SQL Server
一、SQLSERVER的基本数据类型
1、整数数据类型
- int(Interger):范围:[-2^31, 2^31] 2^31=2,147,483,648
- smallint:范围:[-2^15, 2^15] 2^15=32,767
- tinyint:范围:[0,255]
- bigint:范围:[-2^63, 2^63] 2^63=9223372036854775808
2、浮点数据类型
- real:范围:[-3.40E -38, 3.40E +38 ] 精确到第七位小数
- float:范围:[-1.79E -308,1.79E +308] 精确到第15位小数【近似求值】
- decimal:范围:[-10^38 -1,10^38-1] 精确到第38位小数【精准度比较高】
- numberic和decimal完全相同
- monty:范围:[-263,263] 2^63=9223372036854775808 精确到第四位小数
- smallmoney:范围:[-214,748.3648 ,214,748.3648 ] 精确到第四位小数
3、二进制数据类型
- binary:范围:[18000] 长度固定,要不varbinary快
- varbinary:范围:[18000]
4、逻辑数据类型
- bit:值为0【否】或1【是】,不能为null,如果输入0、1以外的值都将被视为1
5、字符数据类型
- char:范围:[18000] 长度固定,要比varchar快
- nchar:范围:[14000]
- varchar:范围:[18000]
- nvarchar:范围:[14000]
6、文本和图形数据类型
- text:范围:[1, 2^31-1]
- ntext:容量为230-1
- image和text一样
7、日期和时间数据类型
- date:例如:2021年1月12日
- datetime:例如:2021年1月12日 13时00分00秒
- 公元1753 年1 月1 日零时起到公元9999 年12 月31 日23 时59 分59 秒之间
- datetime2:例如:2021-01-12 13:03:00.3830000
- 相比datetime加入了毫秒、纳秒(ms、ns)小数点后七位
- datetimeoffset:例如:2020-05-25 18:14:53.2470000 +00:00
- 相比datetime加入了时区偏移量部分
- timestamp: 数据类型与时间和日期无关 插入或更新包含 timestamp 列的行时,将产生一个新的时间戳值
8、特殊类型
- uniqeidentifier:使用newid()来获取GUID,唯一标识,36个字符【无序】 使用NewSequentialID()
二、SQLSERVER基础语法
1、SQLServer安装
- 视频:连接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1MnFKjlFp-_WmJUcEA7cZEg 提取码:njf4
- 文档:连接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1BeLlR_lF2lCzTGV7gt4Z0Q 提取码:xxw8
2、创建数据库
- 创建数据库语法:create database 数据库名
- 使用数据库语法:use 数据库名
- 删除数据库语法:drop database 数据库名
3、创建数据表
create table productCategory(
cid int identity(1,1) primary key, --自增,主键约束
cname varchar(50) not null -- 非空约束
)
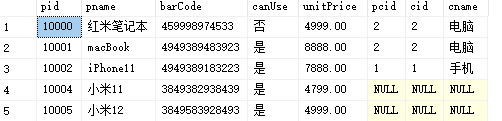
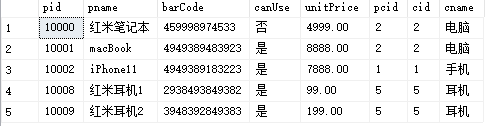
create table product(
pid int identity(10000,1) primary key, --自增,主键约束
pname nvarchar(max) not null, -- 非空约束
barCode char(13) unique, --唯一约束
canUse char(2) default '是', --默认值约束
unitPrice money check(unitPrice>=0), --检查约束
pcid int,
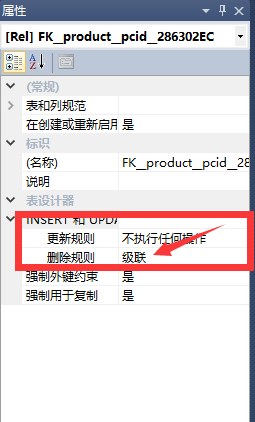
foreign key(pcid) references productCategory(cid) --外键约束
)
4、SQL语言的分类
- DDL(Data Definition Language)【定义】:建库、表、视图、存储过程、索引等
- DCL(Data Control Language)【控制】:授权某些表或表中的某些列的查看权限
- DML(Data Manipulation Language)【操纵】:增删改
- DQL(Data Query Language)【查询】:查询
5、增删改
-
添加:
-
完整写法:
insert into Product(pname,barCode,unitPrice,pcid) values('macBook','4949389483923',8888,2), ('iPhone11','4949389183223',7888,1), ('三星耳机','4939383483923',288,3) -
省略写法:
insert into Product values('红米笔记本','459998974533','否',4999,2) --或者 insert into ProductCategory values('平板'),('耳机')- 添加数据的时候,自增列默认不管
-
省略写法即省去“列名”,但必须保证 values 中的值和表中的列一一对应起来
-
获取自增值:
insert into Product values('红米笔记本','459998974533','否',4999,2) select @@IDENTITY -- 获取自增值- @@identity,是一个系统变量,表示当前 “会话”中最后一条 insert 语句 产生的自增值。
-
修改:
-
删除:
6、查询
-
内连接
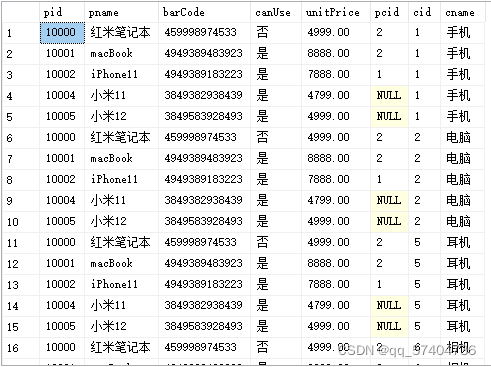
-- 内连接 select * from Product p inner join ProductCategory pc on p.pcid=pc.cid -
外连接
-
完全连接
-
交叉连接(笛卡尔乘积)
7、控制语句
-
声明变量:declare @变量名 数据类型 declare @i int
-
分支结构:判断@i的值
declare @i int set @i=10 if(@i>10) begin print 'i的值大于10' end else begin print 'i的值小于等于10' end -
循环结构:求1-100之间所有数字之和
declare @i int, @sum int set @i=1; set @sum=0 while(@i<=100) begin set @sum = @sum + @i; set @i = @i + 1; end print @sum
8、内置函数
--判断为null函数
declare @abc varchar(5)
set @abc='mnw'
select isnull(@abc,0); --如果变量abc值为null,则取0,否则取被赋的值
--查找索引函数
