cs231n assignment3 q4 Generative Adversarial Networks
文章目录
- 嫌墨迹直接看代码
- Q4 :Generative Adversarial Networks
-
- sample_noise
-
- 题面
- 解析
- 代码
- 输出
- discriminator
-
- 题面
- 解析
- 代码
- 输出
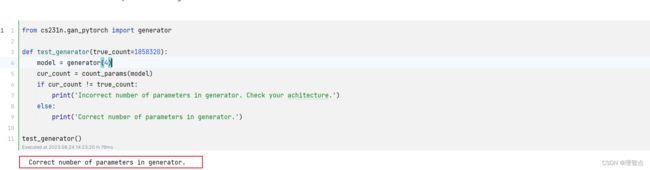
- generator
-
- 题面
- 解析
- 代码
- 输出
- discriminator_loss
-
- 题面
- 解析
- 代码
- 输出
- generator_loss
-
- 题面
- 解析
- 代码
- get_optimizer
-
- 题面
- 解析
- 代码
- 输出
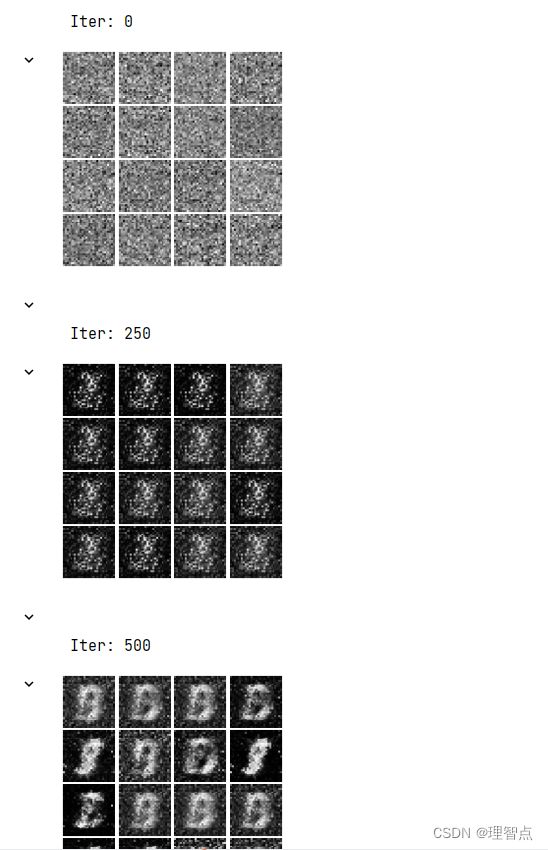
- ls_discriminator_loss ls_generator_loss
-
- 题面
- 解析
- 代码
- 输出
- build_dc_classifier
-
- 题面
- 解析
- 代码
- 输出
- build_dc_generator
-
- 题面
- 解析
- 代码
- 输出
嫌墨迹直接看代码
Q4 :Generative Adversarial Networks
sample_noise
题面


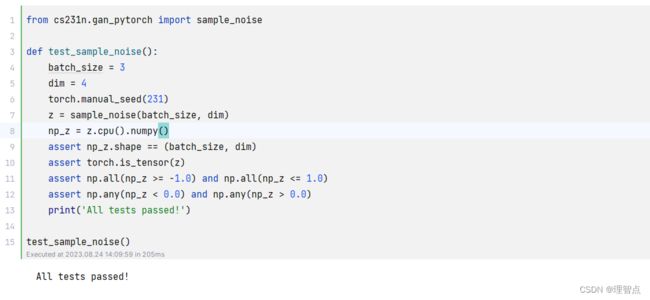
就是让我们生成噪音,使用torch.rand就好了注意我们的噪音区间应该在 (-1,1)
而torch.rand生成的在(0,1)
解析
看代码就好了
代码
def sample_noise(batch_size, dim, seed=None):
"""
Generate a PyTorch Tensor of uniform random noise.
Input:
- batch_size: Integer giving the batch size of noise to generate.
- dim: Integer giving the dimension of noise to generate.
Output:
- A PyTorch Tensor of shape (batch_size, dim) containing uniform
random noise in the range (-1, 1).
