kvm虚拟化
kvm虚拟化
文章目录
- kvm虚拟化
-
-
- 一. 虚拟化介绍
-
- 1. 常见的虚拟化软件
- 2. 介绍
-
- 2.1 全虚拟化
- 2.2 半虚拟化
- 2.3理论上讲:
- 3. kvm介绍
- 二. centos7部署kvm
-
- 1. 部署
-
- 1.1 环境
- 1.2 部署前请确保你的CPU虚拟化功能已开启。分为两种情况:
- 1.3 关闭防火墙与SELINUX
- 1.4 kvm安装
- 1.5 配置网卡
- 1.6 启动服务并验证
- 2. kvm web管理界面安装
-
- 2.1 安装依赖包
- 2.2 从github上下载webvirtmgr代码
- 2.3 拷贝web网页至指定目录
- 2.4 生成密钥
- 2.5 配置端口转发
- 2.6 配置nginx
- 2.7 设置supervisor
- 2.8 配置nginx用户
- 3. kvm web界面管理
-
- 3.1 第一次通过web访问kvm时可能会一直访问不了,一直转圈,而命令行界面一直报错(too many open files)
- 3.2 kvm连接管理
- 3.3 kvm存储管理
- 3.4 通过远程连接软件上传ISO镜像文件至存储目录/var/lib/libvirt/images/
- 3.5 在 web 界面查看ISO镜像是否存在
- 3.6 创建系统安装镜像
- 3.7 kvm网络管理
- 4. 实例管理
-
- 1. 实例(虚拟机)创建
-
一. 虚拟化介绍
1. 常见的虚拟化软件
-
vmware 面向个人,支持windows,linux,macos
- VMware workstation
- VMware fusion
-
esxi 面向企业,VMware企业版,装到服务器上,有客户端进行管理
-
kvm 面向企业,底层是一个linux操作系统,有一个web界面进行管理
-
xen 面向桌面化,是一个直接运行在计算机硬件之上的用以替代操作系统的软件层,它能够在计算机硬件上并发的运行多个客户操作系统(Guest OS)。目前Xen支持Linux、NetBSD、FreeBSD、Solaris、 Windows和其他常用的操作系统作为客户操作系统在其管理程序上运行。
-
citrix 银行
-
virtualbox 面向个人,亦可面向服务器
-
hyper-v 微软,只能在Windows server上使用
2. 介绍
-
虚拟化是云计算的基础。简单的说,虚拟化使得在一台物理的服务器上可以跑多台虚拟机,虚拟机共享物理机的 CPU、内存、IO 硬件资源,但逻辑上虚拟机之间是相互隔离的。
-
物理机称为宿主机(Host),宿主机上面的虚拟机称为客户机(Guest)。
-
根据 Hypervisor(程序) 的实现方式和所处的位置,虚拟化又分为两种:
- 全虚拟化
- 半虚拟化
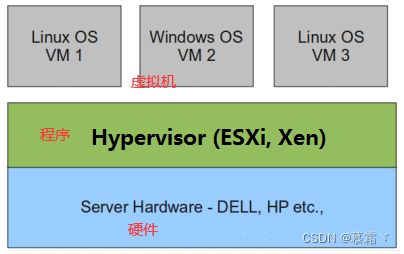
2.1 全虚拟化
- Hypervisor 直接安装在物理机上,多个虚拟机在 Hypervisor 上运行。Hypervisor 实现方式一般是一个特殊定制的 Linux 系统。Xen 和 VMWare 的 ESXi 都属于这个类型
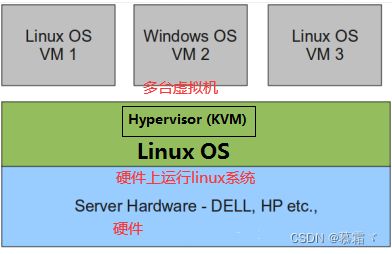
2.2 半虚拟化
- 物理机上首先安装常规的操作系统,比如 Redhat、Ubuntu 和 Windows。Hypervisor 作为 OS 上的一个程序模块运行,并对管理虚拟机进行管理。KVM、VirtualBox 和 VMWare Workstation 都属于这个类型
2.3理论上讲:
- 全虚拟化一般对硬件虚拟化功能进行了特别优化,性能上比半虚拟化要高,不需要操作系统,效率上高
- 半虚拟化因为基于普通的操作系统,会比较灵活,比如支持虚拟机嵌套。嵌套意味着可以在KVM虚拟机中再运行KVM,多层虚拟,需要资源足够
3. kvm介绍
-
kVM 全称是 Kernel-Based Virtual Machine。 KVM 是基于 Linux 内核实现的。kvm是管理虚拟化的软件
-
KVM有一个内核模块叫 kvm.ko,只用于管理虚拟 CPU 和内存。
-
IO 的虚拟化,比如存储和网络设备则是由 Linux 内核与Qemu来实现
-
作为一个 Hypervisor,KVM 本身只关注虚拟机调度和内存管理这两个方面。
-
IO 外设的任务交给 Linux 内核和 Qemu。
-
Libvirt 就是 KVM 的管理工具。
-
Libvirt 除了能管理 KVM 这种 Hypervisor,还能管理 Xen,VirtualBox 等。
Libvirt 包含 3 个东西:后台 daemon 程序 libvirtd(服务)、API 库和命令行工具 virsh
