);
Student s3 = new Student("王五", 4, 29);
Student s4 = new Student("赵六", 3, 9);
Student s5 = new Student("左七", 2, 34);
heap.add(s1);
heap.add(s2);
heap.add(s3);
heap.add(s4);
heap.add(s5);
System.out.println("=========");
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
Student s = heap.poll();
System.out.println(s.name + ", " + s.id + ", " + s.age);
}
}
}
题目一:给出K条升序链表,合并成1条链表,并且这个链表保证有序。(时间复杂度o(N*logK),其中,N代表的是总的结点数量,因为一直是进一个出一个,总的队列结点数量不会超过K长度,所以为logK)
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
// 测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
public class Test {
public static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public static class ListNodeComparator implements Comparator<ListNode> {
@Override
public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2) {
return o1.val - o2.val;
}
}
public static ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null) {
return null;
}
PriorityQueue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(new ListNodeComparator());
for (int i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {
if (lists[i] != null) {
heap.add(lists[i]);
}
}
if (heap.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
ListNode head = heap.poll();
ListNode pre = head;
if (pre.next != null) {
heap.add(pre.next);
}
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
ListNode cur = heap.poll();
pre.next = cur;
pre = cur;
if (cur.next != null) {
heap.add(cur.next);
}
}
return head;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1);
node1.next = new ListNode(2);
node1.next.next = new ListNode(7);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(2);
node2.next = new ListNode(4);
node2.next.next = new ListNode(6);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(1);
node3.next = new ListNode(2);
node3.next.next = new ListNode(6);
ListNode[] lists = {node1,node2,node3};
ListNode result = mergeKLists(lists);
while(result != null){
System.out.println(result.val);
result = result.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
题目二:二叉树的递归
哪怕没有写过难的也打个1,好吧,我们从头讲一下。
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
// 测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
public class Test {
public static class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode left;
public ListNode right;
public ListNode(int val,ListNode left,ListNode right){
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
// 中序遍历:左头右
public static void in(ListNode head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
in(head.left);
System.out.printf(head.val + " ");
in(head.right);
}
public static void pre(ListNode head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
System.out.printf(head.val + " ");
pre(head.left);
pre(head.right);
}
// 前序遍历:左右头
public static void pos(ListNode head){
if(head == null){
return;
}
pos(head.left);
pos(head.right);
System.out.printf(head.val + " ");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ListNode node = new ListNode(1,null,new ListNode(7,null,null));
node.left = new ListNode(2,new ListNode(3,null,null),null);
in(node);
System.out.println();
pre(node);
System.out.println();
pos(node);
}
}
扩展:什么是递归序?就是指针移动的顺序。
这个玩意非常有用!来,干几道题!
题目三: 给你两个结点,代表两棵树。请你写出一个函数,判断这两棵树是否相等?(相等的意思是两棵树的结构相等、值也相等)
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
// 测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
public class Test {
public static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
}
public static boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
// 相同则0,不同则1,即返回非零数字
if(p == null ^ q == null){
return false;
}
// 从上面出来,只能说明两个相同,要么都是null,要么都不是。
// 这是是null的情况。
if(p == null && q == null){
return true;
}
// 这是都不是null的情况。
return p.val == q.val && isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
}
}
题目三-扩展: 判断一颗树是否为镜面数。
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
// 测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
public class Test {
public static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
}
public static boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root){
return isMirror(root,root);
}
public static boolean isMirror(TreeNode h1,TreeNode h2){
if(h1 == null ^ h2 == null){
return false;
}
// 到了这里只能说是否为null肯定相同,要么都为null,要么都不是。
// 都是
if(h1 == null && h2 == null){
return true;
}
// 都不是null
return h1.val == h2.val && isMirror(h1.left,h2.right) && isMirror(h1.right,h2.left);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
//.......
}
}
题目四: 返回一棵以root为头树的最大深度。
// 测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree
public class Test{
public static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
}
// 以root为头的树,最大高度是多少返回!
public static int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// 这棵树的最大高度就是((我的左树的高度和我的右树的高度)的最大值)+1
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
题目五: 用先序数组(里面每个数字都不一样)和中序数组(里面每个数字都不一样)重建一棵树。
import java.util.HashMap;
// 测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
public class Test {
public static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public static TreeNode buildTree(int[] pre, int[] in) {
if (pre == null || in == null || pre.length != in.length) {
return null;
}
return f(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, in, 0, in.length - 1);
}
// 有一棵树,先序遍历是pre[L1...R1],中序结果是in[L2...R2]
// 请建立出整棵树返回头结点
public static TreeNode f(int[] pre, int L1, int R1, int[] in, int L2, int R2) {
// 左树为空或右树为空应该返回null,计算下来的话递归式的参数会出现L1 > R1的情况。当然,如果L1 > R1,肯定也返回null。如果看不懂这句话就看视频吧,02:07:11处。
if (L1 > R1) {
return null;
}
// 记录头结点
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(pre[L1]);
if (L1 == R1) {
return head;
}
int find = L2;
// 现在找出L1,R1,L2,R2
while (in[find] != pre[L1]) {
find++;
}
head.left = f(pre, L1 + 1, L1 + find - L2, in, L2, find - 1);
head.right = f(pre, L1 + find - L2 + 1, R1, in, find + 1, R2);
return head;
}
// 中序遍历:左头右
public static void in(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
in(head.left);
System.out.printf(head.val + " ");
in(head.right);
}
public static void pre(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.printf(head.val + " ");
pre(head.left);
pre(head.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] pre = {1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7};
int[] in = {4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 3, 7};
pre(buildTree(pre, in));
System.out.println();
in(buildTree(pre, in));
}
}
发现每次都要进行查找,很浪费时间,我们在这里做一个map表,从而实现快速查找。
import java.util.HashMap;
// 测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
public class Test {
public static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
// 有一棵树,先序遍历是pre[L1...R1],中序结果是in[L2...R2]
// 请建立出整棵树返回头结点
public static TreeNode buildTree2(int[] pre, int[] in) {
if (pre == null || in == null || pre.length != in.length) {
return null;
}
HashMap<Integer,Integer> valueIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < in.length ; i++){
valueIndexMap.put(in[i],i);
}
return g(pre, 0, pre.length - 1, in, 0, in.length - 1,valueIndexMap);
}
public static TreeNode g(int[] pre, int L1, int R1, int[] in, int L2, int R2,HashMap<Integer,Integer> valueIndexMap) {
// 左树为空或右树为空应该返回null,计算下来的话递归式的参数会出现L1 > R1的情况。当然,如果L1 > R1,肯定也返回null。如果看不懂这句话就看视频吧,02:07:11处。
if (L1 > R1) {
return null;
}
// 记录头结点
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(pre[L1]);
if (L1 == R1) {
return head;
}
int find = valueIndexMap.get(pre[L1]);
head.left = g(pre, L1 + 1, L1 + find - L2, in, L2, find - 1,valueIndexMap);
head.right = g(pre, L1 + find - L2 + 1, R1, in, find + 1, R2,valueIndexMap);
return head;
}
// 中序遍历:左头右
public static void in(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
in(head.left);
System.out.printf(head.val + " ");
in(head.right);
}
public static void pre(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.printf(head.val + " ");
pre(head.left);
pre(head.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] pre = {1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7};
int[] in = {4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 3, 7};
pre(buildTree(pre, in));
System.out.println();
in(buildTree(pre, in));
}
}