Java基础学习
Java基础
- 第1章.java小白入门
-
- 1.1 初识java
- 1.2 dos命令
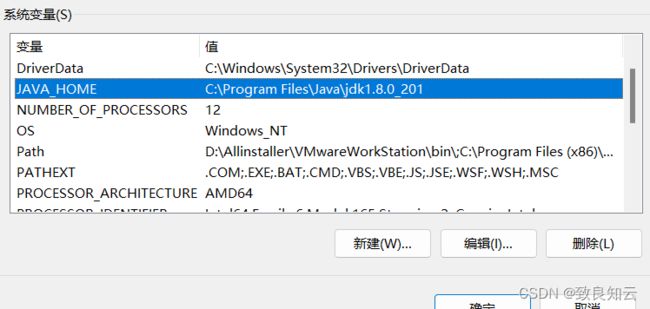
- 1.3 搭建java环境
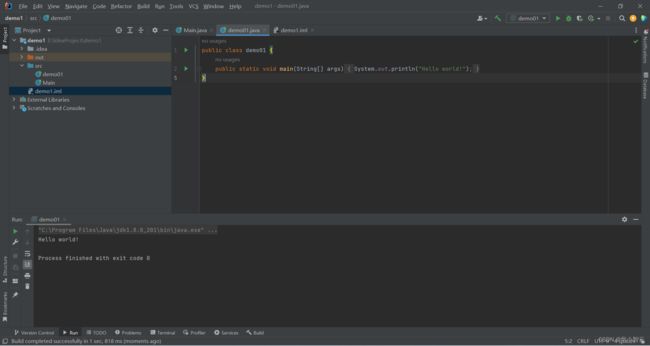
- 1.4 helloworld
- 1.5 集成开发环境
- 1.6 IDEA安装
- 1.7 IDEA配置
- 1.8 验证配置
- 1.9 IDEA运行HelloWorld
- 1.11 换行和制表符
- 1.12 注释
- 第2章 Java基础结构与数组
-
- 2.1 ASCII码表
- 2.2 每个国家都有独有的码表
- 2.3 国际化UTF-8
- 2.4 乱码
- 第3章
-
- 3.1 变量的本质
- 3.2 变量的用例
- 3.3 常用的数据类型
- 3.4 变量的使用步骤
- 3.5 常量
- 3.6 变量命名规则
- 3.7 变量小驼峰法命名
- 3.8 赋值运算符
- 3.9 Scanner用法
- 3.10 Scanner用法
- 3.11 Scanner实战
- 3.12 数据类型的转换
- 3.13八种基本数据类型-整数
- 3.14 八种基本数据类型-小数字符
- 3.15 数据类型强制转换
- 3.16 关系运算符
- 第4章
-
- 4.1 if else结构
- 4.2 if结构
- 4.3 if else if else 结构(多重选择)
- 4.4 if结构的省略写法
- 4.5 与 或 非
- 4.6 幸运抽奖程序
- 4.7字符串的比较
- 4.9 参加编程比赛
- 4.10 switch支持数据类型
- 4.11switch的透传
- 4.12 商品换购
- 第5章
-
- 5.1 为什么要学习循环
- 5.2 while循环
- 5.3 do while 循环
-
- 5.4 偶数之和
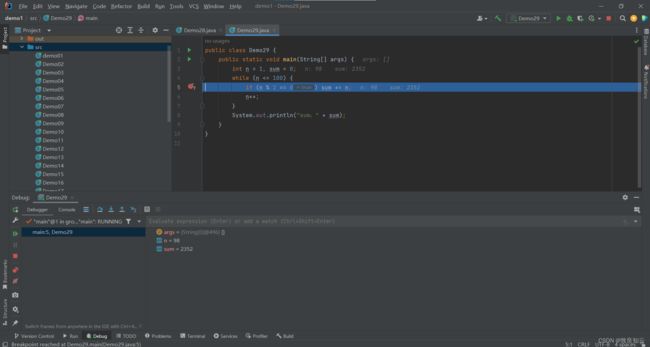
- 5.5 断点调试
- 5.6 购物结算
- 5.7 循环的选择
- 5.8 类名和全类名
- 5.9 摄氏华氏对照表
- 5.10 for循环
- 5.11 for执行次序
- 5.12 五门功课成绩
- 5.13 for的特殊写法
- 5.14 break和continue
- 5.15 录入客户信息_continue 使代码优雅
- 小数的比较不能用==或!=
- 第6章 数组
-
- 6.1 数组由来
第1章.java小白入门
1.1 初识java
1.2 dos命令
1.3 搭建java环境
1.4 helloworld
1.5 集成开发环境
1.6 IDEA安装
1.7 IDEA配置
1.8 验证配置
1.9 IDEA运行HelloWorld
1.11 换行和制表符
1.12 注释
第2章 Java基础结构与数组
2.1 ASCII码表
2.2 每个国家都有独有的码表
2.3 国际化UTF-8
2.4 乱码
第3章
3.1 变量的本质
代码.class,本身是在硬盘上,想运行,代码加载进内存中,然后运行。
int age = 18; //18数字送到一小块内存中
3.2 变量的用例
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 18;
System.out.println("年龄:" + age); //shift+alt+上下箭头,上下移动代码行;
age = 20;
System.out.println("年龄:" + age); // ctrl+d复制行
}
}
3.3 常用的数据类型
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//常用数据类型
int i = 10; //整数
double d = 3.14; //小数
char c = '中'; // 字符
String s = "中国"; // 字符串
System.out.println("整数:" + i + "小数:" + d + "字符:" + c + "字符串:" + s);
}
}
3.4 变量的使用步骤
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args){
// 1.声明
int age;
// 2.赋值(java是在c++基础上改进过的, 要求变量使用前先行赋值)
age = 1;
// 3.使用
System.out.println(age);
}
}
3.5 常量
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 常量命名法则,全大写,如果有多个英文单词,用下划线隔开
final int AGE = 10;
System.out.println(AGE);
final String CHINA = "中华人民共和国";
System.out.println(CHINA);
}
}
3.6 变量命名规则
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args){
/*
首字母必须是:字符、$、_;不能是关键字
*/
int a = 1;
}
}
3.7 变量小驼峰法命名
// 类名大驼峰法命名
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args){
// 变量名小驼峰法命名
int myAge = 18;
int age = 18;
//循环因子 i j k
// 尽量使用有意义的单词(循环因子除外)
}
}
3.8 赋值运算符
public class Demo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 赋值运算符
int age = 10;
age += 2; //等价于 age = age + 2
// age++ ; // += 等于 age = age + 1;简化为age++
/*
+= ++
-= --
*=
/=
%=
*/
int year = 2022;
int result = year % 10; //余数
System.out.println(result);
year %= 100; // year = year % 100;
System.out.println("余数:" + year);
}
}
3.9 Scanner用法
import java.util.Scanner; // 引入该类的声明 alt + enter 自动导入
public class Demo08 {
public static void main(String[] args){
// 键盘输入功能 Scanner
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); //固定写法
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:");
String name = scanner.next(); // 等待你输入姓名
System.out.println("你输入你的姓名是:" + name);
}
}
在服务器编程,它是不用的, 不需要过多关注
3.10 Scanner用法
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入整数:");
int age = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入小数:");
double money = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.println("整数:" + age + ".小数:" + money);
}
}
3.11 Scanner实战
从控制台输入王浩3门课程成绩,编写程序实现
(1)Java课和SQL课的分数之差
(2) 3门课程的平均分
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入李华的3门课程的成绩:");
System.out.println("Java:");