select charindex('abc','bac abc fmd abc'); --获取字符串abc在长字符串bac abc fmd abc中的索引位置,索引默认从1开始找
select charindex('abc','bac abc fmd abc',9); --索引从9开始找
--重复获取函数
select replicate('m',3); --按指定次数重复字符表达式,将m字符重复三次
select replicate('abc',2);--将字符串abc重复2次
--大小写转换函数
select len('datazsrt'); --获取字符串长度
select lower('ADRTddd'); --转小写
select upper('data');--转大写
--替换截取函数
select substring('abcdef111',2,3); --截取字符串
select replace('dadt123','t1','AA'); --替换字符串
--类型转换函数
select cast('2015-08-02' as datetime) as 日期类型; --数据类型转换,CAST是ANSI兼容的,而CONVERT则不是
select 'ab'+cast(1 as varchar);-- 将1转化为字符串与ab相加
select convert(datetime,'2015-08-02'); --数据类型转换,与cast相同
select convert(varchar(19),getdate(),113); --不同的是convert还提供一些特别的日期格式转换,而cast没有这个功能
select format(getdate(),'yyyy/mm/dd'); --将日期转化为规定的格式
--数学函数
select round(2.15,1); --四舍五入,第二个参数索引从0开始,即:0表示小数后第一位进行判断
select ceiling(2.158); --向上取整
select floor(2.713); --向下取整
--日期函数
select getdate();
select datepart(mm,'2015-08-04 15:28:26'); --返回日期的某一部分 yy,mm,dd,hh,mi,ss,
select dateadd(dd,-25,'2015-08-04 15:28:26'); --在日期中加上或减去制定的时间间隔,给天数减25天
select datediff(day,'2008-06-05','2008-08-05') as 天数; --返回两个日期之间的天数
--聚合函数
count(),min(),max(),avg(),sum()
三、函数、视图、索引
1、自定义函数
-
标量值函数:返回值为一个数据点的函数被称为标量值函数
-
表值函数:返回值为一个结果集的函数
-
内连表值函数:只有一个查询语句
-
表变量:将查询的结果集临时存起来可以使用表变量
-- 三个一起运行才行,否则@i没声明 declare @t table(id int identity(1,1),name varchar(50)) insert into @t values('张三'),('李四') select * from @t -
多语句表值函数:多个语句
create function GetPrice(@cid int) returns @t table(pid int, productName varchar(50), price money) as begin insert into @t select pid, pname, unitPrice from product where pcid=@cid update @t set price=price+1000 return end select * from GetPrice(5)
-
-
小节:
- 掌握三种函数的语法结构和区别
- 函数只能做查询,不能做增删改
- 函数可以将常用的功能模块化,便于重用
- 函数性能一般,尽量避免大量使用
2、架构
- 架构是用于存储数据库对象的一个命名空间,类似于Java中的包(Java包可以多层,但是架构只能一层)。当我们创建数据库后,默认使用的架构是 dbo,我们可以创建和使用自己命名的架构,从而使各种数据库对象能够更好的被组织起来。
3、视图
1、概念
- 视图是一个虚拟表,其内容由查询定义。同真实的表一样,视图包含一系列带有名称的列和行数据。但是,视图并不在数据库中以存储的数据值集形式存在。行和列数据来自由定义视图的查询所引用的表,并且在引用视图时动态生成。
2、创建视图
-
任务:创建一个简单的视图
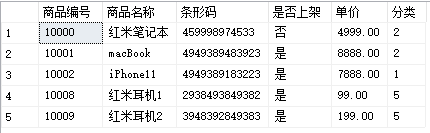
create view product_category_view as select * from product p join productCategory pc on p.pcid=pc.cid select * from product_category_view -
任务:带别名的视图(别名要和查到的列一一对应)
create view product_category_view2(商品编号,商品名称,条形码,是否上架,单价,分类) as select p.pid,p.pname,p.barCode,p.canUse,p.unitPrice,p.pcid from product p join productCategory pc on p.pcid=pc.cid
3、视图操作
-
使用视图更新数据
-
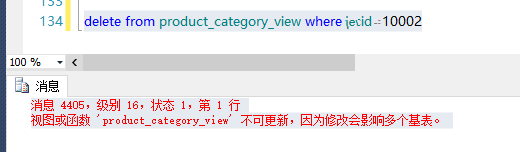
定义视图的 SELECT 语句不能包含以下任何元素:
聚合函数; distinct 子句;
group by 子句; having 子句;
union 和 union all 子句; 外连接 -
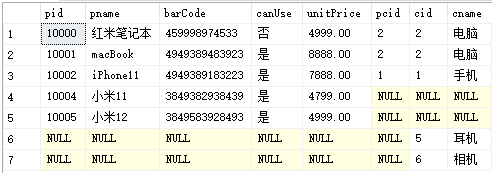
任务:将product_category_view视图里面的单价都全部+100
-- 有别名的视图 update product_category_view2 set 单价=单价+100 where 分类=5 -- 没有别名的视图 update product_category_view set unitPrice=unitPrice+100 where pcid=5当视图里面的数据发生改变以后,原数据也会改变
-
-
使用视图删除数据
4、视图管理
-
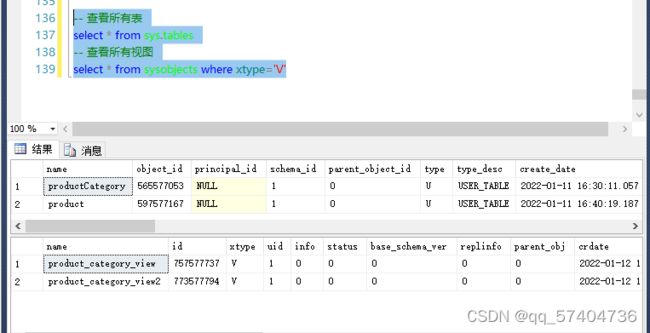
查看视图
-- 查看所有表 select * from sys.tables -- 查看所有视图 select * from sysobjects where xtype='V' -
删除视图
drop view product_category_view2
5、小结
-
优点:
-
简单性
- 可以把视图看做一张虚拟的表, 直接"select * from 视图"即可查询
-
安全性
- 可以对用户隐藏一些敏感的字段
-
逻辑数据独立性
-
本表修改后, 视图的使用者不需要关心(甚至根本不知道)
视图或者原表进行修改,都会修改原数据
-
-
-
缺点:
- 性能一般
- 当视图中有多表的话,修改和删除受到限制
4、索引
- 概念:概念:系统根据某种算法,将已有的数据(未来可能新增的数据),单独简历一个文件,文件能够实现快速的匹配数据,并且能够快速找到对应表中的记录。
四、存储过程、事务、隔离级别
存储过程
1、概念
- 存储过程Procedure是一组为了完成特定功能的SQL语句集合,经编译后存储在数据库中,用户通过指定存储过程的名称并给出参数来执行。
- 存储过程中可以包含逻辑控制语句和数据操纵语句,它可以接受参数、输出参数、返回单个或多个结果集以及返回值。
