激光雷达和相机联合标定
前言
最近搞了一下激光和相机的联合标定,分别用c艹+pcl与python+open3d写了写linux/windows上相应的联合标定软件,记录一下。
绪论

方法基于标定板,目的就为了求取传感器之间的外参。
小编的代码主要做了一件事,就是选取各传感器对应的关键点,如激光中标定板的角点的3d坐标和图像中标定板角点的像素坐标。
整体流程分为以下四部分:
1. 标定板点云提取
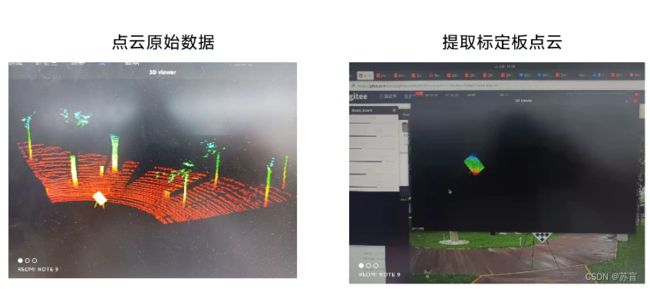 2. 标定板点云和图像角点提取
2. 标定板点云和图像角点提取

1. 标定板点云提取
1.1 初筛
使用直通滤波初步限制点云范围(甚至可以根据航向角限制),通过opencv滑动条和pcl、open3d库,我们可以实时调节并显示限制范围后的点云。
之后,用统计滤波器将一些离群点去除
下面分别给一下python和c++的核心代码
python的
调用部分
# 直通滤波
create_trackbar()
while 1:
xyz = get_trackbar()
point_cloud_copy = cloud_passthrough(point_cloud_numpy, xyz)
pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(point_cloud_copy)
vis.update_geometry(pcd) #open3d is terrible 这句话可有可无
vis.poll_events()
vis.update_renderer()
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord('q'):
vis.remove_geometry(pcd)
break
# 统计滤波
out, _ = pcd.remove_statistical_outlier(20, 1) # parms: (在进行统计时考虑的临近点个数,判断是否为离群点的阀值)
out.paint_uniform_color([1, 1, 1])
vis.add_geometry(out)
while 1:
vis.update_geometry(out)
vis.poll_events()
vis.update_renderer()
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord('q'):
vis.remove_geometry(out)
break
函数实现
def cloud_passthrough(cloud_np, xyz):
x_min = xyz[0]
x_max = xyz[1]
y_min = xyz[2]
y_max = xyz[3]
z_min = xyz[4]
z_max = xyz[5]
cloud_np = cloud_np[cloud_np[:, 0] < x_max]
cloud_np = cloud_np[cloud_np[:, 0] > x_min]
cloud_np = cloud_np[cloud_np[:, 1] < y_max]
cloud_np = cloud_np[cloud_np[:, 1] > y_min]
cloud_np = cloud_np[cloud_np[:, 2] < z_max]
cloud_np = cloud_np[cloud_np[:, 2] > z_min]
return cloud_np
c++的
while(!viewer1->wasStopped())
{
// 判断标定板点云是否直通滤波完毕
if(chose_bd)
{
chose_bd = 0;
break;
}
// 每次都对原始点云进行直通滤波操作
pcl::copyPointCloud(*cloud, *cloud_show);
// 更新直通滤波参数
xyzMutex.lock();
x0 = x_min;
x1 = x_max;
y0 = y_min;
y1 = y_max;
z0 = z_min;
z1 = z_max;
xyzMutex.unlock();
// 进行直通滤波
cloudPassThrough(cloud_show, "y", y0, y1);
cloudPassThrough(cloud_show, "x", x0, x1);
cloudPassThrough(cloud_show, "z", z0, z1);
// 更新可视化viewer
viewer1->removePointCloud("test");
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<pcl::PointXYZ> fildColor(cloud_show, "z");
viewer1->addPointCloud(cloud_show,fildColor, "test");
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(1000));
viewer1->spinOnce(100);
}
// 统计滤波 去除离群点
cloudStatisticalOutlierRemoval(cloud_show);
1.2 拟合平面并投影
初筛完标定板点云后,仍有离群点和波动存在,我们通过拟合平面,并且将原始点云投影于该平面的方法,让标定板点云在空间处于统一平面。
python的
调用部分
# 拟合平面
inlier_cloud = copy.copy(out)
plane_model, inliers = get_plane(inlier_cloud)
[a, b, c, d] = plane_model
print(f"Plane equation: {a:.2f}x + {b:.2f}y + {c:.2f}z + {d:.2f} = 0")
inlier_cloud = inlier_cloud.select_by_index(inliers)
inlier_cloud.paint_uniform_color([0, 1, 0])
vis.add_geometry(inlier_cloud)
while 1:
vis.update_geometry(inlier_cloud)
vis.poll_events()
vis.update_renderer()
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord('q'):
