2021_AAAI_Knowledge-aware Coupled Graph Neural Network for Social Recommendation
[论文阅读笔记]2021_AAAI_Knowledge-aware Coupled Graph Neural Network for Social Recommendation
论文下载地址: https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/download/16533/16340
发表期刊:AAAI
Publish time: 2021
作者及单位:
- Chao Huang1*,
- Huance Xu2∗,
- Yong Xu2,3,4†,
- Peng Dai1,
- Lianghao Xia2,
- Mengyin Lu1,
- Liefeng Bo1,
- Hao Xing5,
- Xiaoping Lai5,
- Yanfang Y e6
- 1JD Finance America Corporation, USA
- 2South China University of Technology, China,
- 3Peng Cheng Laboratory, China
- 4Communication and Computer Network Laboratory of Guangdong, China
- 5VIPS Research, China,
- 6Case Western Reserve University, USA
[email protected], {cshuance.xu, cslianghao.xia}@mail.scut.edu.cn, [email protected],
{peng.dai,mengyin.lu,liefeng.bo}, {hao.xing,tom.lai}vipshop.com, [email protected]
数据集:
- Epinions (Fan et al. 2019)
- Yelp
- E-Com
代码:
- https://github.com/xhcdream/KCGN
其他人写的文章
- Knowledge-aware Coupled Graph Neural Network for Social Recommendation
- 2021-AAAI-KGCN-面向社会推荐的知识感知耦合图神经网络
简要概括创新点: (有点难读懂,需要把Related Work都读一读)
- (1) this work proposes a Knowledge-aware Coupled Graph Neural Network (KCGN) (本文提出了一种知识感知的耦合图神经网络(KCGN))
- that jointly injects the inter-dependent knowledge (across items and users) into the recommendation framework. (该网络将跨项目和用户的相互依赖的知识联合注入到推荐框架中。)
- we further augment KCGN with the capability of capturing dynamic multi-typed user-item interactive patterns. (此外,我们还通过捕获动态多类型用户项交互模式的能力进一步增强了KCGN。)
- We propose to capture both user-user and item-item relations with the developed coupled graph neural network. Through the joint modeling of user- and item-wise dependent structures, our KCGN can enhance the social-aware user embeddings with the preservation of knowledge-aware cross-item relations in a more thorough way. (我们提出用所开发的耦合图神经网络捕捉用户和项目之间的关系。通过用户和项目相关结构的联合建模,我们的KCGN可以更彻底地保留知识感知的跨项目关系,从而增强社会感知的用户嵌入。)
- We propose a relation-aware graph neural module to encode the multi-typed user-item interactive patterns, and further incorporate the temporal information into the message passing kernel to enhance the learning of collaborative relations for recommendation. (我们提出了一个关系感知图神经模块来编码多类型用户项交互模式,并进一步将时间信息纳入消息传递内核,以增强推荐协作关系的学习。)
- (2) we propose KCGN, an end-to-end framework that naturally incorporates knowledge-aware item dependency into the social recommender systems. (我们提出了KCGN,这是一个端到端的框架,它自然地将知识感知项依赖性融入到社会推荐系统中。)
- KCGN unifies the user-user and item-item relation structure learning with a coupled graph neural network under a mutual information-based neural estimator (KCGN将用户-用户和项目-项目关系结构学习与基于互信息的神经估计器下的耦合图神经网络相结合).
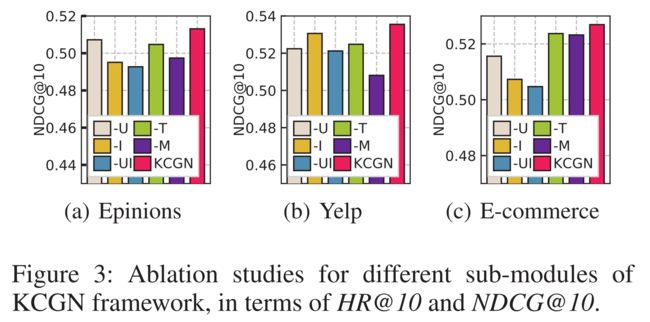
- (3) Figure 3 shows the comparison results of different variants. We can see that the joint model KCGN achieves the best performance. As such, it is necessary to build a joint framework to simultaneously capture social dimension (users’ social influence), item dimension (knowledge-aware inter-item relations), multi-typed interactions, and time-aware user’s interest, for making recommendations. In addition, KCGN-UI performs worse than KCGN-U and KCGN-I, which again confirms the efficacy of our designed relation aggregation functions. (显示不同变体的比较结果。我们可以看到,联合模型KCGN实现了最佳性能。因此,有必要建立一个联合框架,同时捕获社会维度(用户的社会影响)、项目维度(知识感知的项目间关系)、多类型交互和时间感知的用户兴趣,以便提出建议。此外,KCGN-UI的性能不如KCGN-U和KCGN-I,这再次证实了我们设计的关系聚合函数的有效性。)
Abstract
- (1) Social recommendation task aims to predict users’ preferences over items with the incorporation of social connections among users, so as to alleviate the sparse issue of collaborative filtering. While many recent efforts show the effectiveness of neural network-based social recommender systems,
- (2) several important challenges have not been well addressed yet:
- (i) The majority of models only consider users’ social connections, while ignoring the inter-dependent knowledge across items; (大多数模型只考虑用户的社会联系,而忽略了项目间的相互依赖的知识;)
- (ii) Most of existing solutions are designed for singular type of user-item interactions, making them infeasible to capture the interaction heterogeneity; (现有的大多数解决方案都是针对单一类型的用户项交互而设计的,因此无法捕获交互异构性)
- (iii) The dynamic nature of user-item interactions has been less explored in many social-aware recommendation techniques. (在许多具有社会意识的推荐技术中,对用户项交互的动态性质的研究较少。)
- (2) To tackle the above challenges, this work proposes a Knowledge-aware Coupled Graph Neural Network (KCGN) that jointly injects the inter-dependent knowledge (across items and users) into the recommendation framework. (为了应对上述挑战,本研究提出了一种知识感知耦合图神经网络(KCGN),该网络将跨项目和用户的相互依赖的知识联合注入到推荐框架中。)
- (3) KCGN enables the high-order user- and item-wise relation encoding by exploiting the mutual information for global graph structure awareness. (KCGN通过利用全局图结构感知的互信息实现高阶用户和项目关系编码。)
- (4) Additionally, we further augment KCGN with the capability of capturing dynamic multi-typed user-item interactive patterns. (此外,我们还通过捕获动态多类型用户项交互模式的能力进一步增强了KCGN。)
- (5) Experimental studies on real-world datasets show the effectiveness of our method against many strong baselines in a variety of settings. Source codes are available at: https://github.com/xhcdream/KCGN.