"""
if seed is not None:
torch.manual_seed(seed)
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return torch.rand(batch_size, dim) * 2 - 1
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)****
输出
discriminator
题面
解析
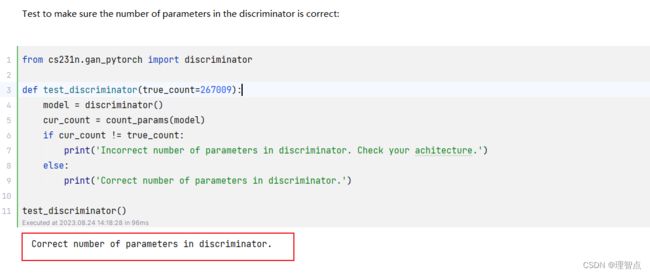
没啥好说的,pytorch的使用在之前我们也学习过了,直接调用相关api就好了,如果又不懂得看代码就好了
代码
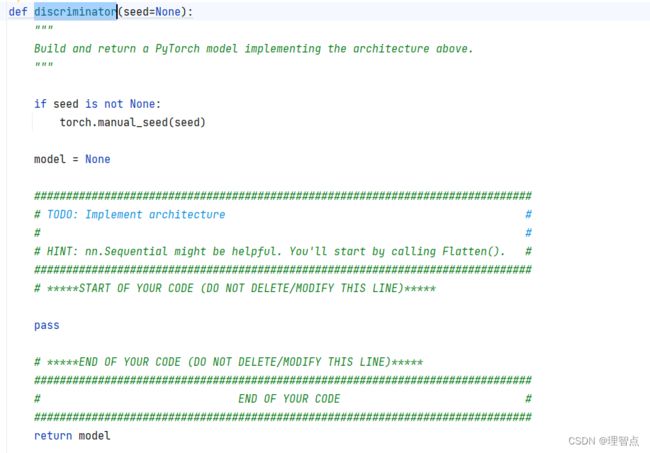
def discriminator(seed=None):
"""
Build and return a PyTorch model implementing the architecture above.
"""
if seed is not None:
torch.manual_seed(seed)
model = None
##############################################################################
# TODO: Implement architecture #
# #
# HINT: nn.Sequential might be helpful. You'll start by calling Flatten(). #
##############################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(784, 256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.01),
nn.Linear(256, 256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.01),
nn.Linear(256, 1)
)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
##############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
##############################################################################
return model
输出
generator
题面
解析
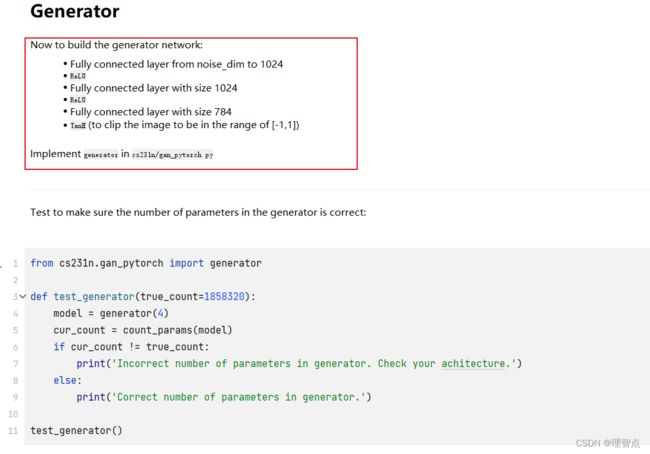
看代码就好了
代码
def generator(noise_dim=NOISE_DIM, seed=None):
"""
Build and return a PyTorch model implementing the architecture above.
"""
if seed is not None:
torch.manual_seed(seed)
model = None
##############################################################################
# TODO: Implement architecture #
# #
# HINT: nn.Sequential might be helpful. #
##############################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(noise_dim, 1024),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(1024, 1024),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(1024, 784),
nn.Tanh()
)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
##############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
##############################################################################
return model
输出
discriminator_loss
题面



让我们计算判别器的损失,具体怎么计算在上面的公式里写了,其中需要使用的bce_loss函数已经让我们使用了pytorch的函数
关于bce_loss 交叉熵损失函数的讲解
解析
结合上面的材料,同时我的代码注释吧
代码
def bce_loss(input, target):
"""
Numerically stable version of the binary cross-entropy loss function in PyTorch.