- 由于存储过程在创建时即在数据库服务器上进行了编译并存储在数据库中,所以存储过程运行要比单个的SQL语句块要快。同时由于在调用时只需用提供存储过程名和必要的参数信息,所以在一定程度上也可以减少网络流量、简单网络负担。
2、语法结构
1、创建
create proc proc_product_insert
@pname varchar(50), @bcode char(13), @uprice money, @cid int, -- 输入参数
@id int output -- 输出参数
as
insert into product(pname,barCode,unitPrice,pcid) values(@pname,@bcode,@uprice,@cid)
set @id=SCOPE_IDENTITY() -- 获得自增值,等同于:set @id=@@identity
2、调用
declare @id int
exec proc_product_insert '小米13','2938293849382',4999,1,@id output
print @id
3、修改
alter proc proc_product_insert
@pname varchar(50), @bcode char(13), @uprice money, @cid int, --输入参数
@num int output -- 输出参数
as
insert into product(pname,barCode,unitPrice,pcid) values(@pname,@bcode,@uprice,@cid)
set @num=@@ROWCOUNT -- 获取受影响行数
4、删除
drop proc proc_product_insert
3、优缺点
优点:
- 运行速度:对于很简单的sql,存储过程没有什么优势。对于复杂的业务逻辑,因为在存储过程创建的时候,数据库已经对其进行了一次解析和优化。存储过程一旦执行,在内存中就会保留一份这个存储过程,这样下次再执行同样的存储过程时,可以从内存中直接调用,所以执行速度会比普通sql快。
- 减少网络传输:存储过程直接就在数据库服务器上跑,所有的数据访问都在数据库服务器内部进行,不需要传输数据到其它服务器,所以会减少一定的网络传输。但是在存储过程中没有多次数据交互,那么实际上网络传输量和直接sql是一样的。而且我们的应用服务器通常与数据库是在同一内网,大数据的访问的瓶颈会是硬盘的速度,而不是网速。
- 可维护性:存储过程有些时候比程序更容易维护,这是因为可以实时更新DB端的存储过程。 有些bug,直接改存储过程里的业务逻辑,就搞定了。
- 增强安全性:提高代码安全,防止 SQL注入。这一点sql语句也可以做到。
- 可扩展性:应用程序和数据库操作分开,独立进行,而不是相互在一起。方便以后的扩展和DBA维护优化。
缺点:
- SQL本身是一种结构化查询语言,但不是面向对象的的,本质上还是过程化的语言,面对复杂的业务逻辑,过程化的处理会很吃力。同时SQL擅长的是数据查询而非业务逻辑的处理,如果把业务逻辑全放在存储过程里面,违背了这一原则。
- 如果需要对输入存储过程的参数进行更改,或者要更改由其返回的数据,则您仍需要更新程序集中的代码以添加参数、更新调用,等等,这时候估计会比较繁琐了。
- 开发调试复杂,由于IDE的问题,存储过程的开发调试要比一般程序困难。
- 没办法应用缓存。虽然有全局临时表之类的方法可以做缓存,但同样加重了数据库的负担。如果缓存并发严重,经常要加锁,那效率实在堪忧。
- 不支持群集,数据库服务器无法水平扩展,或者数据库的切割(水平或垂直切割)。数据库切割之后,存储过程并不清楚数据存储在哪个数据库中。
和视图的比较
- 它们本身都不存储数据,都可以返回查询到的结果集。
- 视图可以像表一样用在 from 中,而存储过程不能。
- 视图不支持动态参数,而存储过程可以输入查询参数。
- 存储过程中一次性返回多个结果集而视图只能返回一个。
和函数的比较
- 函数必须有返回值,存储过程没有。
事务
1、事务特性(ACID)
1.原子性
- 原子性(Atomicity)就是刚才提到的不可分割,要么都执行要么都不执行。
- 解释:同时成功或同时失败
2.一致性
- 一致性(Consistency)事务在完成时,必须使相关数据保持一致的状态,所有的内部数据结构都必须是正确的,符合完整性的要求。
- 解释:check约束余额必须大于0,卡里只有500,但是要转出1000,此时数据明显不符合
3.隔离性
- 隔离性(Isolation)事务过程中暂时不一致的数据都不能被其他事务应用,直到数据再次一致。在某一个时间点,多个事务有可能同时涉及某些数据行,如果有些行已经在其他事务中并且没有达到一致状态,则此事务不能对其进行操作,直到哪些数据达到一致状态。
4.持久性
- 持久性(Durability)一旦事务提交,他们就变成永久的。事务所完成的操作被永久保存。
2、事务分类
1.自动提交
- 每条单独的语句都是一个事务。例如:delete Users where Sex=‘男’ 此语句有可能删除很多
条数据,这些数据要么一次性都删除成功,要么都删除失败,而不会出现部分成功部分失败。
2.显示提交
-
每个事务以 begin tran 打头,以 commit 或 rollback 结束。
- begin tran[saction] 标记一个本地事务的开始
- commit tran[saction] 标记一个现实或隐式事务的结束,指明事务已经成功执行并将事务内所修改的全部数据保存到数据库中。
- rollback tran[saction]:回滚事务到开头或事务内部的存储点。
- save tran[saction]:在事务内部设置一个保存点,这个保存点是在取消某个事务的一部分后,该事务可以返回的一个位置,在 Sql2005 中才开始提供此项功能。
-
任务:了解事务保存点的使用
-- 开启事务 一行一行执行 begin tran myTran insert into productCategory values('鼠标'),('键盘') save tran sr -- 设置一个保存点sr delete from productCategory -- 删除表中所有的数据 select * from productCategory rollback tran sr -- 回滚到sr保存点 commit tran myTran -- 提交整个事务 go select * from productCategory go
事务的隔离级别
1、四种隔离级别
1.未提交读(READ UNCOMMITED)
- 可以读到别的事务未提交的数据
2.已提交读(READ COMMITTED)默认级别
- 只能读到别的事务已提交的数据
3.重复读(REPEATABLE READ)
- 保证当前事务读取到的数据不被别的事务修改
4.可串行化(SERIALIZEABLE)
- 最严格的级别,事务串行执行,资源消耗最大
2、不同隔离级别会出现的3种情况
1.脏读
- 脏读指的是读到了其他事务未提交的数据,未提交意味着这些数据可能会回滚,也就是可能最终不会存到数据库中,也就是不存在的数据。读到了并一定最终存在的数据,这就是脏读。
2.幻读
- 幻读是针对数据插入(INSERT)操作来说的。假设事务A对某些行的内容作了更改,但是还未提交,此时事务B插入了与事务A更改前的记录相同的记录行,并且在事务A提交之前先提交了,而这时,在事务A中查询,会发现好像刚刚的更改对于某些数据未起作用,但其实是事务B刚插入进来的,让用户感觉很魔幻,感觉出现了幻觉,这就叫幻读。
3.不可重复读
- 当前事务先进行了一次数据读取,然后再次读取到的数据是别的事务修改成功的数据,导致两次读取到的数据不匹配,也就照应了不可重复读的语义