1 Introduction
-
(1) In recent years, social recommendation which aims to exploit users’ social information for modeling users’ preferences in recommendations, has attracted significant attention (Liu et al. 2019). As has been stated in many social-aware recommendation literature (Wu et al. 2019a; Chen et al. 2019b), social influences between users have high impacts on users’ interactive behavior over items in various recommender scenarios, such as e-commence(Lin,Gao,and Li 2019) and online review platforms (Chen et al. 2020a). Hence, researchers propose to incorporate social ties into the collaborative filtering architecture as side information to characterize connectivity information across users. ((1) 近年来,旨在利用用户的社会信息来模拟用户在推荐中的偏好的社会推荐受到了广泛关注(Liu等人,2019年)。正如许多具有社会意识的推荐文献(Wu等人,2019a;Chen等人,2019b)所述,用户之间的社会影响对用户在各种推荐者场景中的互动行为有很大影响,如电子商务(Lin、Gao和Li 2019)和在线评论平台(Chen等人,2020a)。因此,研究人员建议将社会关系作为辅助信息纳入协作过滤体系结构,以描述用户之间的连通性信息。)
-
(2) The most common paradigm for state-of-the-art social recommender systems is to learn an embedding function, which unifies user-user and user-item relations into latent representations. (对于最先进的社会推荐系统来说,最常见的范例是学习嵌入函数,该函数将用户和用户项的关系统一到潜在的表示中。)
- To tackle this problem, many studies have developed various neural network techniques to integrate social information with the user-item interaction encoding as constraints. For example, attention-based mechanism has been utilized to aggregate correlations among different users (Chen et al. 2019a,b). (为了解决这个问题,许多研究开发了各种神经网络技术,将社会信息与用户项目交互编码结合起来作为约束条件。例如,基于注意的机制被用于聚合不同用户之间的相关性(Chen等人,2019a,b)。)
- Furthermore, inspired by the recent advance of graph neural architectures, several attempts are built upon the message passing frameworks over the user-user social graph. For example, social influence is simulated with layer-wise diffusion scheme for information fusion (Wu et al. 2019a). GraphRec (Fan et al. 2019) employs the graph attention network to model the relational structures between users. To enable the modeling context-aware social effects, DANSER (Wu et al. 2019b) stacks two-stage of graph attention layer for distinguishing the multi-faceted social homophily and influence. (此外,受最近图形神经体系结构发展的启发,在用户社交图的消息传递框架上进行了几次尝试。例如,采用分层扩散方案模拟信息融合的社会影响(Wu等人,2019a)。GraphRec(Fan等人,2019年)利用图形注意网络对用户之间的关系结构进行建模。为了能够对情境感知的社会效应进行建模,DANSER(Wu et al.2019b)堆叠了两个阶段的图形注意层,以区分多方面的社会同质性和影响。)
-
While these solutions have provided encouraging results, several key aspects have not been well addressed yet. In particular,
-
(3) First, in real-life scenarios, there typically exist relations between items which characterize item-wise fruitful semantics relatedness, and are helpful to understand user-item interactive patterns (Wang et al. 2019a). (首先,在现实生活场景中,项目之间通常存在关系,这些关系表征了项目之间富有成效的语义关联,并且有助于理解用户项目交互模式(Wang等人,2019a)。)
- For instance, in online retailing systems, products of the same categories (e.g., food & grocery, clothing & shoes) or complement with each other, could be correlated to enrich the knowledge representation of items (Xin et al. 2019). For online review platforms, the exploiting of dependencies among the venues with the same functionality, is able to provide external knowledge in assisting user preference learning (Y u et al. 2019). However, the majority of existing social recommender systems fail to capture item-wise relational structures, which can hardly distill the knowledge-aware collaborative signals from the co-interactive behaviors of users. (例如,在在线零售系统中,相同类别的产品(如食品和杂货、服装和鞋子)或相互补充的产品可以相互关联,以丰富项目的知识表示(Xin等人,2019年)。对于在线审查平台,利用具有相同功能的场馆之间的依赖关系,能够提供外部知识,帮助用户进行偏好学习(Y u等人,2019年)。然而,现有的大多数社会推荐系统都无法捕获项目关系结构,很难从用户的交互行为中提取出知识感知的协作信号。)
-
(4) Second, to simplify the model design, most of current social recommendation methods have thus far focused on modeling singular type of interactive relations between user and item. Yet, many practical recommendation scenarios may involve the diversity of users’ interaction over items (Cen et al. 2019; Xia et al. 2020). (第二,为了简化模型设计,目前大多数社会推荐方法都集中于对用户和项目之间的单一类型的交互关系进行建模。然而,许多实际的推荐场景可能涉及用户在项目上的交互多样性(Cen等人,2019年;Xia等人,2020年)。)
- Take the e-commerce site as an example, the effective encoding of multi-typed user-item interactive patterns (e.g., page view, add-to-favorite and purchase) and their underlying inter-dependencies (e.g., add-to-favorite activities may serve as useful indicators for making purchase decisions), is crucial to more accurately inference of user’s complex interest in social recommendation tasks. (以电子商务网站为例,多类型用户项目交互模式(例如,页面视图、添加到收藏夹和购买)的有效编码及其潜在的相互依赖性(例如,添加到收藏夹活动可能作为做出购买决策的有用指标),对于更准确地推断用户对社交推荐任务的复杂兴趣至关重要。)
-
(5) Third, the time dimension of the social recommendation deserves more investigation, so as to capture behavior dynamics. Most of recent approaches ignore the dynamic nature of user-item interactions and assume that the factor influencing the interactive behavior is only the identity of items (Song et al. 2019).
- While there exist a handful of recent work that consider the sequential information in social recommendation (Song et al. 2019; Sun, Wu, and Wang 2018), their are limited in their intrinsic design for singular type of user-item relations. This makes them insufficient to yield satisfactory embeddings with the preservation of different interaction signals in a dynamic manner for more complex scenarios. (第三,社会推荐的时间维度值得更多的研究,以便捕捉行为动态。大多数最近的方法忽略了用户项目交互的动态性质,并假设影响交互行为的因素只是项目的身份(Song等人,2019)。虽然存在一些最近的工作,考虑社会信息中的顺序信息(Sun等人,2019;Sun,吴和Wang 2018),但它们在其固有设计中仅限于用户类型项关系的单一类型。这使得它们不足以在更复杂的场景中以动态方式保留不同的交互信号,从而产生令人满意的嵌入。)
-
(6) While intuitively useful to integrate the above dimensions into social recommendation frameworks, two unique technical challenges arise in achieving this goal. Specifically, graph-structured neural network can be applied to naturally model the topological information of social node instances, such as the graph-based convolutional network (Wu et al. 2019a) or attention mechanism (Wu et al. 2019b; Fan et al. 2019). (虽然直观上可以将上述维度集成到社会推荐框架中,但在实现这一目标时会遇到两个独特的技术挑战。具体而言,图结构神经网络可用于自然建模社会节点实例的拓扑信息,例如基于图的卷积网络(Wu等人2019a)或注意机制(Wu等人2019b;Fan等人2019)。)
- However, their non-linear aggregation functions can only learn the local proximity between users and are incapable of capturing the broader context of the graph structure (e.g., users with the isomorphic social structures) (Y ou, Ying, and Leskovec 2019). (然而,它们的非线性聚合函数只能学习用户之间的局部接近度,无法捕获图形结构的更广泛上下文(例如,具有同构社会结构的用户)(You、Ying和Leskovec 2019)。)
- Hence, how to jointly capture knowledge-aware user-user and item-item local relations, as well as retain the high-order social influence and item dependencies under global context, remains a significant challenge. (因此,如何联合捕获知识感知的用户-用户和项目-项目局部关系,以及在全局上下文保持高阶社会影响和项目依赖性,仍然是一个重大挑战。)
- Additionally, it is also very challenging to handle the dynamic multi-typed user-item interactions, so as to capture the dynamic relation-aware structural dependencies across users and items with arbitrary duration. (此外,处理动态的多类型用户-项目交互,以便捕获具有任意持续时间的用户和项目之间的动态关系感知结构依赖,也是一个非常具有挑战性的问题。)
-
(7) The Present Work. In light of the aforementioned motivations and challenges, we study the social recommendation problem by proposing the Knowledge-aware Coupled Graph Neural Network (KCGN). (目前的工作。鉴于上述动机和挑战,我们通过提出知识感知耦合图神经网络(KCGN)来研究社会推荐问题。)
- To jointly deal with the user-user and item-item local and global relational structure awareness, we incorporate the mutual information estimation schema into the coupled graph neural architecture. This design enables the collaboration between neural mutual information estimator and graph-structured representation learning paradigm, which preserves the node-level unique characteristics and graph-level substructure knowledge across users and items. (为了联合处理用户和项目的局部和全局关系结构感知,我们将互信息估计模式合并到耦合图神经结构中。这种设计实现了神经互信息估计器和图结构表示学习范式之间的协作,从而在用户和项目之间保留了节点级的独特特征和图级的子结构知识。)
- In addition, to capture the dynamic multi-typed interactive patterns, we integrate a relation-aware message passing framework with the relative temporal encoding strategy, which endows KCGN with the capability of incorporating the temporal information into the multi-typed user-item interaction graph learning.
