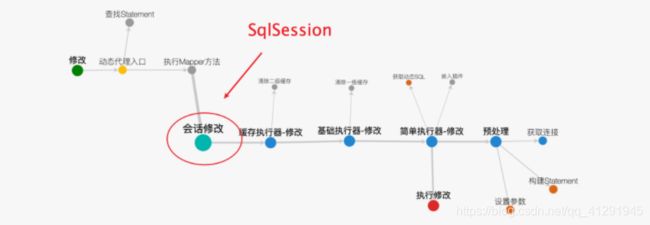
Mybatis 执行流程探究
Mybatis 执行流程探究
先了解一级缓存和二级缓存之后对理解Mybatis执行流程有很大帮助。
- Mybatis 一级缓存
- Mybatis 二级缓存
工程
配置文件
Mybatis 配置文件
<configuration>
configuration>
SQL文件
-- auto Generated on 2020-11-23
-- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user`(
id INT (11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id',
`name` VARCHAR (50) DEFAULT '' COMMENT 'name',
pwd VARCHAR (50) DEFAULT '' COMMENT 'pwd',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT 'user';
Mapper配置文件
<mapper namespace="com.cuiyt.mapper.UserMapper">
<cache>cache>
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.cuiyt.domain.User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="pwd" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="pwd"/>
resultMap>
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
id, `name`, pwd
sql>
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="string">
insert into user(name,pwd)
values (#{name} , #{pwd})
insert>
<select id="selectOne" resultType="com.cuiyt.domain.User" parameterType="string" useCache="true">
select * from user where name = #{name}
select>
mapper>
MybatisContact
public class MybatisContact {
public final static String INSERT = "com.cuiyt.mapper.UserMapper.insertUser";
public final static String SELECT = "com.cuiyt.mapper.UserMapper.selectOne";
public final static RowBounds DEFAULT = RowBounds.DEFAULT;
public final static ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = SimpleExecutor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER;
}
基础配置
使用SqlSessionFactoryBean 来构建SqlSessionFactory
测试程序
@Test
public void tetTx() throws Exception {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("123456");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3309/ssm?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=GMT&useSSL=false");
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
ResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
Interceptor[] plugins = new PageInterceptor[1];
//配置分页插件
PageInterceptor pageInterceptor = new PageInterceptor();
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("helperDialect", "mysql");
props.setProperty("supportMethodsArguments", "true");
props.setProperty("rowBoundsWithCount", "true");
pageInterceptor.setProperties(props);
ArrayList<PageInterceptor> pageInterceptors = new ArrayList<PageInterceptor>();
pageInterceptors.add(pageInterceptor);
factory.setPlugins(pageInterceptors.toArray(plugins));
factory.setConfigLocation(resolver.getResource("classpath:mybatis.xml"));
factory.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources("classpath:UserMapper.xml"));
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
/**
* 1 得到 sqlsessionfactory
* 2 得到 sqlsession
* 3 得到想要的mapper
*/
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = factory.getObject();
SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.selectOne("tx").forEach(System.out::println);
// User user = new User();
// user.setName("tx").setPwd("tx");
// mapper.insertUser("tx", "ts");
}
获取 sqlSessionFactory
使用 afterPropertiesSet(); 方法来构建 sqlSessionFactory
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
afterPropertiesSet()
- 判断 datasource
- sqlsessionfactorybuilder
- configuration、configLocation
是否已经配置加载! 最后开始SqlSessionFactory 的构建工作!
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
// 请记住这个buildSqlSessionFactory(); 方法
// 以及 sqlSessionFactoryBuilder
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);
**这个就是上面说到的 sqlSessionFactoryBuilder **具体的构建过程就是使用的它
private SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
- 具体的构建方法, 可以看到构建的是一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
构建SqlSessionFactory的过程
构建 一个sqlsessionfactory的实例, 默认实现标准的mybatis api 去创建一个基于读的实例
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
// 定义一个 新的配置类
Configuration configuration;
// 定义一个 XML配置解析器
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
// 如果设置了配置
if (this.configuration != null) {
// 得到当前的配置类, 并且把它赋值给上面定义好的配置类
configuration = this.configuration;
// 如果新的配置类中没有设置属性, 进行属性的设置
if (configuration.getVariables() == null) {
configuration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
} else if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
// 同样是设置属性
configuration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties);
}
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
// 走到这里的话, 就意味着没有为 mybatis 设置编码上的配置
// 开始从配置文件中获取配置信息
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
// 把配文件中的信息填充到新建的配置类中
configuration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
// 走到这里, 用户即 没有自己编码设置属性、也没有指定配置文件, 那就会使用mybatis默认的配置
// 直接新建一个 new Configuration();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration");
}
configuration = new Configuration();
if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
// 并且为新建的配置类, 添加属性
configuration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
}
}
// 检查是否配置
if (this.objectFactory != null) {
configuration.setObjectFactory(this.objectFactory);
}
// 检查是否配置
if (this.objectWrapperFactory != null) {
configuration.setObjectWrapperFactory(this.objectWrapperFactory);
}
// 检查是否配置
if (this.vfs != null) {
configuration.setVfsImpl(this.vfs);
}
// 检查是否配置
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
String[] typeAliasPackageArray = tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeAliasesPackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
for (String packageToScan : typeAliasPackageArray) {
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(packageToScan,
typeAliasesSuperType == null ? Object.class : typeAliasesSuperType);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for aliases");
}
}
}
// 检查是否配置
if (!isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
for (Class<?> typeAlias : this.typeAliases) {
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'");
}
}
}
// 检查是否配置 如果添加了插件的配置, 就会遍历,添加所有配置的插件
if (!isEmpty(this.plugins)) {
for (Interceptor plugin : this.plugins) {
configuration.addInterceptor(plugin);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registered plugin: '" + plugin + "'");
