spring 源码解读二 AbstractApplicationContext refresh
今天我们重点来看下 AbstractApplicationContext 的 refresh()方法,上次说了这个方法算是spring最核项的方法了大概可以归为 13个方法
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
/**
* 1、
* 创建spring 容器之前的准备工作
* 包括设置启动时间、活跃状态、加载当前环境变量、准备监听器集合
*/
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
/**
* 2、
* 创建BeanFactory容器对象:实际对象为 DefaultListableBeanFactory
* 加载xml配置文件到当前工厂中
*/
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
/**
* 3、
* 初始化BeanFactory
* 设置各种系统对象的初始值
*/
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 4、子类可扩展方法,留给用户扩展
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
/**
* 5、
* 调用各种BeanFactoryPostProcessor处理器与BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 处理器
* 可参考 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor -- 解析各种注解配置的bean
* 包括 @Configuration
* @Component
* @ComponentScan
* @PropertySource-这里是将配置文件加载到环境变量里面
* @Bean
* @Import
* 可参考 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer -- 解析配置文件中的${name}这种变量
*/
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
/**
* 6、
* 注册BeanPostProcessor处理器
* 可参考 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor -- 执行除了 BeanNameAware BeanClassLoaderAware BeanFactorAware 之外的其他aware
* 可参考 ApplicationListenerDetector -- 监听器的探测器
*
* 这里要注意的是
* @CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor --处理@Resource等注解
* @InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor --处理 @PostConstruct 注解与 @PreDestroy
* @AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor --处理 @Autowire 注解与 @Value 注解
* 这几个类也是 BeanPostProcessor 的实现类,这几个类我们将在后面的bean初始化的时候重点研究
*/
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 7、不同语言的消息体,国际化处理
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 8、初始化事件广播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 9、子类可扩展方法,留给用户扩展
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 10、在BeanFactory 中查找listener bean,注册到事件广播器
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 11、初始化用户定义的还未被实例化的单例bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 12、完成spring容器的初始化与刷新,设置生命周期处理器,发布ContextRefreshEvent 事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
// 13、清理在BeanFactory创建过程中以及用户bean实例化初始化过程中产生的缓存
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}后面会逐个解析标注的 13个方法
首先是 prepareRefresh()
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
//设置了俩标志位
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
//用户扩展方法
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
//之前设置的环境资源,并可以验证某个属性在环境资源中是否存在
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
//设置刷新前的监听器集合
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
//设置刷新前的监听事件集合
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}obtainFreshBeanFactory()
/**
* Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
* @return the fresh BeanFactory instance
* @see #refreshBeanFactory()
* @see #getBeanFactory()
*/
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
//初始化一个BeanFactory
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}refreshBeanFactory() -> AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
//如果之前已经存在BeanFactory则销毁之前的beanFactory中的bean并关闭beanFactory
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//新建一个 DefaultListableBeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
//给beanFactory设置一个id值
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
//这里可以设置bean定义信息是否允许被覆盖和是否允许循环引用
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//加载 myApplicationContext.xml 配置文件并解析里面的bean内容为beanDefinition
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
} createBeanFactory()
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {
return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory())
public DefaultListableBeanFactory(@Nullable BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) {
super(parentBeanFactory);
}super(parentBeanFactory) -> AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactorypublic AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory(@Nullable BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) {
this();
setParentBeanFactory(parentBeanFactory);
}public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory() {
super();
//这里有三个aware接口被忽略,记住这里
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanNameAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanFactoryAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanClassLoaderAware.class);
}AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext -> customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory)
protected void customizeBeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 是否允许对象覆盖
if (this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding != null) {
beanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// 是否允许bean之间的循环引用
if (this.allowCircularReferences != null) {
beanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
}
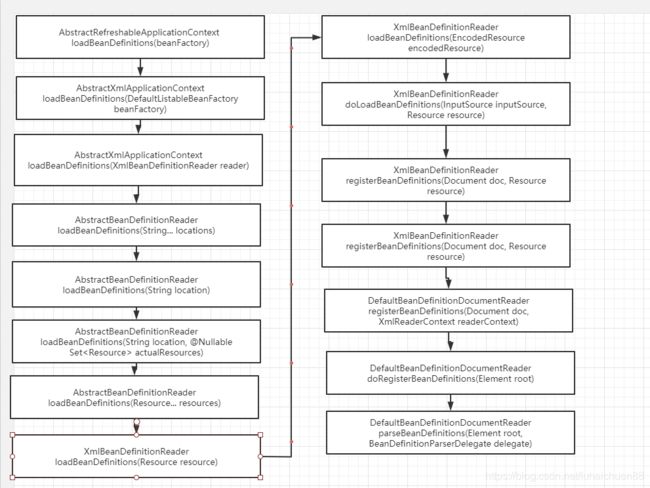
}AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext -> loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory) 这里面的内容太特么绕了多了我用图表示一下吧
经过上面一系列的过程只是把我们定义在 myApplicationContext.xml 的默认标签给解析了
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader -> parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate)/**
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:
* "import", "alias", "bean".
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
//这里解析默认命名空间的标签包括 import、bean、beans、alias
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
//这里解析其他命名空间的标签比如 context、aop、tx或我们自定义的标签
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader -> parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader -> delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
@Nullable
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele) {
return parseCustomElement(ele, null);
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader -> parseCustomElement(ele, null);
@Nullable
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) {
// 根据我们 myApplicationContext.xml 中定义的标签引入文件
// 比如 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
// 根据 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context到resource下的 META-INF 下的
// spring.handlers中找到对应的 NamespaceHandler
// 获取对应NamespaceHandler 下的标签解析类来解析对应标签
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
if (namespaceUri == null) {
return null;
}
// 根据命名空间找到对应的NamespaceHandlerspring
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
// 调用自定义的NamespaceHandler进行解析
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}这里以context标签为例进行说明 我在myApplicationContext.xml 中已经做了如下定义
spring-context -> src->main->resources -> META-INF-> spring.handlers
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context=org.springframework.context.config.ContextNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/jee=org.springframework.ejb.config.JeeNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/lang=org.springframework.scripting.config.LangNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/task=org.springframework.scheduling.config.TaskNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/cache=org.springframework.cache.config.CacheNamespaceHandler因此context标签会直接定位到 org.springframework.context.config.ContextNamespaceHandler
public class ContextNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-placeholder", new PropertyPlaceholderBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("property-override", new PropertyOverrideBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-config", new AnnotationConfigBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("component-scan", new ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("load-time-weaver", new LoadTimeWeaverBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spring-configured", new SpringConfiguredBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-export", new MBeanExportBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("mbean-server", new MBeanServerBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}因为我们定义了 component-scan标签因此会调用 new ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser() 的parse方法
注意这里不是说在配置文件里面写了component-scan 就调 new ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser() 的parse方法,而是init下的所有类的parse方法都会执行
好了我们回到DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader -> parseCustomElement(ele, null) -> handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd))
NamespaceHandlerSupport -> BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext)
@Override
@Nullable
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 获取元素的解析器
BeanDefinitionParser parser = findParserForElement(element, parserContext);
// 根据 registerBeanDefinitionParser("component-scan", new ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser());
//找到 ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser() 解析器并调用ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser()的parse方法解析标签
return (parser != null ? parser.parse(element, parserContext) : null);
}好了 AbstractApplicationContext -> refresh -> obtainFreshBeanFactory 基本看完了操
请大家关注下博客谢谢