3、简图
-
隔离级别 脏读 不可重复读 幻读 未提交读 可能 可能 可能 已提交读 不可能 可能 可能 可重复读 不可能 不可能 可能 可串行化 不可能 不可能 不可能
4、案例
表结构和数据:
create table tb_test(
id int identity(1,1) not null primary key,
text varchar(200) default null,
)
insert tb_test values('first row'),('second row'),('third row')
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
未提交读(READ UNCOMMITED):
A会话:
begin tran
update tb_test set text='1 row' where id=1
B会话:
SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ UNCOMMITTED;
BEGIN TRAN;
select * from tb_test where id=1;
A会话:
rollback
B会话:
select * from tb_test where id=1;
此时会发现B会话可以拿到A未提交的数据,即“脏数据”,如果拿着脏数据去参与运算,肯定会发生错误。
并且发现在B会话中两次查询的结果不一致,即“不可重复读”
接下来演示“幻读”,幻读即“两次查询的结果的行数不一致”
B会话:
commit;
A会话:
begin tran
insert tb_test values('forth row')
B会话:
SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ UNCOMMITTED;
BEGIN TRAN;
select * from tb_test;
A会话:
rollback
B会话:
select * from tb_test;
commit;
此时发现B会话拿到了A会话中添加的行,但是A会话最终回滚了该行数据,此类虚幻的数据即“幻读”
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
已提交读(READ COMMITTED):
B会话:
select * from tb_test; -- 观测数据
B会话:
SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ COMMITTED;
BEGIN TRAN
SELECT * FROM tb_test
A会话:
BEGIN TRAN
UPDATE tb_test SET TEXT='1 row' where id=1;
B会话:
SELECT * FROM tb_test
此时会发现查询阻塞
A会话:
commit
此时B会话查询OK
B会话
commit;
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
重复读(REPEATABLE READ):
A会话:
SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL REPEATABLE READ;
BEGIN TRAN
SELECT * FROM tb_test
B会话:
update tb_test set text='3 row' where id=3
此时发现B会话阻塞,原因是A会话使用了REPEATABLE READ,致使tb_test在提交事务之前被独占。
A会话:
commit
此时观察B会话,提示修改成功
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
可串行化(SERIALIZEABLE):
可串行化隔离级别最高,不会出现脏读、幻读、不可重复读,但是由于独占性太高,会显著阻塞数据库并发性能。
五、游标、触发器
游标
1、概念
- 游标是SQL 的一种数据访问机制 ,游标是一种处理数据的方法。众所周知,使用SQL的select查询操作返回的结果是一个包含一行或者是多行的数据集,如果我们要对查询的结果再进行查询,比如(查看结果的第一行、下一行、最后一行、前十行等等操作)简单的通过select语句是无法完成的,因为这时候索要查询的结果不是数据表,而是已经查询出来的结果集。
- 我们可以将“游标”简单的看成是结果集的一个指针,可以根据需要在结果集上面来回滚动,浏览我需要的数据。
2、编写过程
-
- 定义游标(需要指定一个查询结果集)>> 2. 打开游标 >> 3. 使用游标读取数据 >> 4. 关闭游标 >> 5. 释放游标
1.定义游标
-
DECLARE cursor_name [INSENSITIVE] [SCROLL] CURSOR
FOR select_statement
[FOR {READ ONLY | UPDATE [OF column_name [,…n]]}]
-
INSENSITIVE:如果指定此值,则会把查询结果集存放在 tempdb 数据库的临时表中,通过游标的操作对应的便是临时表中
的结果集而非源表的内容,其他用户对源表中数据的变更无法反映出来。 -
SCROLL:使用此值定义一个可在结果集中滚动的游标,具有以下功能:first:取首行、last:取尾行、prior:取前一行、next:取后一行、relative:按相对位置取、absolute:按绝对位取。如果没有指名 scroll 则游标是只进的,也就是说只能通过 next 来向后取下一行数据。
-
select_statement:一些标准的 Sql 语句,但不允许使用 compute 和 into 等关键字。
-
READ ONLY:只读,不允许通过游标更新数据。
-
UPDATE [ OF column_name [ ,…n ] ]:定义在这个游标里可以更新的列。
2.打开游标
- open cursor_name
- 注意:当打开游标时,服务器才会执行定义游标时的 Sql 查询语句,这将耗费一段时间,时间的长短取决于系统性能和语句的复杂程度。
3.提取数据
-
游标通常情况下,只能一次从 DB 中提取一条记录,我们最常见的操作就是从第一条记录开始提取,直到结束。如下示例代码所示:
-
DECLARE Employee_Cursor CURSOR
……
FETCH NEXT FROM Employee_Cursor;
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
FETCH NEXT FROM Employee_Cursor;
END;
……
GO
-
@@FETCH_STATUS 是一个全局变量,当其值如下:
- 为 0 时:表示提取正常。
- 为-1 时:表示已经取到了结果集的末尾。
- 为其他时:表示操作出了问题。
4.关闭游标
- CLOSE cursor_name
5.释放游标
- DEALLOCATE cursor_name
3、任务
-
任务:
5000元以下的iPhone,每件商品提价 10%;
