.NET(C#) Internals: 以一个数组填充的例子初步了解.NET 4.0中的并行(二)
引言
随着CPU多核的普及,编程时充分利用这个特性越显重要。上篇首先用传统的嵌套循环进行数组填充,然后用.NET 4.0中的System.Threading.Tasks提供的Parallel Class来并行地进行填充,最后对比他们的性能。本文将深入分析Parallel Class并借机回答上篇9楼提出的问题,而System.Threading.Tasks分析,这个将推迟到.NET(C#) Internals: 以一个数组填充的例子初步了解.NET 4.0中的并行(三)中介绍。内容如下:
- 1、Parallel Class
- 1.1、For方法
- 1.2、ForEach方法
- 1.3、Invoke方法
- 2、并发控制疑问?
- 2.1、使用Lock锁
- 2.2、使用PLINQ——用AsParallel
- 2.3、使用PLINQ——用ParallelEnumerable
- 2.4、使用Interlocked操作
- 2.5、使用Parallel.For的有Thread-Local变量重载函数
- 性能比较
1、Parallel Class
Parallel——这个类提供对通常操作(诸如for、foreach、执行语句块)基于库的数据并行替换。它只是System.Threading.Tasks命名空间的一个类,该命名空间中还包括很多其他的类。下面举个例子来说明如何使用Parallel.For(来自MSDN):
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Test
{
static int N = 1000;
static void TestMethod()
{
// Using a named method.
Parallel.For(0, N, Method2);
// Using an anonymous method.
Parallel.For(0, N, delegate(int i)
{
// Do Work.
});
// Using a lambda expression.
Parallel.For(0, N, i =>
{
// Do Work.
});
}
static void Method2(int i)
{
// Do work.
}
}
上面这个例子简单易懂,上篇我们就是用的Parallel.For,这里就不解释了。其实Parallel类的方法主要分为下面三类:
- For方法
- ForEach方法
- Invoke方法
1.1、For方法
在里面执行的for循环可能并行地运行,它有12个重载。这12个重载中Int32参数和Int64参数的方法各为6个,下面以Int32为例列出:
- For(Int32 fromInclusive, Int32 toExclusive, Action<Int32> body),该方法对区间(fromInclusive,toExclusive)之间的迭代调用body表示的委托。body委托有一个迭代数次的int32参数,如果fromInclusive>=toExclusive,则不会执行任何迭代。
- For(Int32 fromInclusive, Int32 toExclusive, Action<Int32, ParallelLoopState>),该方法对区间(fromInclusive, toExclusive)之间的迭代调用body表示的委托。body委托有两个参数——表示迭代数次的int32参数、一个可用于过早地跳出循环的ParallelLoopState实例。如果fromInclusive>=toExclusive,则不会执行任何迭代。
调用Break通知For操作当前迭代之后的迭代不需要执行。然而,在此之前的迭代如果没有完成仍然需要执行。因此,调用Break类似于调用break跳出传统的for循环,不是break的原因是它不保证当前迭代之后的迭代绝对不会执行。
如果在当前迭代之前的迭代不必要执行,应该调用Stop而不是Break。调用Stop通知For循环放弃剩下的迭代,不管它是否在当前迭代之前或之后,因为所以要求的工作已经完成。然而,Break并不能保证这个。 - For(Int32 fromInclusive, Int32 toExclusive, ParallelOptions parallelOptions, Action<Int32> body),跟第一个方法类似,但它的区间是[fromInclusive, toExclusive)。
- For(Int32 fromInclusive, Int32 toExclusive, ParallelOptions parallelOptions, Action<Int32, ParallelLoopState> body),跟第二个方法类似,单的区间是[fromInclusive, toExclusive)。
- For<TLocal>(Int32 fromInclusive, Int32 toExclusive, Func<TLocal> localInit, Func<Int32, ParallelLoopState, TLocal, TLocal> body, Action<TLocal> localFinally),它的迭代区间是[fromInclusive, toExclusive)。另外body有两个local状态变量用于同一线程的迭代之间共享。localInit委托将在每个线程参与循环执行时调用,并返回这些线程初始的local状态。这些初始状态被传递给body,当它在每个线程上第一次调用时。然后,接下来body调用返回一个可能的修改状态值且传递给下一次body调用。最终,最后一次在每个线程上的body调用返回的一个状态值传递给localFinally委托。每个线程执行在自己的loacl 状态上执行最后一个动作时,localFinally委托将被调用。这个委托可能在多个线程上并发执行,因此,你必须同步访问任何共享变量。
- For<TLocal>(Int32, Int32, ParallelOptions, Func<TLocal>, Func<Int32, ParallelLoopState, TLocal, TLocal>, Action<TLocal>),跟上面的方法类似。
下面代码演示了For(Int32 fromInclusive, Int32 toExclusive, ParallelOptions parallelOptions, Action<Int32> body)方法(来自MSDN):
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
class Program
{
// Demonstrated features:
// CancellationTokenSource
// Parallel.For()
// ParallelOptions
// ParallelLoopResult
// Expected results:
// An iteration for each argument value (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) is executed.