- libvirtd是服务程序,接收和处理 API 请求;
- API 库使得其他人可以开发基于 Libvirt 的高级工具, virt-manager,这是图形化的 KVM 管理工具;
- virsh 是KVM 命令行工具
二. centos7部署kvm
1. 部署
1.1 环境
| 系统类型 | IP |
|---|---|
| CentOS Linux release 7.9 | 192.168.232.130 |
1.2 部署前请确保你的CPU虚拟化功能已开启。分为两种情况:
- 虚拟机要关机设置CPU虚拟化
- 物理机要在BIOS里开启CPU虚拟化
1.3 关闭防火墙与SELINUX
[root@node5 ~]# vim /etc/selinux/config
[root@node5 ~]# systemctl disable --now firewalld
[root@node5 ~]# getenforce
Disabled
[root@node5 ~]# yum -y install epel-release
已加载插件:fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
匹配 epel-release-7-11.noarch 的软件包已经安装。正在检查更新。
无须任何处理
验证CPU是否支持KVM;如果结果中有vmx(Intel)或svm(AMD)字样,就说明CPU的支持的
[root@node5 ~]# egrep -o 'vmx|svm' /proc/cpuinfo
vmx
vmx
vmx
vmx
1.4 kvm安装
[root@node5 ~]# yum -y install qemu-kvm qemu-kvm-tools qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils libguestfs-tools
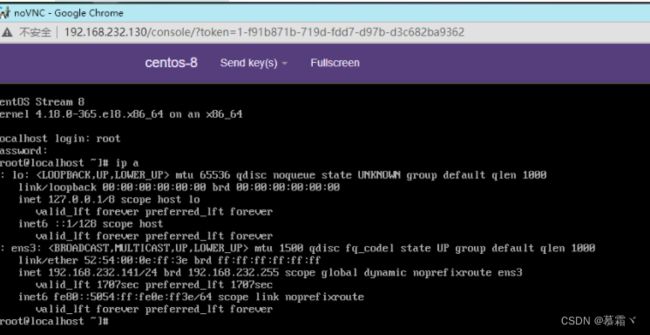
1.5 配置网卡
-
因为虚拟机中网络,我们一般都是和公司的其他服务器是同一个网段,所以我们需要把 \ KVM服务器的网卡配置成桥接模式。这样的话KVM的虚拟机就可以通过该桥接网卡和公司内部 \ 其他服务器处于同一网段
[root@node5 ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
[root@node5 network-scripts]# ls
ifcfg-ens33 ifdown-Team ifup-post
ifcfg-lo ifdown-TeamPort ifup-ppp
ifdown ifdown-tunnel ifup-routes
ifdown-bnep ifup ifup-sit
ifdown-eth ifup-aliases ifup-Team
ifdown-ib ifup-bnep ifup-TeamPort
ifdown-ippp ifup-eth ifup-tunnel
ifdown-ipv6 ifup-ib ifup-wireless
ifdown-isdn ifup-ippp init.ipv6-global
ifdown-post ifup-ipv6 network-functions
ifdown-ppp ifup-isdn network-functions-ipv6
ifdown-routes ifup-plip
ifdown-sit ifup-plusb
[root@node5 network-scripts]# cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-br0
[root@node5 network-scripts]# vim ifcfg-ens33
[root@node5 network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-ens33
TYPE=Ethernet
BOOTPROTO=static
NAME=ens33
DEVICE=ens33
ONBOOT=yes
BRIDGE=br0
NM_CONTROLLED=no
[root@node5 network-scripts]# vim ifcfg-br0
[root@node5 network-scripts]# cat ifcfg-br0
TYPE=Bridge
BOOTPROTO=static
NAME=br0
DEVICE=br0
ONBOOT=yes
NM_CONTROLLED=no
IPADDR=192.168.232.130
