OpenCV持久化(一)
在OpenCV中,采用FileStorage类进行数据持久化,可以采用XML或YAML格式存储数据。
将数据写入XML或YAML文件,可采用以下步骤:
1、创建FileStorage对象。可以调用构造函数 FileStorage::FileStorage(),并传入文件名参数;或者调用默认构造函数,然后调用 FileStorage::open()。
2、利用重载输出操作符<<,在operations.hpp中,输出操作符<<为模板函数:
template<typename _Tp> static inline FileStorage& operator << (FileStorage& fs, const _Tp& value) { if( !fs.isOpened() ) return fs; if( fs.state == FileStorage::NAME_EXPECTED + FileStorage::INSIDE_MAP ) CV_Error( CV_StsError, "No element name has been given" ); write( fs, fs.elname, value ); if( fs.state & FileStorage::INSIDE_MAP ) fs.state = FileStorage::NAME_EXPECTED + FileStorage::INSIDE_MAP; return fs; }
3、调用FileStorage::release(),关闭文件,并释放所有内存。
FileStorage在core.hpp定义如下:
class CV_EXPORTS_W FileStorage { public: //! file storage mode enum { READ=0, //! read mode WRITE=1, //! write mode APPEND=2, //! append mode MEMORY=4, FORMAT_MASK=(7<<3), FORMAT_AUTO=0, FORMAT_XML=(1<<3), FORMAT_YAML=(2<<3) }; enum { UNDEFINED=0, VALUE_EXPECTED=1, NAME_EXPECTED=2, INSIDE_MAP=4 }; //! the default constructor CV_WRAP FileStorage(); //! the full constructor that opens file storage for reading or writing CV_WRAP FileStorage(const string& source, int flags, const string& encoding=string()); //! the constructor that takes pointer to the C FileStorage structure FileStorage(CvFileStorage* fs); //! the destructor. calls release() virtual ~FileStorage(); //! opens file storage for reading or writing. The previous storage is closed with release() CV_WRAP virtual bool open(const string& filename, int flags, const string& encoding=string()); //! returns true if the object is associated with currently opened file. CV_WRAP virtual bool isOpened() const; //! closes the file and releases all the memory buffers CV_WRAP virtual void release(); //! closes the file, releases all the memory buffers and returns the text string CV_WRAP string releaseAndGetString(); //! returns the first element of the top-level mapping CV_WRAP FileNode getFirstTopLevelNode() const; //! returns the top-level mapping. YAML supports multiple streams CV_WRAP FileNode root(int streamidx=0) const; //! returns the specified element of the top-level mapping FileNode operator[](const string& nodename) const; //! returns the specified element of the top-level mapping CV_WRAP FileNode operator[](const char* nodename) const; //! returns pointer to the underlying C FileStorage structure CvFileStorage* operator *() { return fs; } //! returns pointer to the underlying C FileStorage structure const CvFileStorage* operator *() const { return fs; } //! writes one or more numbers of the specified format to the currently written structure void writeRaw( const string& fmt, const uchar* vec, size_t len ); //! writes the registered C structure (CvMat, CvMatND, CvSeq). See cvWrite() void writeObj( const string& name, const void* obj ); //! returns the normalized object name for the specified file name static string getDefaultObjectName(const string& filename); Ptr<CvFileStorage> fs; //!< the underlying C FileStorage structure string elname; //!< the currently written element vector<char> structs; //!< the stack of written structures int state; //!< the writer state };
从XML或YAML文件中读取数据,可采用以下步骤:
1、利用构造函数 FileStorage::FileStorage()或方法 FileStorage::open()打开文件,这个过程包含解析文件,并将文件节点和数据存入内存中。
2、读取节点数据。利用下标操作符 FileStorage::operator [](), FileNode::operator []()或 FileNodeIterator。
3、调用 FileStorage::release() 关闭文件。
OpenCV利用 FileNode 存储XML或YAML文件中的每个节点,并用于读写。FileNode在 core.hpp 文件中定义如下:
class CV_EXPORTS_W_SIMPLE FileNode { public: //! type of the file storage node enum { NONE=0, //!< empty node INT=1, //!< an integer REAL=2, //!< floating-point number FLOAT=REAL, //!< synonym or REAL STR=3, //!< text string in UTF-8 encoding STRING=STR, //!< synonym for STR REF=4, //!< integer of size size_t. Typically used for storing complex dynamic structures where some elements reference the others SEQ=5, //!< sequence MAP=6, //!< mapping TYPE_MASK=7, FLOW=8, //!< compact representation of a sequence or mapping. Used only by YAML writer USER=16, //!< a registered object (e.g. a matrix) EMPTY=32, //!< empty structure (sequence or mapping) NAMED=64 //!