vis.remove_geometry(inlier_cloud)
break
# 投影滤波
project_cloud = copy.copy(inlier_cloud)
project_cloud.points = project_filter(project_cloud, plane_model)
vis.add_geometry(project_cloud)
while 1:
vis.update_geometry(project_cloud)
vis.poll_events()
vis.update_renderer()
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord('q'):
#vis.remove_geometry(inlier_cloud)
break
函数实现部分
def get_plane(pcd):
# parms:
# distance_threshold
# ransac_n
# num_iterations
plane_model, inliers = pcd.segment_plane(0.09, 10, 1000)
# dis应该在0.04-0.05,但是标定板中间凹陷
return plane_model, inliers
def project_filter(cloud, plane_model):
cloud = np.asarray(cloud.points)
[a, b, c, d] = plane_model
dis = a*a+b*b+c*c
x = copy.deepcopy(cloud[:, 0])
y = copy.deepcopy(cloud[:, 1])
z = copy.deepcopy(cloud[:, 2])
cloud[:, 0] = ((b*b+c*c)*x - a*(b*y + c*z + d))/dis
cloud[:, 1] = ((a*a+c*c)*y - b*(a*x + c*z + d))/dis
cloud[:, 2] = ((b*b+a*a)*z - c*(a*x + b*z + d))/dis
return o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(cloud)
c++de
//-------------------------- 模型估计 --------------------------
cout << "->正在估计平面..." << endl;
pcl::SampleConsensusModelPlane<PointT>::Ptr model_plane(new pcl::SampleConsensusModelPlane<PointT>(cloud_show)); //选择拟合点云与几何模型
pcl::RandomSampleConsensus<PointT> ransac(model_plane); //创建随机采样一致性对象
ransac.setDistanceThreshold(0.1); //设置距离阈值,与平面距离小于0.01的点作为内点
ransac.computeModel(); //执行模型估计
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_plane(new PointCloudT);
//---------- 根据索引提取内点 ----------
// 方法1
vector<int> inliers; //存储内点索引的向量
ransac.getInliers(inliers); //提取内点对应的索引
pcl::copyPointCloud<PointT>(*cloud_show, inliers, *cloud_plane);
// 输出模型参数Ax+By+Cz+D=0
Eigen::VectorXf coefficient;
ransac.getModelCoefficients(coefficient);
cout << "平面方程为:\n"
<< coefficient[0] << "x + "
<< coefficient[1] << "y + "
<< coefficient[2] << "z + "
<< coefficient[3] << " = 0"
<< endl;
//----------------------- 可视化拟合结果 -----------------------
viewer1->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud_show, "cloud"); //添加原始点云
viewer1->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 1, 1, 1, "cloud"); //颜色
viewer1->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "cloud"); //点的大小
viewer1->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud_plane, "plane"); //添加平面点云
viewer1->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 0, 1, 0, "plane"); //颜色
viewer1->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "plane"); //点的大
// 创建投影器
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients());
// 由ax+by+cz+d=0设置投影面参数
coefficients->values.resize(4);
coefficients->values[0] = coefficient[0];
coefficients->values[1] = coefficient[1];
coefficients->values[2] = coefficient[2];
coefficients->values[3] = coefficient[3];
// 创建投影滤波对象
pcl::ProjectInliers<pcl::PointXYZ>proj;