5000元以上的iPhone,每件商品提价 5%declare @price money, @name varchar(20) -- 定义变量 declare cur_ChangePrice cursor -- 定义游标 for select pname, unitPrice from Product -- 定义游标中的SQL语句 for update of unitPrice -- 修改 open cur_ChangePrice -- 打开游标 fetch next from cur_ChangePrice into @name, @price -- 游标移动到下一行 while @@FETCH_STATUS=0 -- 读取下一行是否成功,0是成功的状态码 begin if(@price<5000 and Charindex('iPhone',@name)>0) -- 逻辑判断 update Product set unitPrice=unitPrice*1.1 where current of cur_ChangePrice if(@price>=5000 and Charindex('iPhone',@name)>0) -- 逻辑判断 update Product set unitPrice=unitPrice*1.05 where current of cur_ChangePrice fetch next from cur_ChangePrice into @name, @price -- 游标移动到下一行 end close cur_ChangePrice -- 关闭游标 deallocate cur_ChangePrice -- 释放游标 select * from product
4、总结
- 我们正常的更新和删除都是面向集合的操作,而游标提供了面向行的操作,使用游标是一个拿性能换灵活性的方式,我们应尽量避免。
- 通常情况下,能够使用面向集合的操作就不要使用面向行的游标,这是因为创建和使用游标都会耗费系统资源和性能。面向集合的操作比面向行的操作具有多达几倍的性能优势。
- 通常情况下,游标不会像函数或存储过程那样,存储在数据库中。
触发器
1、概念
- 触发器(trigger)是SQL server 提供给程序员和数据分析员来保证数据完整性的一种方法,它是与表事件相关的特殊的存储过程,它的执行不是由程序调用,也不是手工启动,而是由事件来触发,当对一个表进行操作( insert,delete, update)时就会激活它执行。触发器经常用于加强数据的完整性约束和业务规则等。
2、触发器工作原理
-
触发器触发时:
1.系统自动在内存中创建deleted表或inserted表;
2.只读,不允许修改,触发器执行完成后,自动删除。
-
inserted表:
1.临时保存了插入或更新后的记录行;
2.可以从inserted表中检查插入的数据是否满足业务需求;
3.如果不满足,则向用户发送报告错误消息,并回滚插入操作。
-
deleted表:
1.临时保存了删除或更新前的记录行;
2.可以从deleted表中检查被删除的数据是否满足业务需求;
3.如果不满足,则向用户报告错误消息,并回滚插入操作。
如果被修改的表的列为null值的话则不执行修改语句
3、触发器分为两类
- instead of 触发器:在数据更新到数据库之前执行的操作,该类触发器既可在表上定义,也可在视图上定义。
- after(for)触发器:在数据更新到数据后再执行的操作
4、语法结构
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
ON table_name
[WITH ENCRYPTION]
FOR | AFTER | INSTEAD OF [DELETE, INSERT, UPDATE]
AS
T-SQL语句
GO
--with encryption 表示加密触发器定义的sql文本
--delete,insert,update指定触发器的类型
5、任务
-
表结构:
--创建学生表 create table student( stu_id int identity(1,1) primary key, stu_name varchar(10), stu_gender char(2), stu_age int ) --创建班级人数表 被修改的列必须不能为null,否则不执行 create table student_num( stu_num int default 0 )
after触发器:
-
创建insert触发器
create trigger tri_insert -- 创建触发器 on student -- 在student表上 after insert -- 在insert之后 as begin declare @num int --声明变量 set @num = (select count(*) from student) -- 获得学生表总条数 update student_num set stu_num=@num -- 给student_num赋值 end insert into student values('张三','男',18) select * from student_num -
创建delete触发器
-
用户执行delete操作,就会激活delete触发器,从而控制用户能够从数据库中删除数据记录,触发delete触发器后,用户删除的记录会被添加到deleted表中,原来表的相应记录被删除,所以在deleted表中查看删除的记录。
create trigger tri_delete -- 创建触发器 on student --在student表上 after delete -- 在删除之后 as begin --从系统生成的delete表中获取已删除的信息 select stu_id 已删除的学生编号, stu_name, stu_gender, stu_age from deleted end delete from student where stu_id=2
-
-
创建update触发器
-
update触发器是当用户在指定表上执行update语句时被调用被调用,这种类型的触发器用来约束用户对数据的修改。update触发器可以执行两种操作:更新前的记录存储在deleted表中,更新后的记录存储在inserted表中。
create trigger tri_update on student after update -- 修改之后 as begin declare @num int -- 声明变量 set @num=(select count(*) from student) -- 获得学生表总人数 update student_num set stu_num=@num select stu_id,stu_name 更新前的名字 ,stu_gender,stu_age from deleted -- 获得更新前的数据 select stu_id,stu_name 更新后的名字 ,stu_gender,stu_age from inserted -- 获得更新后的数据 end update student set stu_name='王五' where stu_id=3
-
instead of(替代)触发器
-
与前面介绍的三种after触发器不同,SqlServer服务器在执行after触发器的sql代码后,先建立临时的inserted表和deleted表,然后执行代码中对数据库操作,最后才激活触发器中的代码。而对于替代(instead of)触发器,SqlServer服务器在执行触发instead of 触发器的代码时,先建立临时的inserted表和deleted表,然后直接触发instead of触发器,而拒绝执行用户输入的DML操作语句。instead of触发器一般用来验证数据完整性,拥有比check约束更强大的功能。
create trigger tri_insteadof on student instead of insert -- 创建添加的代替触发器 as begin declare @age int -- 声明变量 set @age=(select stu_age from inserted) -- 从inserted表中查出刚添加的年龄,赋值给age if(@age<0 or @age>120) --如果刚添加的年龄<0或>120 select '年龄有误' end insert into student values('李四','男',150) -- 年龄有误,添加失败
