【EntityFramework系列教程九,翻译】在ASP.NET MVC程序中实现存储与单元工作模式
上一章中你通过继承已经减少了Instructor和Student类中的冗余代码,本章节中你将使用一些封装好的单元工作类去完成增删改查的任务。像上一章一样,你将改变代码与已经创建的页面间的工作方式,并非需要额外创建新页面。
【封装单元代码工作】
“封装单元代码工作”方式将在一个应用程序的“数据访问层”和“业务逻辑层”之间创建一个抽象层,通过实现此设计方式可以把你的程序从数据存储变化中隔离开来,同时便于“自动单元化测试”或者是“驱动测试开发(TDD)”。
本章节中你要为每一个类型实现一个存储封装类:对于Student类型而言你将创建存储封装接口,以及实现的对应类;当你在控制器中实例化这个存储接口时,你将使用到这个控制器,该控制器将接受任意实现此存储封装接口的类;当该控制器在服务器下运行之时,它获得一个能够和EntityFramework协同工作的存储实体;当它运行于测试模式时,它获得一个存储实体,该实体可以和存储的数据配合工作,而存储数据的方式却让你可以非常容易地操纵数据(比如操作“内存中数据集合”)等……。
稍后在本章中,位于Course控制器里你将使用多种多样针对Course和Department实体类型实现的存储封装类以及一个单元工作类,该单元工作类通过创建一个由这些存储工作类共享的单利数据库上下文来协调他们的工作,如果你想进行单元测试,那么你采用和“Student类的存储封装类与接口”同样的办法为其余的一些列相关类创建并且使用这些存储类和接口。不过为了简化此教程,你只将创建并且使用这些类,而不是接口。
以下截图“概念化地”展示了“控制器和上下文间的关系”与“根本不使用存储工作单元”的比较:
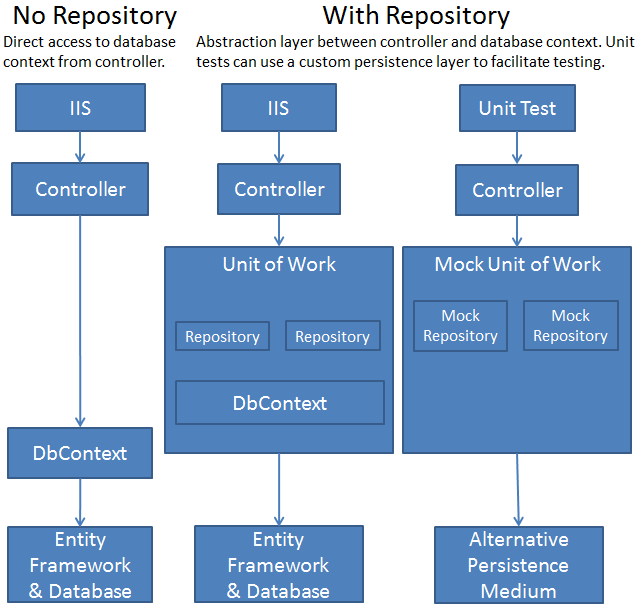
在本系列教程中你不会创建单元测试,关于ASP.NET MVC,使用存储模型的TDD测试相关介绍资料您可以从MSDN资料库( Walkthrough: Using TDD with ASP.NET MVC);关于存储设计更多信息,可以通过EntityFramework团队的博客 Using Repository and Unit of Work patterns with Entity Framework 4.0,或者是Julie Lerman的系列博文(Agile Entity Framework 4 Repository)中找到。
注意:其实你有很多方式去实现实现存储与单元工作模式,你可以单独存储类,或者加以单元工作类混合使用;你可以为所有的实体类型单独实现一个存储类,或者每个类型都去实现一个……如果你选择“每个类型都有一个对应的存储类”,那么你可以使用一些分散的类,一个基类以及众多的继承类,或者是抽象继承类和继承类……;你可以把业务逻辑处理包含到存储类中,或者强制放入数据访问逻辑中;你也可以通过使用IDbSet的方式,而不是直接使用DbSet为您的数据库上下文去创建一个抽象层,本示例中实现的抽象层只是提供你的一种方法而已,并不对所有的场合都推荐使用。
【创建学生存储类】
在DAL文件夹中创建一个名字为“IStudentRepository.cs”的文件,并用以下代码替换:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using ContosoUniversity.Models; namespace ContosoUniversity.DAL { public interface IStudentRepository : IDisposable { IEnumerable<Student> GetStudents(); Student GetStudentByID(int studentId); void InsertStudent(Student student); void DeleteStudent(int studentID); void UpdateStudent(Student student); void Save(); } }
以上代码声明了一组非常典型的增删改查方法,其中包含两个获取数据的方法——一个是获取全部数据,另外一个则是根据特定学生Id获取对应的学生实体。
在DAL文件夹中再创建一个“StudentRepository.cs”文件,用以下实现上面接口所定义的类代码做替换:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Data; using ContosoUniversity.Models; namespace ContosoUniversity.DAL { public class StudentRepository : IStudentRepository, IDisposable { private SchoolContext context; public StudentRepository(SchoolContext context) { this.context = context; } public IEnumerable<Student> GetStudents() { return context.Students.ToList(); } public Student GetStudentByID(int id) { return context.Students.Find(id); } public void InsertStudent(Student student) { context.Students.Add(student); } public void DeleteStudent(int studentID) { Student student = context.Students.Find(studentID); context.Students.Remove(student); } public void UpdateStudent(Student student) { context.Entry(student).State = EntityState.Modified; } public void Save() { context.SaveChanges(); } private bool disposed = false; protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing) { if (!this.disposed) { if (disposing) { context.Dispose(); } } this.disposed = true; } public void Dispose() { Dispose(true); GC.SuppressFinalize(this); } } }
数据库上下文被定义成了一个变量,其构造函数把传入的参数赋值给这个变量。
private SchoolContext context; public StudentRepository(SchoolContext context) { this.context = context; }