Inputs:
- input: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N, ) giving scores.
- target: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) containing 0 and 1 giving targets.
Returns:
- A PyTorch Tensor containing the mean BCE loss over the minibatch of input data.
"""
bce = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
# 注意,原来给的代码是下面的代码,使用了Input.squeezed().后来我发现这样的话会导致input的size变成(N,)而target的size变成(N,1)
# 导致报错,所以我把squeeze()去掉了,这样就不会出现这个问题了,或者你也可以两个都加上squeeze()
# return bce(input.squeeze(), target)
# 下面是我修改后的代码
return bce(input, target)
def discriminator_loss(logits_real, logits_fake):
"""
Computes the discriminator loss described above.
Inputs:
- logits_real: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the real data.
- logits_fake: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the fake data.
Returns:
- loss: PyTorch Tensor containing (scalar) the loss for the discriminator.
"""
loss = None
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
# 获取正确分类的标签
true_labels = torch.ones_like(logits_real).type(dtype)
# 获取错误分类的标签
false_labels = torch.zeros_like(logits_fake).type(dtype)
# 为什么公式里是两个减法,而这里是两个加法呢?
# 因为bce_loss已经帮我们取负值了,所以加法就可以了
loss = bce_loss(logits_real, true_labels) + bce_loss(logits_fake, false_labels)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return loss
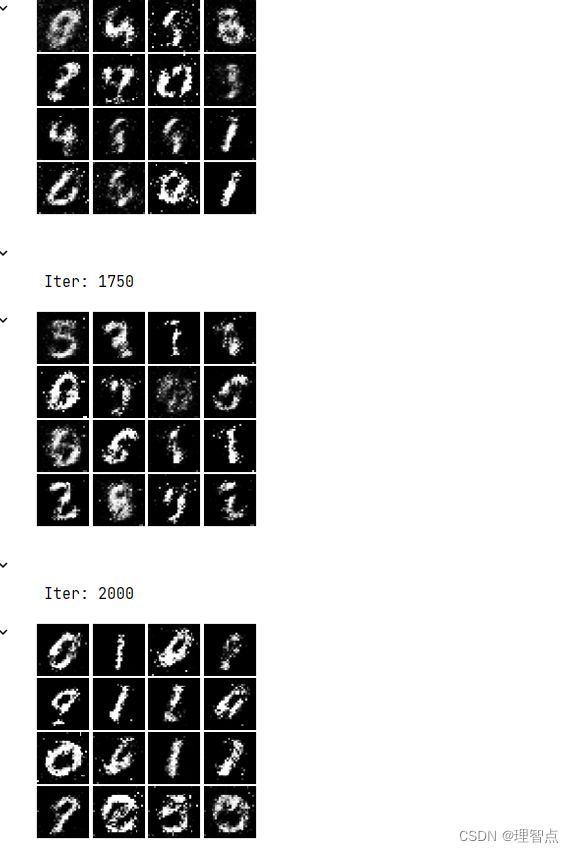
输出
generator_loss
题面
解析
看代码吧
代码
def generator_loss(logits_fake):
"""
Computes the generator loss described above.
Inputs:
- logits_fake: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the fake data.
Returns:
- loss: PyTorch Tensor containing the (scalar) loss for the generator.
"""