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.232.2
DNS1=114.114.114.114
重启网络
[root@node5 network-scripts]# cd
[root@node5 ~]# systemctl restart network
[root@node5 ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master br0 state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:c6:ab:3e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fec6:ab3e/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: br0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:c6:ab:3e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.232.130/24 brd 192.168.232.255 scope global br0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fec6:ab3e/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[root@node5 ~]#
1.6 启动服务并验证
[root@node5 ~]# systemctl enable --now libvirtd
[root@node5 ~]# lsmod|grep kvm
kvm_intel 188740 0
kvm 637289 1 kvm_intel
irqbypass 13503 1 kvm
[root@node5 ~]# virsh -c qemu:///system list
Id 名称 状态
----------------------------------------------------
[root@node5 ~]#
[root@node5 ~]# virsh --version
4.5.0
[root@node5 ~]# virt-install --version
1.5.0
[root@node5 ~]#
[root@node5 ~]# ln -s /usr/libexec/qemu-kvm /usr/bin/qemu-kvm
[root@node5 ~]# ll /usr/bin/qemu-kvm
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 21 8月 19 22:35 /usr/bin/qemu-kvm -> /usr/libexec/qemu-kvm
[root@node5 ~]#
查看网桥信息
[root@node5 ~]# brctl show
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
br0 8000.000c29c6ab3e no ens33
virbr0 8000.525400bdf9c5 yes virbr0-nic
[root@node5 ~]#
stp:生成树协议
2. kvm web管理界面安装
- kvm 的 web 管理界面是由 webvirtmgr 程序提供的
2.1 安装依赖包
[root@node5 ~]# yum -y install git python-pip libvirt-python libxml2-python python-websockify supervisor nginx python-devel
2.2 从github上下载webvirtmgr代码
[root@node5 ~]# cd /usr/local/src/
[root@node5 src]# git clone https://github.com/retspen/webvirtmgr.git
正克隆到 'webvirtmgr'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 5614, done.
remote: Total 5614 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 5614
接收对象中: 100% (5614/5614), 2.97 MiB | 828.00 KiB/s, done.
处理 delta 中: 100% (3606/3606), done.