你可以在存储类中实例化一个新的上下文对象,不过你在一个控制器中有多个这样的对象的话,每个都将以不同的数据库上下文结束;后面你将在Course控制器中使用到多个存储类,并且你将会看到一个单元工作类是如何协调工作,保证所有的存储类都使用同一个数据库上下文的。
正如你早起在控制器中所看到的一样——存储类实现了IDisposible接口,用于及时释放数据库上下文对象。CRUD方法也正如你先前所看到的一样:
【改变Student控制器,使用您的存储类】
在“StudentController.cs”中,用以下代码替换原有代码:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Data; using System.Data.Entity; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.Mvc; using ContosoUniversity.Models; using ContosoUniversity.DAL; using PagedList; namespace ContosoUniversity.Controllers { public class StudentController : Controller { private IStudentRepository studentRepository; public StudentController() { this.studentRepository = new StudentRepository(new SchoolContext()); } public StudentController(IStudentRepository studentRepository) { this.studentRepository = studentRepository; } // // GET: /Student/ public ViewResult Index(string sortOrder, string currentFilter, string searchString, int? page) { ViewBag.CurrentSort = sortOrder; ViewBag.NameSortParm = String.IsNullOrEmpty(sortOrder) ? "Name desc" : ""; ViewBag.DateSortParm = sortOrder == "Date" ? "Date desc" : "Date"; if (Request.HttpMethod == "GET") { searchString = currentFilter; } else { page = 1; } ViewBag.CurrentFilter = searchString; var students = from s in studentRepository.GetStudents() select s; if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(searchString)) { students = students.Where(s => s.LastName.ToUpper().Contains(searchString.ToUpper()) || s.FirstMidName.ToUpper().Contains(searchString.ToUpper())); } switch (sortOrder) { case "Name desc": students = students.OrderByDescending(s => s.LastName); break; case "Date": students = students.OrderBy(s => s.EnrollmentDate); break; case "Date desc": students = students.OrderByDescending(s => s.EnrollmentDate); break; default: students = students.OrderBy(s => s.LastName); break; } int pageSize = 3; int pageNumber = (page ?? 1); return View(students.ToPagedList(pageNumber, pageSize)); } // // GET: /Student/Details/5 public ViewResult Details(int id) { Student student = studentRepository.GetStudentByID(id); return View(student); } // // GET: /Student/Create public ActionResult Create() { return View(); } // // POST: /Student/Create [HttpPost] public ActionResult Create(Student student) { try { if (ModelState.IsValid) { studentRepository.InsertStudent(student); studentRepository.Save(); return RedirectToAction("Index"); } } catch (DataException) { //Log the error (add a variable name after DataException) ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists see your system administrator."); } return View(student); } // // GET: /Student/Edit/5 public ActionResult Edit(int id) { Student student = studentRepository.GetStudentByID(id); return View(student); } // // POST: /Student/Edit/5 [HttpPost] public ActionResult Edit(Student student) { try { if (ModelState.IsValid) { studentRepository.UpdateStudent(student); studentRepository.Save(); return RedirectToAction("Index"); } } catch (DataException) { //Log the error (add a variable name after DataException) ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists see your system administrator."); } return