< the node has a name (i.e. it is element of a mapping) }; //! the default constructor CV_WRAP FileNode(); //! the full constructor wrapping CvFileNode structure. FileNode(const CvFileStorage* fs, const CvFileNode* node); //! the copy constructor FileNode(const FileNode& node); //! returns element of a mapping node FileNode operator[](const string& nodename) const; //! returns element of a mapping node CV_WRAP FileNode operator[](const char* nodename) const; //! returns element of a sequence node CV_WRAP FileNode operator[](int i) const; //! returns type of the node CV_WRAP int type() const; //! returns true if the node is empty CV_WRAP bool empty() const; //! returns true if the node is a "none" object CV_WRAP bool isNone() const; //! returns true if the node is a sequence CV_WRAP bool isSeq() const; //! returns true if the node is a mapping CV_WRAP bool isMap() const; //! returns true if the node is an integer CV_WRAP bool isInt() const; //! returns true if the node is a floating-point number CV_WRAP bool isReal() const; //! returns true if the node is a text string CV_WRAP bool isString() const; //! returns true if the node has a name CV_WRAP bool isNamed() const; //! returns the node name or an empty string if the node is nameless CV_WRAP string name() const; //! returns the number of elements in the node, if it is a sequence or mapping, or 1 otherwise. CV_WRAP size_t size() const; //! returns the node content as an integer. If the node stores floating-point number, it is rounded. operator int() const; //! returns the node content as float operator float() const; //! returns the node content as double operator double() const; //! returns the node content as text string operator string() const; //! returns pointer to the underlying file node CvFileNode* operator *(); //! returns pointer to the underlying file node const CvFileNode* operator* () const; //! returns iterator pointing to the first node element FileNodeIterator begin() const; //! returns iterator pointing to the element following the last node element FileNodeIterator end() const; //! reads node elements to the buffer with the specified format void readRaw( const string& fmt, uchar* vec, size_t len ) const; //! reads the registered object and returns pointer to it void* readObj() const; // do not use wrapper pointer classes for better efficiency const CvFileStorage* fs; const CvFileNode* node; };
写XML、YAML文件时主要注意的几点:
1、XML和YAML可以嵌套的两种集合类型:映射(mappings)、序列(sequences)。映射集合类似STL中的std::map和Python中的字典,序列集合类似STL中std::vector和 Python的序列;
2、当写入映射结构的数据时,节点的值(value)紧跟着节点的键(key);当写入序列结构的数据时,一个一个写入即可;
3、写入映射结构数据时,格式如下:fs << "{" << element_key << element_value << "}"
4、写入序列结构数据时,格式如下:fs << "[" << element_value << …… << "]"
5、写入映射、序列嵌套的数据时,以"{:"代替"{","[:" 代替 "["。
示例代码如下:
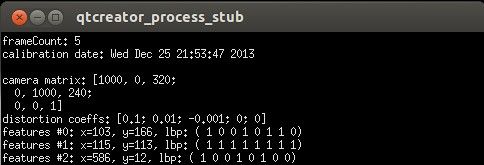
#include <QtCore/QCoreApplication> #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <time.h> #include <iostream> void writeYAML() { cv::FileStorage fs("../file/test.yml", cv::FileStorage::WRITE); fs << "frameCount" << 5; time_t rawtime; time(&rawtime); fs << "calibrationDate" << asctime(localtime(&rawtime)); cv::Mat cameraMatrix = (cv::Mat_<double>(3,3) << 1000,0,320,0,1000,240,0,0,1); cv::Mat distCoeffs = (cv::Mat_<double>(5,1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0); fs << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMatrix << "distCoeffs" << distCoeffs; fs << "features" << "["; for(int i=0; i < 3; i++) { int x = rand() % 640; int y = rand() % 480; unsigned char lbp = rand() % 256; fs << "{:" << "x" << x << "y" << y << "lbp" << "[:"; for(int j=0; j < 8; j++) fs << ((lbp >> j) & 1); fs << "]" << "}"; } fs << "]"; fs.release(); } void readYAML() { cv::FileStorage fs2("../file/test.yml",cv::FileStorage::READ); int frameCount = (int)fs2["frameCount"]; std::string date; fs2["calibrationDate"] >> date; cv::Mat cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2; fs2["cameraMatrix"] >> cameraMatrix2; fs2["distCoeffs"] >> distCoeffs2; std::cout << "frameCount: " << frameCount << std::endl; std::cout << "calibration date: " << date << std::endl; std::cout << "camera matrix: " << cameraMatrix2 << std::endl; std::cout << "distortion coeffs: " << distCoeffs2 << std::endl; cv::FileNode features = fs2["features"]; cv::FileNodeIterator it = features.begin(), it_end = features.end(); int idx = 0; std::vector<unsigned char> lbpval; for(; it != it_end; ++it, idx++) { std::cout << "features #" << idx << ": "; std::cout << "x=" << (int)(*it)["x"] << ", y=" << (int)(*it)["y"] << ", lbp: ("; (*it)["lbp"] >> lbpval; for(int i = 0; i < (int)lbpval.size(); i++) std::cout << " " << (int)lbpval[i]; std::cout << ")" << std::endl; } fs2.release(); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { // QCoreApplication a(argc, argv); // return a.exec(); // writeYAML(); readYAML(); return 0; }
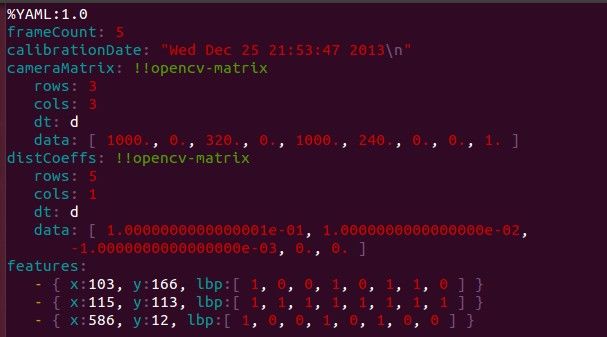
写入的YAML文件如下:
读取YAML文件输出如下: