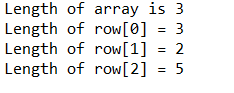学习Java,你需要知道这些——Java数组
目录
- 数组的概念
- 数组的创建
-
- 数组的引用
- 数组的创建
- 数组元素的初始化
- 数组的使用
-
- 使用数组
- 数组的复制
- 多维数组
数组的概念
-
数组由同一类型的对象或者基本数据组成,并封装在同一一个标识符(数组名称)下。
-
数组是对象
-
动态初始化
-
可以赋值给Object类型的变量
-
在数组中可以调用类Object的所有方法
-
二每个数组都有一 个由public final修饰的成员变量: length,即数组含有元素的个数( length可以是正数或零)
-
-
数组元素
- 数组中的变量被称作数组的元素
- 元素没有名字,通过数组名字和非负整数下标值引用数组元素
注意:光理论是不够的,在此送大家一套2020最新Java架构实战教程+大厂面试题库,点击此处 进来获取 一起交流进步哦!
数组的创建
数组的引用
- 声明数组时无需指明数组元素的个数,也不为数组元素分配内存空间
- 不能直接使用,必须经过初始化分配内存后才能使用
数组声明举例:
- 括号在数组名前:
Type[] arrayName;
int[] intArray;
String[] stringArray;
- 括号在数组名后:
Type arrayName[];
int intArray[];
String stringArray[];
数组的创建
- 用关键字new构成数组的创建表达式,可以指定数组的类型和数组元素的个数。元素个数可以是常量也可以是变量。
- 基本类型数组的每个元素都是一个基本类型的变量;引用类型数组的每个元素都是对象的的引用。
数组的创建举例:
- 直接创建
int[] a;
a = new int [10];
String[] s;
s = new String[3]
- 可以将数组的声明和创建一并执行
int a[]=new int[1o];
- 可以在一条声明语句中创建多个数组
String[] s1=new String[3], s2=new String[8];
数组元素的初始化
- 声明数组名时,给出了数组的初始值,程序便会利用数组初始值创建数组并对它的各个元素进行初始化
int a[]={22, 33, 44, 55}; - 创建数组的时,如果没有指定初始值,数组便被赋予默认值初始值。
- 基本类型数值数据 ,默认的初始值为0 ;
- boolean类型数据,默认值为false;
- 引用类型元素的默认值为null。
数组的使用
使用数组
- 引用数组的一个元素:
arrayName[index]- 数组下标必须是int,short, byte,或者char。
- 下标从零开始计数。
- 元素的个数即为数组的长度,可以通过arrayName.length得到。
- 元素下标最大值为length- 1,如果超过最大值,将会产生数组越界异常( ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException )
- 数组名是一个引用,以以下代码为例:
public class Arrays {
public static void main(String []args) {
int [] a1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int [] a2 = a1;
for(int i=0; i<a2.length; i++)
a2[i]++;
for(int i=0; i<a1.length; i++)
System.out.println("a1[" + i + "] = " + a1[i]);
}
}
运行结果:
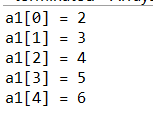
当运行int [] a2 = a1; 这一步时,并不是复制一个数组给a2,只是把引用a1赋值给引用a2。实际上a1,a2操作的是同一个数组。
数组的复制
- 使用方法
System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length);
其中src为被复制数组,srcPos为被复制数组起始下标,dest为复制数组,destPos为复制数组下标,length为想要复制的长度。
以下代码用于复制copyFrom从下标2开始的长度为7的数组。
public class ArraysCopy {
public static void main(String []args) {
char[] copyFrom = {'a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','j','k'};
char[] copyTo = new char[7];
System.arraycopy(copyFrom, 2, copyTo, 0, 7);
System.out.println(new String(copyTo));
}
}
多维数组
类似一维数组,以二维数组为例:
- 声明
- 定义引用
int[][] a;
- 定义引用+构造数组
int[][] a = new int[3][3];
- 定义引用,构造数组,初始化数组元素。
int[][] a ={{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9}};
- 二维数组的长度及每行的长度
- 二维数组的长度为行数
- 二维数组每一行的长度为每一行的列数
public class Arrays {
public static void main(String []args) {
int[][] Array = {{1, 2, 3}, {1, 2}, {8, 9, 10, 20, 50}};
System.out.println("Length of array is " + Array.length);
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
System.out.println("Length of row[" + i +"] = " + Array[i].length);
}
}