loss = None
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
# 为什么上面判别器loss的代码里fake的标签是0,而这里是1呢?
# 因为这里是希望生成器生成的图片能够被判别器判别为真,所以标签是1
false_label = torch.ones_like(logits_fake).type(dtype)
loss = bce_loss(logits_fake, false_label)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return loss
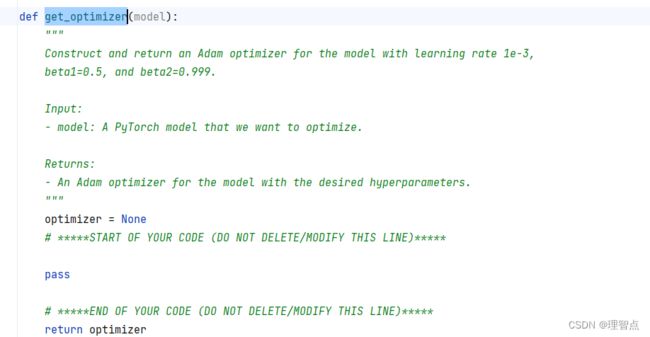
get_optimizer
题面
解析
看代码吧,这个就是个调用api
代码
def get_optimizer(model):
"""
Construct and return an Adam optimizer for the model with learning rate 1e-3,
beta1=0.5, and beta2=0.999.
Input:
- model: A PyTorch model that we want to optimize.
Returns:
- An Adam optimizer for the model with the desired hyperparameters.
"""
optimizer = None
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return optimizer
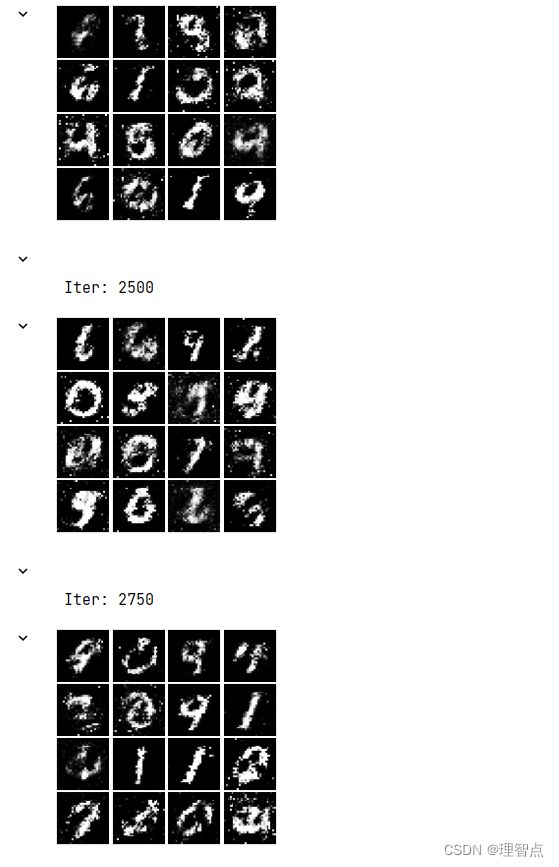
输出
ls_discriminator_loss ls_generator_loss
题面
注意我们现在不需要使用二元交叉熵的函数,因为上面这个公式里的loss计算公式
对于生成器而言,就是生成的图片经识别后被认为是真实的可能性与1的距离越小越好,
因此我们只需要(计算他们两之间的距离)
而对于鉴别器而言,就是原始数据集的图片经识别后被认为是真实的可能性与1的距离越小越好,
生成的图片经识别后被认为是真实的可能性与0的距离越小越好,
所以有了上面的loss计算公式
解析
看上面和代码
代码
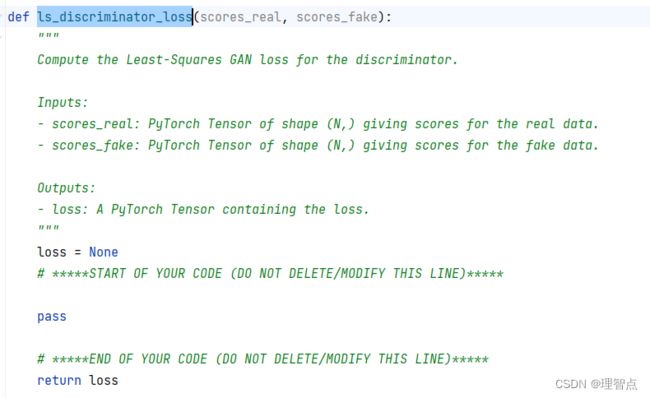
def ls_discriminator_loss(scores_real, scores_fake):
"""
Compute the Least-Squares GAN loss for the discriminator.
Inputs:
- scores_real: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the real data.
- scores_fake: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the fake data.