// 设置对象对应的投影模型
proj.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
// 设置输入点云
proj.setInputCloud(cloud_plane);
// 设置模型对应的系数
proj.setModelCoefficients(coefficients);
// 执行投影滤波
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_filtered(new PointCloudT);
proj.filter(*cloud_filtered);
做到这一步,我们搞个效果视频看一下,不然太抽象了
calibration
2. 标定板点云和图像角点提取
我们想通过3d to 2d,来简化点云聚类、拟合、最终寻找到角点的过程。
2.1 点云降维
我们先将投影得到同一平面上的点云进行平移、旋转,将其移动至xoy面,
经此操作,3d点云z坐标均为0,我们可以对点云进行图像层面操作。
c++的
// 将标定板点云旋转平移至xoy面
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_hhh(new PointCloudT);
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_rotate(new PointCloudT);
while(!viewer1->wasStopped())
{
// 判断投影是否完成
if(chose_bd)
{
viewer1->removeAllPointClouds();
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_hhh(new PointCloudT);
PointCloudT::Ptr cloud_rotate(new PointCloudT);
// 计算过原点平面法线方程
float A = coefficient[0];
float B = coefficient[1];
float C = coefficient[2];
float D = coefficient[3];
float Z0 = -D/C;
float x0 = cloud_filtered->points[0].x;
float y0 = cloud_filtered->points[0].y;
float z0 = cloud_filtered->points[0].z;
// 将点云平面平移至原点所在平面
for (int i=0; i<cloud_filtered->points.size(); i++)
{
float x = cloud_filtered->points[i].x-x0;
float y = cloud_filtered->points[i].y-y0;
float z = cloud_filtered->points[i].z-z0;
PointT t0 = {x, y, z};
cloud_hhh->points.push_back(t0);
}
// 法线可视化
PointT a,b;
a.x = -10*A;
a.y = -10*B;
a.z = -10*C;
b.x = 10*A;
b.y = 10*B;
b.z = 10*C;
viewer1->addLine<pcl::PointXYZ>(a, b, 255, 255, 255, "line1");
PointCloudT::Ptr linePoint(new PointCloudT);
linePoint->points.push_back(a);
linePoint->points.push_back(b);
// 将点云绕Y轴旋转
Eigen::Affine3f transform_2=Eigen::Affine3f::Identity();
float theta = - atan(A/C);
cout << theta*180/M_PI << endl;
transform_2.rotate(Eigen::AngleAxisf(theta, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitY()));
printf ("\n Method #2: using an Affine3f \n");
std::cout << transform_2.matrix() << std::endl;
pcl::transformPointCloud(*cloud_hhh, *cloud_rotate, transform_2);
// 绘制旋转后平面法线
pcl::transformPointCloud(*linePoint, *linePoint, transform_2);
a = linePoint->points[0];
b = linePoint->points[1];
viewer1->addLine<pcl::PointXYZ>(a, b, 255, 0, 0, "line2");
// 将点云绕X轴旋转
float new_B = b.y/10;
float new_C = b.z/10;
Eigen::Affine3f transform_1=Eigen::Affine3f::Identity();
float theta1 = atan(new_B/new_C);
cout << theta1*180/M_PI << endl;
transform_1.rotate(Eigen::AngleAxisf(theta1, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitX()));
std::cout << transform_1.matrix() << std::endl;
pcl::transformPointCloud(*cloud_rotate, *cloud_rotate, transform_1);
// 绘制旋转后平面法线
pcl::transformPointCloud(*linePoint, *linePoint, transform_1);
a = linePoint->points[0];
b = linePoint->points[1];
viewer1->addLine<pcl::PointXYZ>(a, b, 0, 255, 0, "line3");
