Unity延迟,协程
Unity (学习笔记)
主要记录一些重要以及易错的知识点。
笔记目录
- Unity (学习笔记)
-
- 1.unity延时方法Invoke和InvokeRepeating
-
- 1.Unity Time类
- 2.Invoke(延迟后调用一次)
- 3.InvokeRepeating(延迟后在规定的时间周期重复调用N次)
- 4.CancelInvoke(); (取消该脚本上的所有延时方法)
- 2.协程(Coroutines)
-
- Unity的协程系统是基于C#的一个简单而强大的接口 ,IEnumerator,它允许你为自己的集合类型编写枚举器。
- 简写协程就是这样的:
- 3.区分相识的东西
-
- transform.position和transform.localPosition区别
- Awake() 和Start()的区别
- 4.Unity本地持久化类Playerprefs使用详解
-
- 1.PlayerPrefs是什么?
- 2.PlayerPrefs有什么用?
- 3.PlayerPrefs如何用?
-
- 1. 存储数据:
- 2. 取出数据:
- 3. 删除数据与查数据:
- 4. 注意事项:
- 5.场景切换
1.unity延时方法Invoke和InvokeRepeating
1.Unity Time类
- 1.Time.time 表示从游戏开发到现在的时间,会随着游戏的暂停而停止计算。
- 2.Time.timeSinceLevelLoad 表示从当前Scene开始到目前为止的时间,也会随着暂停操作而停止。
- 3.Time.deltaTime 表示从上一帧到当前帧时间,以秒为单位。
MonoBehaviour里面有两个内置的延时方法
2.Invoke(延迟后调用一次)
Invoke(methodName: string, time: float);
methodName:方法名
time:多少秒后执行
3.InvokeRepeating(延迟后在规定的时间周期重复调用N次)
InvokeRepeating(methodName: string, time: float, repeatRate: float);
methodName:方法名
time:多少秒后执行
repeatRate:重复执行间隔
4.CancelInvoke(); (取消该脚本上的所有延时方法)
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class DelayScript : MonoBehaviour {
//当前时间
private float nowTime;
//执行重复方法的次数
private int count;
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
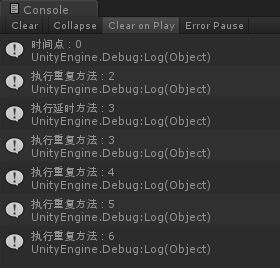
nowTime = Time.time;
Debug.Log("时间点:"+nowTime);
this.Invoke("setTimeOut", 3.0f);
this.InvokeRepeating("setInterval", 2.0f, 1.0f);
}
private void setTimeOut()
{
nowTime = Time.time;
Debug.Log("执行延时方法:" + nowTime);
}
private void setInterval()
{
nowTime = Time.time;
Debug.Log("执行重复方法:" + nowTime);
count += 1;
if(count==5)
this.CancelInvoke();
}
}
2.协程(Coroutines)
Unity的协程系统是基于C#的一个简单而强大的接口 ,IEnumerator,它允许你为自己的集合类型编写枚举器。
using System.Collections;//用协程必须要这个命名空间
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class GameManager : MonoBehaviour
{
public enum STATE{//枚举类型
IDLE,
PLAYERA,
PLAYERB,
FINISHED
}
[Space(10)]//与上面的间隔
[Header("== Game State ==")]//添加标题
public STATE state;//枚举类型的state就会是一个下拉框
private bool firstEnter = true;
void Update()
{
if (state == STATE.IDLE)
{
if (firstEnter == true)
{//Trigger once
StartCoroutine("TaskIDLE");
firstEnter = false;
}
else
{//Regular tasks
CheakVictory();
}
}
else if (state == STATE.PLAYERA)
{
CheakVictory();
if (firstEnter == true)
{
StartCoroutine("TaskPLAYERA");
firstEnter = false;
}
else
{
CheakVictory();
}
}
else if (state == STATE.PLAYERB)
{
CheakVictory();
if (firstEnter == true)
{
StartCoroutine("TaskPLAYERB");
firstEnter = false;
}
else
{
CheakVictory();
}
}
else if (state == STATE.FINISHED)
{