[root@node5 src]# ls
webvirtmgr
[root@node5 src]#
安装webvirtmgr
[root@node5 src]# cd webvirtmgr/
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]# ls
conf images networks setup.py
console instance README.rst storages
create interfaces requirements.txt templates
deploy locale secrets Vagrantfile
dev-requirements.txt manage.py serverlog vrtManager
hostdetail MANIFEST.in servers webvirtmgr
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]# cat requirements.txt
django==1.5.5
gunicorn==19.5.0
# Utility Requirements
# for SECURE_KEY generation
lockfile>=0.9
# Uncoment for support ldap
#django-auth-ldap==1.2.0
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]# pip2 install -r requirements.txt
Collecting django==1.5.5 (from -r requirements.txt (line 1))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/38/49/93511c5d3367b6b21fc2995a0e53399721afc15e4cd6eb57be879ae13ad4/Django-1.5.5.tar.gz (8.1MB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 8.1MB 14kB/s
Collecting gunicorn==19.5.0 (from -r requirements.txt (line 2))
Retrying (Retry(total=4, connect=None, read=None, redirect=None)) after connection broken by 'ReadTimeoutError("HTTPSConnectionPool(host='pypi.org', port=443): Read timed out. (read timeout=15)",)': /simple/gunicorn/
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/f9/4e/f4076a1a57fc1e75edc0828db365cfa9005f9f6b4a51b489ae39a91eb4be/gunicorn-19.5.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (113kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 122kB 30kB/s
Collecting lockfile>=0.9 (from -r requirements.txt (line 5))
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/c8/22/9460e311f340cb62d26a38c419b1381b8593b0bb6b5d1f056938b086d362/lockfile-0.12.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Installing collected packages: django, gunicorn, lockfile
Running setup.py install for django ... done
Successfully installed django-1.5.5 gunicorn-19.5.0 lockfile-0.12.2
You are using pip version 8.1.2, however version 22.2.2 is available.
You should consider upgrading via the 'pip install --upgrade pip' command.
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]#
检查sqlite3是否安装
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]# python
Python 2.7.5 (default, Jun 28 2022, 15:30:04)
[GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import sqlite3
>>> exit()
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]#
初始化帐号信息
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]# pwd
/usr/local/src/webvirtmgr
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]# python manage.py syncdb
WARNING:root:No local_settings file found.
Creating tables ...
Creating table auth_permission
Creating table auth_group_permissions
Creating table auth_group
Creating table auth_user_groups
Creating table auth_user_user_permissions
Creating table auth_user
Creating table django_content_type
Creating table django_session
Creating table django_site
Creating table servers_compute
Creating table instance_instance
Creating table create_flavor
You just installed Django's auth system, which means you don't have any superusers defined.
Would you like to create one now? (yes/no): yes//问你是否创建超级管理员帐号
Username (leave blank to use 'root'):
Email address: 1@2.com //设置超级管理员邮箱
Password: admin//设置超级管理员密码
Password (again): //再次输入超级管理员密码
Superuser created successfully.
Installing custom SQL ...
Installing indexes ...
Installed 6 object(s) from 1 fixture(s)
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]#
2.3 拷贝web网页至指定目录
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]# mkdir /var/www
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]# cp -a /usr/local/src/webvirtmgr /var/www/
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]# chown -R nginx.nginx /var/www/webvirtmgr/
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]# ll /var/www
总用量 4
drwxr-xr-x 20 nginx nginx 4096 8月 20 10:01 webvirtmgr
[root@node5 webvirtmgr]#
2.4 生成密钥
[root@node5 ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:MWr33xMiXMGi/wJJqWDpmxm+v46FLfqokE5JfiKkTNQ root@node5
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| . |
| . . o |
| . E . oo . . |
|. + .+o . |
| + o .ooS+ . |
|B.. o+..o.+ . . |
|=* oo=o ..o . . |
|= oo=+ ..... |
|.oo.+++. .. .. |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@node5 ~]#
由于这里webvirtmgr和kvm服务部署在同一台机器,所以这里本地信任。如果kvm部署在其他机器,那么这个是它的ip
[root@node5 ~]# ssh-copy-id 192.168.232.130
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.232.130 (192.168.232.130)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:yI7Vw6dzG3BFR36FymKEbCEWMvFYxbAGF8uB5x8LlXc.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:17:9d:66:e9:d1:80:f4:c8:42:ba:78:db:03:d3:87:18.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.232.130's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh '192.168.232.130'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
[root@node5 ~]# ssh 192.168.232.130
Last login: Sat Aug 20 10:12:30 2022 from node5
[root@node5 ~]# exit
登出
Connection to 192.168.232.130 closed.