6、触发器和存储过程的区别
- 触发器与存储过程的区别是运行方式的不同,触发器不能执行EXECUTE语句调用,而是在用户执行Transact-SQL语句时自动触发执行;而存储过程需要用户,应用程序或者触发器来显示地调用并执行。
六、关键字、函数
运算符
1、数学运算符
-
任务:将所有商品价格+1000
update product set unitPrice=unitPrice+1000
2、比较运算符
-
< = >= <=
-
任务:查询价格大于5000的商品信息
select * from product where unitPirce>5000 -
<>,!= 不等于
-
任务:查询价格不等于5000的商品信息
select * from product where unitPrice != 5000 -
! 非
3、逻辑运算符
-
and or not
-
任务:查询价格大于3000并且小于5000的商品信息
select * from product where unitPrice>3000 and unitPrice<5000
常用关键字
1、通配符
-
‘_’表示一个字符
-
‘%’表示0-n个字符
-
[] 表示括号中所指定范围内的一个字符
- select * from product where pname like ‘iPhone[4-5]’
- select * from student where stu_name like ‘[张王]三丰’
-
[^] 表示不在括号中所指定范围内的任意一个字符
- select * from product where pname like ‘iPhone[^4-5]’
- select * from student where stu_name like ‘[^张李]三丰’
-
训练
--查询一下名字当中含有王字的学生信息 select * from student where name like '%王%' --查询一下名字姓王的学生信息 select * from student where name like '王%' --查询一下名字姓王的学生信息并且名字是两个字 select * from student where name like '王_' --查询一下名字姓王并且名字是三个字,并且第三个字是"三"或者"四"或者"五"或者"六"或者"七" select * from student where name like '王_三' or name like '王_四' or name like '王_五' or name like '王_六' or name like '王_七' select * from student where name like '王_[三四五六七]' --查询一下名字姓王并且名字是三个字,并且第三个字不是三或者四或者五或者六或者七 select * from student where name like '王_[^三四五六七]'
2、as或者空格起别名
3、null值
-
NULL值要用特殊的关键字IS 或IS NOT,而不能用!=或<>之类的符号
-
任务:查询谁的姓名为null
select * from student where stu_name is null
4、in匹配离散值
-
任务:查询一下年龄是19,22,24的学生信息
select * from student where stu_age in (19,22,24)
其他函数
-
可以用 ALL 或 ANY 关键字修改引入子查询的比较运算符。SOME 是与 ANY 等效的
-
创建两张表
create table a( num int ) create table b( num int ) -----随意添加几条测试数据 -
any/some
-
例如:num>=(1,2,3) 只要年龄大于其中的某一个值就成立
-
任务:查询a表中的哪些数据比b表中某些数据值要大
select * from a where num > any(select * from b)- a表中大于b表的最小值的都会被查出来
-
=ANY 运算符与 IN 等效
-
-
all
-
任务:查询a表中的哪些数据比b表中的数据值都要大
select * from a where num > all(select * from b)- a表中大于b表的最大值的才会被查出来
-
< >ANY 运算符则不同于 NOT IN
-
-
总结
-
< >ANY(a,b,c) 表示不等于 a,或者不等于 b,或者不等于 c
-
NOT IN 表示不等于 a、不等于 b 并且不等于 c
-
<>ALL 与 NOT IN 表示的意思相同
-
大白话
--a表中的哪些数据可以把b当中的其中一个数据干掉那你就赢了 select num from a where num > any(select num from b) --a表中的哪些数据可以把b当中的每一个数据都干掉那你就赢了 select num from a where num > all(select num from b)- 如果看到了any/some就可以理解为或者关系
- 如果看到了all就可以为并且
-
特殊关键字
1、BETWEEN匹配连续值
-
任务:查询出年龄介于20到22之间
select * from student where stu_age>=20 and stu_age<=22 -- 或 select * from student where stu_age between 20 and 22 -
任务:查询出年龄不介于20到22之间的学生数据
select * from student where stu_age<20 or stu_age>22 -- 或 select * from student where stu_age not between 20 and 22
2、having分组后的筛选条件
3、TOP限制结果集
-
任务:查询年龄最大的三个人
select top(3) * from student order by stu_age desc -
任务:查询年龄排名是4,5,6人的
--任务:查询年龄排名是4,5,6人的 --1.我们可以先查询出年龄最大的三个人 --2.然后排除这三个人进行查询 --最牛逼的三个人都走了,剩下的4,5,6是不是就是123名了 select top(3) * from student order by age desc select top(3) * from student where id not in (select top(3) id from student order by age desc ) order by age desc -
一般是与ORDER BY连用,而且TOP 必须放在*型号或者列名的前面。不和ORDER BY也可以使用,但是查询结果不确定
4、DISTINCT去除重复数据
-
任务:查询学生性别有几种
select distinct stu_sex from student -
备注:只能查询列的结果集。DISTINCT要放在SELECT之后,和所有列名的前面
5、PERSISTED
CREATE TABLE OrderDetails
(
ListPrice money NOT NULL,
Quantty int NOT NULL,
LineItemTotal AS (ListPrice * Quantty) PERSISTED
)
- 如果Persisted属性被关掉了,那么计算列只是虚拟列。该列将没有数据存储到磁盘上,并且这些值每次在一个脚本中参照时都会被计算。如果这个属性被设置成激活的,那么计算列的数据将会存储在磁盘中。
- 如果它是Persisted,那么参照列的任何更新将会在计算中自动同步。
- 随着其他一些情况的出现,Persisted将被要求在计算列中创建一个索引。
- 限制
- 对于SQL Server 2000,你不能创建一个persisted计算列。
- 你不能从其它表中参照列直接用于一个计算列。
- 你不能在计算列中应用插入或者更新的语句。
- 如果你在你的语句中连接两种不同数据类型的处理器,那么低优先级的处理器将转化为高优先级的处理器。如果潜在的转化是不可能的,那么将产生错误。
七、日期转换函数
日期函数
1、获取当前系统时间
-
GETDATE()
select getdate()
2、计算增加以后的日期
-
DATEADD(datepart, number, date)
-
datepart:计量单位(year、quarter季度、
month、day、week、hour、minute、second等)
number:增量(正数为:加时间 负数为:减时间) -
-- 当前时间增加两季度 select DATEADD(quarter,2, GETDATE()) -- 指定时间增加两季度 select DATEADD(quarter, 2, '2020-01-01')
3、日期格式化
-
FORMAT(value,format)
-
yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss【格式写法和java一样】
select FORMAT(GETDATE(),'yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒')
4、计算两个日期之间的差额
-
DATEDIFF(datepart, startdate, enddate)
select DATEDIFF(day,'2002-02-13',GETDATE())
5、返回一个日期的特点部分
-
DATEPART(datepart,date)
-- 获取当前星期几 select DATEPART(WEEKDAY,GETDATE()-1) -- 因为美国人1代表星期日,我们可以上面减一。 -- 也可以修改@@datefirst的值,例如:set datefirst 1 set datefrist 1 -
拓展
-
DATENAME(datepart,date)
-- 获取当前星期几 不用-1 结果是:星期日 select DATENAME(WEEKDAY,GETDATE()) -
获取哪个国家的语音
-
select alias, * from master..syslanguages -
数据显示用什么语言
set language N'Simplified Chinese'
-
6、获取特定月份最后一天的日期
-
EOMONTH(GETDATE(),-2)
select EOMONTH(GETDATE(),-2)-
获取08年二月【必须也得写个日,不然报错】
select EOMONTH('2008/2/4') -
获取当前时间-3个月
select EOMONTH(GETDATE(),-3)
-
转换函数
1、CAST(expression AS data_type)
- expression是要转换的对象; data_type是要转换的数据类型
- 例如:select CAST(‘123’ AS varchar)+‘a’
- 例如:select CAST(‘123’ AS int)+‘a’
2、CONVERT(data_type, expression, style)
-
style 规定日期/时间的输出格式(可选)
-
例如:
-- 将后面的类型转换成前面 select CONVERT(datetime,'2012-12-12') -- 将后面的类型转换成前面的然后以特定格式显示 select CONVERT(nvarchar(100),GETDATE(),21) -- 将当前日期转换为date类型然后加1天 select DATEADD(day,1,CONVERT(DATE,GETDATE())) select CONVERT(varchar, GETDATE(), 112)
3、parse和try_parse
-
parse(string_value AS data_type)
-- 执行成功 值为123 select parse('123' AS int) -- 执行成功 值为null 如果失败则为null select TRY_PARSE('123a' AS int)
4、iff(布尔表达式,value1,value2)
-
例如:
select iif(1>2,'张三','李四')
5、ISNULL(expression,value)
-
例如:
create table stus( id int identity(1,1) primary key, name varchar(50) ) insert into stus(name) values('张三'),(null) -- 查询所有名字,将null值替换为未知 select isnull(name,'未知') from stus
上机任务
-
-- 查询距现在日期,两年前的日期是多少 select DATEADD(year,-2,GETDATE()) -- 查询2000年的2月最后一天的日期 select EOMONTH('2000/2/1') -- 查询现在为周几 select DATEPART(WEEKDAY,GETDATE()-1) select DATENAME(WEEKDAY,GETDATE()) -- 查询将字符串202000202转换成日期格式'2020/02/02' select FORMAT(CONVERT(date,'20200202',111),'yyyy/MM/dd') -- 查询20080808日距离现在有多少天 select DATEDIFF(day,'2008-08-08',GETDATE()) -- 查询一年后的今天日期为多少 select DATEADD(year,1,GETDATE()) -
完成任务
-
根据脚本创建表添加测试数据
-
create table students( id int identity primary key, name varchar(50), age int ) insert into students(name,age) values('张三',11),('李四',22),('22',33),(null,77) -
查询学生姓名、年龄;把名字当中含有张字的年龄+1,否则年龄-1
-- 查询学生姓名、年龄;把名字当中含有张字的年龄+1,否则年龄-1 select name,IIF(name like '%张%',age+1,age-1) from students -
查询学生姓名、年龄;将名字转换为int类型,转换错误时候以null显示
-- 查询学生姓名、年龄;将名字转换为int类型,转换错误时候以null显示 select try_parse(name AS int),age from students -
查询学生姓名、年龄;姓名如果为null则显示未知
-- 查询学生姓名、年龄;姓名如果为null则显示未知 select ISNULL(name,'未知'),age from students
-
八、分组和排序
排序
1、order by
- desc降序/asc升序(默认升序)
- 可以将多列按照多种规则排序
分组
1、group by
-
千万注意: 在标准SQL中, 查询的列名只能是出现在group by之后的列以及聚合函数
由于MYSQL不是标准SQL, 导致MYSQL中也可以使用未出现在group by后的列, 但是结果不一定正确。 -
使用Group By进行分组查询(一般出现"每个",“各个”,"分别"等词时都会使用group by)。
-
任务:查询一下每个班级有多少人
select class,count(*) from students group by class -
查询一下男女生学生分别有多少人
select sex,count(*) from students group by sex
-
-
多列分组查询
-
– 任务:按照班级、性别进行分组查询【每个班级的男生、女生各有多少人】
select class,sex,count(*) from students group by class,sex
-
-
Having 子句- - 分组查询的条件筛选
-
任务:查询一下班级人数大于等于2人的班级
select class,count(*) from students group by class having count(*)>=2 -
任务:在上一个任务基础上,按照人数降序排序
select class,count(*) from students group by class having count(*)>=2 order by count(*) desc -
任务:在上一个任务基础上,不用统计103班级
select class,count(*) from students where class != 103 group by class having count(*)>=2 order by count(*) desc
-
-
小结
- 分组查询关键字Group By。
- 分组查询通常和聚合函数一起使用来统计数据。
- 使用 GROUP BY 关键字后,在 SELECT 语句的字段部分仅允许被分组的列或者聚合函数。
- 执行顺序 WHERE --> GROUP BY --> HAVING --> Order by
2、group by 列名 with rollup
-
with rollup对分组统计的结果再次统计
select count(*),sex from students group by sex with rollup -
测试脚本
--分组查询一下每个班级里面有多少学生 --【分组查询的select 后面显示的列只能是聚合函数或者是被分组的列】 select class,count(*) from students group by class --我想通过上面分组查询的结果来看到学生的总人数是多少 select class,count(*) from students group by class with rollup --分组查询一下每个班级里面有多少男生和多少女生 select class,sex,count(*) from students group by class,sex --我想通过上面分组查询的结果来看到每个班级的总人数、以及学生的总人数 select class,sex,count(*) from students group by class,sex with rollup
3、自定义分组group by grouping sets()
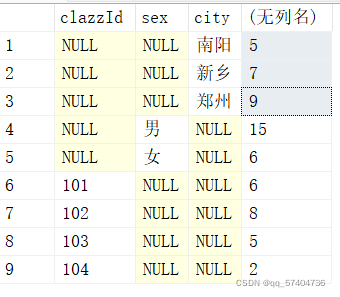
select sex,class,count(*) from students group by grouping sets(sex,class)
select clazzId,sex,city,count(*) from student group by grouping sets((clazzId,sex),city)
排名函数
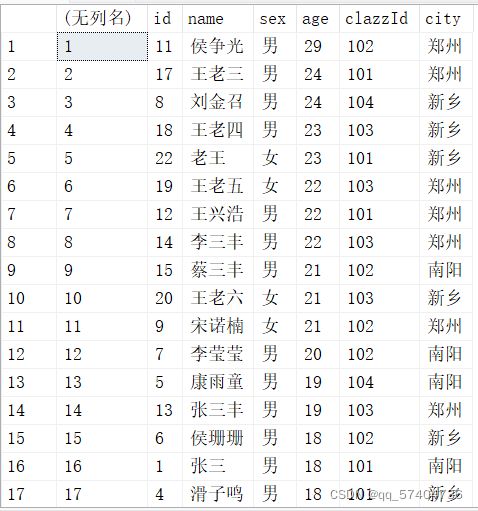
1、row_number()
select row_number() over(order by age desc),* from student
-
注意over里面的order by和真正sql查询后面的order by排序可以完全不一样
select row_number() over(order by age desc),* from student order by id
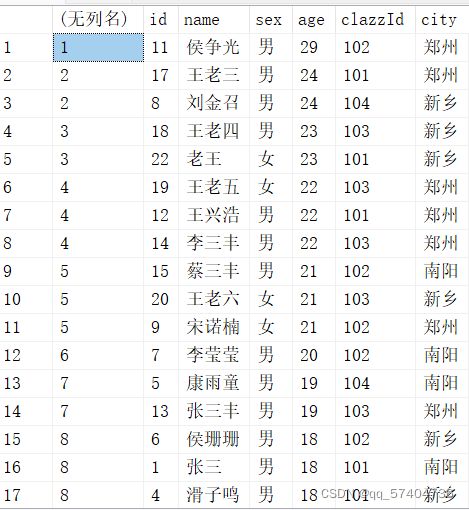
2、rank()
-
rank over子句中排序字段值相同的序号是一样的,后面字段值不相同的序号将跳过相同的排名号排下一个,也就是相关行之前的排名数加一,可以理解为根据当前的记录数生成序号,后面的记录依此类推。
select rank() over(order by age desc),* from student
3、dense_rank()
-
用法和rank一样,只不过rank如果值相等序号是跳跃式的(1,1,3,4),但是dense_rank会是一直连续的(1,1,2,3)
select dense_rank() over(order by age desc),* from student
九、索引
什么是索引
- 就像一本书的目录,根据目录就可以查到自己想看的内容。数据库中使用索引查询数据的时候就不必扫描整个表。书中目录是一个字词以及各字词所在的页码列表。数据库中的索引是表中的值以及各值存储位置的列表
索引的用途
- 我们对数据查询及处理速度已成为衡量应用系统成败的标准,而采用索引来加快数据处理速度通常是最普遍采用的优化方法。索引是增加查询效率的重要手段。
索引的利弊
-
优点
- 大大加快数据的检索速度。
- 创建唯一性索引,保证数据库表中每一行数据的唯一性。
- 加速表和表之间的连接。
- 在使用分组和排序子句进行数据检索时,同样可以显著减少查询中分组和排序的时间。
-
缺点
- 索引需要占物理空间,除了数据表占数据空间之外,每一个索引还要占一定的物理空间,如果要建立聚簇索引,那么需要的空间就会更大。
- 创建索引和维护索引要耗费时间,这种时间随着数据量的增加而增加。
- 当对表中的数据进行增加、删除和修改的时候,索引也要动态的维护,降低了数据的维护速度。
索引的分类
1、聚集索引
- Clustered
- 逻辑顺序与物理顺序一致(int类型的主键, 默认顺序排列)
- 主键是聚集索引, 一张表只可以有一个聚集索引
2、非聚集索引
- NonClustered
- 逻辑顺序与物理顺序不一致
- 唯一值是非聚集索引, 一张表可以有多个非聚集索引
3、对比
-
大多数情况下,聚集索引的速度比非聚集索引要略快一些.因为聚集索引的B树叶子节点直接存储数据,而非聚集索引还需要额外通过叶子节点的指针找到数据.
还有,对于大量连续数据查找,非聚集索引十分乏力,因为非聚集索引需要在非聚集索引的B树中找到每一行的指针,再去其所在表上找数据,性能因此会大打折扣.有时甚至不如不加非聚集索引.
因此,大多数情况下聚集索引都要快于非聚集索引。但聚集索引只能有一个,因此选对聚集索引所施加的列对于查询性能提升至关紧要.
4、语法
create [unique][clustered][nonclustered] index name on table(column)
create nonclustered index name on students(name)
特殊用法
- Columnstore索引(SQLSERVER 2012之后添加)
- 列存储索引包含的列数不能超过 1024。
- 无法聚集。只有非聚集列存储索引才可用。
- 非聚集索引也只能创建一个。
- 不能是唯一索引。
- 不能基于视图或索引视图创建。
- 不能作为主键或外键。
- 不能使用 ALTER INDEX 语句更改。而应在删除后重新创建列存储索引。
- 更多详细见:https://www.cnblogs.com/worfdream/articles/2836219.html