int java = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("PS:");
int ps = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("SQL:");
int sql = scanner.nextInt();
int chazhi = java - sql;
System.out.println("Java和SQL的差:" + chazhi); //方法一
System.out.println("java和SQL的差:" + (java - sql)); // 方法二 要加(),调整优先级,字符串不可以做剑法
int average = (java + ps + sql) / 3;
System.out.println("平均值:" + average); // 法一
System.out.println("平均值:" + (java + ps + sql)); // 法二
}
}
3.12 数据类型的转换
public class Demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args){
double java1 =81.29;
int duoliao = 2;
double java2 = java1 + duoliao; // 如果一个操作数为double,则整个表达式提升为double
System.out.println("第二次平均分:" + java2);
//满足自动转换的条件:两种类型要兼容,目标类型大于原类型
}
}
3.13八种基本数据类型-整数
public class Demo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 八种基本数据整数类型
/* 整数
1个字节 byte -128-> +127
2个字节 short -32768 -> +32767
*/
byte b1 = -128;
System.out.println(b1);
short s1 = -32768;
System.out.println(s1);
int i1 = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
System.out.println(i1);
long l1 = Long.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println(l1);
}
}
3.14 八种基本数据类型-小数字符
public class Demo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 八种基本数据整数类型
/* 小数
4个字节 float
8个字节 double
*/
//float f = 3.14f;
float f = Float.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println(f);
double d = Double.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println(d);
/* 字符
2个字节 char 0-65535 唯一没有负数概念的
*/
char c1 = Character.MIN_VALUE;
char c2 = Character.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println((int)c1);
System.out.println((int)c2);
/* 布尔
一个字符 boolean 不是数值,而是一个真假
*/
char c1 = Character.MIN_VALUE;
char c2 = Character.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println(bool1);
System.out.println(bool2);
}
}
3.15 数据类型强制转换
public class Demo13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c1 = '中';
int i = 1;
// 强制转换 (目标类型)表达式
char c2 = (char)(c1 + i);
}
}
3.16 关系运算符
public class Demo14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
关系运算符 > >= < <= !=
经历了运算之后,结果的数据类型是布尔类型
*/
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
boolean r1 = a > b;
boolean r2 = a >= b;
boolean r3 = a < b;
boolean r4 = a <= b;
boolean r5 = a != b;
System.out.println(r1);
System.out.println(r2);
System.out.println(r3);
System.out.println(r4);
System.out.println(r5);
}
}
第4章
4.1 if else结构
public class Demo15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// boolean flag = true;
// if (flag) {
// System.out.println("真");
// }
// else {
// System.out.println("假");
int score = 99;
boolean flag = score >= 90;
if (flag){
System.out.println("优秀");
}
else {
System.out.println("一般");
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("优秀");
}
else {
System.out.println("一般");
}
}
}
4.2 if结构
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo16 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
if (score >= 90){
System.out.println("奖励");
}
System.out.println("程序结束");
}
}
4.3 if else if else 结构(多重选择)
public class Demo17 {
public static void main(String[] args){
/*
1.多选一
2.从上到下,逐一判断,一旦为真,不会继续判断
*/
// 有逻辑上的错误
int score = 90;
if (score >=90) {
System.out.println("优秀");
} else if (score >= 80) {
System.out.println("良好");
} else if (score >= 70) {
System.out.println("中等");
} else if (score >= 60) {
System.out.println("及格");
} else {
System.out.println("不及格差");
}
}
}
4.4 if结构的省略写法
public class Demo18 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 如果一个条件下的执行代码只有一行此时可以省略 {}
int score = 88;
if (score >= 90)
System.out.println("优秀");
