- 深入理解汇编语言子程序设计与系统调用
网安spinage
汇编语言开发语言汇编算法
本文将全面解析汇编语言中子程序设计的核心技术以及系统调用的实现方法,涵盖参数传递的多种方式、堆栈管理、API调用等关键知识点,并提供实际案例演示。一、子程序设计:参数传递的艺术1.寄存器传参:高效简洁.386.modelflat,stdcalloptioncasemap:none.dataxdd5;定义变量ydd6sumdd?.code;函数定义:addxy1addxy1procpushebpmo
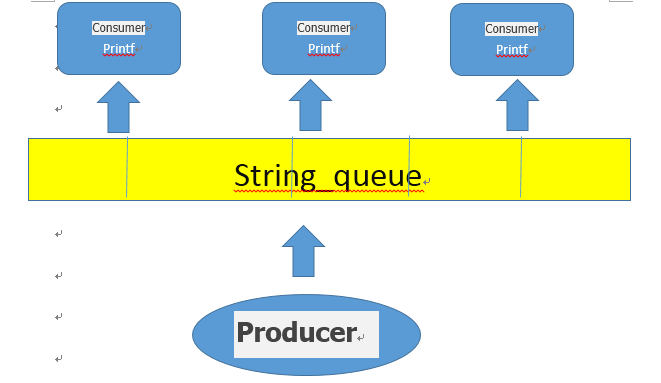
- Java 笔记 lambda
五行缺弦
Java笔记java笔记
✅Lambda基本语法(parameters)->expression或(parameters)->{statements}//无参数Runnabler=()->System.out.println("Hello");//单个参数(小括号可省略)Consumerc=s->System.out.println(s);//多参数+多语句Comparatorcomp=(a,b)->{System.out
- C++-coroutines协程 协程之间相互切换
mrbone11
C++#Coroutinesc++服务器算法协程coroutines
C++协程切换的机制基于如下C++协程标准的规定:await_suspend如果直接返回一个coroutine_handle协程句柄。那么被返回的句柄会立即恢复,即调用返回coroutine_handle的resume()方法查看如下例子:#include#include#include//前向声明structTask;//一个简单的Awaiter,用于触发协程切换structSwitchTo{s
- C++-coroutines协程 将自定义类型转为awaitable(可等待)类型的两种方法
mrbone11
#Coroutinesc++开发语言协程coroutines
文章目录前言重载operatorco_await定义promise_type::await_transform函数前言阅读本篇文章时,已经假定你有对协程的基本概念,如果没有,可以阅读我写的这篇协程入门文章我们已经知道,对于co_await\,expression的返回值必须是awaitable类型,即正确实现了如下三个函数:await_readyawait_suspendawait_resume对
- 周一 2021-05-17 06:29 - 22:00 雨 08h20m
么得感情的日更机器
一时间记录二概述早上醒来,看小说,洗漱,吃饭上午论文,吃饭下午小说,午休,总结,打疫苗,吃饭晚上日常任务,小说,洗漱,睡觉三总结(Summary)今天是论文和打疫苗的一天,总体感觉良好,学习感觉没咋学四反思今天收获了什么?哪里做的不好?做得不好的原因是什么?以后怎样避免或改进?4.1今日收获论文4.2今日不足编程学习醒了因为实验室没开门,就不愿意去,这可怎么办
- 尚庭公寓-学习跟敲笔记(二)
wenbinglin66
学习笔记springbootjava
管理端后端开发-租赁管理模块1.看房预约管理1.1根据ID更新预约状态在ViewAppointmenController中增加内容@Operation(summary="根据id更新预约状态")@PostMapping("updateStatusById")publicResultupdateStatusById(@RequestParamLongid,@RequestParamAppointme
- 力扣 hot100 Day52
124.二叉树中的最大路径和二叉树中的路径被定义为一条节点序列,序列中每对相邻节点之间都存在一条边。同一个节点在一条路径序列中至多出现一次。该路径至少包含一个节点,且不一定经过根节点。路径和是路径中各节点值的总和。给你一个二叉树的根节点root,返回其最大路径和。//自己写的classSolution{public:intmaxpasssum(TreeNode*root,int&maxtmp){i
- [LeetCode 169/229] Majority Element I/II (easy / medium)
灰睛眼蓝
LeetCode169IGivenanarrayofsizen,findthemajorityelement.Themajorityelementistheelementthatappearsmorethan⌊n/2⌋times.Youmayassumethatthearrayisnon-emptyandthemajorityelementalwaysexistinthearray.Example
- python进行常见的数学计算(方差,一元二次方程,求导,积分等等)
ccut 第一混
python
代码如下:importnumpyasnpimportmathimportcmathimportscipy#平均数defaverage(lst):sum_lst=0forninlst:sum_lst=sum_lst+nreturnsum_lst/len(lst)#方差defvariance(lst):average_lst=average(lst)sum_variance=0forninlst:su
- 如何在 Apache Ignite 中创建和使用自定义 SQL 函数(Custom SQL Functions)
lang20150928
其他apacheIgnite
