Android7.1.1 ActivityManagerService关于Activity生命周期分析
前言
对于Android开发者而言,最经常接触的就是四大组件了,Activity、Service、BroadcastReceiver、ContentProvider,其中Activity是我们使用频率最多的,这四个都是通过ActivityManagerService(下文简称AMS)进行管理的,本文就分析AndroidFramework中是如何管理Activity、以及如何创建Activity的。ActivityManagerService(以下简称AMS)启动Activity过程之前,要先弄明白几个重要的类及概念。
1、ActivityRecord介绍
这个对应的就是应用开发过程AndroidManifest.xml以〈activity/>定义的各个Activity。这个表示的是Activity在AMS中的表示方式。下面介绍ActivityRecord一些重要的变量.
final class ActivityRecord {
/*表示AMS在创建ActivityRecord时候指定*/
final ActivityManagerService service; // owner
/*这个是和WindomMangerService通信的,該值会赋值给Activity中*/
final IApplicationToken.Stub appToken; // window manager token
/*这个描述是AndroidManifest.xml中定义activity相关信息*/
final ActivityInfo info; // all about me
/*这个描述是AndroidManifest.xml中定义application相关信息*/
final ApplicationInfo appInfo; // information about activity's app
。。。。。。。。
/*应用的包名*/
final String packageName; // the packageimplementing intent's component
final String processName; // process where this component wants torun
/**Activity亲和性,这上简单的描述就是该Activity应属于是哪个Task*/
final String taskAffinity; // as per ActivityInfo.taskAffinity
。。。。。。。
/**以下三个表示该Activity类型*/
static final int APPLICATION_ACTIVITY_TYPE= 0;
static final int HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE = 1;
static final int RECENTS_ACTIVITY_TYPE = 2;
int mActivityType;
。。。。。。。
/**Activity属于哪个Task*/
TaskRecord task; // the task this is in.
/**通过startActivityForResult启动时,接收返回值的Activity*/
ActivityRecord resultTo; // who startedthis entry, so will get our reply
/**通过startActivityForResult启动时设置的requestCode*/
final int requestCode; // code given by requester (resultTo)
。。。。。。。
/*Activity所属的进程*/
ProcessRecord app; // ifnon-null, hosting application
/*表示Activity的当前状态, INITIALIZING,RESUMED,PAUSING,PAUSED,STOPPING,STOPPED,FINISHING,DESTROYING,DESTROYED
有这几种状态*/
ActivityState state; // current state we are in
/*标记是否为Task的root Activity,比如每个应用有一个mainActivity,一般
*情况下该main Activity即为对应Task的rootActivity*/
boolean frontOfTask; // isthis the root activity of its task?
/*标记该ActivityRecord是否已经stoped*/
boolean stopped; // isactivity pause finished?
/*标记ActivityRecord是否已经finishing,这在activity finish时置为true*/
boolean finishing; // activity in pending finish list?
boolean deferRelaunchUntilPaused; //relaunch of activity is being deferred until pause is
//completed
boolean visible; // does this activity's window need tobe shown?
boolean sleeping; // have we told the activity to sleep?
boolean nowVisible; // is thisactivity's window visible?
/*ActivityStack管理类*/
final ActivityStackSupervisormStackSupervisor;2、TaskRecord介绍
这个是管理一个应用中ActivityRecord的容器,比如一个应用有很多的Activity,而这些Activity都是以Task栈方式进行管理,Task个人认为可以简单的认为一个应用,一个应用对应一个Task。下面说下TaskRecord一些重要的变量。
final class TaskRecord {
/*该Task的id*/
final int taskId; // Unique identifier for this task.
/*Task 亲合性,这个值可能会变化,这个值和ActivityRecord的taskAffinity对应*/
String affinity; // The affinity name for this task, ornull; may change identity.
/*这个值标记Task中rootActivity的亲和性,和第一次启动该Task的root ActivityRecord中的taskAffinity对应,但是该值后续不会改变*/
String rootAffinity; // Initial base affinity, or null; does notchange from initial root.
/**启动Task的Activity的intent*/
Intent intent; // The original intent that startedthe task.
IntentaffinityIntent; // Intent ofaffinity-moved activity that started this task.
int effectiveUid; // The current effective uid of theidentity of this task.
ComponentNameorigActivity; // The non-alias activity component of the intent.
ComponentNamerealActivity; // The actual activity component that started the task.
int numFullscreen; // Number of fullscreen activities.
。。。。。。。。。
/*这个即是用来保存一个Task中所有的 Activtiy,按栈的方式管理*/
/** List of all activitiesin the task arranged in history order */
finalArrayList mActivities;
/** Current stack
*该Task所属的ActivityStack */
ActivityStack stack;
/** Takes on same set ofvalues as ActivityRecord.mActivityType
*task类型和ActivityRecord的mActivityType对应*/
int taskType;
/** Indication of what torun next when task exits. Use ActivityRecord types.
*ActivityRecord.APPLICATION_ACTIVITY_TYPE indicates to resume the task belowthis one in the
* task stack. */
private intmTaskToReturnTo = APPLICATION_ACTIVITY_TYPE;
/** If original intent didnot allow relinquishing task identity, save that information */
booleanmNeverRelinquishIdentity = true;
// Used in the unique casewhere we are clearing the task in order to reuse it. In that case we
// do not want to deletethe stack when the task goes empty.
private boolean mReuseTask= false;
//这是截屏相关的
private BitmapmLastThumbnail; // Last thumbnail captured for this item.
private final FilemLastThumbnailFile; // File containing last thumbnail.
。。。。。。。。
finalActivityManagerService mService;
// Whether or not thistask covers the entire screen; by default tasks are fullscreen.
boolean mFullscreen =true;
// Bounds of the Task.null for fullscreen tasks
//这是Task在屏幕显示区域
Rect mBounds = null;
。。。。。。。
} 这个是管理TaskRecord的容器,也是系统中多窗口的概念读者参考
http://blog.csdn.net/guoqifa29/article/details/54863237,目前在Android7.1.2上面有以下几个,这些定义在android.app.ActivityManager.StackId中。
/** Homeactivity stack ID.这个包括Launcher的Activity以及recentsAPP */
HOME_STACK_ID = FIRST_STATIC_STACK_ID;
/** ID ofstack where fullscreen activities are normally launched into. 这个即为我们应用启动的Activity所处于的ActivityStack*/
FULLSCREEN_WORKSPACE_STACK_ID = 1;
/** ID of stack where freeform/resizedactivities are normally launched into. */ FREEFORM_WORKSPACE_STACK_ID =FULLSCREEN_WORKSPACE_STACK_ID + 1;
/** ID of stack that occupies a dedicatedregion of the screen. 这个是分屏应用所处于的ActivityStack*/
DOCKED_STACK_ID = FREEFORM_WORKSPACE_STACK_ID+ 1;
/** ID of stack that always on top (alwaysvisible) when it exist.这个好像是画中画模式的Activity所处的 ActivityStack */
PINNED_STACK_ID = DOCKED_STACK_ID + 1;
/** Last static stack stack ID. */
LAST_STATIC_STACK_ID = PINNED_STACK_ID;ActivityStack一些重要变量如下:
final classActivityStack {
。。。。。。。
/**Activity状态值*/
enum ActivityState {
INITIALIZING,
RESUMED,
PAUSING,
PAUSED,
STOPPING,
STOPPED,
FINISHING,
DESTROYING,
DESTROYED
}
。。。。。。。
final ActivityManagerService mService;
final WindowManagerService mWindowManager;
private final RecentTasks mRecentTasks;
/**
* The back history of all previous (andpossibly still
* running) activities. It contains #TaskRecord objects.
* 系统中的所有Task都保存在这里面,以栈的方式管理
*/
private final ArrayListmTaskHistory = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Activities that specify No History mustbe removed once the user navigates away from them.
* If the device goes to sleep with such anactivity in the paused state then we save it here
* and finish it later if another activityreplaces it on wakeup.
*/
ActivityRecord mLastNoHistoryActivity =null;
/**
* Current activity that is resumed, ornull if there is none.
* 这个表示当前ActivityStack处于running中的activity
*/
ActivityRecord mResumedActivity = null;
/**
* When we are in the process of pausing anactivity, before starting the
* next one, this variable holds theactivity that is currently being paused.
* 一般是mResumedActivity赋值
* 这个表示此时正在pausing过程的activity
*/
ActivityRecord mPausingActivity = null;
/**
* This is the last activity that we putinto the paused state. This is
* used to determine if we need to do anactivity transition while sleeping,
* when we normally hold the top activitypaused.
*这个表示此时正在paused过程的activity
*/
ActivityRecord mLastPausedActivity = null;
/**
* This is the last activity that has beenstarted. It is only used to
* identify when multiple activities arestarted at once so that the user
* can be warned they may not be in theactivity they think they are.
*/
ActivityRecord mLastStartedActivity = null;
final int mStackId;
。。。。。。
/**在每个ActivityStack中保存着一份所有的ActivityStack*/
ArrayList mStacks;
/** The attached Display's uniqueidentifier, or -1 if detached */
int mDisplayId;
/** Run all ActivityStacks through this
*这个是管理ActivityStack的*/
final ActivityStackSupervisor mStackSupervisor; ActivityStackSupervisor这个是ActivityStack的管理类。以下几个比较重要的变量。读者看下。
/** The stack containing the launcherapp. Assumed to always be attached to
* Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY. */
ActivityStack mHomeStack;
/** The stack currently receiving input orlaunching the next activity. */
ActivityStack mFocusedStack;
/** If this is the same as mFocusedStackthen the activity on the top of the focused stack has
* been resumed. If stacks are changingposition this will hold the old stack until the new
* stack becomes resumed after which itwill be set to mFocusedStack. */
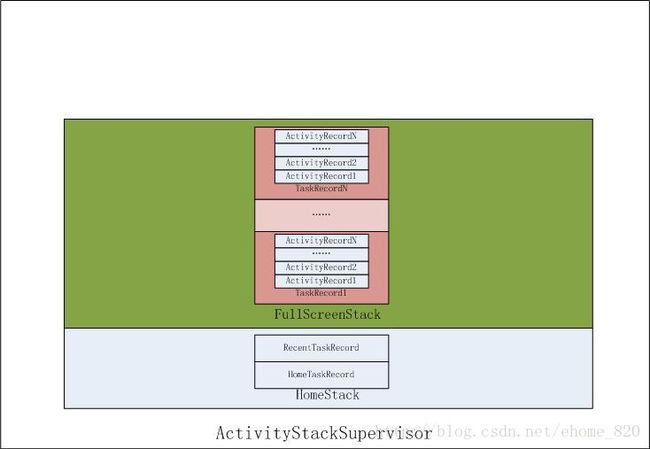
private ActivityStack mLastFocusedStack;Android7.1.1系统存在以上几个ActivityStack,以栈的方式管理ActivityStack,而不同的应用处于不同的ActivityStack,每个ActivityStack以栈的方式管理多个TaskRecord,而每个TaskRecord又以栈的方式管理多个ActivityRecord。可以用图一表示。
图一
5、ActivityThread介绍
final ApplicationThread mAppThread =new ApplicationThread();
这个是定义在ActivityThread中的变量,我们开发过程都一直说应用主线程,主线程即表示的是ActivityThread,一个应用它的主线程只有一个,应用中消息比如Acrivity的生命周期都是通过ActivityThread中的mAppThread这个进行分发。本文只是涉及ActivityManagerService其中Activity这一小部分,很多东西像WindowmanagerService的交互本文没有涉及。另外本文只是关注了ActivityStackID为HOME_STACK_ID的HomeStack和ActivityStack ID为FULLSCREEN_WORKSPACE_STACK_ID的FullscreenStack,像PINNED_STACK、FREEFORM_WORKSPACE_STACK、DOCKED_STACK这方面没有介绍。简单的认为只存在HomeStack和FullScreenStack两个ActivityStack这样有利于抓住主线。
在分析AMS启动Activty之前,大家有必要先弄明白下Android的启动模式,这样有利于弄明白代码。启动模式和Task的介绍可以参考点击打开链接
我们知道Android系统启动之后启动的第一个应用为Launcher那么我们以Launcher为例,结合代码分析AMS是如何启动一个Activity的,以下代码会忽略些和启动无关的代码,这样有利于我们抓住启动Activity这条主线。
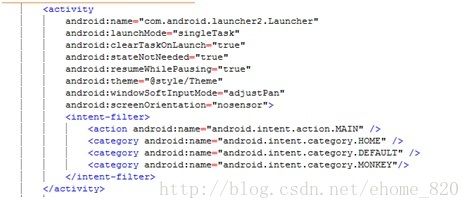
从AMS启动过程我们知道在AMS中是通过函数startHomeActivityLocked启动Launcher的,我们先来看下Launcher应用中AndroidManifest.xml中关于HomeActivity的Activity定义(请看图二),其中的launchMode、clearTaskOnLaunch、android.intent.category.HOME重点关注。
图 二
代码如下:
/*函数主要作用为获取HomeActivity(即应用AndroidManifest.xml中有设置android.intent.category.HOME,下文中HomeActivity即指该Activty)中的intent以及ActivityInfo*/
boolean startHomeActivityLocked(int userId, String reason) {
if (mFactoryTest ==FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL && mTopAction == null) {
。。。。。。。。。
return false;
}
//这边获取到的即为Launcher中AndroidManifest.xml有定义android.intent.category.HOME的Activity
Intent intent = getHomeIntent();
ActivityInfo aInfo =resolveActivityInfo(intent, STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
if (aInfo != null) {
intent.setComponent(newComponentName(aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
// Don't do this if the home app iscurrently being
// instrumented.
aInfo = new ActivityInfo(aInfo);
aInfo.applicationInfo =getAppInfoForUser(aInfo.applicationInfo, userId);
ProcessRecord app =getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
aInfo.applicationInfo.uid,true);
/**因为是第一次启动Home 应用,所以对应的进程会null*/
if (app == null || app.instrumentationClass== null) {
intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
mActivityStarter.startHomeActivityLocked(intent, aInfo, reason);
}
} else {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "No home screen found for " + intent, newThrowable());
}
return true;
}接下去mActivityStarter.startHomeActivityLocked代码如下:
void startHomeActivityLocked(Intent intent, ActivityInfo aInfo, String reason) {
/**这是把HomeActivity所属的HomeStack移动到前台,
*但是由于第一次启动HomeActivity还未创建,
*其中所属的TaskRecord、以及ActivityRecrod为null
*/
mSupervisor.moveHomeStackTaskToTop(ActivityRecord.HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE,reason);
startActivityLocked(null /*caller*/,intent, null /*ephemeralIntent*/,
null /*resolvedType*/, aInfo,null /*rInfo*/, null /*voiceSession*/,
null /*voiceInteractor*/, null/*resultTo*/, null /*resultWho*/,
0 /*requestCode*/, 0/*callingPid*/, 0 /*callingUid*/, null /*callingPackage*/,
0 /*realCallingPid*/, 0/*realCallingUid*/, 0 /*startFlags*/, null /*options*/,
false /*ignoreTargetSecurity*/,false /*componentSpecified*/, null /*outActivity*/,
null /*container*/, null/*inTask*/);
if (mSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity) {
。。。。。。
mSupervisor.scheduleResumeTopActivities();
}
}说明以下的代码我会删除一些对于第一次启动HOME应用不必要的代码,读者可以自行看源码进行分析,大家千万要自己对着代码分析,因为本文这个涉及太多,另外一个作者能力有限有些内容会表述不清楚,会遗漏一些细节,读者对着代码看就会比较清晰了
接下来部分是任何一个Activity的启动都会经历的流程。
Activity的启动过程
Activity启动过程可以概括以下几个步骤。
1、前期准备工作
2、计算Activity所属的Task、ActivityStack,及操作。
3、paused之前Activity、resumed当前启动的Activity过程
4、进程的创建
5、Activity初始化流程
接下去我会按照这几个步骤,对照着源码进行下会析。
一、前期准备工作
前期准备工作,其实就是初始化当前启动Activity相关的变量。我们进入ActivityStarter中的startActivityLocked(Android系统中任何Activity启动显示都会进入该函数)。代码如下:
final int startActivityLocked(
IApplicationThreadcaller/*表示启动者所属的应用主线程,在ActivityThread中定义*/,
Intent intent/*当前启动的Activity的Intent*/,
IntentephemeralIntent,/*当前启动的Activity的Intent的复本*/
String resolvedType,/*当前启动的Activity的resolvedType*/
ActivityInfoaInfo,/*当前启动的Activity的ActivityInfo(PackageManger解析获得)*/
ResolveInforInfo,/*当前启动的Activity的ResolveInfo */
IVoiceInteractionSessionvoiceSession,/*暂时忽略为null&/
IVoiceInteractorvoiceInteractor,/*暂时忽略为null*/
IBinderresultTo, String resultWho,
intrequestCode, /*通过startActivityForResult设置的值*/
intcallingPid, int callingUid,
String callingPackage,/*表示调用者即启动当前Activity所属的包名*/
int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid,int startFlags,
ActivityOptions options, booleanignoreTargetSecurity,
boolean componentSpecified,
ActivityRecord[]outActivity,
ActivityStackSupervisor.ActivityContainercontainer, TaskRecord inTask) {
int err = ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS;
ProcessRecord callerApp = null;
/*如果调用者不为null,查询是否已经创建了ProcessRecord,如果创建了,则
*设置调用者的callingpid、callingUid*/
if (caller != null) {
callerApp =mService.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
if (callerApp != null) {
callingPid = callerApp.pid;
callingUid =callerApp.info.uid;
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable tofind app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" +callingPid + ") when starting: "
+ intent.toString());
err =ActivityManager.START_PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
}
final int userId = aInfo != null ?UserHandle.getUserId(aInfo.applicationInfo.uid) : 0;
if (err ==ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS) {
Slog.i(TAG, "START u" +userId + " {" + intent.toShortString(true, true, true, false)
+ "} from uid " +callingUid
+ " on display "+ (container == null ? (mSupervisor.mFocusedStack == null ?
Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY :mSupervisor.mFocusedStack.mDisplayId) :
(container.mActivityDisplay== null ? Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY :
container.mActivityDisplay.mDisplayId)));
}
ActivityRecord sourceRecord = null;
ActivityRecord resultRecord = null;
/**这边判断的是,当前启动方式是以startActivityForResult启动的,
*则保存调用者Activity在sourceRecord中,
*如果启动时候设置了requestCode并且大于是0,那么接收
*startActivityForResult返回值的Activity保存在resultRecord中。
*其实读者可以看出来,调用者和接收返回者的Activity是相同的
*举个例子:
*Activity A通过startActivityForResult启动B,并且requestCode>0
*那么此时sourceRecord和resultRecord都为A
*/
if (resultTo != null) {
sourceRecord =mSupervisor.isInAnyStackLocked(resultTo);
if (DEBUG_RESULTS)Slog.v(TAG_RESULTS,
"Will send result to" + resultTo + " " + sourceRecord);
if (sourceRecord != null) {
if (requestCode >= 0&& !sourceRecord.finishing) {
resultRecord =sourceRecord;
}
}
}
final int launchFlags =intent.getFlags();
/**
*FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT这个FLAG作用,举个例子:
*应用中存在有ActivityA,B,C,A以startActivityForResult方式启动了B,
* 此时B设置了FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT启动了C,注意此时B启动C
* 时requestCode不设置或者设置值要小于0,不然会报错。
* 那么原来在A中接收返回值从B返回的,但这时A接收的返回值变成从C返回。
*/
if ((launchFlags &Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT) != 0 && sourceRecord != null) {
// Transfer the result target fromthe source activity to the new
// one being started, including anyfailures.
if (requestCode >= 0) {
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
returnActivityManager.START_FORWARD_AND_REQUEST_CONFLICT;
}
resultRecord =sourceRecord.resultTo;
if (resultRecord != null &&!resultRecord.isInStackLocked()) {
resultRecord = null;
}
resultWho = sourceRecord.resultWho;
requestCode =sourceRecord.requestCode;
sourceRecord.resultTo = null;
if (resultRecord != null) {
resultRecord.removeResultsLocked(sourceRecord, resultWho, requestCode);
}
if (sourceRecord.launchedFromUid ==callingUid) {
// The new activity is beinglaunched from the same uid as the previous
// activity in the flow, and askingto forward its result back to the
// previous. In this case the activity is serving as atrampoline between
// the two, so we also want toupdate its launchedFromPackage to be the
// same as the previousactivity. Note that this is safe, sincewe know
// these two packages come fromthe same uid; the caller could just as
// well have supplied that samepackage name itself. This specifially
// deals with the case of anintent picker/chooser being launched in the app
// flow to redirect to anactivity picked by the user, where we want the final
// activity to consider it tohave been launched by the previous app activity.
callingPackage =sourceRecord.launchedFromPackage;
}
}
。。。。。。。
/**
*创建需要启动的Activity对应的ActvityRecord
*此时对应图一中AndroidManifest.xml中定义的HOME Activity
*/
ActivityRecord r = newActivityRecord(mService, callerApp, callingUid, callingPackage,
intent, resolvedType, aInfo,mService.mConfiguration, resultRecord, resultWho,
requestCode,componentSpecified, voiceSession != null, mSupervisor, container,
options, sourceRecord);
if (outActivity != null) {
outActivity[0] = r;
}
。。。。。
/**
*这个是先启动延迟启动的Activity
*对于本文启动Launcher时应该是为null的
*/
doPendingActivityLaunchesLocked(false);
try {
/*windowmangerservice相关*/
mService.mWindowManager.deferSurfaceLayout();
err = startActivityUnchecked(r,sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, startFlags,
true, options, inTask);
}finally {
mService.mWindowManager.continueSurfaceLayout();
}
postStartActivityUncheckedProcessing(r,err, stack.mStackId, mSourceRecord, mTargetStack);
return err;
}接下来进入ActivityStarter中的startActivityUnchecked,在该函数中做的事情挺多的,也是最复杂的一部分。本文分析以HOME应用启动为主线,不涉及到HOME应用相关的代码我会先标注,一些其它的分析是在比较复杂的情况下,读者可以对应着启动模式对应着分析,这样会比较深刻明白。该函数主要包含以下几个步骤
1、计算launchFlag
2、计算调用者的ActivityStack
3、检查是否存在复用的TaskRecord
4、对于存在复用的TaskRecord则进行相应的ActivityStack、TaskRecord的移动(这个比较复杂).
5、计算当前启动Activity所属的TaskRecord
6、把当前启动的Activity放到所属TaskRecord的栈顶
7、最后调用resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked创建正在启动的Activity、Paused当前resumed的Activity,以及resumed当前启动的Activity
HOME应用的launchMode为singleTask、以及设置了clearTaskOnLaunch为true,结合这两点我们开始分析。
startActivityUnchecked代码如下:
private intstartActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSessionvoiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume,ActivityOptions options,
TaskRecord inTask){
/*初始化一些值,读者自己看下*/
setInitialState(r, options, inTask,doResume, startFlags,
sourceRecord,voiceSession, voiceInteractor);
/*计算当前启动Activity的是否要增加Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK*/
computeLaunchingTaskFlags();
/*获取调用者的ActivityStack*/
computeSourceStack();
mIntent.setFlags(mLaunchFlags);
/**
*这边主要是判断当前启动的Activity是否存在可以利用的Task
* 当启动模式launchMode为singleTask、singleInstance,或者启动时
* Flag设置为FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK并没设置FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK
* 并且当前启动的Activity不是以startActivityForResult启动的,
* 满足以上情况才会寻找是否存在有复用的Task。
* 匹配规则:
* 1、对于启动模式为singleInstance,遍历所有ActivityStack和Task的堆栈中查找
*是否存在以当前启动Activity相同的Activity。
* 2、其它情况下,遍历所有ActivityStack和Task的堆栈,查找Task中intent变量 * 是否当前启动Activity相匹配,如果不存在,则去匹配task的亲和性(即
*在AndroidManifest中android:taskAffinity定义的。
*对于本文介绍启动Launcher应用mResuedActivity为null
*/
mReusedActivity =getReusableIntentActivity();
。。。。。。。
}到这儿本章开头说的第一部分前期准备工作算是结束,我们总结下,前期准备工作主要做了什么:
1、在ActivityStarter的startActivityLocked计算调用者的PID和UID,得到调用者的Activity sourceRecord、以及接收返回值的Activity resultRecord。创建当前启动的Activity对应的ActivityRecord,并且在ActivityRecord保存当前启动的Activity保存调用者、接收返回值的Activity,让Activity有迹可寻。
2、在ActivityStarter的startActivityUnLocked中重置一些变量、对于调用者不为null情况下,得到调用者Activty所属的ActivityStack,接着判断对于当前启动的Activity,是否存在复用的Task,这部分主要是决定按何种方式启动Activity。
二、寻找Activity所属的Task、ActivityStack,及操作
寻找Task、ActivityStack可以大致可以分为两种情况。
1、 存在复用的Task情况。
2、 不存在复用Task情况。
接着第一章查找完复用Task之后的代码流程分析。
private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSessionvoiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume,ActivityOptions options,
TaskRecordinTask) {
。。。。。。。。。
final int preferredLaunchStackId = (mOptions != null) ?mOptions.getLaunchStackId() : ActivityManager.StackId.INVALID_STACK_ID;
/**
*表明当前的Task列表中存在有复用的Activity
*可能为相同的Activity或者具有相同的affinity的task
*如果是第一次启动某个应用或者从adb am中启动以及第一次启动Launcher
*那么复用的TaskRecord为null
*对于本文介绍启动Launcher应用中HOME Activity ,此时mResuedActivity为null
*读者可以先忽略这分支代码
*这边对应的是存在复用Task的情况
*/
if (mReusedActivity != null) {
/*由于对于系统刚启动时启动HOMEActivity,还不存在有task,此时mResusedActivity为null所以可以先忽略这部分代码
*这部分代码主要是对于存在复用的TaskRecord则进行相应的ActivityStack、 *TaskRecord的移动,以及对于启动过程中设置相关的FLAG进行处理
*/
// When theflags NEW_TASK and CLEAR_TASK are set, then the task gets reused but
// still needsto be a lock task mode violation since the task gets cleared out and
// the devicewould otherwise leave the locked task.
if (mSupervisor.isLockTaskModeViolation(
mReusedActivity.task,
(mLaunchFlags &(FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK))
==(FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK))) {
mSupervisor.showLockTaskToast();
Slog.e(TAG,"startActivityUnchecked: Attempt to violate Lock Task Mode");
returnSTART_RETURN_LOCK_TASK_MODE_VIOLATION;
}
//设置当前启动Activity的Task为复用的Task
if (mStartActivity.task == null) {
mStartActivity.task =mReusedActivity.task;
}
if (mReusedActivity.task.intent ==null) {
// This task was started because ofmovement of the activity based on affinity...
// Now that we are actually launchingit, we can assign the base intent.
mReusedActivity.task.setIntent(mStartActivity);
}
// This codepath leads to delivering a new intent, we want to make sure we schedule it
// as thefirst operation, in case the activity will be resumed as a result of later
//operations.
/*
*这边处理启动时设置FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP时,要清除复用Task中存在与当前启动
*Activity相同的Activity之上的Activity
*举个例子:比如复用Task1中存在有Activity A,B,C,D,此时正在启动的Activity B,那么C**和D也要finish,另外此时如果B *为标准启动模式,并且没有设置FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP,那么B也会finish。具体的读者可以跟进
*mReusedActivity.task.performClearTaskForReuseLocked看下。
*/
if ((mLaunchFlags &FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP) != 0
|| mLaunchSingleInstance ||mLaunchSingleTask) {
// In this situation we want toremove all activities from the task up to the one
// being started. In most casesthis means we are resetting the task to its initial
// state.
final ActivityRecord top =mReusedActivity.task.performClearTaskForReuseLocked(
mStartActivity,mLaunchFlags);
if (top != null) {
if (top.frontOfTask) {
// Activity aliases maymean we use different intents for the top activity,
// so make sure thetask now has the identity of the new intent.
top.task.setIntent(mStartActivity);
}
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(AM_NEW_INTENT, mStartActivity, top.task);
if(shouldActivityBeBroughtToFront(mReusedActivity)) {
mStartActivity.intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT);
}
//这边调用Activity中的onNewIntent
top.deliverNewIntentLocked(mCallingUid, mStartActivity.intent,
mStartActivity.launchedFromPackage);
}
}
sendPowerHintForLaunchStartIfNeeded(false /* forceSend */);
//这边开始设置当前启动Activity所属的ActivityStack,如果需要要把Activity
//所属的Task、ActivityStack移动到前台,见下面分析。
mReusedActivity =setTargetStackAndMoveToFrontIfNeeded(mReusedActivity);
//对于复用Task情况下START_FLAG_ONLY_IF_NEEDED这个FLAG只是resumed
//具体这个Flag是啥意思不是很清楚,读者知道的可以告诉我下。
if ((mStartFlags &START_FLAG_ONLY_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
// We don't need to start a newactivity, and the client said not to do anything
// if that is the case, so thisis it! And for paranoia, make sure wehave
// correctly resumed the topactivity.
resumeTargetStackIfNeeded();
returnSTART_RETURN_INTENT_TO_CALLER;
}
setTaskFromIntentActivity(mReusedActivity);
//如果不需要把当前启动的Activity增加到Task并且不存在复用Task
//那么仅仅进行resumed过程。
if (!mAddingToTask &&mReuseTask == null) {
// We didn't doanything... but it was needed (a.k.a.,client don't use that
// intent!) And for paranoia, make sure we have correctlyresumed the top activity.
resumeTargetStackIfNeeded();
return START_TASK_TO_FRONT;
}
}我们看下setTargetStackAndMoveToFrontIfNeeded这个函数里面是怎么操作Task和stack的。代码如下:
private ActivityRecord setTargetStackAndMoveToFrontIfNeeded(ActivityRecord intentActivity){
//targetStack设置成复用task所属的stack
mTargetStack =intentActivity.task.stack;
mTargetStack.mLastPausedActivity =null;
// If the target task is not in thefront, then we need to bring it to the front...
// except... well, with SINGLE_TASK_LAUNCH it's notentirely clear. We'd like to have
// the same behavior as if a newinstance was being started, which means not bringing it
// to the front if the caller is notitself in the front.
final ActivityStack focusStack =mSupervisor.getFocusedStack();
//这边是当前前台的Task和复用task不同,那么需要进行Task的移动
if(shouldActivityBeBroughtToFront(intentActivity)) {
if (mSourceRecord == null ||(mSourceStack.topActivity() != null &&
mSourceStack.topActivity().task == mSourceRecord.task)) {
// We really do want to pushthis one into the user's face, right now.
if (mLaunchTaskBehind&& mSourceRecord != null) {
intentActivity.setTaskToAffiliateWith(mSourceRecord.task);
}
mMovedOtherTask = true;
// If the launch flags carryboth NEW_TASK and CLEAR_TASK, the task's activities
// will be cleared soon by ActivityStarterin setTaskFromIntentActivity().
// So no point resuming any ofthe activities here, it just wastes one extra
// resuming, plus enter ANDexit transitions.
// Here we only want to bringthe target stack forward. Transition will be applied
// to the new activity that'sstarted after the old ones are gone.
final boolean willClearTask =
(mLaunchFlags &(FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK))
== (FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK |FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK);
/*如果FlagFLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK设置这两个时候,它会 *在接下来的代码中ActivityStarterin setTaskFromIntentActivity().清除该Task(后面会分析到
*此处我们分析没有设置Flag的情况
*/
if (!willClearTask) {
//计算当前启动的Activity所属的stack
final ActivityStacklaunchStack = getLaunchStack(
mStartActivity,mLaunchFlags, mStartActivity.task, mOptions);
//如果当前启动的Activity即为复用Task所属的ActivityStack
if (launchStack == null ||launchStack == mTargetStack) {
// We onlywant to move to the front, if we aren't going to launch on a
// differentstack. If we launch on a different stack, we will put the
// task on topthere.
//这边就是进行相关task和activityStack的移动了,这个只是在Task所属的ActivityStack中 //的移动不涉及把Task移动到其它ActivityStack,见下面分析。
mTargetStack.moveTaskToFrontLocked(
intentActivity.task, mNoAnimation, mOptions,
mStartActivity.appTimeTracker,"bringingFoundTaskToFront");
mMovedToFront = true;
} else if(launchStack.mStackId == DOCKED_STACK_ID
||launchStack.mStackId == FULLSCREEN_WORKSPACE_STACK_ID) {
if ((mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_LAUNCH_ADJACENT) != 0) {
/*If we want to launch adjacent and mTargetStack is not the computed
*launch stack - move task to top of computed stack.
*这边是把复用的Task移动到其它的ActivityStack*/
mSupervisor.moveTaskToStackLocked(intentActivity.task.taskId,launchStack.mStackId,
ON_TOP, FORCE_FOCUS,"launchToSide",ANIMATE);
} else {
// TODO: Thisshould be reevaluated in MW v2.
// We choose to move task to front instead oflaunching it adjacent
// when specific stack was requestedexplicitly and it appeared to be
// adjacent stack, butFLAG_ACTIVITY_LAUNCH_ADJACENT was not set.
mTargetStack.moveTaskToFrontLocked(intentActivity.task, mNoAnimation,
mOptions,mStartActivity.appTimeTracker,
"bringToFrontInsteadOfAdjacentLaunch");
}
mMovedToFront = true;
}
mOptions = null;
}
updateTaskReturnToType(intentActivity.task, mLaunchFlags, focusStack);
}
}
//这边表示如果不需要Task移动,移动targetStack到前台,见下文分析。
if (!mMovedToFront &&mDoResume) {
if (DEBUG_TASKS) Slog.d(TAG_TASKS,"Bring to front target: " + mTargetStack
+ " from " +intentActivity);
mTargetStack.moveToFront("intentActivityFound");
}
mSupervisor.handleNonResizableTaskIfNeeded(intentActivity.task,INVALID_STACK_ID,
mTargetStack.mStackId);
// If the caller has requested that thetarget task be reset, then do so.
if ((mLaunchFlags &FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
returnmTargetStack.resetTaskIfNeededLocked(intentActivity, mStartActivity);
}
return intentActivity;
}我们进入ActivitityStack中的moveTaskToFrontLocked分析Task如何在所属的Activity移动。代码如下:
final void moveTaskToFrontLocked(TaskRecord tr, boolean noAnimation,
ActivityOptions options,
AppTimeTrackertimeTracker, String reason) {
final int numTasks= mTaskHistory.size();
final int index =mTaskHistory.indexOf(tr);
if (numTasks == 0 ||index < 0) {
// nothing to do!
if (noAnimation) {
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
} else {
updateTransitLocked(TRANSIT_TASK_TO_FRONT, options);
}
return;
}
。。。。。。
// Shift allactivities with this task up to the top
// of the stack,keeping them in the same internal order.