-
(8) Our contributions can be highlighted as follows:
- We propose to capture both user-user and item-item relations with the developed coupled graph neural network. Through the joint modeling of user- and item-wise dependent structures, our KCGN can enhance the social-aware user embeddings with the preservation of knowledge-aware cross-item relations in a more thorough way. (我们提出用所开发的耦合图神经网络捕捉用户和项目之间的关系。通过用户和项目相关结构的联合建模,我们的KCGN可以更彻底地保留知识感知的跨项目关系,从而增强社会感知的用户嵌入。)
- We propose a relation-aware graph neural module to encode the multi-typed user-item interactive patterns, and further incorporate the temporal information into the message passing kernel to enhance the learning of collaborative relations for recommendation. (我们提出了一个关系感知图神经模块来编码多类型用户项交互模式,并进一步将时间信息纳入消息传递内核,以增强推荐协作关系的学习。)
- We conduct extensive experiments on three real-world datasets to show the superiority of our KCGN when competing with several baselines from various research lines. Further studies on scalability evaluation validate the model efficiency of KCGN over state-of-the-art social recommender systems. We also show that our model maintains strong performance in the cold-start scenarios when user-item interactions are sparse. (我们在三个真实数据集上进行了广泛的实验,以显示我们的KCGN在与不同研究线的多个基线竞争时的优势。进一步的可伸缩性评估研究验证了KCGN在最先进的社会推荐系统上的模型效率。我们还表明,当用户项交互稀疏时,我们的模型在冷启动场景中保持了良好的性能。)
2 Problem Definition
- We first introduce key definitions of social recommendation with item relational knowledge and different types of user-item interactions. We consider a typical recommendation scenario, in which we have I I I users U = { u 1 , . . . , u i , . . . , u I } U = \{u_1, ..., u_i, ..., u_I\} U={u1,...,ui,...,uI} and J J J items V = { v 1 , . . . , v j , . . . , v J } V = \{v_1, ..., v_j, ..., v_J\} V={v1,...,vj,...,vJ}. To capture the multi-typed user-item interaction signals, we define a multi-typed interaction tensor as below:
2.1 Definition 1 Multi-typed Interaction Tensor X.
- We define a three-way tensor X ∈ R I × J × K X \in R^{I \times J \times K} X∈RI×J×K to represent the different types of interactions between user and item,
- where K K K (indexed by k k k) denotes the number of interaction types (page view, purchase, or like, dislike).
- In X X X, the element x i , j k = 1 x^k_{i,j} = 1 xi,jk=1 if user u i u_i ui interacts with item v j v_j vj with the interaction type of k k k and x i , j k = 0 x^k_{i,j}=0 xi,jk=0 otherwise.
- To deal with the interaction dynamics, we also define a temporal tensor T ∈ R I × J × K T \in R^{I \times J \times K} T∈RI×J×K with the same size of X X X to record the timestamp information ( t i , j k t^k_{i, j} ti,jk) of each corresponding interaction x i , j k x^k_{i, j} xi,jk.
2.2 Definition 2 User Social Graph G u G_u Gu.
- G u = { U , E u } G_u= \{U, E_u\} Gu={U,Eu} represents the social relationships (edges E u E_u Eu) among users (nodes U U U), where there exists an edge e i , i ′ e_{i, i'} ei,i′ between user u i u_i ui and u i ′ u_{i'} ui′ given they are socially connected
2.3 Definition 3 Item Inter-Dependency Graph G v G_v Gv.
- We further define G v = { V , E v } G_v= \{V, E_v\} Gv={V,Ev} to represent the inter-dependence of items. In particular , we characterize the item-wise relations with a triple { v j , e j , j ′ , v j ′ ∣ v j , v j ′ ∈ V } \{v_j, e_{j, j'}, v_{j'}|v_j, v_{j'} \in V \} {vj,ej,j′,vj′∣vj,vj′∈V}, where edge e j , j ′ e_{j, j'} ej,j′ describes the relationship between item v j v_j vj and v j ′ v_{j'} vj′, e.g., v j v_j vj and v j ′ v_{j'} vj′ belong to the same product categories and have similar functionality, or are interacted by the same user under the same interaction type of k k k. (属于相同的产品类别且具有相似的功能,或由同一用户在同一交互类型k下进行交互。)
2.4 Task Formulation.
- We formulate the studied recommendation task in this paper as:
- Input: multi-typed interaction tensor X ∈ R I × J × K X \in R^{I \times J \times K} X∈RI×J×K, user social graph G u G_u Gu and item inter-dependence graph G v G_v Gv.
- Output: a predictive function that effectively forecasts the future user-item interaction
3 Methodology
3.1 Multi-typed Interactive Pattern Modeling

Figure 1: The architecture of the multi-typed interactive pat-tern modeling. ⊕ \oplus ⊕ denotes the element-wise addition.
- (1) To encode the multi-typed collaborative relations, we propose a relation-aware graph neural architecture, which is built upon the message passing paradigm (as shown in Figure 1), to empower KCGN to capture the dedicated patterns of different types of user-item interactions. (为了对多类型协作关系进行编码,我们提出了一种基于消息传递范式(如图1所示)的关系感知图神经架构,以使KCGN能够捕获不同类型用户项交互的专用模式。)
- Specifically, given the multi-typed interaction tensor X X X, we first construct a multi-typed relation graph G m G_m Gm by representing the interaction heterogeneity with type-specific item subvertices v j → ( v j 1 , . . . , v j k , . . . , v j K ) v_j \to (v^1_j, ..., v^k_j, ..., v^K_j) vj→(vj1,...,vjk,...,vjK),
- where K K K denotes the number of interaction types.
- Each edge between u i u_i ui and v j k v^k_j vjk represents the corresponding interaction with the k k k-th type.