View(student); } // // GET: /Student/Delete/5 public ActionResult Delete(int id, bool? saveChangesError) { if (saveChangesError.GetValueOrDefault()) { ViewBag.ErrorMessage = "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists see your system administrator."; } Student student = studentRepository.GetStudentByID(id); return View(student); } // // POST: /Student/Delete/5 [HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")] public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(int id) { try { Student student = studentRepository.GetStudentByID(id); studentRepository.DeleteStudent(id); studentRepository.Save(); } catch (DataException) { //Log the error (add a variable name after DataException) return RedirectToAction("Delete", new System.Web.Routing.RouteValueDictionary { { "id", id }, { "saveChangesError", true } }); } return RedirectToAction("Index"); } protected override void Dispose(bool disposing) { studentRepository.Dispose(); base.Dispose(disposing); } } }
控制器为实现IStudentResponsity接口的实体声明了一个类级别的变量,该变量并非是某个特定的数据库上下文实体:
private IStudentRepository studentRepository;
默认的构造函数创建了新的数据库上下文实体,带有一个可选参数的则把传入的参数赋值给类级变量:
public StudentController() { this.studentRepository = new StudentRepository(new SchoolContext()); } public StudentController(IStudentRepository studentRepository) { this.studentRepository = studentRepository; }
如果你在使用“依赖注入”(简称DI),你不需要默认的构造函数,因为DI总是时刻保证提供一个正确的存储实体给你。
CRUD方法这样调用:
var students = from s in studentRepository.GetStudents() select s; Student student = studentRepository.GetStudentByID(id); studentRepository.InsertStudent(student); studentRepository.Save(); studentRepository.UpdateStudent(student); studentRepository.Save(); studentRepository.DeleteStudent(id); studentRepository.Save();
Dispose方法现在用于销毁这个存储实体,并非简单的数据库上下文:
studentRepository.Dispose();
运行整个应用程序,点击Students选项卡:
页面看上去的效果以及运行的结果和你先前在未对此代码做任何改变时候是一样的,同样地,另外一些Students页面亦如此;不过在处理排序和搜索功能的Index页面的方法明显不同:原始版本包含了以下的代码片段:
var students = from s in context.Students select s; if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(searchString)) { students = students.Where(s => s.LastName.ToUpper().Contains(searchString.ToUpper()) || s.FirstMidName.ToUpper().Contains(searchString.ToUpper())); }
原始版中的“students”被视作“IQueryable”类型使用,这段代码不会立即向数据库发送查询请求——直至使用了诸如ToList一类的方法,把Where方法转化成了SQL语句中的Where条件在数据库中执行查询并处理。反过来说,那意味着只是选中的课程实体从数据库中查询并且返回。但是,如果把“context.Students”改为“studentRepository.GetStudents()”,后者中的“students”是IEnumerable类型的实体结果集,包含了所有数据表中的Students;Where的处理结果与先前相同,不过处理方式不是在数据库中进行,而是在内存中完成;当然对于大批量数据而言这个方法可能效率低下,以下内容告诉你如何实现一个存储实体,并且该实体允许你指定(是否)使用从数据库查询的方式完成查询内容。
现在你已经在控制器和EntityFramework数据库上下文之间创建了抽象层,如果你打算用该程序执行单元测试任务的话,你应该创建另外一个存储类,并且实现IStudentResposity接口。该类实现的是操纵内存中的集合数据并非读写操作,以便测试控制器功能。
【实现一个通用的存储类及单元工作类】
为每个实体类型单独创建一个存储类势必会带来大量冗余代码,并且可能导致“局部更新”问题(比如:作为同一个事物处理的部分,你更新两个完全不同的实体类型。如果每个部分使用独立的数据库上下文,那么可能的情况是“一个成功,一个失败”)。尽可能减少冗余代码的处理方式之一是使用“通用型”的存储类,保证所有这些存储类共享同一个数据库上下文对象(以便协调同步更新)的方法是使用单元工作类。
在本教程的这部分,你将创建一个“”(通用型的存储类)和“”(单元工作类),并将它们应用于Course控制器中以便访问Department和Course实体集。正如早先所解释的那样——为了使得示例看上去更简单,我们不会为这些类创建接口。不过你如果想做TDD测试的话请用你实现Student存储类的方式一样去实现一些接口即可。
【创建一个通用型的存储类】