[root@node5 ~]#
2.5 配置端口转发
[root@node5 ~]# ssh-copy-id 192.168.232.130
[root@node5 ~]# ssh 192.168.232.130 -L localhost:8000:localhost:8000 -L localhost:6080:localhost:60
Last login: Sat Aug 20 10:13:24 2022 from node5
[root@node5 ~]# ss -antl
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:111 *:*
LISTEN 0 5 192.168.122.1:53 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:6080 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:8000 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:111 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 100 [::1]:25 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:6080 [::]:*
LISTEN 0 128 [::1]:8000 [::]:*
[root@node5 ~]#
2.6 配置nginx
[root@node5 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
[root@node5 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
}
[root@node5 ~]#
[root@node5 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/webvirtmgr.conf
[root@node5 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/webvirtmgr.conf
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name $hostname;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/webvirtmgr_access_log;
location /static/ {
root /var/www/webvirtmgr/webvirtmgr;
expires max;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-for $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $host:$server_port;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $remote_addr;
proxy_connect_timeout 600;
proxy_read_timeout 600;
proxy_send_timeout 600;
client_max_body_size 1024M;
}
}
[root@node5 ~]#
确保bind绑定的是本机的8000端口
[root@node5 ~]# vim /var/www/webvirtmgr/conf/gunicorn.conf.py
bind = '0.0.0.0:8000'
backlog = 2048
重启nginx
[root@node5 ~]# systemctl enable --now nginx
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.
[root@node5 ~]#
[root@node5 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
2.7 设置supervisor
[root@node5 ~]# vim /etc/supervisord.conf
在最后加入以下内容
[program:webvirtmgr]
command=/usr/bin/python2 /var/www/webvirtmgr/manage.py run_gunicorn -c /var/www/webvirtmgr/conf/gunicorn.conf.py
directory=/var/www/webvirtmgr
autostart=true
autorestart=true
logfile=/var/log/supervisor/webvirtmgr.log
log_stderr=true
user=nginx
[program:webvirtmgr-console]
command=/usr/bin/python2 /var/www/webvirtmgr/console/webvirtmgr-console
directory=/var/www/webvirtmgr
autostart=true
autorestart=true
stdout_logfile=/var/log/supervisor/webvirtmgr-console.log
redirect_stderr=true
user=nginx
启动supervisor并设置开机自启
[root@node5 ~]# systemctl enable --now supervisord
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/supervisord.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/supervisord.service.
2.8 配置nginx用户
[root@node5 ~]# su - nginx -s /bin/bash
-bash-4.2$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/var/lib/nginx/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:jcPXGJ7PGc+mQMzIvmE2xZk2QVA+VvwooTc8k5DNTAQ nginx@node5
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| E@=.. |
| oo=.. |
| +*o o |
| o.XOX. . |
| S.^=o |
| . * + = |
| * . + + |
| o + . o |
| . . |
+----[SHA256]-----+
-bash-4.2$
-bash-4.2$ touch ~/.ssh/config && echo -e "StrictHostKeyChecking=no\nUserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null" >> ~/.ssh/config
-bash-4.2$ chmod 0600 ~/.ssh/config
-bash-4.2$ cat ~/.ssh/config
StrictHostKeyChecking=no //不验证主机身份
UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null
-bash-4.2$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.232.130
/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/var/lib/nginx/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.232.130' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
root@192.168.232.130's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.232.130'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
-bash-4.2$ exit
logout
[root@node5 ~]#
[root@node5 ~]# vim /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/50-libvirt-remote-access.pkla
[root@node5 ~]# cat /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/50-libvirt-remote-access.pkla
[Remote libvirt SSH access]
Identity=unix-user:root
Action=org.libvirt.unix.manage
ResultAny=yes
ResultInactive=yes
ResultActive=yes
[root@node5 ~]# systemctl restart nginx libvirtd
[root@node5 ~]# ll /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/50-libvirt-remote-access.pkla
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 133 8月 20 10:34 /etc/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/50-libvirt-remote-access.pkla
[root@node5 ~]#
3. kvm web界面管理
- 访问出现too many open files
3.1 第一次通过web访问kvm时可能会一直访问不了,一直转圈,而命令行界面一直报错(too many open files)
- 需要对nginx进行配置
[root@node5 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
....此处省略N行
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
worker_rlimit_nofile 655350; //添加此行配置
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/nginx/README.dynamic.