// The order of execution of the iterations is undefined.
// The iteration when i=2 cancels the loop.
// Some iterations may bail out or not start at all; because they are temporally executed in unpredictable order,
// it is impossible to say which will start/complete and which won't.
// At the end, an OperationCancelledException is surfaced.
// Documentation:
// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.threading.cancellationtokensource(VS.100).aspx
static void Main(string[] args)
{
CancellationTokenSource cancellationSource = new CancellationTokenSource();
ParallelOptions options = new ParallelOptions();
options.CancellationToken = cancellationSource.Token;
try
{
ParallelLoopResult loopResult = Parallel.For(
0,
10,
options,
(i, loopState) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Start Thread={0}, i={1}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, i);
// Simulate a cancellation of the loop when i=2
if (i == 2)
{
cancellationSource.Cancel();
}
// Simulates a long execution
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
Thread.Sleep(1 * 200);
// check to see whether or not to continue
if (loopState.ShouldExitCurrentIteration) return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Finish Thread={0}, i={1}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, i);
}
);
if (loopResult.IsCompleted)
{
Console.WriteLine("All iterations completed successfully. THIS WAS NOT EXPECTED.");
}
}
// No exception is expected in this example, but if one is still thrown from a task,
// it will be wrapped in AggregateException and propagated to the main thread.
catch (AggregateException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Parallel.For has thrown an AggregateException. THIS WAS NOT EXPECTED.\n{0}", e);
}
// Catching the cancellation exception
catch (OperationCanceledException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("An iteration has triggered a cancellation. THIS WAS EXPECTED.\n{0}", e.ToString());
}
}
}
}
1.2、ForEach方法
在迭代中执行的foreach操作可能并行地执行,它有20个重载。这个方法太多,但用法大概跟For方法差不多,请自行参考MSDN。
1.3、Invoke方法
提供的每个动作可能并行地执行,它有2个重载。
- Invoke(params Action[] actions):actions是一个要执行的动作数组,这些动作可能并行地执行,但并不保证执行的顺序及一定并行执行。这个方法直到提供的所有操作完成时才返回,不管是否正常地完成或异常终止。
- Invoke(ParallelOptions parallelOptions, params Action[] actions):跟上面的方法类似,只是增加了一个parallelOptions参数,可以用户调用者取消整个操作。
例如下面代码执行了三个操作(来自MSDN):
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
try
{
Parallel.Invoke(
BasicAction, // Param #0 - static method
() => // Param #1 - lambda expression
{
Console.WriteLine("Method=beta, Thread={0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
},
delegate() // Param #2 - in-line delegate
{
Console.WriteLine("Method=gamma, Thread={0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
);
}
// No exception is expected in this example, but if one is still thrown from a task,
// it will be wrapped in AggregateException and propagated to the main thread.
catch (AggregateException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("An action has thrown an exception. THIS WAS UNEXPECTED.\n{0}", e.InnerException.ToString());
}
}
static void BasicAction()
{
Console.WriteLine("Method=alpha, Thread={0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
}
}
2、并发控制疑问?