在DAL文件夹中创建一个“GenericRepository.cs”文件,用以下代码进行替换:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Data; using System.Data.Entity; using ContosoUniversity.Models; using System.Linq.Expressions; namespace ContosoUniversity.DAL { public class GenericRepository<TEntity> where TEntity : class { internal SchoolContext context; internal DbSet<TEntity> dbSet; public GenericRepository(SchoolContext context) { this.context = context; this.dbSet = context.Set<TEntity>(); } public virtual IEnumerable<TEntity> Get( Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter = null, Func<IQueryable<TEntity>, IOrderedQueryable<TEntity>> orderBy = null, string includeProperties = "") { IQueryable<TEntity> query = dbSet; if (filter != null) { query = query.Where(filter); } foreach (var includeProperty in includeProperties.Split (new char[] { ',' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries)) { query = query.Include(includeProperty); } if (orderBy != null) { return orderBy(query).ToList(); } else { return query.ToList(); } } public virtual TEntity GetByID(object id) { return dbSet.Find(id); } public virtual void Insert(TEntity entity) { dbSet.Add(entity); } public virtual void Delete(object id) { TEntity entityToDelete = dbSet.Find(id); Delete(entityToDelete); } public virtual void Delete(TEntity entityToDelete) { if (context.Entry(entityToDelete).State == EntityState.Detached) { dbSet.Attach(entityToDelete); } dbSet.Remove(entityToDelete); } public virtual void Update(TEntity entityToUpdate) { dbSet.Attach(entityToUpdate); context.Entry(entityToUpdate).State = EntityState.Modified; } } }
我们分别对数据库上下文和实体集做了类级变量的定义:
internal SchoolContext context; internal DbSet dbSet;
这里的Get方法允许调用代码指定过滤条件,以及根据某个特定列排序;后面的字符串参数则允许调用者传入以逗号分割的属性,用于“饥饿模式”加载:
public virtual IEnumerable<TEntity> Get( Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter = null, Func<IQueryable<TEntity>, IOrderedQueryable<TEntity>> orderBy = null, string includeProperties = "")
“Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter”代码表示调用者需要传入一个基于TEntity类型的Lambda表达式,这个表达式需要返回一个布尔类型的结果。譬如这个存储类基于Student实体类,那么代码应该写成“student => student.LastName == "Smith”。
“Func<IQueryable<TEntity>, IOrderedQueryable<TEntity>> orderBy”一句则表示调用者应该传入一个Lambda表达式,不过在这种情况下表达式的输入方是IQueryable<TEntity>类型的,表达式执行的结果也将返回一个排序了的IQueryable对象集合;又比如存储是基于Student的,那么调用此方法的代码可能是“q => q.OrderBy(s => s.LastName)”。
在Get方法中的代码创建了一个IQueryable对象集合,然后判断如果有过滤条件,则应用之:
IQueryable<TEntity> query = dbSet; if (filter != null) { query = query.Where(filter); }
下一步在解析了由逗号分割组合而成的属性字符串之后,应用“饥饿加载”模式:
foreach (var includeProperty in includeProperties.Split (new char[] { ',' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries)) { query = query.Include(includeProperty); }
最后判断如果拥有排序表达式,那么也直接应用并返回结果;否则就输出无序的对象序列。
if (orderBy != null) { return orderBy(query).ToList(); } else { return query.ToList(); }
当你调用Get方法之时,其实你是在返回的IEnumerable集合上做排序和过滤,并非为这些函数提供参数;这些排序和索引将在服务器的内存中得以完成。如果你通过指定这些参数,你就指定这任务是在数据库中执行完成,而不是在服务器内存中进行处理。另外一种替代方案是为特定的实体类型创建其继承类,然后指定特别的方法(诸如:“GetStudentsInNameOrder”或“GetStudentsByName”……);不过在非常复杂的项目中该做法会导致产生大量的继承类以及“特别方法”,维护量很大。
“GetByID”、“Insert”和“Update”这些方法和你先前在非泛型通用方法的代码很类似(在“GetById”函数签名中你没有提供一个“饥饿模式”的参数,是因为用Find方法你无法做到使用此模式)。