这段内容讲的是如何在ApacheIgnite中创建和使用自定义SQL函数(CustomSQLFunctions)。我们可以分步骤来理解它的含义和用法。一、什么是CustomSQLFunction?ApacheIgnite的SQL引擎支持标准SQL函数(如COUNT、SUM、AVG等),但有时这些内置函数无法满足业务需求。这时,你可以通过编写Java代码,创建自己的SQL函数,并在SQL查询中使用它
- R拟合 | 一个分布能看到三个峰,怎么拟合出这三个正态分布的参数? | 高斯混合模型 与 EM算法
biomooc
R数学与统计r语言
1.效果已知数据符合上图分布,怎么求下图的三个分布的参数mu,sigma,及每个分布的权重lambda?2.代码:高斯混合模型(GaussianMixtureModel,简称GMM)library(mixtools)set.seed(123)#确保结果可重复#假设x是你的观测数据xsummary(mix)summaryofnormalmixEMobject:comp1comp2comp3lambd
- 大模型基础知识(万字详解)
掘金安东尼
python机器学习人工智能
在数学上,deepseek多轮自蒸馏可以理解为对学生模型施加一系列滚动KL散度约束:LMSD=∑i=1nαi⋅KL(pTi(x)∥pSi(x))\mathcal{L}_{MSD}=\sum_{i=1}^{n}\alpha_i\cdot\text{KL}(p_{T_i}(x)\parallelp_{S_i}(x))LMSD=i=1∑nαi⋅KL(pTi(x)∥pSi(x))其中,TiT_iTi和Si
- 【大模型LLM学习】function call/agent学习记录
威化饼的一隅
大模型LLM学习agentlangchain意图识别functioncall工具调用
【大模型LLM学习】functioncall/agent学习记录0前言1langchain实现functioncall2调用本地模型3微调本地模型3.1few-shot调用Claude生成Q-A对3.2tools格式3.3agent微调格式3.4swift微调p.s.0前言 记录一下使用langchain做简单的functioncall/agent(或者说意图识别,如果函数有返回值再进行summ
- 交叉熵损失函数
onlyzzr
深度学习pytorch深度学习机器学习
importtorchimporttorch.nn.functionalasFimporttorch.nnasnnimportmathdefcross_entropyloss(y_pred,y_true):#y_pred'sshapeis[N,C]y_pred=torch.log_softmax(y_pred,dim=-1)loss=-torch.sum(y_true*y_pred,dim=-1)
- Missing Coin Sum 硬币可以组成的连续面额上限
YouQian772
贪心算法
题目描述Youhavencoinswithpositiveintegervalues.Whatisthesmallestsumyoucannotcreateusingasubsetofthecoins?输入Thefirstinputlinehasanintegern(1≤n≤2*105):thenumberofcoins.Thesecondlinehasnintegersx1,x2,...,xn(
- leetcode-112. 二叉树路径总和
JlexZzzz
leetcode数据结构leetcode深度优先算法二叉树
leetcode-112.二叉树路径总和给你二叉树的根节点root和一个表示目标和的整数targetSum。判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和targetSum。如果存在,返回true;否则,返回false。叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。示例1:输入:root=[5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1],target
- HDFS常用命令
BenChuat
大数据学习hdfshadoop大数据
常用命令说明:-put和-get:上传和下载文件,是HDFS和本地文件系统交互的关键命令。-rm和-mkdir:删除和创建文件/目录,-rm支持递归删除。-ls和-cat:文件查看操作中最常用的命令,分别用于列出文件和查看内容。权限管理:通过-chmod、-chown和-chgrp命令对HDFS文件的权限、所有者和所属组进行管理。检查文件状态:通过-stat和-checksum命令,可以查看文件的
- 2024泰剧《死生时刻》无删减全集更至05集【1080p超清泰语中字】4Minutes百度云夸克迅雷网盘提取码
小小编007
《死生时刻》(4Minutes),又名《生死四分钟》,是一部2024年泰国原创电视剧,由SammonIsareeSiriwankulthon编剧,杰迪帕·迪拉朋帕(JespipatTilapornputt)、温查帕·苏梅提固(WichapasSumettikul)等主演。该剧集属于奇幻、爱情、剧情类型,共10集,每周更新,目前已播出至第05集。生死四分钟资源链接:(尽快保存,随时失效)https:
- iOS —— 天气预报仿写总结
想和她去卡塔尼亚
ios
在iOS中,最常见的网络请求方式是NSURLSession,它是苹果推荐的现代API,简单安全且易于拓展。一次完整的网络请求流程:构造NSURL对象创建NSURLSessionDataTask发起请求(resume)在回调中解析数据回到主线程更新UI下面,我们用一个简单的程序来试一下。NSString*city=@"Beijing";NSString*apiKey=@"你的API密钥";NSStr
- 什么是 CPython?