//这边就是把Task移动到ActivityStack的栈顶端
//代码比较简单不列了
insertTaskAtTop(tr,null);
。。。。。。。。。
// Set focus to the top running activity ofthis stack.
//这时候stack的topActivity应该是上一步已经移到栈顶
//复用的Task
ActivityRecord r =topRunningActivityLocked();
//更新AMS中的focusedActivity
//这边会把当前Activity所属的Stack移到栈顶,
//并且会更新ActivityStackSupervisor中的
//mLastFocusedStack、mFocusedStack这两个变量
mService.setFocusedActivityLocked(r, reason);
。。。。。。。。
//相应Activity状态的切换,这个后面章节会介绍
mStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
。。。。。。。。。。
}经过上面的setTargetStackAndMoveToFrontIfNeeded这个函数之后,当前启动Activity复用的Task、以它所属的ActivityStack均已经移动到了栈顶。接着是调用setTaskFromIntentActivity,代码如下:
//这个主要是处理一些FLAG,
private void setTaskFromIntentActivity(ActivityRecordintentActivity) {
if ((mLaunchFlags& (FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK))
==(FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK)) {
// The caller has requested to completely replace any existing taskwith its new
// activity. Well that should not be too hard...
//设置了FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TASK复用的Task会finish所有的Activity,并且重新
//更新复用Task信息的当前启动的Activity
intentActivity.task.performClearTaskLocked();
intentActivity.task.setIntent(mStartActivity);
mReuseTask =intentActivity.task;
// When we clear the task - focus will be adjusted, which will bringanother task
// to top before we launch the activity we need. This will temporaryswap their
// mTaskToReturnTo values and we don't want to overwrite themaccidentally.
mMovedOtherTask =true;
} else if((mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP) != 0
||mLaunchSingleInstance || mLaunchSingleTask) {
ActivityRecord top =intentActivity.task.performClearTaskLocked(mStartActivity,
mLaunchFlags);
if (top == null) {
// A special case: we needto start the activity because it is not currently
// running, and the callerhas asked to clear the current task to have this
// activity at the top.
mAddingToTask= true;
// Now pretend like thisactivity is being started by the top of its task, so it
// is put in the rightplace.
mSourceRecord= intentActivity;
finalTaskRecord task = mSourceRecord.task;
if (task !=null && task.stack == null) {
// Target stack got cleared when we allactivities were removed above.
// Goahead and reset it.
mTargetStack = computeStackFocus(mSourceRecord, false /* newTask */,
null /* bounds */, mLaunchFlags, mOptions);
mTargetStack.addTask(task,
!mLaunchTaskBehind /* toTop */, "startActivityUnchecked");
}
}
} else if(mStartActivity.realActivity.equals(intentActivity.task.realActivity)) {
// In this case the top activity on the task is the same as the onebeing launched,
// so we take that as a request to bring the task to the foreground.If the top
// activity in the task is the root activity, deliver this newintent to it if it
// desires.
if (((mLaunchFlags& FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP) != 0 || mLaunchSingleTop)
&&intentActivity.realActivity.equals(mStartActivity.realActivity)) {
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(AM_NEW_INTENT,mStartActivity,
intentActivity.task);
if(intentActivity.frontOfTask) {
intentActivity.task.setIntent(mStartActivity);
}
intentActivity.deliverNewIntentLocked(mCallingUid,mStartActivity.intent,
mStartActivity.launchedFromPackage);
} else if(!intentActivity.task.isSameIntentFilter(mStartActivity)) {
// In this case weare launching the root activity of the task, but with a
// different intent.We should start a new instance on top.
mAddingToTask= true;
mSourceRecord= intentActivity;
}
} else if((mLaunchFlags & FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED) == 0) {
// In this case anactivity is being launched in to an existing task, without
// resetting thattask. This is typically the situation of launching an activity
// from anotification or shortcut. We want to place the new activity on top of the
// current task.
mAddingToTask =true;
mSourceRecord =intentActivity;
} else if(!intentActivity.task.rootWasReset) {
// In this case weare launching into an existing task that has not yet been started
// from its frontdoor. The current task has been brought to the front. Ideally,
// we'd probablylike to place this new task at the bottom of its stack, but that's
// a little hardto do with the current organization of the code so for now we'll
// just drop it.
intentActivity.task.setIntent(mStartActivity);
}
}接着上面分析完存在复用Task的操作之后,我们代码还得继续往下接着看代码:
private int startActivityUnchecked(final ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSessionvoiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume,ActivityOptions options,
TaskRecordinTask) {
。。。。。。。。。
if (mReusedActivity != null){
。。。。。。。
}
if (mStartActivity.packageName == null){
/**异常处理*/
if (mStartActivity.resultTo != null&& mStartActivity.resultTo.task.stack != null) {
mStartActivity.resultTo.task.stack.sendActivityResultLocked(
-1,mStartActivity.resultTo, mStartActivity.resultWho,
mStartActivity.requestCode, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null);
}
ActivityOptions.abort(mOptions);
returnActivityManager.START_CLASS_NOT_FOUND;
}
// If the activity being launched isthe same as the one currently at the top, then
// we need to check if it should onlybe launched once.
/**
*对于系统刚启动HOME应用,此时FocusedStack即为HomeStack,
* 这个在AMS初始化中ActivityStackSupervisor的setWindowManager初始化完成
*/
final ActivityStack topStack =mSupervisor.mFocusedStack;
/**对于本文启动Launcher中的HOME Activity这时候TOP为nulll*/
final ActivityRecord top =topStack.topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(mNotTop);
/*这个是对于Flag设置了SINGLE_TOP的和launchmode为singleTOp和singleTask时候,对于当前启动的Activity在 *TaskRecord栈顶时候,调用onNewIntent*/
final boolean dontStart = top != null&& mStartActivity.resultTo == null
&&top.realActivity.equals(mStartActivity.realActivity)
&& top.userId == mStartActivity.userId
&& top.app != null &&top.app.thread != null
&& ((mLaunchFlags &Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP) != 0
|| mLaunchSingleTop ||mLaunchSingleTask);
if (dontStart) {
ActivityStack.logStartActivity(EventLogTags.AM_NEW_INTENT, top,top.task);
// For paranoia, make sure we havecorrectly resumed the top activity.
topStack.mLastPausedActivity =null;
if (mDoResume) {
mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
}
ActivityOptions.abort(mOptions);
if ((mStartFlags &ActivityManager.START_FLAG_ONLY_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
// We don't need to start a newactivity, and the client said not to do
// anything if that is thecase, so this is it!
returnActivityManager.START_RETURN_INTENT_TO_CALLER;
}
top.deliverNewIntentLocked(mCallingUid,mStartActivity.intent,
mStartActivity.launchedFromPackage);
// Don't use mStartActivity.task toshow the toast. We're not starting a new activity
// but reusing 'top'. Fields inmStartActivity may not be fully initialized.
mSupervisor.handleNonResizableTaskIfNeeded(
top.task,preferredLaunchStackId, topStack.mStackId);
returnActivityManager.START_DELIVERED_TO_TOP;
}
boolean newTask = false;
final TaskRecord taskToAffiliate =(mLaunchTaskBehind && mSourceRecord != null)
? mSourceRecord.task : null;
// Should this be considered a newtask?
/**
*对于本文启动Launcher中的HOME Activity,需要创建TaskRecord,所以进入第
*一个if流程
*这这对应的是不存在复用Task的情况,需要重新创建一个Task
*/
if (mStartActivity.resultTo == null&& mInTask == null && !mAddingToTask
&&(mLaunchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0) {
newTask = true;
/*计算当前启动Activity所属的ActivityStack以及为它创建一个新的TaskRecord*/
setTaskFromReuseOrCreateNewTask(taskToAffiliate);
。。。。。。。。
}
}
。。。。 。。。进入setTaskFromResuseOrCreateNewTask函数,代码如下:
private void setTaskFromReuseOrCreateNewTask(TaskRecord taskToAffiliate) {
/*这就是计算当前启动的Activity所属的ActivityStack
*对于本文介绍的启动Launcher中的HomeActivity,它对应
* 的ActivityStack为HomeStack
*/
mTargetStack = computeStackFocus(mStartActivity,true, mLaunchBounds,
mLaunchFlags, mOptions);
if (mReuseTask == null) {
/**
*开始创建TaskRecord,并且把新的TaskRecord加入到targetStack的栈顶
*/
final TaskRecord task =mTargetStack.createTaskRecord(
mSupervisor.getNextTaskIdForUserLocked(mStartActivity.userId),
mNewTaskInfo != null ?mNewTaskInfo : mStartActivity.info,
mNewTaskIntent != null ?mNewTaskIntent : mIntent,
mVoiceSession,mVoiceInteractor, !mLaunchTaskBehind /* toTop */);
/*
*设置正在启动的Activity所属的TaskRecord,
*其实到这儿还没有把当前启动的Activity加入到该TaskRecord中,
*/
mStartActivity.setTask(task,taskToAffiliate);
if (mLaunchBounds != null) {
final intstackId = mTargetStack.mStackId;
if(ActivityManager.StackId.resizeStackWithLaunchBounds(stackId)) {
mService.resizeStack(
stackId, mLaunchBounds, true, !ActivityStackSupervisor.PRESERVE_WINDOWS,ActivityManagerService.ANIMATE, -1);
} else {
mStartActivity.task.updateOverrideConfiguration(mLaunchBounds);
}
}
if (DEBUG_TASKS)Slog.v(ActivityStackSupervisor.TAG_TASKS,
"Starting new activity" +
mStartActivity + " in new task" + mStartActivity.task);
} else {
mStartActivity.setTask(mReuseTask,taskToAffiliate);
}
}经过上一步正在启动的Activity所以对应的TaskRecord以及ActivityStack已经准备好,那么接下去ActivityStarter中未完成分析。
startActivityUnchecked(){
……
setTaskFromReuseOrCreateNewTask(taskToAffiliate);
if(mSupervisor.isLockTaskModeViolation(mStartActivity.task)) {
Slog.e(TAG,"Attempted Lock Task Mode violation mStartActivity=" +mStartActivity);
return ActivityManager.START_RETURN_LOCK_TASK_MODE_VIOLATION;
}
if(!mMovedOtherTask) {
// If stack idis specified in activity options, usually it means that activity is
// launchednot from currently focused stack (e.g. from SysUI or from shell) - in
// that casewe check the target stack.
/*这是设置对应TaskRecord返回前一个ActivityStack的类型*/
updateTaskReturnToType(mStartActivity.task, mLaunchFlags,
preferredLaunchStackId != ActivityManager.StackId.INVALID_STACK_ID ?mTargetStack : topStack);
}
}
/*
*这个if分支是不需要创建Task,并且调用者不为空
*这个流程对应的也是存在复用Task的情况
*对于本文是以启动Launcher中的HOME应用分析,这部分分支代码可以先忽略*/
else if (mSourceRecord != null) {
if(mSupervisor.isLockTaskModeViolation(mSourceRecord.task)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "AttemptedLock Task Mode violation mStartActivity=" + mStartActivity);
return ActivityManager.START_RETURN_LOCK_TASK_MODE_VIOLATION;
}
/*
*1、首先计算当前启动Activity所归属的ActivityStack
*2、把该ActivityStack移动到前台
*3、其中处理相关的Flag
*4、设置当前启动的Activity的Task
**/
final int result =setTaskFromSourceRecord();
if (result !=ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS) {
return result;
}
} else if (mInTask != null) {
/*对于本文是以启动HOME应用分析,这部分代码先忽略*/
// The caller is asking that thenew activity be started in an explicit
// task it has provided to us.
if(mSupervisor.isLockTaskModeViolation(mInTask)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "AttemptedLock Task Mode violation mStartActivity=" + mStartActivity);
return ActivityManager.START_RETURN_LOCK_TASK_MODE_VIOLATION;
}
/*这个从调用中指定的TaskRecord设定当前Activity所属的TaskRecord**/
final int result =setTaskFromInTask();
if (result !=ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS) {
return result;
}
} else {
// This not being started from anexisting activity, and not part of a new task...
// just put it in the top task,though these days this case should never happen.
setTaskToCurrentTopOrCreateNewTask();
}
mService.grantUriPermissionFromIntentLocked(mCallingUid,mStartActivity.packageName,
mIntent,mStartActivity.getUriPermissionsLocked(), mStartActivity.userId);
/*这个表示从任务列表中启动Activity,
*对于本文是以启动HOME Activity分析不是从最近任务列表中启动*/
if (mSourceRecord != null &&mSourceRecord.isRecentsActivity()) {
mStartActivity.task.setTaskToReturnTo(ActivityRecord.RECENTS_ACTIVITY_TYPE);
}
mTargetStack.mLastPausedActivity =null;
sendPowerHintForLaunchStartIfNeeded(false /* forceSend */);
/*把当前启动的Activity加入TaskRecord以及绑定WindowManagerService*/
mTargetStack.startActivityLocked(mStartActivity, newTask,mKeepCurTransition, mOptions);
。。。。。。。。。。
}我们进入ActivityStack中的startActivityLocked中分析,代码如下:
final void startActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean newTask, booleankeepCurTransition, ActivityOptions options) {
TaskRecord rTask = r.task;
/**
* rTask即之前创建的TaskRecord,或者为复用的TaskRecord,
*对于本文是以启动Launcher HOMEActivity它为setTaskFromReuseOrCreateNewTask* 这个创建的TaskRecord
*/
final int taskId = rTask.taskId;
// mLaunchTaskBehind tasks get placedat the back of the task stack.
if (!r.mLaunchTaskBehind &&(taskForIdLocked(taskId) == null || newTask)) {
// Last activity in task had beenremoved or ActivityManagerService is reusing task.
// Insert or replace.
// Might not even be in.
insertTaskAtTop(rTask, r);/*插入新创建或复用的TaskRecord到栈顶*/
mWindowManager.moveTaskToTop(taskId);/*同时在Windowmanager中也移动到栈顶*/
}
TaskRecord task = null;
/*
* 对于本文是以启动Launcher HOMEActivity,这时候是有创建
* 一个新的TaskRecord,所以该分支不走
*/
if (!newTask) {//这是表示存在复用的TaskRecord
// If starting in an existing task,find where that is...
boolean startIt = true;
/**遍历TaskRecord
*从这儿也可以得出TaskRecord在ActivityStack是以栈的方式管理的*/
for (int taskNdx =mTaskHistory.size() - 1; taskNdx >= 0; --taskNdx) {
task =mTaskHistory.get(taskNdx);
if (task.getTopActivity() ==null) {
// All activities in taskare finishing.
continue;
}
/*在Task堆栈中找到了复用的Task*/
if (task == r.task) {
// Here it is! Now, if this is not yet visible to the
// user, then just add itwithout starting; it will
// get started when theuser navigates back to it.
if (!startIt) {
if(ActivityManagerDebugConfig.DEBUG_ADD_REMOVE) Slog.i(TAG, "Adding activity" + r + " to task "
+ task, newRuntimeException("here").fillInStackTrace());
//把当前启动的Activity加入到复用的Task栈顶*/
task.addActivityToTop(r);
r.putInHistory();
/*绑定到windowmanager中*/
addConfigOverride(r,task);
if (VALIDATE_TOKENS) {
validateAppTokensLocked();
}
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return;
}
break;
} else if (task.numFullscreen> 0) {
startIt = false;
}
}
}
task = r.task;
/**当前启动的Activity加到所属Task栈顶中
*对于本文是以启动Launcher HOMEActivity*/
task.addActivityToTop(r);
/*这个是标记Task中Activity堆栈的堆底Activity元素*/
task.setFrontOfTask();
r.putInHistory();
/*如果当前ActivityStack不为 HomeStack,
*或者该ActivityStack中activity个数不为0
*对于本文是以启动Launcher HOMEActivity,所以该流程不走
*/
if (!isHomeStack() || numActivities()> 0) {
// We want to show the startingpreview window if we are
// switching to a new task, or thenext activity's process is
// not currently running.
boolean showStartingIcon = newTask;
ProcessRecord proc = r.app;
if (proc == null) {
proc =mService.mProcessNames.get(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo.uid);
}
/*对于刚启动HOME应用时,表示进程ProcessReocrd还为空*/
if (proc == null || proc.thread ==null) {
showStartingIcon = true;
}
if (DEBUG_TRANSITION)Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION,
"Prepare opentransition: starting " + r);
/*动画相关*/
if ((r.intent.getFlags() &Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_ANIMATION) != 0) {
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(AppTransition.TRANSIT_NONE,keepCurTransition);
mNoAnimActivities.add(r);
} else {
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(newTask
? r.mLaunchTaskBehind
?AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN_BEHIND
:AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN
:AppTransition.TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_OPEN, keepCurTransition);
mNoAnimActivities.remove(r);
}
/*当前启动的Activity绑定到WIndowManagerService当中*/
addConfigOverride(r, task);
boolean doShow = true;
if (newTask) {
// Even though this activity isstarting fresh, we still need
// to reset it to make sure weapply affinities to move any
// existing activities from other tasks into it.