python的
调用部分
# 平移旋转至xoy面
trans_cloud = copy.copy(project_cloud)
trans_cloud.points, euler, xyz0 = transform(trans_cloud, plane_model)
vis.add_geometry(trans_cloud)
while 1:
vis.update_geometry(trans_cloud)
vis.poll_events()
vis.update_renderer()
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord('q'):
vis.remove_geometry(trans_cloud)
break
函数实现部分
def transform(cloud, plane_model):
cloud = np.asarray(cloud.points)
[a, b, c, d] = plane_model
# same
# R = o3d.geometry.get_rotation_matrix_from_axis_angle(np.array([pitch,0,0],dtype='float64'))
yaw = atan(a/c)
Ry = np.array([[cos(yaw), 0, sin(yaw)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-sin(yaw), 0, cos(yaw)]], dtype='float64')
Euler = np.array([a, b, c], dtype='float64')
a, b, c = np.dot(Euler, Ry)
pitch = -atan(b/c)
Rx = np.array([[1, 0, 0],
[0, cos(pitch), -sin(pitch)],
[0, sin(pitch), cos(pitch)]], dtype='float64')
R = np.dot(Ry, Rx)
cloud = np.dot(cloud, R)
x0 = cloud[0][0]
y0 = cloud[0][1]
z0 = cloud[0][2]
# 平移
cloud[:, 0] -= x0
cloud[:, 1] -= y0
cloud[:, 2] -= z0
return o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(cloud), [-pitch, -yaw], np.array([x0,y0,z0],dtype='float64')
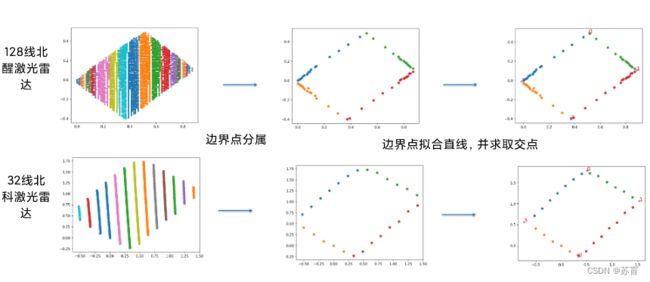
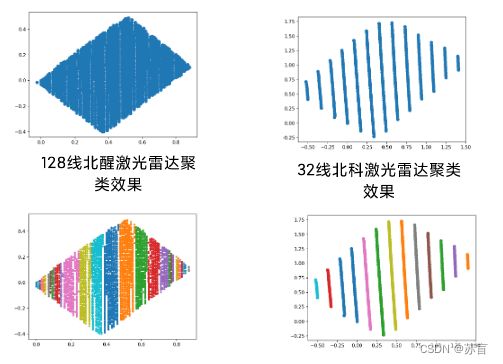
2.2 聚类求取角点
这里采用了dbscan的聚类算法,点
之间距离的计算是以x方向的欧氏
距离。
 python实现
python实现
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
dis_draw = []
#计算两点之间的欧式距离
def calDist(p1 , p2):
sum = 0
for x1 , x2 in zip(p1 , p2):
sum += (x1 - x2) ** 2
return sum ** 0.5
# 计算X方向距离
def calDistX(p1, p2):
return abs(p1[0] - p2[0])
# 点云结构体
class CloudPoint():
def __init__(self, xyz):
self.visited = 0 # 是否遍历过
self.coreobj = 0 # 是否是核心点
self.clusterid = -1 # 类别
self.neibor = [] # 邻域索引
self.xyz = xyz # 坐标
def setVisited(self):
self.visited = 1
def setClusterid(self, id):
self.clusterid = id
def setCoreobj(self):
self.coreobj = 1
def getNeibor(self):
return self.neibor
#获取一个点的ε-邻域(记录的是索引)
def getNeibor(dataSet , e, minPts):
for i in range(len(dataSet)):
for j in range(len(dataSet)):
if i != j:
dis_draw.append(calDistX(dataSet[j].xyz, dataSet[i].xyz))
if calDistX(dataSet[j].xyz, dataSet[i].xyz) < e:
dataSet[i].neibor.append(j)
if len(dataSet[i].getNeibor()) > minPts: # 设置核心点
dataSet[i].setCoreobj()
# 在点的邻域内聚类
def keyPointCluster(dataSet, id, clusterid):
if dataSet[id].coreobj == 0: return
for j in dataSet[id].neibor: # 遍历对象邻域域内点ID列表
if dataSet[j].visited == 0: # 未遍历过则加入当前的类中
dataSet[j].setClusterid(clusterid)
dataSet[j].visited = 1
if dataSet[j].coreobj == 1:
keyPointCluster(dataSet, j, clusterid) # 递归地对该领域点数据的领域内的点执行聚类操作
# 密度聚类算法
def DBSCAN(dataSet , e , minPts):
C = []
n = len(dataSet)
# 获取点的邻域、核心点
getNeibor(dataSet, e, minPts)
clusterid = 0 # 聚类id计数,初始化为0
for i in range(n):
if dataSet[i].visited == 0 and dataSet[i].coreobj == 1: # 未遍历且是核心点
dataSet[i].setClusterid(clusterid) # 设置该对象所属类ID为clusterid
dataSet[i].setVisited() # 设置该对象已被访问过
keyPointCluster(dataSet, i, clusterid) # 对该对象邻域内点进行聚类
clusterid += 1
# 结果存入list
s = set()
for i in range(n):
if dataSet[i].clusterid != -1:
if dataSet[i].clusterid not in s: # 类别id没有在s中则新建一个list
C.append([dataSet[i].xyz])
s.add(dataSet[i].clusterid)
else:
C[dataSet[i].clusterid].append(dataSet[i].xyz)
return C
def draw(c, clouds):
for i in list(range(len(c))):
index = c[i]
x, y = [], []
for j in index:
x.append(j[0])
y.append(j[1])
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
# 计算轮廓点
def getBoundpoint(c, clouds):
bPointList = []
for i in list(range(len(c))):
cloud = c[i]
cenp = [np.mean([i[0] for i in cloud]), np.mean([i[1] for i in cloud]), np.mean([i[2] for i in cloud])] # 类中心点
disList = [calDist(cenp, i) for i in cloud] # 计算到中心点的距离
bPoint1 = cloud[disList.index(max(disList))]
disList = [calDist(bPoint1, i) for i in cloud] # 计算到一个轮廓点的距离
bPoint2 = cloud[disList.index(max(disList))]
if bPoint1[1] > bPoint2[1]: # 从上到下排序
bPointList.append(([bPoint1, bPoint2], cenp[0]))
else:
bPointList.append(([bPoint2, bPoint1], cenp[0]))
bPointList.sort(key=lambda x:x[1]) # 从左到右排序
return [x[0] for x in bPointList]
# 轮廓点分类
def bPointSep(bPointList):
result = []
ulist = [i[0][1] for i in bPointList]
llist = [i[1][1] for i in bPointList]
uMax = ulist.index(max(ulist))
lMin = llist.index(min(llist))
result.append([bPointList[i][0] for i in range(len(ulist)) if i <= uMax])
result.append([bPointList[i][1] for i in range(len(ulist)) if i <= lMin])
result.append([bPointList[i][0] for i in range(len(ulist)) if i >= uMax])
result.append([bPointList[i][1] for i in range(len(ulist)) if i >= lMin])
return result
# 直线拟合
def linefit(x, y):
N = float(len(x))
sx, sy, sxx, syy, sxy=0, 0, 0, 0, 0
for i in range(0,int(N)):
sx += x[i]
sy += y[i]
sxx += x[i] * x[i]
syy += y[i] * y[i]
sxy += x[i] * y[i]
a = (sy * sx / N - sxy) / (sx * sx / N - sxx)
b = (sy - a * sx) / N
return a, b
def findCornerPoint(clouds):
# 点云聚类
C = DBSCAN(clouds, 0.12, 1)
# 寻找轮廓点
bPointList = getBoundpoint(C, clouds)
# 轮廓点分类
result = bPointSep(bPointList)
# 拟合直线
lines = []
for i in list(len(result)):
x, y = [], []
for j in range(len(result[i])):
x.append(result[i][j][0])
y.append(result[i][j][1])
lines.append(linefit(x, y))
# 计算角点
cornerPoint = []
for i in [[0, 2], [2, 3], [1, 3], [0, 1]]:
a, b = i
x = (lines[a][1] - lines[b][1]) / (lines[b][0] - lines[a][0])
y = lines[a][0] * x + lines[a][1]
cornerPoint.append([x, y])
return cornerPoint
c++实现
/* 获取标定板算法由python程序改写,逻辑较难理解,请参考python提取标定板程序 */
void keyPointCluster(vector<MyPointCloud>& my_clouds, int id, int clusterid)
{
// 获取分类关键点
if(my_clouds[id].coreobj != 0)
{
for (int k=0; k<my_clouds[id].useNum+1; k++)
{
int j = my_clouds[id].neibor[k];
if(my_clouds[j].visited == 0)
{
my_clouds[j].clusterid = clusterid;
my_clouds[j].visited = 1;
if(my_clouds[j].coreobj == 1)
keyPointCluster(my_clouds, j, clusterid);
}
}
}
else return ;
}
vector<vector<vector<float> > > DBSCAN(vector<MyPointCloud>& my_clouds, float e, float minPts)
{
// 密度聚类算法
int n = my_clouds.size();
// get neibor
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<n; j++)
{
if (i!=j)
{
float x0 = my_clouds[i].x;
float y0 = my_clouds[i].y;
float x1 = my_clouds[j].x;
float y1 = my_clouds[j].y;
float dis = pow(pow(x0-x1,2),0.5);
int index = 0;
if (dis < e)
{
while(my_clouds[i].neibor[index] != -1)
{
index++;
}
my_clouds[i].neibor[index] = j;
my_clouds[i].useNum = index;
}
}
if(my_clouds[i].useNum+1 > minPts)
my_clouds[i].coreobj = 1;
}
}
int clusterid = 0;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(my_clouds[i].visited == 0 && my_clouds[i].coreobj == 1)
{
my_clouds[i].clusterid = clusterid;
my_clouds[i].visited = 1;
keyPointCluster(my_clouds, i, clusterid);
clusterid ++;
}
}
vector<vector<vector<float> > > C_out;
// 结果存入C_out
for(int j=0; j<clusterid+1; j++)
{
vector<vector<float> > points;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(my_clouds[i].clusterid == j)
{
vector<float> point;
point.push_back(my_clouds[i].x);
point.push_back(my_clouds[i].y);
point.push_back(my_clouds[i].z);
points.push_back(point);
}
}
C_out.push_back(points);
}
return C_out;
}
vector<vector<vector<float> > > getBoundPoint(vector<vector<vector<float> > >& c)
{
// 计算轮廓点并进行边属分类
vector<vector<vector<float> > > bPointList;
vector<float> meanX;
for(int i=0; i<c.size()-1; i++)
{
float x_mean=0; // 万万需要初始化
float y_mean=0;
for(int j=0; j<c[i].size(); j++)
{
x_mean += c[i][j][0];
y_mean += c[i][j][1];
}
x_mean /= c[i].size();
y_mean /= c[i].size();
meanX.push_back(x_mean);
float maxDistoCenter = -9;
int index1 = 0;
for(int j=0; j<c[i].size(); j++)
{
float dis = pow(pow(x_mean-c[i][j][0],2)+pow(y_mean-c[i][j][1],2),0.5);
if (dis > maxDistoCenter)
{
index1 = j;
maxDistoCenter = dis;
}
}
vector<vector<float> > pts;
vector<float> pt0;
pt0.push_back(c[i][index1][0]);
pt0.push_back(c[i][index1][1]);
float maxDistoEdge = -9;
int index2=0;
for(int j=0; j<c[i].size(); j++)
{
float dis = pow(pow(c[i][index1][0]-c[i][j][0],2)+pow(c[i][index1][1]-c[i][j][1],2),0.5);
if (dis > maxDistoEdge)
{
index2 = j;
maxDistoEdge = dis;
}
}
vector<float> pt1;
pt1.push_back(c[i][index2][0]);
pt1.push_back(c[i][index2][1]);
if(pt0[1] > pt1[1])
{
pts.push_back(pt0);
pts.push_back(pt1);
}
else
{
pts.push_back(pt1);
pts.push_back(pt0);
}
bPointList.push_back(pts);
}
/*
for(int i=0; i
// bubblesort 尽量迭代,就不快排了
bool sorted = false;
while(!sorted)
{
sorted = true;
for(int j=0; j<meanX.size()-1; j++)
{
if(meanX[j] > meanX[j+1])
{
vector<vector<float> > temp;
temp = bPointList[j];
bPointList[j] = bPointList[j+1];
bPointList[j+1] = temp;