文章目录什么是CPython?背景介绍CPython的工作原理CPython的特点除了CPython还有哪些实现?总结什么是CPython?CPython是Python编程语言的最主流且官方的实现。简单来说,CPython就是用C语言写成的Python解释器,它负责将我们用Python写的代码转换成机器能够执行的指令。背景介绍Python是一种高级编程语言,由GuidovanRossum于1991
- Kafka消费者负载均衡策略
⼀个消费者组中的⼀个分⽚对应⼀个消费者成员,他能保证每个消费者成员都能访问,如果组中成员太多会有空闲的成员Kafka消费者负载均衡策略详解从分区分配算法到Rebalance机制,全面解析Kafka如何实现消费者间的负载均衡,并提供调优建议和问题解决方案。1.核心概念术语作用类比ConsumerGroup共享消费任务的消费者组外卖骑手团队PartitionTopic的物理分片配送区域划分Rebala
- Kafka消费者负载均衡和数据积压问题
抱紧大佬大腿不松开
kafka负载均衡分布式大数据
在大数据领域中,ApacheKafka是一个常用的分布式消息队列系统,它被广泛应用于实时数据处理和流式数据处理场景。Kafka的消费者负载均衡机制和数据积压问题是使用Kafka时需要关注和解决的重要议题。消费者负载均衡机制是指如何将消息分配给多个消费者,以实现高吞吐量和高可扩展性。Kafka通过使用消费者组(consumergroup)的概念来实现负载均衡。一个消费者组可以包含多个消费者,每个消费
- kafka的消费者负载均衡机制
不辉放弃
kafka负载均衡分布式数据库
Kafka的消费者负载均衡机制是保证消息高效消费的核心设计,通过将分区合理分配给消费者组内的消费者,实现并行处理和负载均衡。以下从核心概念、分配策略、重平衡机制等方面详细讲解。一、核心概念理解消费者负载均衡前,需明确三个关键概念:消费者组(ConsumerGroup)多个消费者组成的逻辑组,共同消费一个或多个主题的消息。组内消费者共享一个group.id标识,Kafka通过该标识区分不同消费组。分
- 《死生时刻4minute》泰剧【生死四分钟1080p超清泰语中字】4分钟免费在线观看Minutes(2024)全集完整未删减版夸克网盘高清迅雷网盘百度云
全网优惠分享
《死生时刻》(泰语:สี่นาที,英文名:4Minutes)是一部2024年上映的泰国电视剧,由SammonIsareeSiriwankulthon编剧,杰迪帕·迪拉朋帕(JespipatTilapornputt)和温查帕·苏梅提固(WichapasSumettikul)主演。这部剧以剧情、爱情和奇幻为题材,讲述了一个关于生死、爱情和超能力的故事。资源链接:(尽快保存,随时失效)https://
- Java 高频算法
Java高频算法面试题以下是Java面试中常见的高频算法题目,涵盖了数据结构、算法思想和实际应用场景。一、数组与字符串1.两数之和publicint[]twoSum(int[]nums,inttarget){Mapmap=newHashMapmap=newHashMap=upper)returnfalse;returnisValidBST(node.left,lower,node.val)&&is
- mysql page header_由InnoDB: Space id in fsp header ,but in the page header 展开的思考
首先说明我是做ORACLE的,但是工作需要,并且加上兴趣,现在正在学习INNODB。如果有不对的结论大家一起讨论,在这篇文章中修改了块的字节,没有出现问题,而ORACLE却是不能随意修改的,因为他有自己的一套算法来计算CHECKSUM。但是几个小工具可以有助大家学习和研究!谢谢!今天启动MYSQL的时候发现如下问题:2015-12-1420:51:592098[ERROR]InnoDB:Space
- c莫比乌斯函数_莫比乌斯函数总结
weixin_39905624
c莫比乌斯函数
莫比乌斯函数总结性质:\(\sum_{d|n}\mu(d)=[n==1]\)这个可以用组合数的性质来证,形象点的话就是杨辉三角。因为恒等式:\(\sum_{i=0}^{n}(-1)^nC_{n}^{i}=0\).莫比乌斯反演:形式一:已知:\(g(n)=\sum_{d|n}f(d)\),则有:\(f(n)=\sum_{d|n}\mu(d)g(\frac{n}{d})\).证明如下:\[\sum_{
- 2024年泰剧《死生时刻》4分钟/生死四分钟/4 Minutes全集高清HD免费完整版观看-4分钟百度云/夸克网盘资源
优惠攻略官
《死生时刻》(又名《4分钟》或《生死四分钟》)是一部泰国剧情、爱情、奇幻类型的电视剧,由SammonIsareeSiriwankul编剧,杰迪帕·迪拉朋帕(JespipatTilapornputt)、温查帕·苏梅提固(WichapasSumettikul)主演。这部剧集融合了剧情、爱情、奇幻类型,讲述了一个拥有超自然力量的大学生Great的故事。Great就读于工商管理学院,同时也是一位富有企业主
- oracle数据库表空间碎片整理
GottdesKrieges
Oracle实践篇(二)数据库oracle
oracle数据库表空间碎片整理表空间碎片情况检查表空间碎片问题处理收缩表表空间手动整理exp/imp导出再导入移动表到新的表空间表空间碎片情况检查对比表实际使用空间和数据文件占用空间:--实际数据占用空间selecttablespace_name,round(sum(bytes/1024/1024/1024),2
- 盘点一道Python取整的基础题目
皮皮_f075
大家好,我是Python进阶者。一、前言前几天在小小明大佬的Python群里边看到一个昵称为【Big.白】的粉丝问了一道Python取整的基础题目,后来拿到钻石交流群问了一下,如下图所示。题目二、实现过程这是个基础题目,看上去确实不难,关键是逻辑实现。一开始自己给了一个解答,如下所示:defbrf_cnt(consume_number):ifabs(consume_number)<13:retur
- rust的指针作为函数返回值是直接传递,还是先销毁后创建?
wudixiaotie
返回值
这是我自己想到的问题,结果去知呼提问,还没等别人回答, 我自己就想到方法实验了。。
fn main() {
let mut a = 34;
println!("a's addr:{:p}", &a);
let p = &mut a;
println!("p's addr:{:p}", &a
- java编程思想 -- 数据的初始化
百合不是茶
java数据的初始化
1.使用构造器确保数据初始化
/*
*在ReckInitDemo类中创建Reck的对象
*/
public class ReckInitDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Reck对象
new Reck();
}
}
- [航天与宇宙]为什么发射和回收航天器有档期
comsci
地球的大气层中有一个时空屏蔽层,这个层次会不定时的出现,如果该时空屏蔽层出现,那么将导致外层空间进入的任何物体被摧毁,而从地面发射到太空的飞船也将被摧毁...
所以,航天发射和飞船回收都需要等待这个时空屏蔽层消失之后,再进行
&
- linux下批量替换文件内容
商人shang
linux替换
1、网络上现成的资料
格式: sed -i "s/查找字段/替换字段/g" `grep 查找字段 -rl 路径`
linux sed 批量替换多个文件中的字符串
sed -i "s/oldstring/newstring/g" `grep oldstring -rl yourdir`
例如:替换/home下所有文件中的www.admi
- 网页在线天气预报
oloz
天气预报
网页在线调用天气预报
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transit
- SpringMVC和Struts2比较
杨白白
springMVC
1. 入口
spring mvc的入口是servlet,而struts2是filter(这里要指出,filter和servlet是不同的。以前认为filter是servlet的一种特殊),这样就导致了二者的机制不同,这里就牵涉到servlet和filter的区别了。
参见:http://blog.csdn.net/zs15932616453/article/details/8832343
2
- refuse copy, lazy girl!
小桔子
copy
妹妹坐船头啊啊啊啊!都打算一点点琢磨呢。文字编辑也写了基本功能了。。今天查资料,结果查到了人家写得完完整整的。我清楚的认识到:
1.那是我自己觉得写不出的高度
2.如果直接拿来用,很快就能解决问题
3.然后就是抄咩~~
4.肿么可以这样子,都不想写了今儿个,留着作参考吧!拒绝大抄特抄,慢慢一点点写!