下面是Delete方法的两个重载函数版本:
public virtual void Delete(object id) { TEntity entityToDelete = dbSet.Find(id); dbSet.Remove(entityToDelete); } public virtual void Delete(TEntity entityToDelete) { if (context.Entry(entityToDelete).State == EntityState.Detached) { dbSet.Attach(entityToDelete); } dbSet.Remove(entityToDelete); }
第一个函数仅带有一个id参数作为要删除的实体主键,第二个函数则直接附带了一个要被删除的实体;正如你在“处理并发冲突”一章所看到的那样——你需要一个携带着原始跟踪属性的实体记录作为参数的Delete方法。
此通用存储类将处理典型的CRUD需求,如果当某个实体类型有特殊的需求时(譬如更为复杂的查询或者排序),你应该创建一个包含此特殊方法的继承类。
【创建单元工作类】
单元工作类只有一个目的:确保多个存储类在使用之时共享同一个数据库上下文实例。那意味着一旦该类完成,你调用SaveChanges方法,这些存储类中相关数据等都自动协调更新。这个类只需要一个Save方法,以及每个实体的属性;每个实体属性返回一个存储类实体,它们都已经被同一个数据库上下文实体类实例化。
在DAL文件夹中,创建一个“UnitOfWork.cs”类,用以下代码对现有代码进行替换:
using System; using ContosoUniversity.Models; namespace ContosoUniversity.DAL { public class UnitOfWork : IDisposable { private SchoolContext context = new SchoolContext(); private GenericRepository<Department> departmentRepository; private GenericRepository<Course> courseRepository; public GenericRepository<Department> DepartmentRepository { get { if (this.departmentRepository == null) { this.departmentRepository = new GenericRepository<Department>(context); } return departmentRepository; } } public GenericRepository<Course> CourseRepository { get { if (this.courseRepository == null) { this.courseRepository = new GenericRepository<Course>(context); } return courseRepository; } } public void Save() { context.SaveChanges(); } private bool disposed = false; protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing) { if (!this.disposed) { if (disposing) { context.Dispose(); } } this.disposed = true; } public void Dispose() { Dispose(true); GC.SuppressFinalize(this); } } }
以上代码为数据库上下文实体以及每个对应的存储类创建了类级别的实体,对于“数据库上下文实体”而言,预先已经被实例化了:
private SchoolContext context = new SchoolContext(); private GenericRepository<Department> departmentRepository; private GenericRepository<Course> courseRepository;
每个存储实例属性都将先检查该实例是否存在——如果不存在的话则立即实例化一个并且把当前的数据库上下文对象传入其中,这也就确保了所有的存储实体对象共享同一个上下文实体对象。
public GenericRepository<Department> DepartmentRepository { get { if (this.departmentRepository == null) { this.departmentRepository = new GenericRepository<Department>(context); } return departmentRepository; } }
Save方法实际是调用了数据库上下文对象的SaveChanges方法。
正如以类级实例化数据库上下文实例的类一样——UnitOfWork类实现了IDisposable接口并销毁这个对象。
【更新Course控制器并应用此单元工作类及相关联的存储类】
用以下代码替换当前在Course控制器中的代码:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Data; using System.Data.Entity; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.Mvc; using ContosoUniversity.Models; using ContosoUniversity.DAL; namespace ContosoUniversity.Controllers { public class CourseController : Controller { private UnitOfWork unitOfWork = new UnitOfWork(); // // GET: /Course/ public ViewResult Index() { var courses = unitOfWork.CourseRepository.Get(includeProperties: "Department"); return View(courses.ToList()); } // // GET: /Course/Details/5 public ViewResult Details(int id) { Course course = unitOfWork.CourseRepository.GetByID(id); return View(course); } // // GET: /Course/Create public ActionResult