- After that, there are ( I + J ⋅ K ) (I + J \cdot K) (I+J⋅K) vertices in our multi-typed graph G m = ( V m , E m ) G_m= (V_m, E_m) Gm=(Vm,Em),
- where V m = U ∪ V ′ V_m = U \cup V' Vm=U∪V′ and v j k ∈ V ′ v^k_j \in V' vjk∈V′.
- Here, V ′ V' V′ is the new type-aware item set.
- where V m = U ∪ V ′ V_m = U \cup V' Vm=U∪V′ and v j k ∈ V ′ v^k_j \in V' vjk∈V′.
- Specifically, given the multi-typed interaction tensor X X X, we first construct a multi-typed relation graph G m G_m Gm by representing the interaction heterogeneity with type-specific item subvertices v j → ( v j 1 , . . . , v j k , . . . , v j K ) v_j \to (v^1_j, ..., v^k_j, ..., v^K_j) vj→(vj1,...,vjk,...,vjK),
3.2 Message Construction Phase.
- (1) We first generate the message between user vertex u i u_i ui and his/her interacted type-specific item vertex v j k v^k_j vjk as follows:
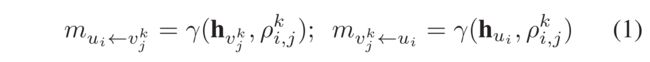
- where γ ( ⋅ ) \gamma(\cdot) γ(⋅) denotes the information encoding function over the input feature embeddings h v j k ∈ R ( J ⋅ K ) × d h_{v^k_j} \in R^{(J\cdot K)\times d} hvjk∈R(J⋅K)×d, h u i ∈ R I × d h_{u_i} \in R^{I \times d} hui∈RI×d
- ρ i , j k \rho^k_{i, j} ρi,jk is the decay factor to normalize the propagated influence with node degrees (Chen et al. 2020b), i.e., ρ = 1 ∣ N i ∣ ∣ N j k ∣ \rho = \frac{1}{\sqrt{|N_i||N^k_j|}} ρ=∣Ni∣∣Njk∣1,
- where N i N_i Ni denotes the number of neighboring nodes of user u i u_i ui and (表示用户 u i u_i ui的相邻节点数)
- N j k N^k_j Njk represents the number of connected user nodes of item v j v_j vj under the relation type of k k k. (在关系类型k下与项目 v j v_j vj相连接的用户节点数量)
- Hence, the constructed message can be unfolded as:
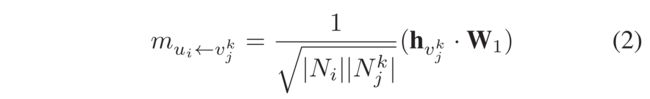
3.3 Temporal Context Encoding Scheme.
- Inspired by the recommendation techniques with the modeling of temporal information (Sun et al. 2019; Huang et al. 2019), in our framework, we allow the user-item interactions happening at different timestamps interweave with each other, by introducing a temporal context encoding scheme to model the dynamic dependencies across different types of users’ interactions. Motivated by the positional encoding algorithm in Transformer architecture (Vaswani et al. 2017; Sun et al. 2019; Wu et al. 2020), we map the timestamp t i , j k t_{i,j^k} ti,jk of individual interaction x i , j k x^k_{i,j} xi,jk into separate time slot as: T ~ ( t i , j k ) \tilde{T}(t^k_{i,j}) T~(ti,jk). We employ the sinusoid functions to generate the relative time embedding for edge e i , j k ∈ E m e^k_{i,j} \in E_m ei,jk∈Em in G m G_m Gm as: (受时态信息建模推荐技术(Sun等人2019;Huang等人2019)的启发,在我们的框架中,我们允许在不同时间戳发生的用户项交互相互交织,通过引入一种时态上下文编码方案来建模不同类型用户交互的动态依赖关系。受变压器体系结构中的位置编码算法(Vaswani et al.2017;Sun et al.2019;Wu et al.2020)的启发,我们映射了个体相互作用 x i , j k x^k_{i,j} xi,jk的时间戳 t i , j k t_{i,j^k} ti,jk进入离散的的时隙,如: T ~ ( t i , j k ) \tilde{T}(t^k_{i,j}) T~(ti,jk) 。我们利用 正弦函数 来生成边 e i , j k ∈ E m e^k_{i,j} \in E_m ei,jk∈Em 在 G m G_m Gm中的相对时间嵌入:
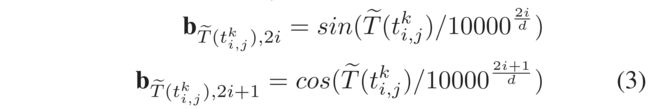
- where ( 2 i ) (2i) (2i) and ( 2 i + 1 ) (2i + 1) (2i+1) denotes the element index with the even and odd position in embedding b T ~ ( t i , j k ) b_{\tilde{T}(t^k_{i,j})} bT~(ti,jk), respectively. (表示嵌入中具有奇偶位置的元素索引)
3.4 High-Order Message Aggregation Phase.
- (1) We incorporate the propagated message between user u i u_i ui and item v i , j k v^k_{i,j} vi,jk, as well as temporal context b T ~ ( t i , j k ) b_{\tilde{T}(t^k_{i,j})} bT~(ti,jk) on their interaction edge e i , j k e^k_{i,j} ei,jk, into our information propagation paradigm as below:
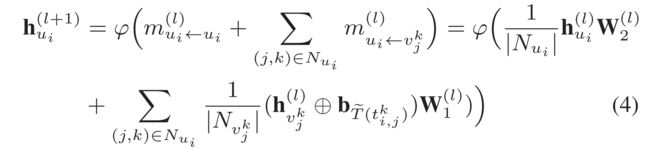
- where φ ( ⋅ ) \varphi(\cdot) φ(⋅) denotes the LeakyReLU function to perform the transformation.
- m u i ← u i ( l ) m^{(l)}_{ui\leftarrow ui} mui←ui(l) is the self-ropagated message with the weight matrix W 2 ( l ) ∈ R d × d W^{(l)}_2 \in R^{d\times d} W2(l)∈Rd×d. (是带有权重矩阵的自映射消息)
- ⊕ \oplus ⊕denotes the element-wise addition.
- l l l is the index of L L L graph layers.