// If the caller has requestedthat the target task be
// reset, then do so.
if ((r.intent.getFlags() &Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
resetTaskIfNeededLocked(r,r);
doShow =topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(null) == r;
}
} else if (options != null&& options.getAnimationType()
==ActivityOptions.ANIM_SCENE_TRANSITION) {
doShow = false;
}
if (r.mLaunchTaskBehind) {
// Don't do a starting windowfor mLaunchTaskBehind. More importantly make sure we
// tell WindowManager that r is visibleeven though it is at the back of the stack.
mWindowManager.setAppVisibility(r.appToken, true);
ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0,!ActivityStackSupervisor.PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
} else if(SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW && doShow) {
// Figure out if we aretransitioning from another activity that is
// "has the same startingicon" as the next one. This allowsthe
// window manager to keep theprevious window it had previously
// created, if it still hadone.
ActivityRecord prev =r.task.topRunningActivityWithStartingWindowLocked();
if (prev != null) {
// We don't want to reusethe previous starting preview if:
// (1) The current activityis in a different task.
if (prev.task != r.task) {
prev = null;
}
// (2) The current activityis already displayed.
else if (prev.nowVisible) {
prev = null;
}
}
r.showStartingWindow(prev,showStartingIcon);
}
} else {
// If this is the first activity,don't do any fancy animations,
// because there is nothing for itto animate on top of.
/*当前启动的Activity绑定到WIndowManagerService当中*/
addConfigOverride(r, task);
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
options = null;
}
if (VALIDATE_TOKENS) {
validateAppTokensLocked();
}
}经过以上步骤,Task也创建了,也把当前启动的Activity加入到Task正确的位置,
ActivityStack也移动到了正确位置。那么剩下的可以分为两种情况
1、对于当前启动的Activity所属的进程已经创建情况,并且当前正在启动的Activity也已经创建过实例了,那么接下来调用resumed、 paused流程。
2、对于当前启动的Activity还没有实例化,他需要走实例化流程。
对于本文启动Launcher 他是需要先创建一个进程,所以接下去我们介绍,应用程序进程创建的过程。
三、Paused之前Activity、resumed当前启动的Activity过程
这一部分其实对应的是Activity的生命周期,这个会在第五章节《Activity的生命周期》中介绍,目前先以系统刚跑起来,第一次启动Launcher 的HomeActivity作简单分析,这时候只是主要看到如何调用到Launcher的进程启动过程。因为经过前两的步骤,到这儿其实相关的Activity所属的Task 、ActivityStack都是移到了正确位置。
我们继续ActivityStarter中的startActivityUnchecked未分析代码。
startActivityUnchecked()
。。。。。。。。
if (mDoResume) {
if (!mLaunchTaskBehind) {
// TODO(b/26381750): Remove this codeafter verification that all the decision
// points above moved targetStack tothe front which will also set the focus
// activity.
/*
* 设置当前focused,因为经过以上几步,启动的activity已经转移到
*栈顶端,这时候设置AMS当前focused的Activity,对于本文分析
*启动Launcher HomeActivity,这时候focusedActivity即
*为Launcher中的Home Activity
*另外调用这个函数也会有ActivityStack、Task栈的移动,即调用各自栈把当
*前正在启动的Activity所属的Task、ActivityStack移动到栈顶
*/
mService.setFocusedActivityLocked(mStartActivity,"startedActivity");
}
/*这时应该为当前启动的Activity,对于本文即为图二表示的HomeActivity*/
final ActivityRecord topTaskActivity =mStartActivity.task.topRunningActivityLocked();
//当前HomeStack为focusable 所以该分支不走
if (!mTargetStack.isFocusable()
|| (topTaskActivity != null&& topTaskActivity.mTaskOverlay
&& mStartActivity != topTaskActivity)) {
。。。。。。
} else {
//最终调用该函数
mSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(mTargetStack,mStartActivity,
mOptions);
}
} else {
mTargetStack.addRecentActivityLocked(mStartActivity);
}
mSupervisor.updateUserStackLocked(mStartActivity.userId, mTargetStack);
mSupervisor.handleNonResizableTaskIfNeeded(
mStartActivity.task,preferredLaunchStackId, mTargetStack.mStackId);
return ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS;
}接下来分析一下ActivityStackSupervisor中的resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked,因为AMS对于Activity比较复杂的部分即为复用栈时候的处理以及最后这部分的resumed相关操作,这两部分读者最好以假定某种启动模式,并对应着代码进行分析,其实resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked这个对应的就是Activity生命周期
中的onPaused->onStopped->onDestory,这个我会在第五章节《Activity生命周期》介绍,这边先简单过一下。
boolean resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(
ActivityStack targetStack, ActivityRecord target,ActivityOptions targetOptions) {
/**如果指定的ActivityStack存在,对于本文分析HOMEActivity启动,targetStack即为HomeStack*/
if(targetStack != null && isFocusedStack(targetStack)) {
//进入
resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked
return targetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);
。。。。。。。
}接着进入当前启动Activity所属ActivityStack中的resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked,代码如下:
/**
* Ensure that the top activity in thestack is resumed.
*
* @param prev The previously resumedactivity, for when in the process
* of pausing; can be null to call fromelsewhere.
* @param options Activity options.
*
* @return Returns true if something isbeing resumed, or false if
* nothing happened.
*
* NOTE: It is not safe to call this methoddirectly as it can cause an activity in a
* non-focused stack to be resumed.
* Use {@link ActivityStackSupervisor#resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked}to resume the
* right activity for the current system state.
*/
boolean resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptions options){
。。。。。。
//进入resumeTopActivityInnerLocked
result =resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
return result;
}代码比较简单进入resumeTopActivityInnerLocked,这个函数代码比较长,大伙多看几遍。代码如下:
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptionsoptions) {
。。。。。。。
// Find the first activity that is notfinishing.
/*
*首先获取当前ActivityStack中栈顶Activity
*对于本文分析第一次启动Launcher 该next即为Launcher的HomeActivity
*/
final ActivityRecord next =topRunningActivityLocked();
//Remember how we'll process thispause/resume situation, and ensure
// that the state is reset however wewind up proceeding.
/*这个变量是表示是否回调Activity中的onUserLeaveHint和onUserInteraction函数*/
final boolean userLeaving =mStackSupervisor.mUserLeaving;
mStackSupervisor.mUserLeaving = false;
final TaskRecord prevTask = prev !=null ? prev.task : null;
if (next == null) {//这个表示如果当前ActivityStack不存在未完成的Activity那么会启动Launcher桌面
final Stringreason = "noMoreActivities";
final int returnTaskType = prevTask ==null || !prevTask.isOverHomeStack()
?ActivityRecord.HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE : prevTask.getTaskToReturnTo();
if (!mFullscreen &&adjustFocusToNextFocusableStackLocked(returnTaskType, reason)) {
// Try to move focus to thenext visible stack with a running activity if this
// stack is not covering theentire screen.
returnmStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(
mStackSupervisor.getFocusedStack(), prev, null);
}
// Let's just start up theLauncher...
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
if (DEBUG_STATES)Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked:No more activities go home");
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
// Only resume home if on homedisplay
return isOnHomeDisplay() && mStackSupervisor.resumeHomeStackTask(returnTaskType,prev, reason);
}
next.delayedResume= false;
// If the top activity is the resumedone, nothing to do.
/*这个是如果当前ActivityStack的resumedActivity即为栈顶第一个未finish的Activity,那么表示已经resumed过了就不继续以下的处理*/
if(mResumedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.RESUMED&&
mStackSupervisor.allResumedActivitiesComplete()) {
// Make sure we have executed anypending transitions, since there
// should be nothing left to do atthis point.
mWindowManager.executeAppTransition();
mNoAnimActivities.clear();
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
if (DEBUG_STATES)Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Top activity resumed " + next);
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
final TaskRecord nextTask = next.task;
/*这个是对上一个resumed的Activity的相关处理
*针对本文第一次启动Launcher,HomeActivity即prev的finishing为false
*/
if (prevTask!= null && prevTask.stack == this &&
prevTask.isOverHomeStack()&& prev.finishing && prev.frontOfTask) {
。。。。。。。。。。
}
}
// If we aresleeping, and there is no resumed activity, and the top
// activity is paused, well that is thestate we want.
if(mService.isSleepingOrShuttingDownLocked()
&& mLastPausedActivity == next
&& mStackSupervisor.allPausedActivitiesComplete()) {
// Make sure we have executed anypending transitions, since there
// should be nothing left to do atthis point.
mWindowManager.executeAppTransition();
mNoAnimActivities.clear();
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Going to sleep and all paused");
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
。。。。。。。。
// The activity may be waiting for stop, but thatis no longer
// appropriate for it.
mStackSupervisor.mStoppingActivities.remove(next);
mStackSupervisor.mGoingToSleepActivities.remove(next);
next.sleeping = false;
mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.remove(next);
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,"Resuming " + next);
// If we are currently pausing an activity,then don't do anything until that is done.
if(!mStackSupervisor.allPausedActivitiesComplete()) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_PAUSE ||DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Skip resume: some activitypausing.");
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
mStackSupervisor.setLaunchSource(next.info.applicationInfo.uid);
// We need tostart pausing the current activity so the top one can be resumed...
final boolean dontWaitForPause =(next.info.flags& FLAG_RESUME_WHILE_PAUSING) != 0;
/**这个是pause掉不是FocusedStack的其它ActivityStack的栈顶activity*/
*对于不是当前focusStack的并且存在有mResumedActivity不为null的都要paused
*/
boolean pausing =mStackSupervisor.pauseBackStacks(userLeaving, next, dontWaitForPause);
/*
*这个表示该ActivityStack已经存在resumedActivity
*但是对于本文介绍启动Launcher HOMEActivity时其实到这儿HOME Activity还未实例化,*此时HomeStack中还不存在有 *Activity,这时候该mResumed为null,读者可以先跳过
*/
if (mResumedActivity != null) {
。。。。。。。。。
}
/*对于第一次启动HOME应用pausing为false
*读者可以跳过
*/
if (pausing) {
。。。。。。。
return true;
} else if (
//针对本文分析第一次启动Launcher HomeActivity,此时mResumedAcitivyt还
//为null ,并且next.state状态还为INITIATION,这步可以先跳过
mResumedActivity == next
&&next.state == ActivityState.RESUMED
&&mStackSupervisor.allResumedActivitiesComplete()){
。。。。。。。。。。
return true;
}
// If the most recent activity was noHistory butwas only stopped rather
// than stopped+finished because thedevice went to sleep, we need to make
// sure to finish it as we're making anew activity topmost.
/**
*如果此时处于屏幕灭屏状态,并且当前Resumed的Activity设置了Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_HISTORY
*那么需要finish此Activity
*/
if (mService.isSleepingLocked()&& mLastNoHistoryActivity != null &&
!mLastNoHistoryActivity.finishing) {
if (DEBUG_STATES)Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"no-history finish of" + mLastNoHistoryActivity + " on new resume");
requestFinishActivityLocked(mLastNoHistoryActivity.appToken,Activity.RESULT_CANCELED,
null,"resume-no-history", false);
mLastNoHistoryActivity = null;
}
/*对于第一次启动HOME应用prev和next是相同
*读者可以先跳过
*/
if (prev != null && prev !=next) {
。。。。。。
}
。。。。。。。
// We are starting up the nextactivity, so tell the window manager
// that the previous one will be hiddensoon. This way it can know
// to ignore it when computing thedesired screen orientation.
boolean anim = true;
if (mIsAnimationBoostEnabled == true&& mPerf == null) {
mPerf = new BoostFramework();
}
if (prev != null) {//这边是准备相关的动画
if (prev.finishing) {
if (DEBUG_TRANSITION)Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION,
"Prepare closetransition: prev=" + prev);
if(mNoAnimActivities.contains(prev)) {
anim = false;
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(AppTransition.TRANSIT_NONE, false);
} else {
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(prev.task == next.task
?AppTransition.TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_CLOSE
:AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_CLOSE, false);
}
mWindowManager.setAppVisibility(prev.appToken, false);
} else {
if (DEBUG_TRANSITION)Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION,
"Prepare opentransition: prev=" + prev);
if(mNoAnimActivities.contains(next)) {
anim = false;
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(AppTransition.TRANSIT_NONE, false);
} else {
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(prev.task == next.task
?AppTransition.TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_OPEN
:next.mLaunchTaskBehind
?AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN_BEHIND
:AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN, false);
}
}
} else {
if(DEBUG_TRANSITION) Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION, "Prepare open transition: noprevious");
if (mNoAnimActivities.contains(next)){
anim = false;
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(AppTransition.TRANSIT_NONE, false);
} else {
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(AppTransition.TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_OPEN,false);
}
}
Bundler esumeAnimOptions = null;
if (anim) {
ActivityOptions opts =next.getOptionsForTargetActivityLocked();
if (opts != null) {
resumeAnimOptions =opts.toBundle();
}
next.applyOptionsLocked();
} else {
next.clearOptionsLocked();
}
ActivityStack lastStack =mStackSupervisor.getLastStack();
/**
*如果当前ActivityStack中,此时处于Task最顶端的Activity已经创建过了并且已经纳入相
*应的进程中,那么进入该Activity的resumed过程。
*举个例子:比如你已经通过Launcher启动了应用2中的Activity A,这时候按HOME键
*返回到Launcher桌面,这时你又点击Launcher上应用2的图标,这时候就会调用onResumed
*对于本文第一次启动Launcher HOME Activity next.app为null即还没有创建对应的进程
*读者可以先跳过这一步
*/
if (next.app != null &&next.app.thread != null) {
。。。。。。。。。
return true;
}
} else {
// Whoops, need to restart thisactivity!
if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
} else {
if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW){
next.showStartingWindow(null, true);
}
}
//对于本文第一次启动Launcher HOMEActivity或者第一次启动其它应用,最终调用这边开//始创建应用对应的进程
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
}
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
}以上就是对于当前启动的Activity已经纳入到对应的进程时,paused之前的Activity以及resumed当前启动的Activity过程,这种情况下并没有Activity创建过程,因为他之前已经创建过了,这也符合应用开发过程中所说的Actiivity从后台到前台会调用Activity生命周期的onResumed函数。
四、进程的创建
针对本文paused之前Activity、resumed当前启动的Activity过程这一章节,主要是针对当前启动Activity已经创建的过程的分析,那么对于第一次启动过程,比如从Launcer桌面点击图标启动一个应用时,它是需要为它创建一个对应的进程的,本章节就介绍下一个应用对应的进程创建过程。
我们接着第三章节写的跟踪进入ActivityStackSupervisor中的startSpecificActivityLocked,代码如下:
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean andResume, booleancheckConfig) {
// Is this activity's applicationalready running?
/*
*根据Activity的processName(该值在应用AndroidManifest.xml中
*android:process定义,如果未定义则默认为当前应用包名)在AMS查询当前启动*的Activity对应的进程是否存
* 存在,对于本文第一次启动Launcher或者其它第一次启动应用时,app为null
*/
ProcessRecord app =mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid,true);
r.task.stack.setLaunchTime(r);
/*对于第一次启动HOME应用或第一次启动其它应用,因为还没有创建对应的进程
*所以app此时为null
*读者可以无跳过这一步
*/
if (app != null && app.thread!= null) {
try {
if ((r.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_MULTIPROCESS)== 0
||!"android".equals(r.info.packageName)) {
// Don't add this if it isa platform component that is marked
// to run in multipleprocesses, because this is actually
// part of the framework sodoesn't make sense to track as a
// separate apk in theprocess.
app.addPackage(r.info.packageName, r.info.applicationInfo.versionCode,
mService.mProcessStats);
}
/*如果当前启动的Activity所属的进程已经存在,那么调用
* 该函数只开始Activity初始化生命周期,而不需要再重新创建进程。
*/
realStartActivityLocked(r, app,andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exceptionwhen starting activity "
+r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
}
//如果当前启动的Activity所属的进程还未创建,这边调用AMS为启动的Activity创建进程
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName,r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity",r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);
}关于AMS中进程创建的我会忽略相关代码,抓住创建进程的主线,进入AMS中的startProcessLocked,最终调用到以下函数
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName, ApplicationInfo info,
boolean knownToBeDead, intintentFlags, String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName,
boolean allowWhileBooting, booleanisolated, int isolatedUid, boolean keepIfLarge,
String abiOverride, StringentryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs, Runnable crashHandler) {
//相关代码各位读者可以自行分析
long startTime =SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
ProcessRecord app;
。。。。。。
//对于第一次启动应用此时app为null
if (app != null && app.pid >0) {
。。。。。。
}
。。。。。。
if (app == null) {
//这时候创建用来描述应用进程ProcessRecord
app = newProcessRecordLocked(info,processName, isolated, isolatedUid);
。。。。。。
}
。。。。。。
startProcessLocked(
app, hostingType,hostingNameStr, abiOverride, entryPoint, entryPointArgs);
checkTime(startTime,"startProcess: done starting proc!");
return (app.pid != 0) ? app : null;
}
进入newProcessRecordLocked分析一下
final ProcessRecord newProcessRecordLocked(ApplicationInfo info, String customProcess,boolean isolated, int isolatedUid) {
String proc =customProcess != null ? customProcess : info.processName;
BatteryStatsImpl stats =mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics();
final int userId =UserHandle.getUserId(info.uid);
int uid = info.uid;
。。。。。。。。
}
/**这时候开始创建ProcessRecord对象
*创建的ProcessRecord会保存AMS中的mProcessNames和mPidsSelfLocked这两个
*变量中,记住这两个变量,此时用来描述进程ProcessRecord所表示已经创建
*OK,因为下面在创建Android主线程ActivityThread时
*会用到此时创建的ProcessRecord
*/
final ProcessRecordr = new ProcessRecord(stats, info, proc, uid);
if (!mBooted && !mBooting
&& userId == UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM
&& (info.flags & PERSISTENT_MASK) == PERSISTENT_MASK) {
r.persistent = true;
}
//保存创建的ProcessRecord到变量mProcessNames
addProcessNameLocked(r);
}
分析完newProcessRecordLocked接着进入
startProcessLocked(
app, hostingType,hostingNameStr, abiOverride, entryPoint, entryPointArgs);
。。。。。。
boolean isActivityProcess =(entryPoint == null);
//这个很重要,我们知道Android应用都存在一个应用主线ActivityThread即表示主线程
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint= "android.app.ActivityThread";
//这边开始正式创建进程
Process.ProcessStartResultstartResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName,uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion,app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir,entryPointArgs);
。。。。。。
if (oldApp !=null && !app.isolated) {
// Clean up anything relatingto this pid first
Slog.w(TAG, "Reusing pid" + startResult.pid
+ " while app isstill mapped to it");
cleanUpApplicationRecordLocked(oldApp, false, false, -1,
true /*replacingPid*/);
}
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
//把创建的ProcessRecord保存到mPidsSelfLocked变量中,
this.mPidsSelfLocked.put(startResult.pid,app);
if (isActivityProcess) {
Message msg =mHandler.obtainMessage(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = app;
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, startResult.usingWrapper
?PROC_START_TIMEOUT_WITH_WRAPPER : PROC_START_TIMEOUT);
}
}
。。。。。。。。
}经过以上步骤,AMS中表示应用进程的ProcessRecord已经创建完毕,并且保存在了AMS中的mProcessNames、mPidsSelfLocked这两个变量当中。关于Process.start这块的大家可以上网看下关于Android中zygote如何创建进程的步骤,这边就不列了,本文的目的是梳理Activity的创建,最终进程创建OK之后他会调用ActivityThread中的main函数,这边说下ActivityThread中比较重要的变量。
/**这个mAppThread变量是和ProcessRecord以及AMS进行通信的*/
finalApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();
我们看下ActivityThread中的main函数代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER,"ActivityThreadMain");
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
// CloseGuard defaults to true and canbe quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectivelyenable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, butusing DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Environment.initForCurrentUser();
// Set the reporter for event loggingin libcore
EventLogger.setReporter(new EventLoggingReporter());
// Make sure TrustedCertificateStorelooks in the right place for CA certificates
final File configDir =Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
Process.setArgV0("");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = newActivityThread();
//调用attach,记住传入的是参数为false
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler =thread.getHandler();
}
。。。。。。
} 进入ActivityThread的attach函数
private void attach(boolean system) {
ViewRootImpl.addFirstDrawHandler(newRunnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ensureJitEnabled();
}
});
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("",
UserHandle.myUserId());
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
final IActivityManager mgr =ActivityManagerNative.getDefault(); try{
=//注意传入的变量为IBinder类型的mAppThread
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch(RemoteException ex) {
throwex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
BinderInternal.addGcWatcher(newRunnable() {
@Override public void run() {
if(!mSomeActivitiesChanged) {
return;
}
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long dalvikMax =runtime.maxMemory();
long dalvikUsed =runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
if (dalvikUsed >((3*dalvikMax)/4)) {
if (DEBUG_MEMORY_TRIM) Slog.d(TAG,"Dalvik max=" + (dalvikMax/1024)
+ "total=" + (runtime.totalMemory()/1024)
+ "used=" + (dalvikUsed/1024));
mSomeActivitiesChanged= false;
try {
mgr.releaseSomeActivities(mAppThread);
} catch(RemoteException e) {
throwe.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
});
} else {//此时传入的参数为false以下分支先忽略,该分支是在AMS初始化
//的时候进入该分支
。。。。。。
}
} 这部分代码逻辑还是比较简单,读者自行看下,接着进入AMS中的attachApplication函数
@Override
public final voidattachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid =Binder.getCallingPid();
final long origId =Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}接着进入AMS的attachApplicationLocked,代码如下:
private finalboolean attachApplicationLocked(
IApplicationThread thread,//该参数为ActivityThread中的mAppThread
int pid) {
// Find theapplication record that is being attached... either via
// the pid if we are running inmultiple processes, or just pull the
// next app record if we are emulatingprocess with anonymous threads.
ProcessRecord app;
if (pid != MY_PID && pid >=0) {
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
/**因为之前AMS中的startProcessLocked中已经创建应用对应的ProcessRecord,并且保存**在mPidsSelfLocked
*忘记的可以看AMS中的startProcessLocked
*/
app = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);
}
} else {
app = null;
}
//这时候已经创建了,此时app不为null
if (app == null) {
Slog.w(TAG,"No pending application record for pid " + pid
+ "(IApplicationThread " + thread + "); dropping process");
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_DROP_PROCESS,pid);
if (pid > 0 && pid !=MY_PID) {
Process.killProcessQuiet(pid);
//TODO:killProcessGroup(app.info.uid, pid);
} else {
try {
thread.scheduleExit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore exceptions.
}
}
return false;
}
。。。。。。
/*
*这边是设置ProcessRecord与ActivityThread进行通信的Ibinder对象,而ProcessRecord
*在AMS中所以通过thread就建立了AMS和应用主线程ActivityThread的通信
* thread即为ActivityThread中的mAppThread
*/
app.makeActive(thread,mProcessStats);
。。。。。。
/*
*我们知道thread即为ActivityThread中的mAppThread所以这时候回调
* ActivityThread中的bindApplication
*/
thread.bindApplication(processName,appInfo, providers, app.instrumentationClass,
profilerInfo,
app.instrumentationArguments,app.instrumentationWatcher,
app.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode ||!normalMode, app.persistent,
newConfiguration(mConfiguration), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked());
updateLruProcessLocked(app, false,null);
。。。。。。。
} 这时候进入ActivityThread中的bindApplication代码如下:
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
Listproviders, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo,Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcherinstrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnectioninstrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking,boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode,boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,Map services, Bundle coreSettings) {
if (services != null) {
// Setup the service cache inthe ServiceManager
ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services);
}
setCoreSettings(coreSettings);
AppBindData data = newAppBindData();
data.processName = processName;
data.appInfo = appInfo;
data.providers = providers;
data.instrumentationName =instrumentationName;
data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs;
data.instrumentationWatcher =instrumentationWatcher;
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection =instrumentationUiConnection;
data.debugMode = debugMode;
data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking;
data.trackAllocation =trackAllocation;
data.restrictedBackupMode =isRestrictedBackupMode;
data.persistent = persistent;
data.config = config;
data.compatInfo = compatInfo;
data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo;
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION,data);
} 在这个函数中设置完相应的参数,通过Handler最终调用的函数是handleBindApplication
private voidhandleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
// Register the UI Thread as asensitive thread to the runtime.
//这也是一堆代码,读者对着代码自行分析,这边先删除太占篇幅
。。。。。。
/*
* Before spawning a new process, resetthe time zone to be the system time zone.
* This needs to be done because thesystem time zone could have changed after the
* the spawning of this process.Without doing this this process would have the incorrect
* system time zone.
*/
TimeZone.setDefault(null);
/*
* Set the LocaleList. This may changeonce we create the App Context.
*/
LocaleList.setDefault(data.config.getLocales());
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
/*
* Update the system configurationsince its preloaded and might not
* reflect configuration changes.The configuration object passed
* in AppBindData can be safelyassumed to be up to date
*/
mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(data.config,data.compatInfo);
mCurDefaultDisplayDpi =data.config.densityDpi;
// This calls mResourcesManager sokeep it within the synchronized block.
applyCompatConfiguration(mCurDefaultDisplayDpi);
}
/* 这边为进程创建了一个LoadApk对象并且保存在mPackages变量当中,
* LoadApk主要用于应用的相关的resDir、libDir相关资源的东西,
* 但是此时LoadApk的ClassLoader为null
*/
data.info = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.appInfo,data.compatInfo);
。。。。。。。
final boolean is24Hr ="24".equals(mCoreSettings.getString(Settings.System.TIME_12_24));
DateFormat.set24HourTimePref(is24Hr);
。。。。。。
// Allow application-generated systracemessages if we're debuggable.
// Instrumentation info affects theclass loader, so load it before
// setting up the app context.
final InstrumentationInfo ii;
if (data.instrumentationName != null) {
try {
ii = newApplicationPackageManager(null, getPackageManager())
.getInstrumentationInfo(data.instrumentationName,0);
} catch(PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to findinstrumentation info for: " + data.instrumentationName);
}
mInstrumentationPackageName =ii.packageName;
mInstrumentationAppDir =ii.sourceDir;
mInstrumentationSplitAppDirs =ii.splitSourceDirs;
mInstrumentationLibDir =getInstrumentationLibrary(data.appInfo, ii);
mInstrumentedAppDir =data.info.getAppDir();
mInstrumentedSplitAppDirs =data.info.getSplitAppDirs();
mInstrumentedLibDir =data.info.getLibDir();
} else {
ii = null;
}
//这边开始创建Context大家在开发过程经常使用到的Context上下文了
final ContextImpl appContext =ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, data.info);
updateLocaleListFromAppContext(appContext,
mResourcesManager.getConfiguration().getLocales());
。。。。。。。
// Continue loading instrumentation.
/*
* 1、创建Instrument
* Instrument这个大家在开发过程使用的比较少,这个有点儿类似Android应
*的工具类,对于Activity所有的生命周期比如onCreate、onResume都是通过该
*instrumetn进行分发调用
* 这边说明下如果不是自定义的Instrument此时ii为null,对于自定义的Instrument
* 是通过Context的startInstrumentation来启动一个进程,这时候ii就不会为null了
*/
if (ii != null) {
final ApplicationInfo instrApp = new ApplicationInfo();
ii.copyTo(instrApp);
instrApp.initForUser(UserHandle.myUserId());
final LoadedApk pi =getPackageInfo(instrApp, data.compatInfo,
appContext.getClassLoader(), false, true, false);
final ContextImpl instrContext =ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, pi)
try {
final ClassLoader cl =instrContext.getClassLoader()
mInstrumentation =(Instrumentation)
cl.loadClass(data.instrumentationName.getClassName()).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiateinstrumentation "
+ data.instrumentationName+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
final ComponentName component = new ComponentName(ii.packageName, ii.name);
mInstrumentation.init(this,instrContext, appContext, component,
data.instrumentationWatcher,data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection);
if (mProfiler.profileFile != null&& !ii.handleProfiling
&&mProfiler.profileFd == null) {
mProfiler.handlingProfiling =true;
final File file = newFile(mProfiler.profileFile);
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
Debug.startMethodTracing(file.toString(), 8 * 1024 * 1024);
}
} else {
mInstrumentation = newInstrumentation();
}
。。。。。。。ActivityClientRecord
// Allow disk access during applicationand provider setup. This could
// block processing ordered broadcasts,but later processing would
// probably end up doing the same diskaccess.
final StrictMode.ThreadPolicysavedPolicy = StrictMode.allowThreadDiskWrites();
try {
// If the app is being launched forfull backup or restore, bring it up in
// a restricted environment withthe base application class.
/**
* 2、创建Application
* 对于应用开发者可能会在应用中重载类Application,
* 而这个Application一个应用只存在一个,这儿即创建Application
*/
Application app =data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
mInitialApplication = app;
// don't bring up providers inrestricted mode; they may depend on the
// app's custom Application class
if (!data.restrictedBackupMode) {
if(!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(data.providers)) {
installContentProviders(app,data.providers);
// For process thatcontains content providers, we want to
// ensure that the JIT isenabled "at some point".
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.ENABLE_JIT,10*1000);
}
}
// Do this after providers, sinceinstrumentation tests generally start their
// test thread at this point, andwe don't want that racing.
try {
mInstrumentation.onCreate(data.instrumentationArgs);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Exception thrown inonCreate() of "
+ data.instrumentationName+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
try {
//这儿就开始调用Application的onCreate函数
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if(!mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to createapplication " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " +e.toString(), e);
}
}
} finally {
StrictMode.setThreadPolicy(savedPolicy);
}
}这边我们得分析一下,
Application app =data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);因为这里边涉及很多重要的东西,主要为应用程序中的Application创建Context、LoadApk。我们进入LoadApk中的makeApplication代码如下:
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
Instrumentation instrumentation) {
if (mApplication != null) {
return mApplication;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER,"makeApplication");
Application app = null;
String appClass =mApplicationInfo.className;
//对于应用未重载Application时,默认为android.app.Application
if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass== null)) {
appClass ="android.app.Application";
}
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl =getClassLoader();
if(!mPackageName.equals("android")) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER,
"initializeJavaContextClassLoader");
initializeJavaContextClassLoader();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
/*
* 创建ContextImple对象
*/
ContextImpl appContext =ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this);
/*
*为当前启动的应用创建Application这部分作用
*1、把上一步创建的appContext绑定到了ContextWrapper中mBase中
*2、把当前LoadedApk绑定到应用ApplicationmLoadedApk
*3、必须把创建的Application保存到LoadedApk当中
*/
app =mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(
cl, appClass, appContext);
appContext.setOuterContext(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if(!mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiateapplication " + appClass
+ ": " + e.toString(),e);
}
}
mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
mApplication = app;
if (instrumentation != null) {
try {
instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if(!instrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to createapplication " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " +e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
// Rewrite the R 'constants' for alllibrary apks.
SparseArraypackageIdentifiers = getAssets(mActivityThread)
.getAssignedPackageIdentifiers();
final int N =packageIdentifiers.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
final int id =packageIdentifiers.keyAt(i);
if (id == 0x01 || id == 0x7f) {
continue;
}
rewriteRValues(getClassLoader(),packageIdentifiers.valueAt(i), id);
}
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
return app;
} 经过以上几步,应用中所涉及到的Instrument、Application以有Application中的Context、LoadedApk相关的就已经都准备好了,此时还没有到Activity的生命周期当中,我们继续往下。。。。接下来返回继续AMS的attachApplicationLocked之后的流程。
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
。。。。。。
// See if the top visible activity iswaiting to run in this process...
if (normalMode) {
try {
if(mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG,"Exception thrown launching activities in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
。。。。。。
}进入ActivityStackSupervisor中的attachApplicationLocked代码如下
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord app) throws RemoteException {
final StringprocessName = app.processName;
boolean didSomething = false;
for (int displayNdx =mActivityDisplays.size() - 1; displayNdx >= 0; --displayNdx) {
ArrayList stacks= mActivityDisplays.valueAt(displayNdx).mStacks;
for (int stackNdx = stacks.size() -1; stackNdx >= 0; --stackNdx) {
final ActivityStack stack =stacks.get(stackNdx);
if (!isFocusedStack(stack)) {
continue;
}
ActivityRecord hr =stack.topRunningActivityLocked();
/*因为在ActivityStarter中的startActivityUnchecked,即在本文第二章节<计算Activity所属的*Task、 *ActivityStack,及操作>中已经把要启动Activity所属的
*ActivityStack以及TaskRecord移动到栈顶了,那么时候hr即为当前要启动的
*Activity,本文是分析HOME应用,所以hr即为homeActivity
*/
if (hr !=null) {
if (hr.app == null&& app.uid == hr.info.applicationInfo.uid
&&processName.equals(hr.processName)) {
try {
//这时候真正开始Activity的初始化生命周期
if(realStartActivityLocked(hr, app, true, true)) {
didSomething =true;
}
} catch(RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG,"Exception in new application when starting activity "
+hr.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
throw e;
}
}
}
if (!didSomething) {
ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null,0, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
}
return didSomething;
} 这一章节主要流程是在AMS创建描述进程信息的ProcessRecord,并且保存到AMS中,
并且通过zygote进程来真正创建进程,此过程完成了应用主线程ActivityThread创建、应用Application的创建、Context的创建、LoadApk这些重要类的创建。但到这步Activity初始化流程其实还没有开始,这一部顶多完成了Acitivty初始化的准备工作。Activity生命周期介绍
这一章节是所以Activity都会经历的生命周期。
我们知道activity的生命周期为onCreate->onStart->onResumed->running->onPaused->onStopped->onDestroy。这章节我们分析Activity生命周期分成两部分来介绍。
1、Activity创建过程的生命周期onCreate->onStart->onResumed
这个过程在Activity初始化完成。 我们在第四章节介绍进程创建开头有提到ActivityStackSupervisor中的startSpecificActivityLocked这个函数中,如果当前启动的Activity所属的进程信息已经创建过了,那么直接调用realStartActivityLocked进入Activity初始化生命周期,对于第四章节介绍进程创建的最后对于新建的进程最终也会调用realStartActivityLocked进入Activity初始化生命周期。忘记的读者可以返回第四章节最后一部分回顾一下。
进入ActivityStackSupervisor中的realStartActivityLocked,代码如下:
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app,
boolean andResume, booleancheckConfig) throws RemoteException {
。。。。。。
//当前启动的Activity保存AMS中对Activity进程描述的ProcessRecord信息
r.app = app;
app.waitingToKill= null;
r.launchCount++;
r.lastLaunchTime= SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (DEBUG_ALL) Slog.v(TAG,"Launching: " + r);
int idx = app.activities.indexOf(r);
//如果当前启动的Activty还不存在ProcessRecord中,则把它加到ProcessRecord中
if (idx < 0) {
app.activities.add(r);
}
。。。。。。
final ActivityStack stack = task.stack;
。。。。。。
if (r.isHomeActivity()) {
// Home process is the rootprocess of the task.