Create() { PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(); return View(); } [HttpPost] public ActionResult Create(Course course) { try { if (ModelState.IsValid) { unitOfWork.CourseRepository.Insert(course); unitOfWork.Save(); return RedirectToAction("Index"); } } catch (DataException) { //Log the error (add a variable name after DataException) ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists, see your system administrator."); } PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(course.DepartmentID); return View(course); } public ActionResult Edit(int id) { Course course = unitOfWork.CourseRepository.GetByID(id); PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(course.DepartmentID); return View(course); } [HttpPost] public ActionResult Edit(Course course) { try { if (ModelState.IsValid) { unitOfWork.CourseRepository.Update(course); unitOfWork.Save(); return RedirectToAction("Index"); } } catch (DataException) { //Log the error (add a variable name after DataException) ModelState.AddModelError("", "Unable to save changes. Try again, and if the problem persists, see your system administrator."); } PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(course.DepartmentID); return View(course); } private void PopulateDepartmentsDropDownList(object selectedDepartment = null) { var departmentsQuery = unitOfWork.DepartmentRepository.Get( orderBy: q => q.OrderBy(d => d.Name)); ViewBag.DepartmentID = new SelectList(departmentsQuery, "DepartmentID", "Name", selectedDepartment); } // // GET: /Course/Delete/5 public ActionResult Delete(int id) { Course course = unitOfWork.CourseRepository.GetByID(id); return View(course); } // // POST: /Course/Delete/5 [HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")] public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(int id) { Course course = unitOfWork.CourseRepository.GetByID(id); unitOfWork.CourseRepository.Delete(id); unitOfWork.Save(); return RedirectToAction("Index"); } protected override void Dispose(bool disposing) { unitOfWork.Dispose(); base.Dispose(disposing); } } }
这段代码为单元工作类创建了类级的变量UnitOfWork(倘若你使用的是接口,那么你此处无需实例化变量;不过你应当实现两个构造函数的设计模式,这和你为Student存储类所做的工作一样)。
private UnitOfWork unitOfWork = new UnitOfWork();
代码其余部分凡是对于数据库上下文实体的引用全部被改成了对特定存储类的引用,它们借助UnitOfWork实体得以完成;Dispose方法则销毁这个UnitOfWork:
var courses = unitOfWork.CourseRepository.Get(includeProperties: "Department"); // ... Course course = unitOfWork.CourseRepository.GetByID(id); // ... unitOfWork.CourseRepository.Insert(course); unitOfWork.Save(); // ... Course course = unitOfWork.CourseRepository.GetByID(id); // ... unitOfWork.CourseRepository.Update(course); unitOfWork.Save(); // ... var departmentsQuery = unitOfWork.DepartmentRepository.Get( orderBy: q => q.OrderBy(d => d.Name)); // ... Course course = unitOfWork.CourseRepository.GetByID(id); // ... unitOfWork.CourseRepository.Delete(id); unitOfWork.Save(); // ... unitOfWork.Dispose();
运行整个网站,点击Course选项卡:
现在看上去的效果和先前一模一样,其他页面也是如此。
直到目前为止你已经完成了存储类和单元工作类的相关设计,在通用的存储类中你使用了Lambda表达式作为参数,关于更多IQueryable的表达式用法信息,请到MSDN库中参阅 IQueryable(T) Interface (System.Linq) ,下一章你将学习对于更高级情形下的一些处理。
关于其它EntityFramework资源您可以本系列最后一篇末尾处找到。