- We finally generate the user/item embeddings $(i.e., h u i ∗ h^∗_{u_i} hui∗, h v i , j k ∗ ) h^∗_{v^k_{i,j}}) hvi,jk∗) with the following concatenation operation ∥ \parallel ∥ as follows:

- (2) We generate the summarized representation h v j ∗ h^∗_{v_j} hvj∗ over all item sub-vertex embeddings h v j , k ∗ h^∗_{v_{j,k}} hvj,k∗ ( k ∈ [ 1 , . . . , K ] ) (k\in [1, ..., K]) (k∈[1,...,K]) with a gating mechanism (Ma, Kang, and Liu 2019), to differentiate the importance of type-specific interaction patterns. (区分特定类型交互模式的重要性)
3.5 Knowledge-aware Coupled Graph Neural Module
- (1) To jointly inject the user- and item-wise inter-dependent knowledge into our user preference modeling, we develop a knowledge-aware coupled graph neural network which enables the collaboration between the mutual information learning and graph representation paradigm. (为了将用户和项目相互依赖的知识共同注入到我们的用户偏好建模中,我们开发了一个知识感知的耦合图神经网络,该网络支持交互信息学习和图表示范式之间的协作。)
- (2) While many efforts have been devoted to modeling graph structural information, they are limited in their ability in capturing both local and global graph substructure awareness (V elickovic et al. 2019), such as the user- and item-specific social/knowledge dependent information and high-order relationships across users/items. (尽管许多研究致力于对图形结构信息进行建模,但它们在捕获局部和全局图形子结构感知方面的能力有限(V elickovic等人,2019年),例如用户和项目特定的社会/知识相关信息以及跨用户/项目的高阶关系。)
- KCGN is equipped with a dual-stage graph learning paradigm (As shown in Figure 2). (KCGN配备了双阶段图学习范式(如图2所示)。)
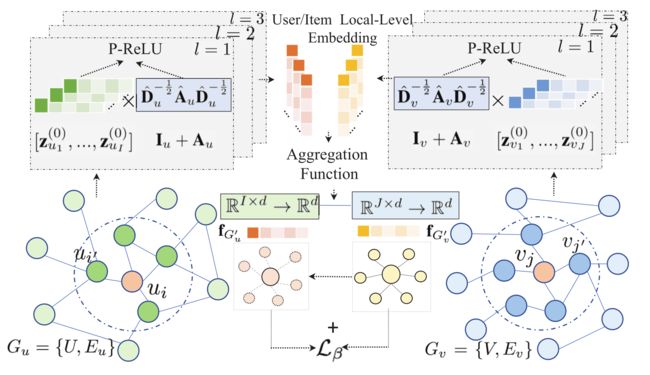
Figure 2: The architecture of joint encoding of user-user and item-item inter-dependent relational structures.
3.6 Local Relational Structure Modeling.
- (1) We first learn the user- and item-specific specific embeddings ( z u i , z v j ) (z_{u_i}, z_{v_j}) (zui,zvj) which preserves the local connection information over user social graph G u G_u Gu and item inter-dependent graph G v G_v Gv with the following graph-based update functions ( z u i 0 = h u i ∗ z^0_{u_i} = h^∗_{u_i} zui0=hui∗, z v j 0 = h v j ∗ z^0_{v_j} = h^∗_{v_j} zvj0=hvj∗):

- (2) where η ( ⋅ ) \eta(\cdot) η(⋅) denotes the adjacent relations of G u G_u Gu and G v G_v Gv with the symmetric normalization strategy in the information aggregation across the neighboring users/items, e . g . , η ( G v ) = D ^ v − 1 2 A ^ v D ^ v − 1 2 e.g., \eta(G_v) =\hat{D}^{-\frac{1}{2}}_v \hat{A}_v \hat{D}^{−\frac{1}{2}}_v e.g.,η(Gv)=D^v−21A^vD^v−21.
- Hence, A ^ v \hat{A}_v A^v is the addition of identity matrix I v I_v Iv and adjacent matrix A v A_v Av, so as to incorporate the information self-propagation (Chen et al. 2020b).
- (3) In this graph learning paradigm, we aim to inject both local- and global-level relational structures over the user social graph and item relation graph into our learned user/item representations. (在这个图学习范式中,我们的目标是将用户社会图和项目关系图上的局部和全局级别的关系结构注入到我们学习的用户/项目表示中。)
- Different from the existing graph neural network approaches (V elickovic et al. 2019; Xu et al. 2020) which model the mutual relations between local feature embeddings and a single global representation, we enrich the global semantics with the consideration of connected graph substructures (e.g., the entire social relations of all users may consist of different connected sub-graphs G u ′ G'_u Gu′). (与现有的图神经网络方法(V elickovic et al.2019;Xu et al.2020)不同,该方法对局部特征嵌入和单个全局表示之间的相互关系进行建模,我们通过考虑连通图子结构(例如,所有用户的整个社会关系可能由不同的连通子图 G u ′ G'_u Gu′组成)来丰富全局语义 ).)
- In particular, we first generate a fused graph-level representation f G u ′ , f G u ′ ∈ R d f_{G'_u}, f_{G'_u} \in R^d fGu′,fGu′∈Rd by applying the mean pooling over node-specific embeddings.
- (4) We design our neural mutual information estimator based on a discriminator D ( x , y ) D(x, y) D(x,y) for node-graph pairwise relationships, to provide probability scores for sampled pairs. (我们设计了基于节点图成对关系鉴别器D(x,y)的神经互信息估计器,以提供采样对的概率分数。)
- To be specific, we generate positive samples as ( z u i , f G u ′ z_{u_i},f_{G'_u} zui,fGu′), ( z v j , f G v ′ z_{v_j},f_{G'_v} zvj,fGv′), and negative samples as ( z ~ u i , f G u ′ \tilde{z}_{u_i}, f_{G'_u} z~ui,fGu′), ( z ~ v j , f G v ′ ) \tilde{z}_{v_j},f_{G'_v}) z~vj,fGv′).
- Here, z ~ u i \tilde{z}_{u_i} z~ui and z ~ u i \tilde{z}_{u_i} z~ui are randomly picked with node shuffling to generate the misplaced node-graph pairwise relations. (使用节点洗牌随机拾取,以生成错位的节点图成对关系。)
- To be specific, we generate positive samples as ( z u i , f G u ′ z_{u_i},f_{G'_u} zui,fGu′), ( z v j , f G v ′ z_{v_j},f_{G'_v} zvj,fGv′), and negative samples as ( z ~ u i , f G u ′ \tilde{z}_{u_i}, f_{G'_u} z~ui,fGu′), ( z ~ v j , f G v ′ ) \tilde{z}_{v_j},f_{G'_v}) z~vj,fGv′).
- (5) Due to the rationality of cross-entropy in mutual information maximization (Wang et al. 2020), we define our noise-contrastive knowledge-aware loss function L β L_{\beta} Lβ as follows: (由于互信息最大化中交叉熵的合理性(Wang et al.2020),我们定义了噪声对比知识感知损失函数L{eta})
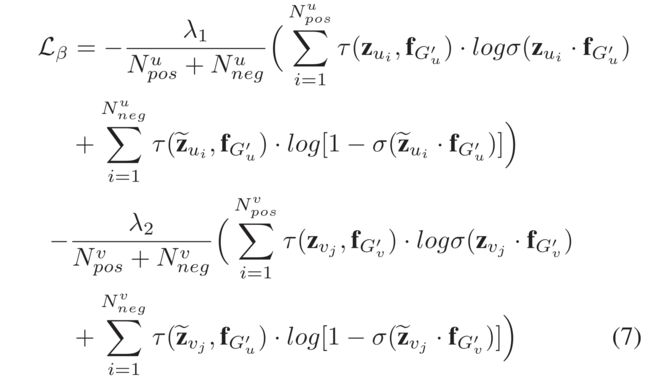
- where N p o s u / N p o s v N^u_{pos}/N^v_{pos} Nposu/Nposv and N n e g u / N n e g v N^u_{neg}/N^v_{neg} Nnegu/Nnegv denotes the number of positive and negative instances sampled over sub-graph G u ′ G'_u Gu′ and G v ′ G'_v Gv′
- τ ( ⋅ ) \tau(\cdot) τ(⋅) is an indicator function, e.g., τ ( z v j , f G v ′ ) = 1 \tau(z_{v_j}, f_{G'_v}) = 1 τ(zvj,fGv′)=1 and τ ( z ~ v j , f G v ′ ) = 1 \tau(\tilde{z}_{v_j}, f_{G'_v}) = 1 τ(z~vj,fGv′)=1 corresponds to the positive and negative pair instances.