- apache与php整合
aichenglong
php apache web
一 apache web服务器
1 apeche web服务器的安装
1)下载Apache web服务器
2)配置域名(如果需要使用要在DNS上注册)
3)测试安装访问http://localhost/验证是否安装成功
2 apache管理
1)service.msc进行图形化管理
2)命令管理,配
- Maven常用内置变量
AILIKES
maven
Built-in properties
${basedir} represents the directory containing pom.xml
${version} equivalent to ${project.version} (deprecated: ${pom.version})
Pom/Project properties
Al
- java的类和对象
百合不是茶
JAVA面向对象 类 对象
java中的类:
java是面向对象的语言,解决问题的核心就是将问题看成是一个类,使用类来解决
java使用 class 类名 来创建类 ,在Java中类名要求和构造方法,Java的文件名是一样的
创建一个A类:
class A{
}
java中的类:将某两个事物有联系的属性包装在一个类中,再通
- JS控制页面输入框为只读
bijian1013
JavaScript
在WEB应用开发当中,增、删除、改、查功能必不可少,为了减少以后维护的工作量,我们一般都只做一份页面,通过传入的参数控制其是新增、修改或者查看。而修改时需将待修改的信息从后台取到并显示出来,实际上就是查看的过程,唯一的区别是修改时,页面上所有的信息能修改,而查看页面上的信息不能修改。因此完全可以将其合并,但通过前端JS将查看页面的所有信息控制为只读,在信息量非常大时,就比较麻烦。
- AngularJS与服务器交互
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJS$http
对于AJAX应用(使用XMLHttpRequests)来说,向服务器发起请求的传统方式是:获取一个XMLHttpRequest对象的引用、发起请求、读取响应、检查状态码,最后处理服务端的响应。整个过程示例如下:
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange
- [Maven学习笔记八]Maven常用插件应用
bit1129
maven
常用插件及其用法位于:http://maven.apache.org/plugins/
1. Jetty server plugin
2. Dependency copy plugin
3. Surefire Test plugin
4. Uber jar plugin
1. Jetty Pl
- 【Hive六】Hive用户自定义函数(UDF)
bit1129
自定义函数
1. 什么是Hive UDF
Hive是基于Hadoop中的MapReduce,提供HQL查询的数据仓库。Hive是一个很开放的系统,很多内容都支持用户定制,包括:
文件格式:Text File,Sequence File
内存中的数据格式: Java Integer/String, Hadoop IntWritable/Text
用户提供的 map/reduce 脚本:不管什么
- 杀掉nginx进程后丢失nginx.pid,如何重新启动nginx
ronin47
nginx 重启 pid丢失
nginx进程被意外关闭,使用nginx -s reload重启时报如下错误:nginx: [error] open() “/var/run/nginx.pid” failed (2: No such file or directory)这是因为nginx进程被杀死后pid丢失了,下一次再开启nginx -s reload时无法启动解决办法:nginx -s reload 只是用来告诉运行中的ng
- UI设计中我们为什么需要设计动效
brotherlamp
UIui教程ui视频ui资料ui自学
随着国际大品牌苹果和谷歌的引领,最近越来越多的国内公司开始关注动效设计了,越来越多的团队已经意识到动效在产品用户体验中的重要性了,更多的UI设计师们也开始投身动效设计领域。
但是说到底,我们到底为什么需要动效设计?或者说我们到底需要什么样的动效?做动效设计也有段时间了,于是尝试用一些案例,从产品本身出发来说说我所思考的动效设计。
一、加强体验舒适度
嗯,就是让用户更加爽更加爽的用你的产品。
- Spring中JdbcDaoSupport的DataSource注入问题
bylijinnan
javaspring
参考以下两篇文章:
http://www.mkyong.com/spring/spring-jdbctemplate-jdbcdaosupport-examples/
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/4762229/spring-ldap-invoking-setter-methods-in-beans-configuration
Sprin
- 数据库连接池的工作原理
chicony
数据库连接池
随着信息技术的高速发展与广泛应用,数据库技术在信息技术领域中的位置越来越重要,尤其是网络应用和电子商务的迅速发展,都需要数据库技术支持动 态Web站点的运行,而传统的开发模式是:首先在主程序(如Servlet、Beans)中建立数据库连接;然后进行SQL操作,对数据库中的对象进行查 询、修改和删除等操作;最后断开数据库连接。使用这种开发模式,对