....此处省略N行
[root@node5 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
- 对系统参数进行设置
[root@node5 ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
[root@node5 ~]# tail -3 /etc/security/limits.conf
# End of file
* soft nofile 655350
* hard nofile 655350
[root@node5 ~]#
- 再次访问
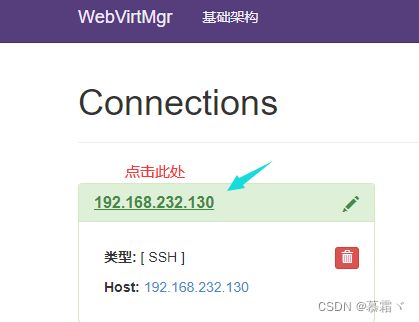
3.2 kvm连接管理
- 创建SSH连接:
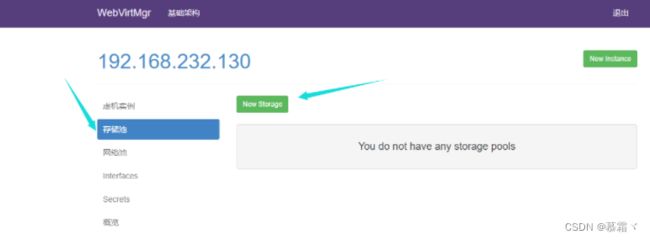
3.3 kvm存储管理
- 创建存储
- 进入存储:
3.4 通过远程连接软件上传ISO镜像文件至存储目录/var/lib/libvirt/images/
[root@node5 ~]# cd /var/lib/libvirt/images/
[root@node5 images]# ls
[root@node5 images]# ls
CentOS-Stream-8-x86_64-20220223-dvd1.iso
[root@node5 images]#
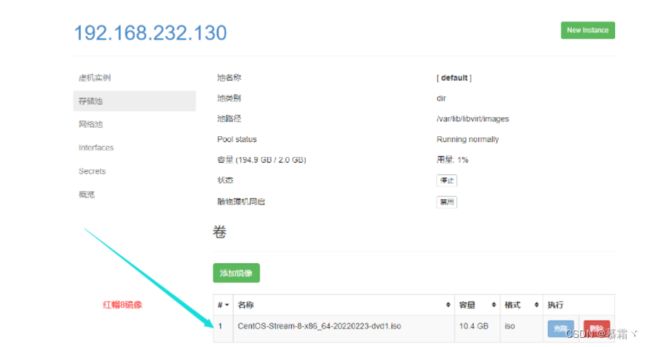
3.5 在 web 界面查看ISO镜像是否存在
3.6 创建系统安装镜像
- 添加镜像
- 查看
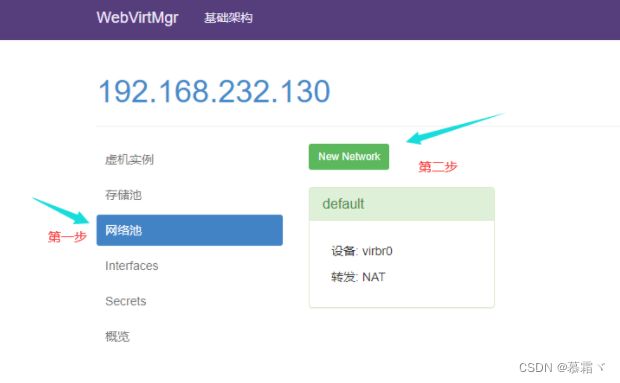
3.7 kvm网络管理
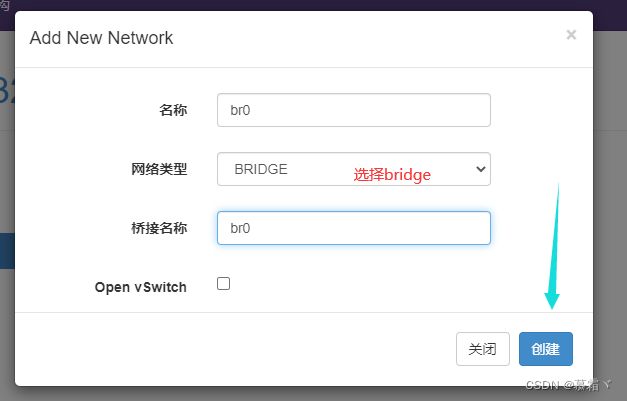
- 添加桥接网络
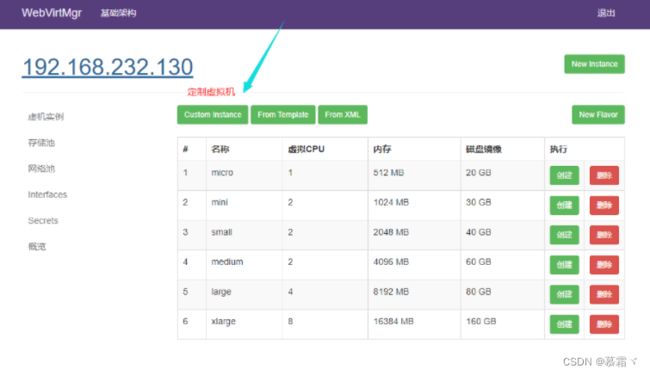
4. 实例管理
1. 实例(虚拟机)创建
- 创建虚拟机
- 定制虚拟机
- 创建虚拟机
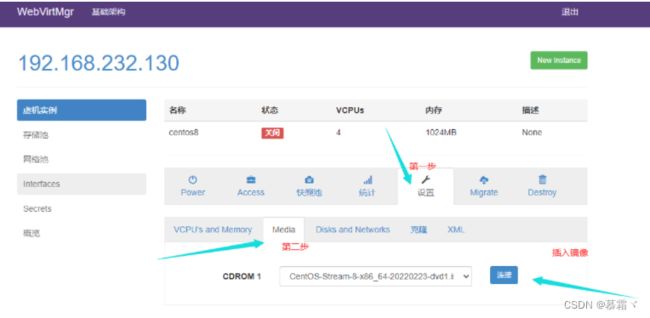
- 虚拟机插入光盘
- 设置在 web 上访问虚拟机的密码
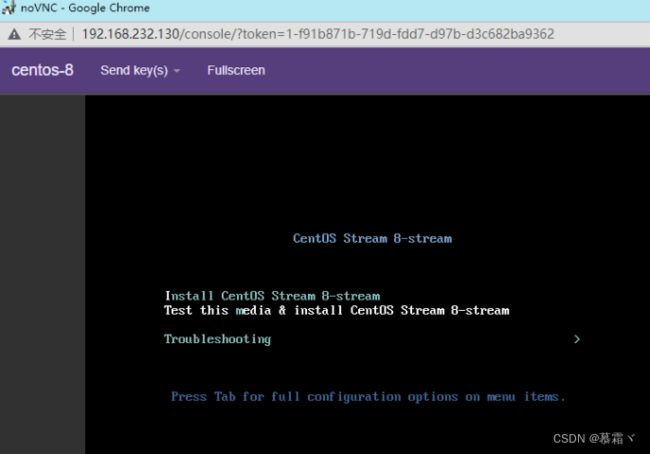
- 启动虚拟机