if (firstEnter == true)
{
StopCoroutine("TaskIDLE");
StopCoroutine("TaskPLAYERA");
StopCoroutine("TaskPLAYERB");
}
}
}
//声明协程
//协程=IEnumerator + 方法名()
IEnumerator TaskIDLE()
{
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1.0f);
fgui.Play("SceneBattleStart");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(2.0f);
state = STATE.PLAYERA;
firstEnter = true;
}
IEnumerator TaskPLAYERA()
{
ac1.anim.SetTrigger("attack");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(2.0f);
state = STATE.PLAYERB;
firstEnter = true;
CheakVictory();
}
IEnumerator TaskPLAYERB()
{
ac2.anim.SetTrigger("attack");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(2.0f);
state = STATE.PLAYERA;
firstEnter = true;
CheakVictory();
}
}
简写协程就是这样的:
using System.Collections;//用协程必须要这个命名空间
StartCoroutine("TaskIDLE");//调用TaskIDLE()这个协程
IEnumerator TaskIDLE()//声明一个TaskIDLE()协程
{
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1.0f);//暂停1秒,再执行下面语句
yield return new WaitForSeconds(5.0f);//暂停5秒,再执行下面语句
}
那我们怎么终止其中的一个协程呢?如果你想要终止某一个特定的协程,那么你必须得在开始协程的时候将它的方法名作为字符串,就像这样:
正确写法
//想开始一个协程,把方法名写入StartCoroutine("这里");即可
StartCoroutine("FirstTimer");
StartCoroutine("SecondTimer");
//想关掉一个协程同理,把方法名写入StopCoroutine("这里");
StopCoroutine("FirstTimer");
错误写法
StartCoroutine(FirstTimer());
StartCoroutine(SecondTimer());
3.区分相识的东西
transform.position和transform.localPosition区别
- 1.position是根据世界原点为中心
- 2.localPosition是根据父节点为中心,如果没有父节点,localpositon和position是没有区别的
Awake() 和Start()的区别
- 加载Scence 时 会先对所有脚本的Awake()先执行. 再执行Start()
- 因此如果脚本A. 在初始化时需要调用到 脚本B 里的变量.
- 那A的调用语句 应放在Start()中,而不是Awake()
- 而B脚本要被调用的变量应 在Awake()中执行初始化.
4.Unity本地持久化类Playerprefs使用详解
1.PlayerPrefs是什么?
PlayerPrefs是Unity3d提供了一个用于数据本地持久化保存与读取的类。工作原理十分简单,就是以key-value的形式将数据保存在本地,然后在代码中可以写入、读取、更新数据。
2.PlayerPrefs有什么用?
可用于存储一些非关键性的数据,尤其在没有服务器的单机游戏中,游戏存档、分数排名等都需要用到数据存储,可以使用PlayerPrefs轻松实现数据存储。
3.PlayerPrefs如何用?
1. 存储数据:
//存储整型数据
PlayerPrefs.SetInt("intKey",999);
//存储浮点型数据
PlayerPrefs.SetFloat("floatKey",1.11f);
//存储字符串数据
PlayerPrefs.SetString("strKey","I am Plane");
2. 取出数据:
//取出key为"intKey"的整型数据
int intVal = PlayerPrefs.GetInt("intKey");
//取出key为"floatKey"的浮点型数据
float floatVal = PlayerPrefs.GetFloat("floatKey");
//获取key为"strKey"的字符串数据
string strVal = PlayerPrefs.GetString("strKey");
3. 删除数据与查数据:
//删除所有存储数据
PlayerPrefs.DeleteAll();
//删除key为"score"的数据
PlayerPrefs.DeleteKey("score");
//查找是否存在key为"score"的数据
bool exist = PlayerPrefs.HasKey("score")
4. 注意事项:
数据以键值对的形式存储,可以看做一个字典。
数据通过键名来读取,当值不存在时,返回默认值。
5.场景切换
制作关卡游戏就特别适合使用这个场景切换
UnityEngine.SceneManagement.SceneManager.LoadScene(1);//切换到1场景