else if (score >= 80)
System.out.println("良好");
else if (score >= 70)
System.out.println("中等");
else if (score >= 60)
System.out.println("及格");
else System.out.println("差");
System.out.println(".....");
}
}
4.5 与 或 非
1.&& 与 一假则假
2. || 或 一真则真
3. !非 取反
public class Demo19 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// java html 只有两门都90分才能去玩,否则学习。
int java = 80, html = 90;
if (java >= 90 && html >= 90) System.out.println("出去玩");
else System.out.println("学习");
}
}
4.6 幸运抽奖程序
需求说明:
抽奖规则:会员号的百位数字等于产生的随机数字即为幸运会员
实现思路:
1.产生随机数
2.从控制台接收一个4位会员号
3.分解获得百位数
4.判断是否为幸运会员
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo20 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("> 幸运抽奖\n");
System.out.print("请输入4位会员号:");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
int baiweishu = id / 100 % 10;
/*
Math.random() 产生一个左闭右开之间的数 [0.0 ~ 1.0)之间的小数
目标产生0-9之间的数,一共10个
[0.0 ~ 1.0) * 10 -> [0.0~10.0) -> 强制转换 [0 ~ 10)
*/
int luck = (int) (Math.random()*10);
System.out.println("幸运数字是:" + luck);
if (baiweishu == luck) System.out.println("奖励一部苹果手机。");
else System.out.println("很遗憾你没有中奖!");
}
}
4.7字符串的比较
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo21 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入是否是会员(y/n):");
String yesno = scanner.next();
// == 用于基本数据类型(byte short int long float double char boolean) 的比较
// 字符串的比较采用字符串equals()方法
if (yesno.equals("y")) {
System.out.println("是会员");
} else {
System.out.println("不是会员");
}
}
}
4.8 嵌套if
嵌套if的选择结构
| 顾客 | 折扣 |
|---|---|
| 会员购物 | 8折 |
| 会员购物满200元 | 7.5 |
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo22 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入是否是会员(y/n):");
String yesno = scanner.next();
System.out.println("请输入购物金额:");
int money = scanner.nextInt();
double zhekou = 1.0; // 默认值没有折扣
if (yesno.equals("y")) {
if (money >= 200) zhekou = 0.75;
else zhekou = 0.8;//嵌套
} else {
if (money >= 100) zhekou = 0.9;//嵌套
}
System.out.println("实际支付:" + money * zhekou);
}
}
4.9 参加编程比赛
- 如果获得第一名,将参加清华大学组织的一个月夏令营
- 如果获得第二名,将获得戴尔笔记本一个
- 如果获得第三名将奖励一个运动手环
- 不给任何奖励
5.解决方法:
使用多重if选择结构实现,结构复杂
使用switch选择结构解决的条件需为等值判断
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入名次:");
int rank = scanner.nextInt();
/*
if (rank == 1) System.out.println("夏令营");
else if (rank == 2) System.out.println("笔记本");
else if (rank == 3) System.out.println("移动手环");
else System.out.println("无奖励");
*/
//使用switch的条件必须为等值判断
switch (rank) { //switch切换开关
case 1: // 当
System.out.println("夏令营");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("笔记本");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("运动手环");
break;
default:
System.out.println("无奖励");
break; //离开域
}
}
}
4.10 switch支持数据类型
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入名次:");
int rank = scanner.nextInt();
/*
1.byte short int char
2.String
3.long float double 不支持
4.enum 枚举
*/
//使用switch的条件必须为等值判断
switch (rank) { //switch切换开关
case 1: // 当
System.out.println("夏令营");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("笔记本");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("运动手环");
break;
default:
System.out.println("无奖励");
break; //离开域
}
}
}
4.11switch的透传
public class Demo24 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String day = "星期一";
switch (day) {
// switch透传的使用
case "星期一":
System.out.println("画画");
// break;
case "星期二":
System.out.println("休息");
break;
case "星期三":
System.out.println("画画");
break;
case "星期四":
System.out.println("休息");
break;
case "星期五":
System.out.println("休息");
break;
case "星期六":
System.out.println("街舞");
break;
default:
System.out.println("街舞");
break;
}
}
}
4.12 商品换购
