c++---优先队列(priority_queue)
C ++中的优先队列是STL中的派生容器,它仅考虑最高优先级元素。队列遵循FIFO策略,而优先队列根据优先级弹出元素,即,优先级最高的元素首先弹出。
与普通队列区别:
-
在优先队列中,队列中的每个元素都与某个优先级相关联,但是优先级在队列数据结构中不存在。
-
优先队列中具有最高优先级的元素将被首先删除,而队列遵循FIFO(先进先出)策略,这意味着先插入的元素将被首先删除。
-
如果存在多个具有相同优先级的元素,则将考虑该元素在队列中的顺序。
语法:
priority_queue variable_name; 其模板声明带有三个参数,priority_queue
priority_queue(),默认按照从小到大排列。所以top()返回的是最大值而不是最小值!
使用greater<>后,数据从大到小排列,top()返回的就是最小值而不是最大值!
如果使用了第三个参数,那第二个参数不能省,用作保存数据的容器!!!!
priority_queue> pq;//这是错误的
priority_queue , greater<>> pq;//这是对的
//升序队列
priority_queue ,greater > q;
//降序队列
priority_queue ,less >q;
//greater和less是std实现的两个仿函数(就是使⼀个类的使⽤看上去像⼀个函数。其实现就是类中实现⼀个operator(),这个类就有了类似函数的⾏为,就是⼀个仿函数类了)
greater
注意:pair的⽐较,先⽐较第⼀个元素,第⼀个相等⽐较第⼆个
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
priority_queue > a;
pair b(1, 2);
pair c(1, 3);
pair d(2, 5);
a.push(d);
a.push(c);
a.push(b);
while (!a.empty())
{
cout << a.top().first << ' ' << a.top().second << '\n';
a.pop();
}
}
2 5
1 3
1 2
对于⾃定义类型比较
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//⽅法1
struct tmp1 //运算符重载<
{
int x;
tmp1(int a) {x = a;}
bool operator<(const tmp1& a) const
{
return x < a.x; //⼤顶堆
}
};
//⽅法2
struct tmp2 //重写仿函数
{
bool operator() (tmp1 a, tmp1 b)
{
return a.x < b.x; //⼤顶堆
}
};
int main()
{
tmp1 a(1);
tmp1 b(2);
tmp1 c(3);
priority_queue d;
d.push(b);
d.push(c);
d.push(a);
while (!d.empty())
{
cout << d.top().x << '\n';
d.pop();
}
cout << endl;
priority_queue, tmp2> f;
f.push(c);
f.push(b);
f.push(a);
while (!f.empty())
{
cout << f.top().x << '\n';
f.pop();
}
}
3
2
1
3
2
1
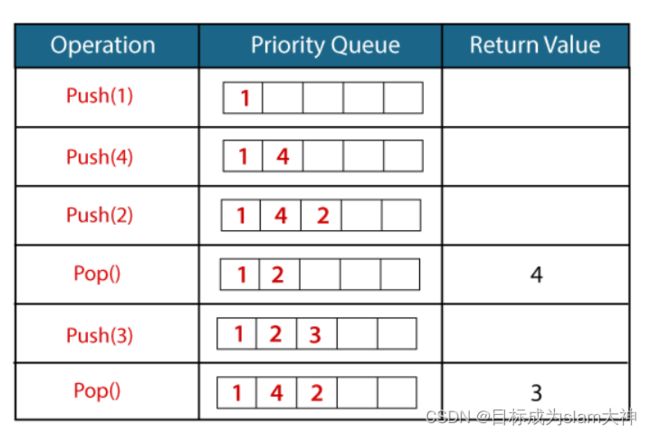
一个简单的示例了解优先队列。
在上图中,我们通过使用push()函数插入了元素,并且插入操作与普通队列相同。但是,当我们使用pop()函数从队列中删除元素时,优先级最高的元素将首先被删除。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
priority_queue p; // 变量声明.
p.push(10); // 插入 10 到队列, top=10
p.push(30); // 插入 30 到队列, top=30
p.push(20); // 插入 20 到队列, top=20
cout<<"可用元素的数量 到 'p' :"< 可用元素的数量 到 'p' :3
30
20
10