有人提出以下疑问:“如果For里面的东西,对于顺序敏感的话,会不会有问题。并行处理的话,说到底应该是多线程。如果需要Lock住什么东西的话,应该怎么做呢?例如这个例子不是对数组填充,是对文件操作呢?对某个资源操作呢?”
关于对顺序敏感的话,也就是说该如何加锁来控制?下面我举个例子来说明:对1~1000求和。如果我们想上篇那样简单地用Parallel.For,将会产生错误的结果,代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int loops=0;
while (loops <= 100)
{
long sum = 0;
Parallel.For(1, 1001, delegate(long i)
{
sum += i;
});
System.Console.WriteLine(sum);
loops++;
}
}
}
}
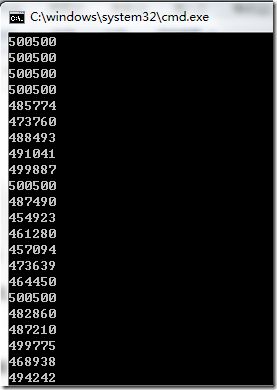
在上述代码中,为了校验正确性我进行了重复做了100次,得出如下结果:
我们知道500500才是正确的答案,这说明Parallel.For不能保证对sum正确的并发执行,对此我们应该加上适当的控制,并借机来回答上面提出的如何加锁的问题。下面有几种方案可以解决这个问题:
2.1、使用Lock锁
这个我就不多解释了,直接上代码:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int loops = 0;
object moniter = new object();
while (loops <= 100)
{
long sum = 0;
Parallel.For(1, 1001, delegate(long i)
{
lock (moniter) { sum += i; }
});
System.Console.WriteLine(sum);
loops++;
}
}
}
}
我们加上lock锁之后就会得出正确的结果。
2.2、使用PLINQ——用AsParallel
关于PLINQ,以后将会介绍到,这里不会详细介绍,感兴趣的自行查阅资料。代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int loops = 0;
while (loops <= 100)
{
long sum = 0;
sum = Enumerable.Range(0, 1001).AsParallel().Sum();
System.Console.WriteLine(sum);
loops++;
}
}
}
}
运行可以得到正确的结果。
2.3、使用PLINQ——用ParallelEnumerable
这个也不多说,直接上代码,因为关于PLINQ将在以后详细介绍,感兴趣的自行查阅资料。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int loops = 0;
while (loops <= 100)
{
long sum = 0;
sum = ParallelEnumerable.Range(0, 1001).Sum();
System.Console.WriteLine(sum);
loops++;
}
}
}
}
运行同样可以得到正确结果。
2.4、使用Interlocked操作
代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int loops = 0;
while (loops <= 100)
{
long sum = 0;
Parallel.For(1, 1001, delegate(long i)
{
Interlocked.Add(ref sum, i);
});
System.Console.WriteLine(sum);
loops++;
}
}
}
}
运行可以得到正确结果。
2.5、使用Parallel.For的有Thread-Local变量重载函数
这个方法已经在1.2中介绍,这里直接上代码,代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int loops = 0;
while (loops <= 100)
{
int sum = 0;
Parallel.For(0, 1001, () => 0, (i, state,subtotal) =>
{
subtotal += i;
return subtotal;
},
partial => Interlocked.Add(ref sum, partial));
System.Console.WriteLine(sum);
loops++;
}
}
}
}
运行可得正确结果。
3、性能比较
上面的解决方案那个比较好呢?请大家各抒己见!关于这个我已经测试了一下。
PS:感觉写这篇的时候很累,思绪也很乱,不知大家对这篇还满意(⊙_⊙)?有什么地方需要改进,或者说不易理解,或者哪个地方错了!