- λ 1 \lambda_1 λ1 and λ 2 \lambda_2 λ2 are balance parameters.
- We aim to minimize λ β \lambda_{\beta} λβ which is equivalent to maximize the mutual information, to jointly preserve the node-specific user/item characteristics and global graph-level dependencies. (这相当于最大化互信息,共同保留特定于节点的用户/项目特征和全局图级依赖关系。)
3.8 Model Optimization
- We define our loss L \mathcal{L} L which includes
- (i) multi-typed user-item interaction encoding; (多类型用户项交互编码;)
- (ii) knowledge-aware user-user and item-item inter-dependent relation learning. Particularly, L \mathcal{L} L integrates the pairwise BPR loss, which is widely adopted in recommendation tasks (Wang et al. 2019c), with the mutual information maximization paradigm as: (具有知识意识的用户和项目相互依赖关系学习。特别是,L将推荐任务中广泛采用的成对BPR损失(Wang等人,2019c)与互信息最大化范式整合为:)

- the pairwise training data is denoted as O = { ( u , j + , j − ) ∈ R + , ( u , j − ) ∈ R − } O = \{(u, j^+, j^-) \in R^+, (u, j^-) \in R^- \} O={(u,j+,j−)∈R+,(u,j−)∈R−}
- ( R + , R − R^+, R^- R+,R− denotes the observed and unobserved interactions, respectively).
- x ^ i , j \hat{x}_{i, j} x^i,j is the calculated score with the inner-product between the embedding of u i u_i ui and v j v_j vj.
- Θ \Theta Θ are trainable parameters,
- σ ( ⋅ ) \sigma(\cdot) σ(⋅)–sigmoid.
- λ \lambda λ controls the strength of L 2 L_2 L2 regularization for overfitting alleviation.
3.9 Time Complexity Analysis.
- KCGN takes O ( ∣ E ∣ × d ) O(|E| \times d) O(∣E∣×d) for the message passing in handling the user-user, user-item and item-item relations, where
- ∣ E ∣ |E| ∣E∣ denotes the number of edges.
- Also, O ( ( I + J ⋅ K ) × d 2 ) O((I + J · K) \times d2) O((I+J⋅K)×d2) computation is spent by the transformations.
- Typically, the first term is dominant due to information compression.
- In conclusion, KCGN is comparable in time efficiency compared with current GNN-based recommendation methods. Our model only utilizes moderate memory to store node embeddings ( O ( ( I + J ⋅ K ) × d ) ) (O((I +J ·K)\times d)) (O((I+J⋅K)×d)), which is similar to the existing methods.
4 Evaluation
- In this section, we conduct experiments on different real-world datasets to evaluate the performance of our method from the following aspects:
- RQ1: Does KCGN consistently outperform other baseline in terms of recommendation accuracy?
- RQ2: How is the performance of KCGN’s variants with the combination of different relation encoders?
- RQ3: How is forecasting performance of compared methods w.r.t different interaction density degrees?
- RQ4: How do the representations benefit from the collectively encoding of global knowledge-aware cross-interactive patterns in social recommendation?
- RQ5: How do different hyper-parameter settings impact the performance of our KCGN framework?
- RQ6: How is the model efficiency of the KCGN?
5 Experimental Settings
5.1 Dataset.
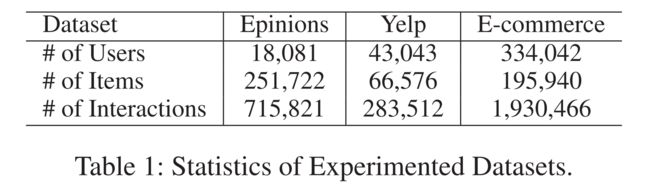
- Table 1 lists the statistics of three datasets. We describe the details of those datasets as follows:
- Epinions. This data records the user’s feedback over different items from a social network-based review system Epinions (Fan et al. 2019). Each explicit rating score (ranging from 1 to 5) is regarded as an individual type of interaction: negative, below average, neutral, above average, positive. (该数据记录了用户对基于社交网络的评价系统Epinions中不同项目的反馈(Fan等人,2019年)。每个明确的评分(从1到5)都被视为一种单独的互动类型:消极、低于平均水平、中性、高于平均水平、积极。)
- Yelp. This data is collected from the Yelp platform, in which user-item interactions are differentiated with the same split rubric in Epinions. Furthermore, user’s social connections (with common interests) are contained in this data. (这些数据是从Yelp平台收集的,在Yelp平台中,用户项目交互使用相同的划分标准进行区分。此外,用户的社会关系(具有共同兴趣)包含在该数据中。)
- E-Commerce. It is collected from a commercial ecommerce platform with different types of interactions, i.e., page view, add-to-cart, add-to-favorite and purchase. User’s relations are constructed with their co-interact patterns. (它是从商业电子商务平台收集的,具有不同类型的交互,即页面查看、添加到购物车、添加到收藏夹和购买。用户关系是通过他们的交互模式构建的。)
- The item inter-dependency graph G v G_v Gv on the above datasets are constructed based on item categories.
5.2 Evaluation Protocols.
- We adopt two widely used evaluation metrics for social recommendation tasks (Chen et al. 2019a):
- Hit Ratio (HR@N) and
- Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG@N).
- We follow the evaluation settings in (Chen et al. 2019b; Wu et al. 2019a) and employ the leave-one-out method for generating training and test data instances. To be consistent with (Sun et al. 2019), we associate each positive instance with 99 negative samples. (为了与(Sun等人,2019年)保持一致,我们将每个阳性实例与99个阴性样本相关联)
5.3 Baselines.
In our experiments, we perform the performance comparison by considering the following baselines:
5.3.1 Probabilistic Matrix Factorization Method.
- PMF (Mnih and et al 2008): it is a probabilistic approach with the matrix factorization for user/item factorization.
5.3.2 Conventional Social Recommendation Methods.
- TrustMF (Yang et al. 2016): this method incorporates the truth relationships between users into the matrix factorization architecture for user interaction embedding.
5.3.3 Attentive Social Recommendation Techniques.
- SAMN (Chen et al. 2019a): this model is a dual-stage attention network which learns the influences between the target user and his/her neighboring nodes.
- EATNN (Chen et al. 2019b): This transfer learning model is also on the basis of attention mechanism to jointly fuse information from user’s interactions and social signals.
5.3.4 Graph Neural Networks Social Recommender Systems.
- DiffNet (Wu et al. 2019a): it is a deep influence propagation framework to model the social diffusion process.
- GraphRec (Fan et al. 2019): it aggregates the social relations between users via a graph neural architecture.
- NGCF+S (Wang et al. 2019c): we incorporate the social ties into the state-of-the-art graph-structured neural collaborative filtering model for joint message propagation.
- Danser (Wu et al. 2019b): it is composed of two graph attention layers for capturing the social influence and homophily, respectively from both users and items.
- LR-GCCF (Chen et al. 2020b): it is a new graph-based collaborative filtering model based on graph convolutional network by removing non-linear transformations.
