pytorch官方教程学习笔记10:embedding
1.embedding等模型的层的参数会随机初始化,而且随机初始化是由所给的torch.manual_seed(1)决定的:
每一个定义的网络层是可以直接用来测试的,因为它是有权重的,但是权重因为是随机的,是没有经过大量训练来优化的,所以直接出来的结果也是肆无忌惮的:
我首先将随机种子设置为1
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
torch.manual_seed(1)
word_to_ix = {"hello": 0, "world": 1}
embeds = nn.Embedding(2, 5) # 2 words in vocab, 5 dimensional embeddings
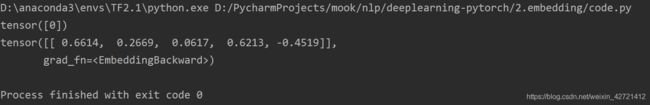
lookup_tensor = torch.tensor([word_to_ix["hello"]], dtype=torch.long)
print(lookup_tensor)
hello_embed = embeds(lookup_tensor)
print(hello_embed)
2.目前为止,见过的获得 word_to_ix 最简单的方法:
vocab = set(test_sentence)
word_to_ix = {word: i for i, word in enumerate(vocab)}
3.不明白这个为什么这个样例要这样使用交叉熵函数:nn.NLLLoss()。
算的预测结果的形状是(1,X)
给的标准结果的形状是(1,)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
loss_function = nn.NLLLoss()
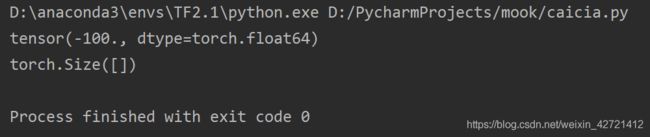
log_probs = torch.tensor([[100, 20]], dtype=torch.double)
loss = loss_function(log_probs, torch.tensor([0], dtype=torch.long))
print(loss)
print(loss.shape)
发现:
log_probs = torch.tensor([[100, 20]], dtype=torch.double)
loss = loss_function(log_probs, torch.tensor([0], dtype=torch.long))
输出:
tensor(-100., dtype=torch.float64)
log_probs = torch.tensor([[200, 20]], dtype=torch.double)
loss = loss_function(log_probs, torch.tensor([0], dtype=torch.long))
输出:
tensor(-200., dtype=torch.float64)
log_probs = torch.tensor([[200, 20]], dtype=torch.double)
loss = loss_function(log_probs, torch.tensor([1], dtype=torch.long))
输出:
tensor(-20., dtype=torch.float64)
你肯定能发现规律,不再赘述。