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo25 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入消费金额:");
int money = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("是否换购:");
System.out.println("1.满50元,加2元换购商品1");
System.out.println("2.满100元,加2元换购商品2");
System.out.println("3.满100元,加2元换购商品3");
System.out.println("4.满200元,加2元换购商品4");
System.out.println("5.满200元,加2元换购商品5");
System.out.println("0,不换购");
System.out.print("请选择:");
int select = scanner.nextInt();
String goods = "不换购";
switch (select) {
case 1:
if (money > 50) {
money += 2;
goods = "商品1";
}
break;
case 2:
if (money > 100) {
money += 3;
goods = "商品2";
}
break;
case 3:
if (money > 100) {
money +=10;
goods = "商品3";
}
break;
case 4:
if (money > 200) {
money +=10;
goods = "商品4";
}
break;
case 5:
if (money > 200) {
money +=20;
goods = "商品5";
}
break;
}
System.out.println("消费金额:"+ money);
System.out.println("成功换购:" + goods);
}
}
第5章
5.1 为什么要学习循环
在编写代码时,业务需求(项目要交)原地打转,符合条件结束循环。
5.2 while循环
public class Demo26 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
while (条件) {
循环体 (内容)
更新条件}
*/
int i = 1, sum = 0;
while (i <= 100) {
sum += i;
i++;
}
System.out.println("和:" + sum);
}
}
5.3 do while 循环
public class Demo27 {
public static void main() {
/*
do {
循环体(内容);
更新条件;
} while(条件);
1 + 到 100; 5050
*/
int i = 1, sum = 0;
do {
sum += i;
i++;
} while (i <= 100);
System.out.println("和:" + sum);
}
}
5.4 偶数之和
public class Demo28 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 1, sum = 0;
while (n <= 100) {
if (n % 2 == 0) sum += n;
n++;
}
System.out.println("sum:" + sum);
}
}
5.5 断点调试
public class Demo29 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 1, sum = 0;
while (n <= 100) {
if (n % 2 == 0) sum += n;
n++;
}
System.out.println("sum:" + sum);
}
}
5.6 购物结算
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo30 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("购物结算");
System.out.println("请选择商品编号:");
System.out.println("1.T恤 2.网球鞋 3.网球拍");
// System.out.println("请输入商品编号:");
String jx = "y";
while (jx.equals("y")) {
System.out.print("请输入商品编号:");
int select = scanner.nextInt();
switch (select) {
case 1:
System.out.println("T恤 100元");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("网球鞋 200元");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("网球拍 300元");
break;
}
System.out.print("是否继续(y/n):");
jx = scanner.next();
}
System.out.println("程序结束!");
}
}
5.7 循环的选择
所有的循环都是可以相互替换,选择的时候选择最适合的较好。在循环至少要走一次最好do-while
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("购物结算");
System.out.println("请选择商品编号:");
System.out.println("1.T恤 2.网球鞋 3.网球拍");
// System.out.println("请输入商品编号:");
String jx;
do {
System.out.print("请输入商品编号:");
int select = scanner.nextInt();
switch (select) {
case 1:
System.out.println("T恤 100元");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("网球鞋 200元");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("网球拍 300元");
break;
}
System.out.print("是否继续(y/n):");
jx = scanner.next();
} while (jx.equals("y"));
System.out.println("程序结束!");
}
}
5.8 类名和全类名
java软件,类名是可以重复的,但是全类名不允许重复,基础的类不需要导,比如java.lang
5.9 摄氏华氏对照表
编程使用do-while实现:输出摄氏温度与华氏温度的对照表,要求它从摄氏温度0度到250度,每隔20度为一项,对照表中的条目不超过10条。
转换关系:华氏温度=摄氏温度*9 / 5.0 + 3
循环操作:计算摄氏温度,并输出对照条目表
循环条件:条目<= 10 && 摄氏温度 <= 250
public class Demo32 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
使用do-while实现:输出摄氏温度与华氏温度的对照表,要求它从摄氏温度0度到250度,每隔20度为一项,对照表中的条目不超过10条。
转换关系:华氏温度=摄氏温度*9 / 5.0 + 3
循环操作:计算摄氏温度,并输出对照条目表
循环条件:条目<= 10 && 摄氏温度 <= 250
*/
double huashidu, sheshidu = 0;
int count = 0;
do {
huashidu = sheshidu * 9 / 5.0 + 3;
System.out.println(sheshidu + "vd. " + huashidu);
sheshidu += 30;
count++;