Outputs:
- loss: A PyTorch Tensor containing the loss.
"""
loss = None
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
loss = 0.5 * torch.mean((scores_real - 1) ** 2) + 0.5 * torch.mean(scores_fake ** 2)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return loss
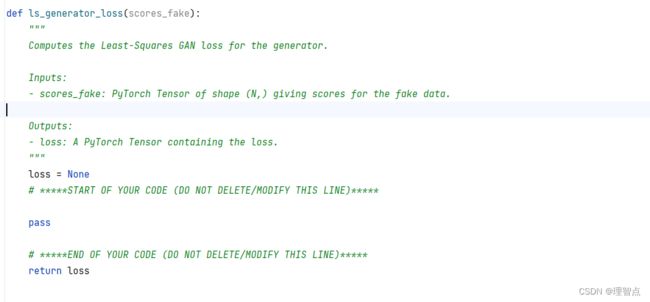
def ls_generator_loss(scores_fake):
"""
Computes the Least-Squares GAN loss for the generator.
Inputs:
- scores_fake: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N,) giving scores for the fake data.
Outputs:
- loss: A PyTorch Tensor containing the loss.
"""
loss = None
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
loss = 0.5 * torch.mean((scores_fake - 1) ** 2)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return loss
输出
build_dc_classifier
题面
解析
照着做就好了
代码
def build_dc_classifier(batch_size):
"""
Build and return a PyTorch model for the DCGAN discriminator implementing
the architecture above.
"""
##############################################################################
# TODO: Implement architecture #
# #
# HINT: nn.Sequential might be helpful. #
##############################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return nn.Sequential(
Unflatten(batch_size, 1, 28, 28),
nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=5, stride=1),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.01),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=5, stride=1),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.01),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
Flatten(),
nn.Linear(1024, 4 * 4 * 64),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.01),
nn.Linear(4 * 4 * 64, 1)
)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
##############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
##############################################################################
输出
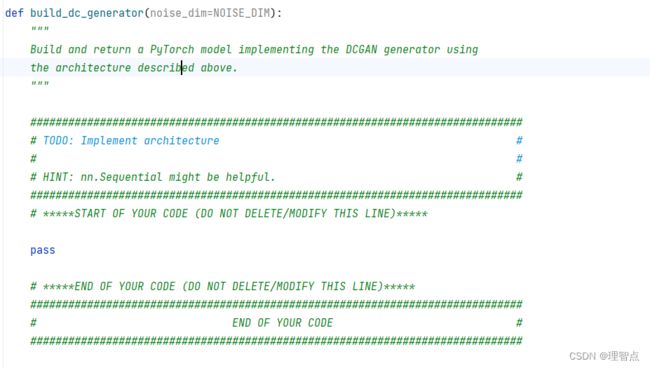
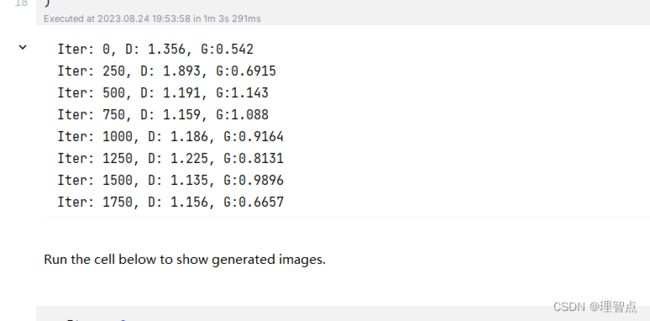
build_dc_generator
题面
解析
同上
代码
def build_dc_generator(noise_dim=NOISE_DIM):
"""
Build and return a PyTorch model implementing the DCGAN generator using
the architecture described above.
"""
##############################################################################
# TODO: Implement architecture #
# #
# HINT: nn.Sequential might be helpful. #
##############################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(noise_dim, 1024),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.BatchNorm1d(1024),
nn.Linear(1024, 7 * 7 * 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.BatchNorm1d(7 * 7 * 128),
Unflatten(-1, 128, 7, 7),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(128, 64, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(64, 1, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.Tanh(),
)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
##############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
##############################################################################