5.3.5 Social Recommendation with Sequential Pattern.
- DGRec (Song et al. 2019): it jointly models the dynamic user’s preference and the underlying social relations.
5.3.6 Knowledge Graph-enhanced Recommendation.
- KGAT (Wang et al. 2019b): it is a graph attentive message passing framework which utilizes the knowledge graph to enhance the recommendation with item side information.
5.4 Implementation Details.
- The KCGN is implemented with Pytorch and Adam optimizer is adopted for hyperparameter estimation. The training process is erformed with the learning rate range of [0.001, 0.005, 0.01], and the batch size selected from [1024,2048,4096,8192]. The embedding size is tuned from the range of [8,16,32,64]. In our evaluations, we employ the early stopping for training termination when the performance degrades for 5 continuous epochs on the validation data. (KCGN采用Pytorch实现,Adam优化器用于超参数估计。执行培训过程时,学习率范围为[0.001,0.005,0.01],批量大小从[1024 2048 4096 8192]中选择。嵌入大小在[8,16,32,64]的范围内进行调整。在我们的评估中,当验证数据连续5个时期性能下降时,我们采用提前停止训练终止。)
6 实验结果
6.1 Overall Model Performance Comparison (RQ1)
- (1) Table 2 reports the results of KCGN and many baselines in predicting the overall interactions in terms of HR@10 and NDCG@10. It can be seen that KCGN consistently obtains the best performance across different recommendation scenarios in terms of two metrics, which justifies the effectiveness of our method in integrating user-user and item-item relations, with the multi-typed user-item interactive patterns. (表2报告了KCGN和许多基线预测总体交互作用的结果HR@10和NDCG@10.可以看出,就两个指标而言,KCGN在不同的推荐场景中始终获得最佳性能,这证明了我们的方法在集成用户-用户和项目-项目关系以及多类型用户-项目交互模式方面的有效性。)

- (2) Compared with traditional approaches, neural network based models usually achieve better performance, due to the modeling of high-level non-linearities during the feature interaction learning phase. Among various compared approaches, the GNN-based models outperforms the attentive social recommender systems, which ascertains the rationality of applying graph neural networks for high-order relations across users/items in a recursive way. Different from those GNN techniques, our framework integrates the social and knowledge-aware relations from global context via a mutual information encoding paradigm, and also captures interaction dynamics, which results in better performance. (与传统方法相比,基于神经网络的模型通常能获得更好的性能,这是由于在特征交互学习阶段对高级非线性进行了建模。在各种比较方法中,基于GNN的模型优于专注的社会推荐系统,后者确定了以递归方式将图形神经网络应用于跨用户/项目的高阶关系的合理性。与那些GNN技术不同,我们的框架通过互信息编码范式整合了全局上下文中的社会和知识感知关系,并捕获了交互动态,从而获得了更好的性能。)
- (3) We further investigate the performance of our KCGN in making recommendations on the target type of interactions (e.g., positive feedback on Epinions and Yelp or user’s purchase on E-commerce). The results are shown in Table 3. We can observe that KCGN still achieves significant improvement, with the careful consideration of different types of user-item interaction signals. While the baseline KGAT proposes to incorporate the auxiliary knowledge graph, it fails to explicitly differentiate type-specific interaction patterns. (我们进一步调查了KCGN在就目标交互类型提出建议方面的表现(例如,对ePionions和Yelp的正面反馈或用户在电子商务上的购买)。结果如表3所示。我们可以观察到,在仔细考虑不同类型的用户项交互信号后,KCGN仍然取得了显著的改进。虽然基线KGAT建议合并辅助知识图,但它无法明确区分特定类型的交互模式。)

6.2 Impact of Different Relation Encoders (RQ2)
-
(1) We next perform experiments to evaluate the impact of the incorporation of multi-typed user-item interactions, user-wise relations, item-wise dependencies, and the temporal context, with the following five contrast variants of KCGN. (接下来,我们通过以下五种KCGN对比变体进行实验,以评估合并多类型用户项交互、用户关系、项依赖和时间上下文的影响。)
- KCGN-M: KCGN without modeling multi-typed interaction patterns and only with singular-type interactions. (无需建模多类型交互模式,仅使用单一类型交互。)
- KCGN-U: KCGN without the social relation encoder for capturing the social signals in the recommendation. (没有用于捕获推荐中的社会信号的社会关系编码器。)
- KCGN-I: KCGN without the external knowledge to characterize the item dependency. (没有外部知识来描述项目依赖性)
- KCGN-UI: KCGN without both the user- and item-wise relation encoders and remove the coupled mutual information paradigms in the joint learning framework. (没有用户和项目的关系编码器,并删除联合学习框架中耦合的互信息范例)
- KCGN-T: KCGN without the temporal context encoding. (没有时间上下文编码)
-
(2) Figure 3 shows the comparison results of different variants. We can see that the joint model KCGN achieves the best performance. As such, it is necessary to build a joint framework to simultaneously capture social dimension (users’ social influence), item dimension (knowledge-aware inter-item relations), multi-typed interactions, and time-aware user’s interest, for making recommendations. In addition, KCGN-UI performs worse than KCGN-U and KCGN-I, which again confirms the efficacy of our designed relation aggregation functions. (显示不同变体的比较结果。我们可以看到,联合模型KCGN实现了最佳性能。因此,有必要建立一个联合框架,同时捕获社会维度(用户的社会影响)、项目维度(知识感知的项目间关系)、多类型交互和时间感知的用户兴趣,以便提出建议。此外,KCGN-UI的性能不如KCGN-U和KCGN-I,这再次证实了我们设计的关系聚合函数的有效性。)
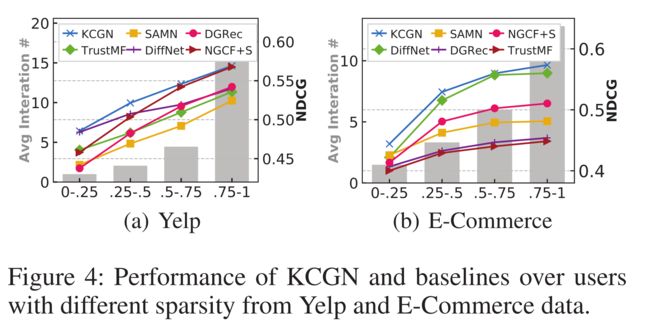
6.3 Performance over Sparsity Degrees (RQ3)
- (1) One key motivation to exploit social- and knowledge-aware side information is to alleviate the sparsity issue, which limits the model robustness. Hence, we further evaluate our KCGN for both inactive and active users. In particular, we partition the target users into four sparsity levels in terms of their interaction densities. Figure 4 presents the evaluation results on different user groups on Yelp and E-Commerce data in terms of NDCG@10. We can observe that KCGN outperforms representative baselines in most cases, especially on sparest user groups. This suggests that incorporating both user and item side knowledge as their external relations, empowers the representations of inactive users through our recursive information aggregation architecture. (利用社会和知识感知的边信息的一个关键动机是缓解稀疏性问题,这限制了模型的鲁棒性。因此,我们进一步评估了非活动用户和活动用户的KCGN。特别地,我们根据目标用户的交互密度将其划分为四个稀疏级别。图4显示了对Yelp和电子商务数据中不同用户组的评估结果NDCG@10.我们可以观察到,在大多数情况下,KCGN优于代表性基线,尤其是在最稀疏的用户组上。这表明,通过我们的递归信息聚合体系结构,将用户和项目端知识合并为它们的外部关系,可以增强非活动用户的表示能力。)
6.4 Qualitative Analyses of KCGN (RQ4)
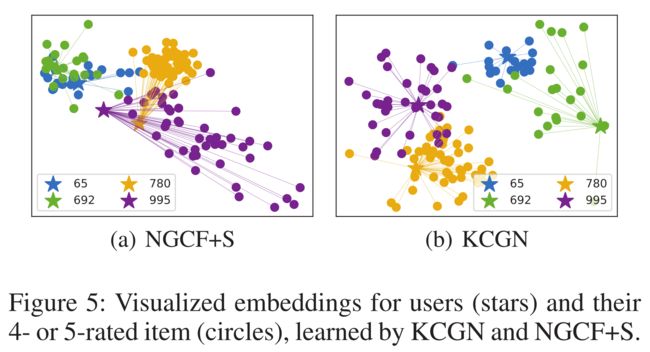
- (1) We illustrate how our side knowledge-aware multi-typed relation encoding schema benefit the ability of embedding user’s preference into the latent learning space. In particular, we sample several users and their four- and five-star rated items from Yelp dataset, and further visualize the corresponding user/item embeddings learned by NGCF+S and our KCGN (as shown in Figure 5). From the results, we can notice that: i) the visualized embeddings could well preserve the relationships between users and their interacted items with a clustering phenomenon (represented with the same color); ii) KCGN could provide a better separation for different users and their interacted items. Hence, the above observations verify the superior representation learning ability of KCGN through the encoding function which maps the side knowledge and interaction units into effective latent space.