float tmp = meanX[j+1];
meanX[j+1] = meanX[j];
meanX[j] = tmp;
sorted = false;
}
}
}
// 轮廓点分类
float uMax = -9;
float uMin = 9;
int uMax_index = 0;
int uMin_index = 0;
for (int i=0; i<bPointList.size(); i++)
{
if(bPointList[i][0][1] > uMax)
{
uMax = bPointList[i][0][1];
uMax_index = i;
}
if(bPointList[i][1][1] < uMin)
{
uMin = bPointList[i][1][1];
uMin_index = i;
}
}
vector<vector<vector<float> > > PointSep;
int length = bPointList.size();
vector<vector<float> > l0;
vector<vector<float> > l1;
vector<vector<float> > l2;
vector<vector<float> > l3;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
{
if (i <= uMax_index)
{
l0.push_back(bPointList[i][0]);
}
if (i <= uMin_index)
{
l1.push_back(bPointList[i][1]);
}
if (i >= uMax_index)
{
l2.push_back(bPointList[i][0]);
}
if (i >= uMin_index)
{
l3.push_back(bPointList[i][1]);
}
}
PointSep.push_back(l0);
PointSep.push_back(l1);
PointSep.push_back(l2);
PointSep.push_back(l3);
for (int i=0; i<PointSep.size(); i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<PointSep[i].size(); j++)
{
cout << "[ ";
for (int k=0; k<2; k++)
{
cout << PointSep[i][j][k] << " ";
}
cout << " ]";
}
cout << endl;
}
return PointSep;
}
vector<vector<float> > findCornerPoint(vector<vector<vector<float> > >& PointSep)
{
// 获取角点
vector<vector<float> > result;
vector<vector<float> > line_kb;
for(int i=0; i<PointSep.size(); i++)
{
vector<float> x;
vector<float> y;
for(int j=0; j<PointSep[i].size(); j++)
{
x.push_back(PointSep[i][j][0]);
y.push_back(PointSep[i][j][1]);
}
// 直线拟合
float N = (float)PointSep[i].size();
float sx = 0;
float sy = 0;
float sxx = 0;
float syy = 0;
float sxy = 0;
for(int j=0; j<(int)N; j++)
{
sx += x[j];
sy += y[j];
sxx += x[j]*x[j];
syy += y[j]*y[j];
sxy += x[j]*y[j];
}
float a = (sy * sx / N - sxy) / (sx * sx / N - sxx);
float b = (sy - a * sx) / N;
vector<float> kb = {a, b};
line_kb.push_back(kb);
}
int a0,b0;
float xc,yc;
vector<float> xy;
a0 = 0;
b0 = 2;
xc = (line_kb[a0][1] - line_kb[b0][1]) / (line_kb[b0][0] - line_kb[a0][0]);
yc = line_kb[a0][0] * xc + line_kb[a0][1];
xy = {xc, yc};
result.push_back(xy);
a0 = 2;
b0 = 3;
xc = (line_kb[a0][1] - line_kb[b0][1]) / (line_kb[b0][0] - line_kb[a0][0]);
yc = line_kb[a0][0] * xc + line_kb[a0][1];
xy = {xc, yc};
result.push_back(xy);
a0 = 1;
b0 = 3;
xc = (line_kb[a0][1] - line_kb[b0][1]) / (line_kb[b0][0] - line_kb[a0][0]);
yc = line_kb[a0][0] * xc + line_kb[a0][1];
xy = {xc, yc};
result.push_back(xy);
a0 = 0;
b0 = 1;
xc = (line_kb[a0][1] - line_kb[b0][1]) / (line_kb[b0][0] - line_kb[a0][0]);
yc = line_kb[a0][0] * xc + line_kb[a0][1];
xy = {xc, yc};
result.push_back(xy);
return result;
}
2.3 结果
参考点云降维的部分,我们将2d转回3d点云原位置即可得到结果
视觉手动选点,采用opencv回调函数,这些略

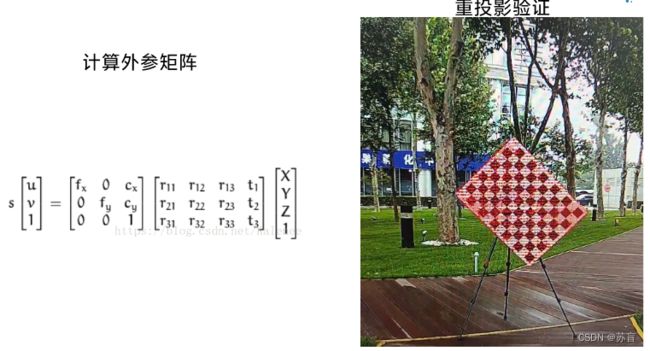
3.PNP解算和重投影
这部分也就给两张图,略
引用参考的东西蛮多蛮碎的,如未指出,请联系。
本人邮箱[email protected],亦欢迎建议。