- java 关键字
CrazyMizzz
java
关键字是事先定义的,有特别意义的标识符,有时又叫保留字。对于保留字,用户只能按照系统规定的方式使用,不能自行定义。
Java中的关键字按功能主要可以分为以下几类:
(1)访问修饰符
public,private,protected
p
- Hive中的排序语法
daizj
排序hiveorder byDISTRIBUTE BYsort by
Hive中的排序语法 2014.06.22 ORDER BY
hive中的ORDER BY语句和关系数据库中的sql语法相似。他会对查询结果做全局排序,这意味着所有的数据会传送到一个Reduce任务上,这样会导致在大数量的情况下,花费大量时间。
与数据库中 ORDER BY 的区别在于在hive.mapred.mode = strict模式下,必须指定 limit 否则执行会报错。
- 单态设计模式
dcj3sjt126com
设计模式
单例模式(Singleton)用于为一个类生成一个唯一的对象。最常用的地方是数据库连接。 使用单例模式生成一个对象后,该对象可以被其它众多对象所使用。
<?phpclass Example{ // 保存类实例在此属性中 private static&
- svn locked
dcj3sjt126com
Lock
post-commit hook failed (exit code 1) with output:
svn: E155004: Working copy 'D:\xx\xxx' locked
svn: E200031: sqlite: attempt to write a readonly database
svn: E200031: sqlite: attempt to write a
- ARM寄存器学习
e200702084
数据结构C++cC#F#
无论是学习哪一种处理器,首先需要明确的就是这种处理器的寄存器以及工作模式。
ARM有37个寄存器,其中31个通用寄存器,6个状态寄存器。
1、不分组寄存器(R0-R7)
不分组也就是说说,在所有的处理器模式下指的都时同一物理寄存器。在异常中断造成处理器模式切换时,由于不同的处理器模式使用一个名字相同的物理寄存器,就是
- 常用编码资料
gengzg
编码
List<UserInfo> list=GetUserS.GetUserList(11);
String json=JSON.toJSONString(list);
HashMap<Object,Object> hs=new HashMap<Object, Object>();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
- 进程 vs. 线程
hongtoushizi
线程linux进程
我们介绍了多进程和多线程,这是实现多任务最常用的两种方式。现在,我们来讨论一下这两种方式的优缺点。
首先,要实现多任务,通常我们会设计Master-Worker模式,Master负责分配任务,Worker负责执行任务,因此,多任务环境下,通常是一个Master,多个Worker。
如果用多进程实现Master-Worker,主进程就是Master,其他进程就是Worker。
如果用多线程实现
- Linux定时Job:crontab -e 与 /etc/crontab 的区别
Josh_Persistence
linuxcrontab
一、linux中的crotab中的指定的时间只有5个部分:* * * * *
分别表示:分钟,小时,日,月,星期,具体说来:
第一段 代表分钟 0—59
第二段 代表小时 0—23
第三段 代表日期 1—31
第四段 代表月份 1—12
第五段 代表星期几,0代表星期日 0—6
如:
*/1 * * * * 每分钟执行一次。
*
- KMP算法详解
hm4123660
数据结构C++算法字符串KMP
字符串模式匹配我们相信大家都有遇过,然而我们也习惯用简单匹配法(即Brute-Force算法),其基本思路就是一个个逐一对比下去,这也是我们大家熟知的方法,然而这种算法的效率并不高,但利于理解。
假设主串s="ababcabcacbab",模式串为t="
- 枚举类型的单例模式
zhb8015
单例模式
E.编写一个包含单个元素的枚举类型[极推荐]。代码如下:
public enum MaYun {himself; //定义一个枚举的元素,就代表MaYun的一个实例private String anotherField;MaYun() {//MaYun诞生要做的事情//这个方法也可以去掉。将构造时候需要做的事情放在instance赋值的时候:/** himself = MaYun() {*
- Kafka+Storm+HDFS
ssydxa219
storm
cd /myhome/usr/stormbin/storm nimbus &bin/storm supervisor &bin/storm ui &Kafka+Storm+HDFS整合实践kafka_2.9.2-0.8.1.1.tgzapache-storm-0.9.2-incubating.tar.gzKafka安装配置我们使用3台机器搭建Kafk
- Java获取本地服务器的IP
中华好儿孙
javaWeb获取服务器ip地址
System.out.println("getRequestURL:"+request.getRequestURL());
System.out.println("getLocalAddr:"+request.getLocalAddr());
System.out.println("getLocalPort:&quo