6.5 Parameter Sensitivity Study (RQ5)
6.5.1 Impact of # Recursive Graph Layers.
- Figure 6 shows the experimental results with different number of embedding propagation layers over user-item interaction graph. We can observe that increasing the depth of KCGN could boost the performance, i.e., KCGN-2 performs better than KCGN-0 (without the graph structure) and KCGN-1 (only consider 1-hop neighbors). The performance improvement lies in the effective modeling of high-order collaborative effects across users and items. KCGN with 3 graph layers performs worse than KCGN-2, suggests that exploring higher-level relations may involve noise. (显示了在用户项交互图上嵌入不同传播层数的实验结果。我们可以观察到,增加KCGN的深度可以提高性能,即KCGN-2比KCGN-0(没有图结构)和KCGN-1(只考虑1跳邻居)的性能要好。性能改进在于跨用户和项目的高阶协作效果的有效建模。具有3个图形层的KCGN的性能比KCGN-2差,这表明探索更高层次的关系可能涉及噪声。)
(一般就是用2层)
6.5.2 Impact of Embedding Dimension.
- (1) We notice that the accuracy is initially improved with larger embedding size due to the stronger representation ability. However, the performance degrades with the further increase of dimensionality, which indicates the overfitting phenomenon. (我们注意到,由于具有更强的表示能力,嵌入尺寸越大,精度越高。然而,随着维数的进一步增加,性能下降,这表明存在过拟合现象。)
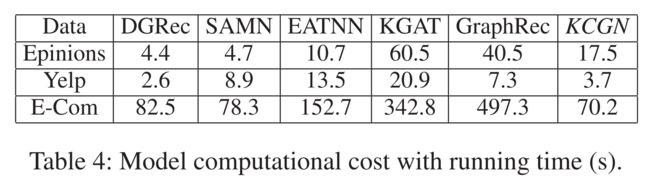
6.6 Model Efficiency Study (RQ6)
- (1) We finally investigate the computation cost of our KCGN when competing with state-of-the-art baselines. As shown in Table 4, we can observe that KCGN achieves competitive time efficiency (measured by running time of each epoch) when compared with neural social recommendation meth-ods. It is worthwhile pointing out that methods with stacking multiple graph attention layers is time-consuming, due to their pairwise attentive weights calculations for social or knowledge graph information aggregation. (最后,我们研究了我们的KCGN在与最先进的基线竞争时的计算成本。如表4所示,我们可以观察到,与神经社会推荐方法相比,KCGN实现了具有竞争力的时间效率(通过每个epoch的运行时间来衡量)。值得指出的是,堆叠多个图形注意层的方法非常耗时,因为它们成对地计算用于社会或知识图形信息聚合的注意权重。)
7 Related Work (灵感的来源,或者说,是根据哪些模型和思想,缝合,提炼升华的)
7.1 Social-aware Recommender Systems.
- (1) Deep learning has been revolutionizing recommender systems and many neural network models have been proposed for social recommendation scenario (Yin et al. 2019; Chen et al. 2020a).
- For example, attention mechanisms are introduced to learn the influences between users, such as SAMN (Chen et al. 2019a) and EATNN (Chen et al. 2019b). It is worth mentioning that several recent efforts explore the GNNs for incorporating social relations into the user-item interaction encoding (Wu et al. 2019b; Fan et al. 2019; Wu et al. 2019a; Xu et al. 2020).
- Different from these methods, KCGN focus on fusing the heterogeneous relations from different aspects (social, item knowledge and temporal), to boost the performance. (与这些方法不同,KCGN侧重于融合不同方面(社会、项目知识和时间)的异构关系,以提高绩效。)
7.2 Graph Methods for Recommendation.
- (1) Many recent efforts have been devoted to exploring insights from GNNs for modeling collaborative signals in recommender systems. (最近的许多工作致力于探索GNNs对推荐系统中的协作信号建模的见解。)
- For example, inspired by the graph convolutional operations, PinSage (Ying et al. 2018) and NGCF (Wang et al. 2019c) aim to aggregate high-hop neighboring feature information over the user-item interaction graph. (例如,受图卷积运算的启发,PinSage(Ying et al.2018)和NGCF(Wang et al.2019c)旨在通过用户项交互图聚合高跳相邻特征信息。)
- Several subsequent extensions have been developed to revisit the graph-based CF effects, such as LightGCN (He et al. 2020), LR-GCCF (Chen et al. 2020b) and KHGT (Xia et al. 2021). Motivated by these works, we propose a new knowledge-aware graph neural architecture for social recommendation.
8 Conclusion
- (1) In this paper, we propose KCGN, an end-to-end framework that naturally incorporates knowledge-aware item dependency into the social recommender systems. (在本文中,我们提出了KCGN,这是一个端到端的框架,它自然地将知识感知项依赖性融入到社会推荐系统中。)
- (2) KCGN unifies the user-user and item-item relation structure learning with a coupled graph neural network under a mutual information-based neural estimator (KCGN将用户-用户和项目-项目关系结构学习与基于互信息的神经估计器下的耦合图神经网络相结合).
- (3) To handle the dynamic user-item interaction heterogeneity, we design a relation-aware graph encoder to empower KCGN to maintain dedicated representations of multi-typed interaction signals with the incorporation of temporal information. (为了处理动态用户项交互的异构性,我们设计了一个关系感知图编码器,使KCGN能够通过合并时间信息来维护多类型交互信号的专用表示。)
- (4) Through extensive experiments on real-world datasets, we demonstrate that KCGN achieves substantial gains over state-of-the-art baselines.