mService.mHomeProcess =task.mActivities.get(0).app;
}
/**
*我们之前在创建ProcessRecord时候,知道thread即为ActivityThread中的mAppThread,
*这时我们进入ActivityThread中
* 这步开始Activity初始化流程。。。
*/
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(
new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,
System.identityHashCode(r),
r.info, new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration),
newConfiguration(task.mOverrideConfig),
r.compat, r.launchedFromPackage,
task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle,r.persistentState, results,
newIntents, !andResume,mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);
。。。。。。
}各位读者,这时候流程跑到这儿,马上就能够看到Activity的生命周期了,大家喝口水继续
进入ActivityThread中scheduleLaunchActivity,代码如下:
//we usetoken to identify this activity without having to send the
// activity itself back to the activitymanager. (matters more with ipc)
@Override
public final voidscheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info,Configuration curConfig, Configuration overrideConfig,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int procState, Bundle state,PersistableBundle persistentState,
ListpendingResults, List pendingNewIntents,
boolean notResumed, booleanisForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) {
updateProcessState(procState,false);
ActivityClientRecord r = newActivityClientRecord();
r.token =token;
r.ident =ident;
r.intent =intent;
r.referrer =referrer;
r.voiceInteractor= voiceInteractor;
r.activityInfo= info;
r.compatInfo =compatInfo;
r.state =state;
r.persistentState= persistentState;
r.pendingResults= pendingResults;
r.pendingIntents= pendingNewIntents;
r.startsNotResumed= notResumed;
r.isForward =isForward;
r.profilerInfo= profilerInfo;
r.overrideConfig= overrideConfig;
updatePendingConfiguration(curConfig);
sendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY,r);
} 通过Handler调用
r.packageInfo =getPackageInfoNoCheck(r.activityInfo.applicationInfo,r.compatInfo);
获取LoadApk,Application在创建进程时候调用makeApplication已经创建,这时候不会再重新创建一个,而是直接采用之前创建的,然后调用handleLaunchActivity,代码如下:
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent, Stringreason) {
// If we aregetting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
if (r.profilerInfo != null) {
mProfiler.setProfiler(r.profilerInfo);
mProfiler.startProfiling();
}
// Make sure we are running with themost recent config.
handleConfigurationChanged(null, null);
// Initialize before creating theactivity
WindowManagerGlobal.initialize();
//这儿就正式调用Activity的onCreate函数我们继续进入分析
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r,customIntent);
。。。。。
}进入performLaunchActivity:代码如下
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
ActivityInfoaInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo =getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
ComponentName component =r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component =r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity !=null) {
component = newComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl =r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
//这儿先创建要启动的Activity的实例,本文分析为Home,所以此时创建的实例
//为HomeActivity,读者可以返回文章之前的图二
activity =mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl,component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity,e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiateactivity " + component
+ ": " +e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
/*
*这个在创建进程时候在调用ActivityThread调用makeApplication已经创
*建过Application,所以此时只是返回之前创建的Application
*/
Application app =r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
if (activity != null) {
//为当前Activity 创建Context,实际上指向的是ContextImpl
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r,activity);
CharSequencetitle = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = newConfiguration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (r.overrideConfig != null) {
config.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig);
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION)Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name +" with config " + config);
Window window = null;
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow !=null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
window =r.mPendingRemoveWindow;
r.mPendingRemoveWindow =null;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null;
}
//这时候调用attach,这个函数很重要,列下几个重要的变量
/**1、它把创建的Context回到了Activity中的context当中,这样Activity就获取到了*context
*2、创建了PhoneWindow
*3、创建了UI线程
*4、得到了应用的主线程
*5、mToken绑定到PhoneWindow。mToken即为ActivityRecord创建时的mAppToken
*6、把创建进程时候创建的Application绑定到Activity
*7、把ActivityRecord的Intent绑定Activity中的mIntent
*8、把创建的Instrument绑定到Activity
*/
activity.attach(appContext,this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent,r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID,r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer,r.voiceInteractor, window);
if(customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent =customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances= null;
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
int theme =r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
activity.mCalled = false;
//Activity实例创建完毕,也attach完之后,就开始调用onCreate
//他是通过Instrument进行调用的,这在ActivityThread中handleBindApplication创建
if(r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state,r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity,r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw newSuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " +r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not callthrough to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity =activity;
r.stopped = true;
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
///开始调用onStart函数
activity.performStart();
r.stopped =false;
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.isPersistable()) {
if (r.state != null ||r.persistentState != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
}
} else if (r.state != null){
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.mCalled= false;
///调用函数onPasCreate
if (r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity,r.state,
r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw newSuperNotCalledException(
"Activity" + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not callthrough to super.onPostCreate()");
}
}
}
r.paused =true;
mActivities.put(r.token,r);
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if(!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to startactivity " + component
+ ": " +e.toString(), e);
}
}
return activity;
}经过以上步骤,当前启动的Activity实例初始化已经完成,每个Activity都要重新创建Context,通过attach初始化相关变量, context、PhoneWindow、UI线程、主线程、mToken绑定到PhoneWindow、Application绑定到Activity、Instrument绑定到Activity。我们应用开发经常碰到的Activity生命周期onCreate、onStart、onPostCreate已经调用,但是onResume还没有调用,我们继续handleLaunchActivity调用完performLaunchActivity之后的代码:
handleLaunchActivity{
。。。。。。。。。
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig= new Configuration(mConfiguration);
reportSizeConfigurations(r);
Bundle oldState = r.state;
//在这儿开始调用onResumed函数
handleResumeActivity(r.token,false, r.isForward,
!r.activity.mFinished&& !r.startsNotResumed, r.lastProcessedSeq, reason);
。。。。。。。。
}通过以上分析我们知道启动Activity生命周期onCreate->onStart->onResumed正式调用完毕。
继续之前ActivityStackSupervisor中的realStartActivityLocked调用完scheduleLaunchActivity之后的步骤。扫尾。。.
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app,
boolean andResume, booleancheckConfig) throws RemoteException {
if (andResume) {
// As part of the process oflaunching, ActivityThread also performs
// a resume.
//因为Activity已经调用完onResumed,所以这时候当前启动的Activity所属的ActivityStack中的mResumedActivity设置为当前启动的Activity,状态为RESUMED。
stack.minimalResumeActivityLocked(r);
} else {
.。。。。。。。。。
}
。。。。。。。
}2、Activity结束过程的生命周期onPasued->onStop->onDestory
这个过程在Activity结束时候完成。到本小章节读者应该以假定此时已经启动了相关应用,并且假在在某种场景下,进
行Activity的切换,读者要记者一个Activity移动前台必然存在上一个Activity的paused过程,有些场景我还没有弄明白,如果有读者明白请指出来。
我们对于第三章节简单分析resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked这边再继续深分析,弄明白Activity生命周期结束的部分。
我们进入ActivityStackSupervisor中的resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked,看函数名字应该是resumed系统中focusedStack的处于栈顶的Activity。代码如下:
boolean resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(
ActivityStack targetStack,//目标ActivityStack,可为null
ActivityRecord target, //上一个resumed的activity,可为null
ActivityOptions targetOptions) {
/*
*对于指定的tagetStack存在,并且为Focused的stack,那么进入
*指定的targetStack进行resume操作。
*/
if (targetStack != null &&isFocusedStack(targetStack)) {
returntargetStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(target, targetOptions);
}
/*
*指定的ActivityStack不存在则获取当前Focused的ActivityStack
*获取focusedStack的处于顶端的Activity,并且此时activity的状态
*不为RESUMED
*/
final ActivityRecord r =mFocusedStack.topRunningActivityLocked();
if (r == null || r.state !=ActivityStack.ActivityState.RESUMED) {
mFocusedStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(null, null);
}
return false;
}接着进入对应的ActivityStack中的resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked,代码如下:
/**
* Ensure that the top activity in thestack is resumed.
*
* @param prev The previously resumedactivity, for when in the process
* of pausing; can be null to call fromelsewhere.
* @param options Activity options.
*
* @return Returns true if something isbeing resumed, or false if
* nothing happened.
*
* NOTE: It is not safe to call this methoddirectly as it can cause an activity in a
* non-focused stack to be resumed.
* Use {@link ActivityStackSupervisor#resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked}to resume the
* right activity for the current system state.
*/
boolean resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord prev,ActivityOptions options) {
//当前系统正在处于resumeTopActivity过程则返回
if(mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity) {
// Don't even start recursing.
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
try {
// Protect against recursion.
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = true;
if (mService.mLockScreenShown ==ActivityManagerService.LOCK_SCREEN_LEAVING) {
mService.mLockScreenShown =ActivityManagerService.LOCK_SCREEN_HIDDEN;
mService.updateSleepIfNeededLocked();
}
result =resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
} finally {
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = false;
}
return result;
}代码比较简单进入resumeTopActivityInnerLocked,这个函数代码比较长,大伙多看几遍。代码如下:
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptionsoptions) {
。。。。。。。
ActivityRecord parent =mActivityContainer.mParentActivity;
if ((parent != null &&parent.state != ActivityState.RESUMED) ||
!mActivityContainer.isAttachedLocked()) {
// Do not resume this stack if itsparent is not resumed.
// TODO: If in a loo, make surethat parent stack resumeTopActivity is called 1st.
return false;
}
mStackSupervisor.cancelInitializingActivities();
// Find the first activity that is notfinishing.
/*
*首先获取当前ActivityStack中栈顶Activity,这个即为我们
*要resumed的Activity
*/
final ActivityRecord next =topRunningActivityLocked();
//Remember how we'll process thispause/resume situation, and ensure
// that the state is reset however we wind upproceeding.
/*这个变量是表示是否回调Activity中的onUserLeaveHint和onUserInteraction函数*/
final boolean userLeaving =mStackSupervisor.mUserLeaving;
mStackSupervisor.mUserLeaving = false;
final TaskRecord prevTask = prev !=null ? prev.task : null;
if (next == null) {//这个表示如果当前ActivityStack不存在未完成的Activity那么会启动Launcher桌面
final Stringreason = "noMoreActivities";
final int returnTaskType = prevTask== null || !prevTask.isOverHomeStack()
?ActivityRecord.HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE : prevTask.getTaskToReturnTo();
if (!mFullscreen &&adjustFocusToNextFocusableStackLocked(returnTaskType, reason)) {
// Try to move focus to thenext visible stack with a running activity if this
// stack is not covering theentire screen.
returnmStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(
mStackSupervisor.getFocusedStack(), prev, null);
}
// Let's just start up theLauncher...
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
if (DEBUG_STATES)Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: No more activities go home");
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
// Only resume home if on homedisplay
return isOnHomeDisplay() &&
mStackSupervisor.resumeHomeStackTask(returnTaskType, prev, reason);
}
next.delayedResume= false;
// If the topactivity is the resumed one, nothing to do.
/*这个是如果当前ActivityStack的resumedActivity即为栈顶Activity,那么表示已经resumed过了就不继续以下的处理*/
if(mResumedActivity == next && next.state == ActivityState.RESUMED&&
mStackSupervisor.allResumedActivitiesComplete()) {
// Make sure we have executed anypending transitions, since there
// should be nothing left to do atthis point.
mWindowManager.executeAppTransition();
mNoAnimActivities.clear();
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
if (DEBUG_STATES)Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Top activity resumed " + next);
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
final TaskRecord nextTask = next.task;
/*
*这个是对上一个resumed的Activity的相关处理
*针对这个,本人不是很不清楚表示的场景
*/
if (prevTask!= null && prevTask.stack == this &&
prevTask.isOverHomeStack()&& prev.finishing && prev.frontOfTask) {
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
if (prevTask == nextTask) {
prevTask.setFrontOfTask();
} else if (prevTask != topTask()) {
// This task is going away butit was supposed to return to the home stack.
// Now the task above it has toreturn to the home task instead.
final int taskNdx = mTaskHistory.indexOf(prevTask)+ 1;
mTaskHistory.get(taskNdx).setTaskToReturnTo(ActivityRecord.HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE);
} else if (!isOnHomeDisplay()) {
return false;
} else if (!isHomeStack()){
if (DEBUG_STATES)Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Launching home next");
final int returnTaskType = prevTask ==null || !prevTask.isOverHomeStack() ?
ActivityRecord.HOME_ACTIVITY_TYPE:prevTask.getTaskToReturnTo();
return isOnHomeDisplay()&&
mStackSupervisor.resumeHomeStackTask(returnTaskType, prev,"prevFinished");
}
}
// If we are sleeping, and there is no resumedactivity, and the top
// activity is paused, well that is thestate we want.
if(mService.isSleepingOrShuttingDownLocked()
&& mLastPausedActivity == next
&& mStackSupervisor.allPausedActivitiesComplete()) {
// Make sure we have executed anypending transitions, since there
// should be nothing left to do atthis point.
mWindowManager.executeAppTransition();
mNoAnimActivities.clear();
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Going to sleep and all paused");
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
// Make sure that the user who ownsthis activity is started. If not,
// we will just leave it as is becausesomeone should be bringing
// another user's activities to the topof the stack.
//这个是多用户相关
if (!mService.mUserController.hasStartedUserState(next.userId)){
Slog.w(TAG, "Skipping resumeof top activity " + next
+ ": user " +next.userId + " is stopped");
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
// Theactivity may be waiting for stop, but that is no longer
// apprpriate for it.
mStackSupervisor.mStoppingActivities.remove(next);
mStackSupervisor.mGoingToSleepActivities.remove(next);
next.sleeping = false;
mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.remove(next);
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,"Resuming " + next);
// If we are currently pausing anactivity, then don't do anything until that is done.
if(!mStackSupervisor.allPausedActivitiesComplete()) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_PAUSE ||DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Skip resume: some activitypausing.");
if (DEBUG_STACK) mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
mStackSupervisor.setLaunchSource(next.info.applicationInfo.uid);
// We need tostart pausing the current activity so the top one can be resumed...
final boolean dontWaitForPause =(next.info.flags& FLAG_RESUME_WHILE_PAUSING) != 0;
/*
*这个是pause掉不是FocusedStack的其它ActivityStack的栈顶activity*/
*对于不是当前focusStack的并且存在有mResumedActivity不为null的都要paused
*举个例子:如果当前处于FULLSCREEN_WORKSPACE_STACK(应用处于的Stack)
*这时候按HOME键切换到Launcher桌面,因为Launcher是处于HOME_STACK,
*那么时候需要把FULLSCREEN_STACK中的resumed 状态的Activity进行pausing过程
*/
boolean pausing =mStackSupervisor.pauseBackStacks(userLeaving, next, dontWaitForPause);
/*
*这个表示当前ActivityStack已经存在resumedActivity,也进行pausing过程。
*/
if (mResumedActivity != null) {
pausing |=startPausingLocked(userLeaving, false, next, dontWaitForPause);
}我们分析关于Activity如何进行Pausing操作。进入startPausingLocked函数,
/**
* Start pausing the currently resumedactivity. It is an error to call this ifthere
* is already an activity being paused orthere is no resumed activity.
*
*@param userLeaving True if this should result in an onUserLeavingto the current activity.
* @param uiSleeping True if this ishappening with the user interface going to sleep (the screen turning off).
* @param resuming The activity we arecurrently trying to resume or null
* if this is not being called as part of resuming the top activity,so we
* shouldn't try to instigate a resume here if not null.
* @param dontWait True if the caller doesnot want to wait for the pause to
* complete. If set to true,we will immediately complete the pause
* here before returning.
* @return Returns true if an activity now is in thePAUSING state, and we are
* waiting for it to tell us when it is done.
*/
//函数的注释大伙可以看下,其中参数dontWait表示如何Activity如果有设置
//android:resumeWhilePausing="true"那么会马上进行PAUSED
final boolean startPausingLocked(booleanuserLeaving, boolean uiSleeping,
ActivityRecord resuming,
boolean dontWait
) {
//这个表示ActivityStack中的已经进行过了pausing操作,那么接下去直接finish操作
if (mPausingActivity != null) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Going to pausewhen pause is already pending for " + mPausingActivity
+ " state=" +mPausingActivity.state);
if (!mService.isSleepingLocked()) {
// Avoid recursion among checkfor sleep and complete pause during sleeping.
// Because activity will bepaused immediately after resume, just let pause
// be completed by the order ofactivity paused from clients.
completePauseLocked(false,resuming);
}
}
ActivityRecord prev = mResumedActivity;
//表示当前ActivityStack还没有resumed 过Activity,直接返回
if (prev == null) {
if (resuming == null) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Trying topause when nothing is resumed");
mStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
}
return false;
}
/*
*这边就是转换过程中一些Activity状态的记录过程,大致这样
*mResumedActivity->mPausingActivity
*mResumedActivity->mLastPausedActivity
*/
mResumedActivity = null;
mPausingActivity = prev;
mLastPausedActivity = prev;
mLastNoHistoryActivity =(prev.intent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_HISTORY) != 0
|| (prev.info.flags &ActivityInfo.FLAG_NO_HISTORY) != 0 ? prev : null;
//这边该ActivityStack中的resumedActivity状态变成了PAUSING状态
prev.state = ActivityState.PAUSING;
。。。。。。
final ActivityRecord next =mStackSupervisor.topRunningActivityLocked();
if (mService.mHasRecents
&&(next == null || next.noDisplay || next.task != prev.task || uiSleeping)) {
//这是标记该ResumedActivity是否需要截屏
prev.mUpdateTaskThumbnailWhenHidden= true;
}
。。。。。。。
//这儿就是该ActivityStack的resumedActivity的调用onPause函数
*注意此时prev.state值为 ActivityState.PAUSING
if (prev.app != null &&prev.app.thread != null) {
try {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PAUSE_ACTIVITY,
prev.userId,System.identityHashCode(prev),
prev.shortComponentName);
mService.updateUsageStats(prev,false);
/*调用Activity的onPaused,这个流程不分析了,读者可以自行分析
*如果dontWait为false(即android:resumeWhilePausing为false时候)
*它调用ActivityThread的schedulePauseActivity之后,
*ActivityThread会通过AMS会回调该ActivityStack的activityPausedLocked*函数并且会调用completePauseLocked这 *个函数下面还会涉及,下面再分*析,在这个函数里面会把该activity的状态prev.state修改成PAUSED,
*/
prev.app.thread.schedulePauseActivity(prev.appToken, prev.finishing,
userLeaving,prev.configChangeFlags, dontWait);
} catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore exception, if processdied other code will cleanup.
Slog.w(TAG, "Exceptionthrown during pause", e);
mPausingActivity = null;
mLastPausedActivity = null;
mLastNoHistoryActivity = null;
}
} else {
mPausingActivity = null;
mLastPausedActivity = null;
mLastNoHistoryActivity = null;
}
// If we are not going to sleep, we wantto ensure the device is
// awake until the next activity isstarted.
if (!uiSleeping &&!mService.isSleepingOrShuttingDownLocked()) {
mStackSupervisor.acquireLaunchWakelock();
}
/如果上步在调用onPaush没有出错,或者resumed对应的进程不为空
//那么继续paused过程
if (mPausingActivity != null) {
// Have the window manager pause its keydispatching until the new
// activity has started. If we're pausing the activity just because
// the screen is being turned offand the UI is sleeping, don't interrupt
// key dispatch; the same activitywill pick it up again on wakeup.
if (!uiSleeping) {
prev.pauseKeyDispatchingLocked();
} else if (DEBUG_PAUSE) {
Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Keydispatch not paused for screen off");
}
//如果AndroidManifest.xml有设置android:resumeWhilePausing="true"该值为true
if (dontWait) {
// If the caller said they don'twant to wait for the pause, then complete
//the pause now.
completePauseLocked(false,resuming);
return false;
} else {
// Schedule a pause timeout incase the app doesn't respond.
// We don't give it much timebecause this directly impacts the
// responsiveness seen by theuser.
//这个其实最终也会调用到completePauseLocked这里面,所以
//我们接下来看看这里面操作
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(PAUSE_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = prev;
prev.pauseTime =SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, PAUSE_TIMEOUT);
if (DEBUG_PAUSE)Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Waiting for pause to complete...");
return true;
}
} else {
// This activity failed to schedulethe
// pause, so just treat it as beingpaused now.
if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE,"Activity not running, resuming next.");
if (resuming == null) {
mStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
}
return false;
}
}我们接着上一步startPausingLocked中调用completePauseLocked过程分析,其实这个是AcrivityRecord中的PAUSING过程到PAUSED的过程。代码如下:
private void completePauseLocked(boolean resumeNext, ActivityRecordresuming) {
//这个mPausingActivity在startPausingLocked赋值
ActivityRecord prev =mPausingActivity;
//表示当前正在pausing的activity不为null
//这个流程表示处理Activity的pausing过程
if (prev != null) {
final booleanwasStopping = prev.state == ActivityState.STOPPING;
//这时候Activity由PAUSIING到PAUSED
prev.state =ActivityState.PAUSED;
//如果这个activity状态为finish的时候直接finish该activity
if(prev.finishing) {
//如果pausingActivty已经finish了直接调用这个这个就不展开分析了,大致说下,如果prev处于前台,那么 //它会把该Activiyt状态切成ActivityState.STOPPGING。如果prev不处于前台,那么Activity状态
//切成ActivityState.FINISHI,且该ActivityRecord中的finish的值改成
//true并且通过r.app.thread.scheduleDestroyActivity调
//用Activity的onStop、onDestory函数,这个流程完了之后通
//过AMS的activityDestroyed函数回调ActivityStack中的
//removeActivityFromHistoryLocked把该Activity中TaskRecord中删除,//且把状态切成 //ActivityState.Destory。
prev =finishCurrentActivityLocked(prev, FINISH_AFTER_VISIBLE, false);
} else if(prev.app != null) {
if(mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.remove(prev)) {
if(DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE,
"Complete pause, no longer waiting: " + prev);
}
//这个是好像Activty configuration变化时候,并且当前activity还处//于pausing时候会置成true,这时候会重新launchActivty过程
// 具体的还没有弄明白
if (prev.deferRelaunchUntilPaused){
//Complete the deferred relaunch that was waiting for pause to complete.
if(DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Re-launching after pause: " + prev);
relaunchActivityLocked(prev, prev.configChangeFlags, false,
prev.preserveWindowOnDeferredRelaunch);
} else if(wasStopping) {
// We arealso stopping, the stop request must have gone soon after the pause.
// We can't clobber it, because the stopconfirmation will not be handled.
// We don't need toschedule another stop, we only need to let it happen.
prev.state= ActivityState.STOPPING;
} else if((!prev.visible && !hasVisibleBehindActivity())
||mService.isSleepingOrShuttingDownLocked()) {
// If we were visiblethen resumeTopActivities will release resources before
// stopping.
addToStopping(prev, true /*immediate */);
}
} else {
prev = null;
}
// It is possible theactivity was freezing the screen before it was paused.
// In that case goahead and remove the freeze this activity has on the screen
// since it is nolonger visible.
if (prev != null){
prev.stopFreezingScreenLocked(true /*force*/);
}
//到这儿pausing过程就已经完成了,重置变量
mPausingActivity =null;
}
//pausing处理完了,resumed下个Activity
if (resumeNext) {
finalActivityStack topStack = mStackSupervisor.getFocusedStack();
if(!mService.isSleepingOrShuttingDownLocked()) {
//继续调用本小章节的函数
mStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked(topStack, prev,null);
} else {
mStackSupervisor.checkReadyForSleepLocked();
ActivityRecordtop = topStack.topRunningActivityLocked();
if (top ==null || (prev != null && top != prev)) {
// Ifthere are no more activities available to run, do resume anyway to start
//something. Also if the top activity on the stack is not the just paused
//activity, we need to go ahead and resume it to ensure we complete an
//in-flight app switch.
mStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
}
}
}
if (prev != null) {
prev.resumeKeyDispatchingLocked();
if (prev.app !=null && prev.cpuTimeAtResume > 0
&& mService.mBatteryStatsService.isOnBattery()) {
long diff =mService.mProcessCpuTracker.getCpuTimeForPid(prev.app.pid)
-prev.cpuTimeAtResume;
if (diff >0) {
BatteryStatsImpl bsi =mService.mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics();
synchronized (bsi) {
BatteryStatsImpl.Uid.Proc ps =
bsi.getProcessStatsLocked(prev.info.applicationInfo.uid,
prev.info.packageName);
if (ps!= null) {
ps.addForegroundTimeLocked(diff);
}
}
}
}
prev.cpuTimeAtResume = 0; // reset it
}
// Notify when thetask stack has changed, but only if visibilities changed (not just
// focus). Also ifthere is an active pinned stack - we always want to notify it about
// task stack changes,because its positioning may depend on it.
if(mStackSupervisor.mAppVisibilitiesChangedSinceLastPause
||mService.mStackSupervisor.getStack(PINNED_STACK_ID) != null) {
mService.notifyTaskStackChangedLocked();
mStackSupervisor.mAppVisibilitiesChangedSinceLastPause = false;
}
mStackSupervisor.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(resuming, 0,!PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
}我们总结下这个过程,调用startPausingLocked,Activity生命周期的onPaused被调用,并且此时ActivityRecord状态经历了RESUMED->PAUSING->PAUSED的变化,经过这一步ActivityStack处于running状态的Activity已经变成PAUSED状态。
我们继续分析startPausingLocked的之后的代码,接上
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, ActivityOptionsoptions) {
。。。。。。。。
pausing |=startPausingLocked(userLeaving, false, next, dontWaitForPause);
。。。。。。。。
//如果当前Activity状态还示切到PAUSED,还处于PAUSING时候
//就不再继续下面的resumed处于栈顶的activity,因为这时候resumed的
//Activtity还未走完paused流程
if (pausing) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_STATES)Slog.v(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Skip resume: need to startpausing");
// At this point we want to put theupcoming activity's process
// at the top of the LRU list,since we know we will be needing it
// very soon and it would be awaste to let it get killed if it
// happens to be sitting towardsthe end.
if (next.app != null &&next.app.thread != null) {
mService.updateLruProcessLocked(next.app, true, null);
}
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
} else if (mResumedActivity == next&&next.state == ActivityState.RESUMED &&
mStackSupervisor.allResumedActivitiesComplete()) {
// It ispossible for the activity to be resumed when we paused back stacks above if the
// next activity doesn't have towait for pause to complete.
// So, nothing else to-do except:
// Make sure we have executed anypending transitions, since there
// should be nothing left to do atthis point.
mWindowManager.executeAppTransition();
mNoAnimActivities.clear();
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
if (DEBUG_STATES)Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Top activity resumed (dontWaitForPause)" + next);
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
}
// If the mostrecent activity was noHistory but was only stopped rather
// than stopped+finished because thedevice went to sleep, we need to make
// sure to finish it as we're making anew activity topmost.
/**
*如果此时处于屏幕灭屏状态,并且当前Resumed的Activity设置了Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_HISTORY
*那么需要finish此Activity
*/
if (mService.isSleepingLocked()&& mLastNoHistoryActivity != null &&
!mLastNoHistoryActivity.finishing) {
if (DEBUG_STATES)Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"no-history finish of" + mLastNoHistoryActivity + " on new resume");
requestFinishActivityLocked(mLastNoHistoryActivity.appToken,Activity.RESULT_CANCELED,
null,"resume-no-history", false);
mLastNoHistoryActivity = null;
}
if (prev != null && prev !=next) {
if(!mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.contains(prev)
&& next != null &&!next.nowVisible) {
mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.add(prev);
if (DEBUG_SWITCH)Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,
"Resuming top,waiting visible to hide: " + prev);
} else {
// The next activity is alreadyvisible, so hide the previous
// activity's windows right nowso we can show the new one ASAP.
// We only do this if theprevious is finishing, which should mean
// it is on top of the onebeing resumed so hiding it quickly
// is good. Otherwise, we want to do the normal route ofallowing
// the resumed activity to beshown so we can decide if the
// previous should actually behidden depending on whether the
// new one is found to befull-screen or not.
if (prev.finishing) {
mWindowManager.setAppVisibility(prev.appToken, false);
if (DEBUG_SWITCH)Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,
"Not waitingfor visible to hide: " + prev + ", waitingVisible="
+mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.contains(prev)
+ ",nowVisible=" + next.nowVisible);
} else {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH)Slog.v(TAG_SWITCH,
"Previous already visiblebut still waiting to hide: " + prev
+ ",waitingVisible="
+mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.contains(prev)
+ ", nowVisible="+ next.nowVisible);
}
}
}
// Launching this app's activity, makesure the app is no longer
// considered stopped.
try {
AppGlobals.getPackageManager().setPackageStoppedState(
next.packageName,false, next.userId); /* TODO: Verify if correct userid */
} catch (RemoteException e1) {
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed trying tounstop package "
+ next.packageName +": " + e);
}
// We are starting up the nextactivity, so tell the window manager
// that the previous one will be hiddensoon. This way it can know
// to ignore it when computing thedesired screen orientation.
boolean anim = true;
if (mIsAnimationBoostEnabled == true&& mPerf == null) {
mPerf = new BoostFramwork();
}
//这边是准备相关的动画,这样用户可以视觉感觉切换过程
/读者看下就好
if (prev != null) {
。。。。
}
Bundle resumeAnimOptions = null;
if (anim) {
ActivityOptions opts =next.getOptionsForTargetActivityLocked();
if (opts != null) {
resumeAnimOptions =opts.toBundle();
}
next.applyOptionsLocked();
} else {
next.clearOptionsLocked();
}
ActivityStack lastStack =mStackSupervisor.getLastStack();
/*
*这之前是pausing上一个resumed的Activity,这时候就要进入栈顶的resumed过程了,
*不然栈顶的Activity永远不显示了。
*如果当前ActivityStack中,此时处于Task栈顶的Activity已经创建过了并且已经纳入相
*应的进程中,那么进入该Activity的resumed过程。
*举个例子:比如你已经通过Launcher启动了应用2中的Activity A,这时候按HOME键
*返回到Launcher桌面,这时你又点击Launcher上应用2的图标,这时候就会调用onResumed
*/
if (next.app != null &&next.app.thread != null) {
// If the previous activity istranslucent, force a visibility update of
// the next activity, so that it'sadded to WM's opening app list, and
// transition animation can be setup properly.
// For example, pressing Homebutton with a translucent activity in focus.
// Launcher is already visible inthis case. If we don't add it to opening
// apps,maybeUpdateTransitToWallpaper() will fail to identify this as a
// TRANSIT_WALLPAPER_OPENnimation, and run some funny animation.
final booleanlastActivityTranslucent = lastStack != null
&& (!lastStack.mFullscreen
||(lastStack.mLastPausedActivity != null
&& !lastStack.mLastPausedActivity.fullscreen));
// This activity is now becomingvisible.
if (!next.visible || next.stopped|| lastActivityTranslucent) {
mWindowManager.setAppVisibility(next.appToken, true);
}
// schedule launch ticks to collectinformation about slow apps.
next.startLaunchTickingLocked();
ActivityRecord lastResumedActivity=
lastStack == null ? null:lastStack.mResumedActivity;
ActivityState lastState =next.state;
mService.updateCpuStats();
if (DEBUG_STATES)Slog.v(TAG_STATES, "Moving to RESUMED: " + next + " (inexisting)");
/**
*这时候栈顶的Activity的activty处于RESUMED状态
*/
next.state = ActivityState.RESUMED;
//重新设置当前ActivityStack的resumed的activity
mResumedActivity = next;
next.task.touchActiveTime();
mRecentTasks.addLocked(next.task);
mService.updateLruProcessLocked(next.app, true, null);
updateLRUListLocked(next);
mService.updateOomAdjLocked();
// Have the window managerre-evaluate the orientation of
// the screen based on the newactivity order.
boolean notUpdated = true;
if(mStackSupervisor.isFocusedStack(this)) {
Configuration config =mWindowManager.updateOrientationFromAppTokens(
mService.mConfiguration,
next.mayFreezeScreenLocked(next.app) ? next.appToken : null);
if (config != null) {
next.frozenBeforeDestroy =true;
}
notUpdated =!mService.updateConfigurationLocked(config, next, false);
}
if (notUpdated) {
// The configuration updatewasn't able to keep the existing
// instance of the activity,and instead started a new one.
// We should be all done, butlet's just make sure our activity
// is still at the top andschedule another run if something
// weird happened.
ActivityRecord nextNext =topRunningActivityLocked();
if (DEBUG_SWITCH ||DEBUG_STATES) Slog.i(TAG_STATES,
"Activity configchanged during resume: " + next
+ ", new next:" + nextNext);
if (nextNext != next) {
// Do over!
mStackSupervisor.scheduleResumeTopActivities();
}
if(mStackSupervisor.reportResumedActivityLocked(next)) {
mNoAnimActivities.clear()
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
}
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return false;
}
try {
// Deliver all pending results.
ArrayList a =next.results;
if (a != null) {
final int N = a.size();
if (!next.finishing&& N > 0) {
if (DEBUG_RESULTS) Slog.v(TAG_RESULTS,
"Delivering results to " + next + ": " + a);
next.app.thread.scheduleSendResult(next.appToken, a);
}
}
boolean allowSavedSurface =true;
if (next.newIntents != null) {
// Restrict saved surfaceto launcher start, or there is no intent at all
// (eg. task being broughtto front). If the intent is something else,
// likely the app is goingto show some specific page or view, instead of
// what's left last time.
for (int i =next.newIntents.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final Intent intent =next.newIntents.get(i);
if (intent != null&& !ActivityRecord.isMainIntent(intent)) {
allowSavedSurface =false;
break;
}
}
next.app.thread.scheduleNewIntent(
next.newIntents,next.appToken, false /* andPause */);
}
// Well the app will no longerbe stopped.
// Clear app token stoppedstate in window manager if needed.
mWindowManager.notifyAppResumed(next.appToken, next.stopped,allowSavedSurface);
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_RESUME_ACTIVITY, next.userId,
System.identityHashCode(next), next.task.taskId,next.shortComponentName);
next.sleeping = false;
mService.showUnsupportedZoomDialogIfNeededLocked(next);
mService.showAskCompatModeDialogLocked(next);
next.app.pendingUiClean = true;
next.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(mService.mTopProcessState);
next.clearOptionsLocked();
//这边即为调用当前处于栈顶的Activity的生命
//周期的onRestart->onResumed
next.app.thread.scheduleResumeActivity(next.appToken,
next.app.repProcState,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(),
resumeAnimOptions);
mStackSupervisor.checkReadyForSleepLocked();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Whoops, need to restart thisactivity!
if (DEBUG_STATES)Slog.v(TAG_STATES, "Resume failed; resetting state to "
+ lastState + ":" + next);
next.state = lastState;
if (lastStack != null) {
lastStack.mResumedActivity= lastResumedActivity;
}
Slog.i(TAG, "Restarting becauseprocess died: " + next);
if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
next.hasBeenLaunched =true;
} else if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW &&lastStack != null &&
mStackSupervisor.isFrontStack(lastStack)) {
next.showStartingWindow(null, true);
}
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, false);
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
}
// From this point on, if somethinggoes wrong there is no way
// to recover the activity.
try {
//这时候activity的状态为visible
completeResumeLocked(next);
} catch (Exception e) {
// If any exception getsthrown, toss away this
// activity and try the nextone.
Slog.w(TAG, "Exceptionthrown during resume of " + next, e);
requestFinishActivityLocked(next.appToken, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED,null,
"resume-exception", true);
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
}
} else {//这个流程创建进程时候已经分析过了
// Whoops, need to restart thisactivity!
if (!next.hasBeenLaunched) {
next.hasBeenLaunched = true;
} else {
if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW){
next.showStartingWindow(null, true);
}
}
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
}
if (DEBUG_STACK)mStackSupervisor.validateTopActivitiesLocked();
return true;
} 经过这一小章节的解析,AMS会先startPausingLocked函数中paused之前的resumed的Activity,这时候Activity生命周期的onPaused被调用,并且此时ActivityRecord状态经历了RESUMED->PAUSING->PAUSED的变化,接下来是resumed当前activityStack处于栈顶的Activity,它把当前ActivityStack的resumed的activity修改成当前栈顶的activity,栈顶Activity的状态对应修改成RESUMED,并且调用Activity的生命周期onStart->onResume,最后设置其visible为true。
到这儿其实关于Activity生命中的onStop和onDestory还没有介绍,因为之前只是在Activity切换,并没有涉及到Activity结束的情况。那么onStop和onDestory何时会调用呢?
举一个情况来分析,我们知道应用中Activity调用finish 函数是会结束当前Activity的,我们以这个作为切入来点分析。调用finish最终会调用到AMS中的finishActivity当中,我们简化当前finsi的activity不是root Activity(即不是AndroidManifest有定义Main的activity)。
finishActivity会它所属的activityStack中的requestFinishActivityLocked函数,代码如下:
final boolean requestFinishActivityLocked(IBinder token, int resultCode,
Intent resultData, String reason, boolean oomAdj) {
ActivityRecord r = isInStackLocked(token);
if (r == null) {
return false;
}
finishActivityLocked(r, resultCode, resultData, reason, oomAdj);
return true;
}
进入finishActivityLocked代码如下:
/**
* @return Returns true if this activityhas been removed from the history
* list, or false if it is still in thelist and will be removed later.
*/
final booleanfinishActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, int resultCode, Intent resultData,
String reason, boolean oomAdj) {
if (r.finishing) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Duplicate finishrequest for " + r);
return false;
}
//在这儿会把activityRecord中的finishing设置为true
//表示该activity正在处于finishing过程
r.makeFinishingLocked();
final TaskRecord task = r.task;
final ArrayListactivities = task.mActivities;
final int index =activities.indexOf(r);
if (index < (activities.size() - 1)){
task.setFrontOfTask();
if ((r.intent.getFlags() &Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_WHEN_TASK_RESET) != 0) {
// If the caller asked thatthis activity (and all above it)
// be cleared when the task isreset, don't lose that information,
// but propagate it up to thenext activity.
ActivityRecord next =activities.get(index+1);
next.intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_WHEN_TASK_RESET);
}
}
r.pauseKeyDispatchingLocked();
//需要重新设置下当前focused的activity
adjustFocusedActivityLocked(r,"finishActivity");
finishActivityResultsLocked(r,resultCode, resultData);
final boolean endTask = index <= 0;
final int transit = endTask ?AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_CLOSE : AppTransition.TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_CLOSE;
/**
当前Resumed的activity(即当前running状态)自身调用finish
*/
if (mResumedActivity == r) {
if (DEBUG_VISIBILITY ||DEBUG_TRANSITION) Slog.v(TAG_TRANSITION,
"Prepare closetransition: finishing " + r);
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(transit, false)
// Tell window manage to preparefor this one to be removed.
mWindowManager.setAppVisibility(r.appToken, false);
if (mPausingActivity == null) {
if (DEBUG_PAUSE)Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE, "Finish needs to pause: " + r);
if (DEBUG_USER_LEAVING)Slog.v(TAG_USER_LEAVING,
"finish() =>pause with userLeaving=false");
//这个之前分析过了,大家注意下参数不同走的流程不同就好
//最终这个也会进入finishCurrentActivityLocked
startPausingLocked(false,false, null, false);
}
if (endTask) {
mStackSupervisor.removeLockedTaskLocked(task);
}
} else if (r.state !=ActivityState.PAUSING) {
//看注释
// If the activity is PAUSING, wewill complete the finish once
// it is done pausing; else we canjust directly finish it here.
if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE,"Finish not pausing: " + r);
if (r.visible) {
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(transit, false);
mWindowManager.setAppVisibility(r.appToken, false);
mWindowManager.executeAppTransition();
if(!mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.contains(r)) {
mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.add(r);
}
}
//这儿正式结束activity
returnfinishCurrentActivityLocked(r, (r.visible || r.nowVisible) ?
FINISH_AFTER_VISIBLE :FINISH_AFTER_PAUSE, oomAdj) == null;
} else {
if (DEBUG_PAUSE) Slog.v(TAG_PAUSE,"Finish waiting for pause of: " + r);
}
return false;
} 我们分析下这个finishCurrentActivityLocked函数,代码如下:
final ActivityRecord finishCurrentActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, int mode, boolean oomAdj) {
// First things first: if this activityis currently visible,
// and the resumed activity is not yetvisible, then hold off on
// finishing until the resumed onebecomes visible.
//经过上一步调用makeFinishingLocked之后,当前处于栈顶的running已经变化了
//比如此时栈有A,B,C这三个,原来如果为topRunning为C,
//这时经过makeFinishingLocked之后,topRunning变成了B
final ActivityRecord next =mStackSupervisor.topRunningActivityLocked();
//这个是比如当前finish的Acity还处于可视状态,那么他的状态先切成了STOPPING
if (mode == FINISH_AFTER_VISIBLE&& (r.visible || r.nowVisible)
&& next != null&& !next.nowVisible) {
if(!mStackSupervisor.mStoppingActivities.contains(r)) {
addToStopping(r, false /*immediate */);
}
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_STATES,
"Moving to STOPPING:"+ r + " (finish requested)");
r.state = ActivityState.STOPPING;
if (oomAdj) {
mService.updateOomAdjLocked();
}
return r;
}
// make sure the record is cleaned out of other places.
mStackSupervisor.mStoppingActivities.remove(r);
mStackSupervisor.mGoingToSleepActivities.remove(r);
mStackSupervisor.mWaitingVisibleActivities.remove(r);
if (mResumedActivity == r) {
mResumedActivity = null;
}
final ActivityState prevState =r.state;
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.v(TAG_STATES,"Moving to FINISHING: " + r);
//这时候Activity状态转换成FINISHING
r.state = ActivityState.FINISHING;
final booleanfinishingActivityInNonFocusedStack
= r.task.stack !=mStackSupervisor.getFocusedStack()
&& prevState ==ActivityState.PAUSED && mode == FINISH_AFTER_VISIBLE;
if (mode == FINISH_IMMEDIATELY
|| (prevState ==ActivityState.PAUSED
&& (mode ==FINISH_AFTER_PAUSE || mStackId == ActivityManager.StackId.PINNED_STACK_ID))
||finishingActivityInNonFocusedStack
|| prevState == ActivityState.STOPPED
|| prevState ==ActivityState.INITIALIZING) {
r.makeFinishingLocked()
/*这边开始调用Activity生命周期的onStop->onDestory,如果当前还未paused*的还会onPaused这个生命周期,这函数 *里面会把Activity从
*对应的进程中删除,nowVisible变成false,,
*把Activity从对应的Task中移除并且状态修改成DESTROYED
*从WindowMangerService删除对应的Activity
*/
boolean activityRemoved =destroyActivityLocked(r, true, "finish-imm");
if(finishingActivityInNonFocusedStack) {
// Finishing activity that was in pausedstate and it was in not currently focused
// stack, need to makesomething visible in its place.
mStackSupervisor.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0,!ActivityStackSupervisor.PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
}
if (activityRemoved){ mStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
}
if (DEBUG_CONTAINERS)Slog.d(TAG_CONTAINERS,
"destroyActivityLocked: finishCurrentActivityLocked r=" + r +
" destroy returnedremoved=" + activityRemoved);
return activityRemoved ? null : r;
}
// Need to go through the full pause cycleto get this
// activity into the stopped state andthen finish it.
if (DEBUG_ALL) Slog.v(TAG,"Enqueueing pending finish: " + r);
mStackSupervisor.mFinishingActivities.add(r);
r.resumeKeyDispatchingLocked();
mStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
return r;
}到这儿我们就能知道Activity生命周期中的onStop->onDestory了,Activity状态转换
FINISHING->DESTORYING->DESTORYED,已经从相关的进程和Task移除Activity。
好了,到了这步一个启动的Activity整个生命流程算是介绍完了,涉及东西异常多、和繁锁,读者需要自己拿着代码,可以对着流程自己梳理,其中还有很多在这篇文章里没有涉及,忽略很多,毕竟AMS涉及东西太多。晕!!!!
开机广播BOOT_COMPLETED发送流程
何时发送BOOT_COMPLETED广播,这章节我简单说下,看下流程怎么走。
我们接上一章节Activity初始化中的minimalResumeActivityLocked进行分析:
void inimalResumeActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r) {
r.state = ActivityState.RESUMED;
mResumedActivity = r;
r.task.touchActiveTime();
mRecentTasks.addLocked(r.task);
///
completeResumeLocked(r);
mStackSupervisor.checkReadyForSleepLocked();
setLaunchTime(r);
if (DEBUG_SAVED_STATE)Slog.i(TAG_SAVED_STATE,
"Launch completed;removing icicle of " + r.icicle);
分析completeResumeLocked:
private voidcompleteResumeLocked(ActivityRecord next) {
next.visible = true;
next.idle = false;
next.results = null;
next.newIntents = null;
next.stopped = false;
if (next.isHomeActivity()) {
ProcessRecord app =next.task.mActivities.get(0).app;
if (app != null && app !=mService.mHomeProcess) {
mService.mHomeProcess = app;
}
}
if (next.nowVisible) {
// We won't get a call toreportActivityVisibleLocked() so dismiss lockscreen now.
mStackSupervisor.reportActivityVisibleLocked(next);
mStackSupervisor.notifyActivityDrawnForKeyguard();
}
// schedule an idle timeout in case theapp doesn't do it for us.
mStackSupervisor.scheduleIdleTimeoutLocked(next);
。。。。。。。。
}进入scheduleIdleTimeoutLocked,这个函数实际上是通过Handler最终调用activityIdleInternalLocked
final ActivityRecord activityIdleInternalLocked(final IBinder token, booleanfromTimeout,
Configuration config) {
。。。。。。
ActivityRecord r = ActivityRecord.forTokenLocked(token);
if (r != null) {
if (isFocusedStack(r.task.stack) ||fromTimeout) {
booting =checkFinishBootingLocked();
}
}
。。。。。。。
}进入checkFinishBootingLocked:代码如下
private boolean checkFinishBootingLocked() {
final boolean booting =mService.mBooting;
boolean enableScreen = false;
mService.mBooting = false;
if (!mService.mBooted) {
mService.mBooted = true;
enableScreen = true;
}
if (booting || enableScreen) {
mService.postFinishBooting(booting,enableScreen);
}
return booting;
}继续进入AMS中的postFinishBooting,在该函数通过Handler,最终进入finishBooting
final void finishBooting() {
synchronized (this) {
。。。。。
/**开始发送广播*/
mUserController.sendBootCompletedLocked(
newIIntentReceiver.Stub() {
@Override
public voidperformReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode,
Stringdata, Bundle extras, boolean ordered,
booleansticky, int sendingUser) {
synchronized(ActivityManagerService.this) {
requestPssAllProcsLocked(SystemClock.uptimeMillis(),
true, false);
}
}
});
scheduleStartProfilesLocked();
}
}
}void sendBootCompletedLocked(IIntentReceiver resultTo) {
for (int i = 0; i 接着进入finishUserBoot
private void finishUserBoot(UserState uss, IIntentReceiver resultTo) {
。。。。。。。。
// We need to delay unlockingmanaged profiles until the parent user
// is also unlocked.
if(getUserManager().isManagedProfile(userId)) {
final UserInfo parent =getUserManager().getProfileParent(userId);
if (parent != null
&&isUserRunningLocked(parent.id, ActivityManager.FLAG_AND_UNLOCKED)) {
Slog.d(TAG, "User" + userId + " (parent " + parent.id
+ "):attempting unlock because parent is unlocked");
maybeUnlockUser(userId);
} else {
String parentId = (parent == null) ?"" : String.valueOf(parent.id);
Slog.d(TAG, "User" + userId + " (parent " + parentId
+ "): delayingunlock because parent is locked");
}
} else {
maybeUnlockUser(userId);
}
}
} 接着进入maybeUnlockUser看看
boolean unlockUserCleared(final int userId, byte[] token, byte[] secret,
IProgressListener listener) {
UserState uss;
。。。。。。
finishUserUnlocking(uss);
。。。。。。。
return true;
}继续进入finishUserUnlocking
private void finishUserUnlocking(finalUserState uss) {
final int userId =uss.mHandle.getIdentifier();
。。。。。。
if (proceedWithUnlock) {
uss.mUnlockProgress.start();
// Prepare app storage before we goany further
uss.mUnlockProgress.setProgress(5,
mService.mContext.getString(R.string.android_start_title));
mUserManager.onBeforeUnlockUser(userId);
uss.mUnlockProgress.setProgress(20);
// Dispatch unlocked to systemservices; when fully dispatched
// that calls through to the next"unlocked" phase
mHandler.obtainMessage(SYSTEM_USER_UNLOCK_MSG, userId, 0, uss)
.sendToTarget();
}
}通过发送一个消息SYSTEM_USER_UNLOCK_MSG到AMS中,AMS中再回调
mUserController.finishUserUnlocked((UserState)msg.obj);
void finishUserUnlocked(final UserState uss) {
final int userId =uss.mHandle.getIdentifier();
。。。。。。。
} else {
finishUserUnlockedCompleted(uss);
}
}
}
}继续分析finishUserUnlockedCompleted
private void finishUserUnlockedCompleted(UserStateuss) {
final int userId =uss.mHandle.getIdentifier();
synchronized (mService) {
// Bail if we ended up with a staleuser
if(mStartedUsers.get(uss.mHandle.getIdentifier()) != uss) return;
final UserInfo userInfo =getUserInfo(userId);
if (userInfo == null) {
return;
}
// Only keep marching forward ifuser is actually unlocked
if (!StorageManager.isUserKeyUnlocked(userId))return;
// Remember that we logged in
mUserManager.onUserLoggedIn(userId);
if (!userInfo.isInitialized()) {
if (userId !=UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM) {
Slog.d(TAG,"Initializing user #" + userId);
Intent intent = newIntent(Intent.ACTION_USER_INITIALIZE);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
mService.broadcastIntentLocked(null,null, intent, null,
newIIntentReceiver.Stub() {
@Override
public voidperformReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode,
String data, Bundle extras, booleanordered,
booleansticky, int sendingUser) {
// Note:performReceive is called with mService lock held
getUserManager().makeInitialized(userInfo.id);
}
}, 0, null, null,null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE,
null, true, false,MY_PID, SYSTEM_UID, userId);
}
}
Slog.d(TAG, "SendingBOOT_COMPLETE user #" + userId);
int uptimeSeconds =(int)(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() / 1000);
MetricsLogger.histogram(mService.mContext,"framework_boot_completed", uptimeSeconds);
//这时候就开始发送BOOT_COMPLETED消息了
final Intent bootIntent = newIntent(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED, null);
bootIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER_HANDLE, userId);
bootIntent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_NO_ABORT
|Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_INCLUDE_BACKGROUND);
mService.broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, bootIntent, null, null, 0,null, null,
new String[] {android.Manifest.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED },
AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, true,false, MY_PID, SYSTEM_UID, userId);
}
}发送BOOT_COMPLETED消息流程简单的描述了下,即在Launcher启动完毕之后,AMS开始发送该广播。
本文介绍了下AMS中关于如何管理Activity,但是没有涉及到WindowManagerService相关界面的显示,这个只是梳理下Activity在AMS中如何表现。文章有错误的地方还请读者指出来,有疑问也可以提出来。