} while (sheshidu <= 250 && count <= 10);
}
}
5.10 for循环
public class Demo33 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
1 + 到100 ,5050
特点:循环次数固定下来的。建议使用for循环。
for(声明初始化循环变量; 条件;修改循环变量) {
循环体;
}
*/
/*
int i = 1, sum = 0;
while ( i <= 100) {
sum += i;
i++;
}
*/
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i<= 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("和:" + sum);
}
}
5.11 for执行次序
通过断点调试进行看具体步骤
5.12 五门功课成绩
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo34 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入姓名:");
String name = scanner.next(); //记录姓名
int sum = 0;// 记录总成绩
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.print("请输入5门功课第" + i + "门的成绩:");
sum += scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(name + "的平均分是:" + sum / 5.0 );
}
}
5.13 for的特殊写法
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo35 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (; ;) { //类似于while(true)死循环
System.out.print("");
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo35 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0, j = 6; i <= 6; i++, j-- ) {
System.out.println(i + "+" + j + "=" + 6);
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo35 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0, j = 6; i <= 6; i++, j-- ) {
System.out.println(i + "+" + j + "=" + 6);
}
}
}
5.14 break和continue
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo36 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i<=5; i++) {
System.out.print("成绩:");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
// if (score < 0) continue; //忽略当次
if (score < 0) break; //结束循环
sum += score;
}
System.out.println("最后");
}
}
5.15 录入客户信息_continue 使代码优雅
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo37 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("> 添加客户信息");
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { // if if 不利于阅读
System.out.print("会员号《4位》:");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
if (id >= 1000 && id <= 9999) {
System.out.print("生日《mm/dd》:");
String birth = scanner.next();
if (birth.length() == 5) {
System.out.print("积分:");
int scorecard = scanner.nextInt();
if (scorecard >= 0) {
System.out.println("会员信息是:\n" + id + "\t" + birth + "\t" + scorecard);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println("程序结束!");
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo38 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(" > 添加客户信息");
for (int i=1; i<=3; i++) {
System.out.print("会员号《4位》:");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
if (id < 1000 || id >9999) continue;
System.out.print("生日《mm/dd》:");
String birth = scanner.next();
if (birth.length() != 5) continue;
System.out.print("积分:");
int scorecard = scanner.nextInt();
if (scorecard < 0) continue;
System.out.println("会员信息是:\n" + id + "\t" + scorecard);
}
System.out.println("程序结束!");
}
}
小数的比较不能用==或!=
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo39 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final double JINDU = 0.00001; //设计一个精度
/*
1.录入一个小数1. 小数2. 小数3,
判断小数1+小数2是否等于小数3.?
小数是模拟出来的数,无法用== != 进行比较的.
*/
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("小数1:");
double d1 = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.print("小数2:");
double d2 = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.print("小数3:");
double d3 = scanner.nextDouble();
// if (d1 + d2 == d3) System.out.print("d1+d2==d3");
if (d1 + d2 <= d3 + JINDU && d1 + d2 >= d3 - JINDU) System.out.print("d1+d2==d3");
else System.out.println("d1+d2!=d3");
System.out.println("程序结束!0.");
}
}