}
}
}
if (hasLength(this.typeHandlersPackage)) {
String[] typeHandlersPackageArray = tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeHandlersPackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
for (String packageToScan : typeHandlersPackageArray) {
configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(packageToScan);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for type handlers");
}
}
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
for (TypeHandler<?> typeHandler : this.typeHandlers) {
configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(typeHandler);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Registered type handler: '" + typeHandler + "'");
}
}
}
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {//fix #64 set databaseId before parse mapper xmls
try {
configuration.setDatabaseId(this.databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(this.dataSource));
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed getting a databaseId", e);
}
}
//是否配置缓存
if (this.cache != null) {
configuration.addCache(this.cache);
}
// 是否有Config XML配置构造器,这里在最初时候就有, 并且是在解析配置文件的时候被实例化的
// 下面的解析代码值得看一下, 它会解析我们在配置文件中定义的一些信息
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
// 开始解析配置文件
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
// 设置事务管理器
if (this.transactionFactory == null) {
this.transactionFactory = new SpringManagedTransactionFactory();
}
// 设置mybatis的基本环境
configuration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment, this.transactionFactory, this.dataSource));
// 开始解析mappper文件
if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
// 遍历所有配置的mapper文件
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
// 没有配置 mapper 直接退出
continue;
}
try {
// 新建 mapper XML文件解析器
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 开始解析mapper文件
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified or no matching resources found");
}
}
// 注意这个地方, 上面我们已经说到了具体的构建方法使用的是 sqlSessionFactoryBuilder来构建的
// 这里之后就已经获得了 sqlsessionfactory 类型是 DefaultSqlSessionFactory
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);
}
mybtais 中的配置类
这个基本的配置类中存放着是否使用缓存、自增 id 、栏目标签等配置
public class Configuration {
protected Environment environment;
protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled;
protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true;
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase;
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading;
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys;
protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
protected boolean callSettersOnNulls;
protected boolean useActualParamName = true;
protected boolean returnInstanceForEmptyRow;
}
Environment
这里存放着 数据源、以及事务处理工厂
public final class Environment {
private final String id;
private final TransactionFactory transactionFactory;
private final DataSource dataSource;
}
解析配置文件
解析配置文件信息的代码段
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
解析节点
public XNode evalNode(String expression) {
return evalNode(document, expression);
}
public XNode evalNode(Object root, String expression) {
Node node = (Node) evaluate(expression, root, XPathConstants.NODE);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
return new XNode(this, node, variables);
}
解析方法
- parsed 默认为 false 进入解析的时候就设置为true 配置文件只能解析一下
- 这里主要解析的是 mybatis配置文件中的信息
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
解析 mapper文件的代码段
public void parse() {
// 判断是否已经加载过了
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 标记已经加载过了
configuration.(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
public XNode evalNode(String expression) {
return evalNode(document, expression);
}
public XNode evalNode(Object root, String expression) {
Node node = (Node) evaluate(expression, root, XPathConstants.NODE);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
return new XNode(this, node, variables);
}
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
// 这个入参: context 就是当前xml中编写的内容
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
获得session
代码走到这里,我们以及得到了SqlSessionFactory , 下面将通过它 来获得Sqlsession 对象, 注意它给我们提供了一个默认的执行器
- protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
openSessionFromDataSource
我们还需要 探究一下这个 SqlSession 的类型, 下面直接就可以看到它的类型是DefaultSqlSession, 以及它内部属性的类型 特别是执行器的类型, 它牵扯到后面二级缓存的理解,这个非常的重要。
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 重点开始分析
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
这个方法中我们将获得在 SqlSession中内置执行器的类型
- 在之前的分析中我们以及知道 executorType 的类型是SimpleExecutor
- 实际上返回的是一个CachingExecutor类型的执行器
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
// 此时将选用 我们传递的SIMPLE 类型
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
// 将在这一行代码创建 SimpleExecutor
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//判断是否开启 缓存
// 注意此时是在创建SqlSession的过程中
// 缓存时默认开启的
if (cacheEnabled) {
// 重点在这里
// 它给我们创建了一个 CachingExecutor 执行器
// 而我们之前传递过来的执行器作为了他的参数
// 从这里就可以把分析二级缓存的流程串到一起了
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
动态代理获得 mapper
接下来我们将使用SqlSession 来获得执行查询所用到的getMapper对象
T getMapper(Class type);
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Configuration config;
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
得到代理的mapper
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
执行查询方法
此时我们已经得到了Mapper对象, 接下来将使用Mapper对象进行查询
mapper.selectOne("tx").forEach(System.out::println);
方法拦截
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
// 在使用Mappe执行查询方法的时候会在这里被拦截
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
执行拦截方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
// 可以判断出我们这个方法的类型, 然后走这一行代码
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
executeForMany
- 这里是使用 SqlSession 中的方法来做出查询操作的
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
// 走这一行
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// issue #510 Collections & arrays support
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}
真正干过的地方
List
此时是在 DefaultSqlSession 这个类中, 在上面的探究中我们也知道 SqlSession默认就是使用DefaultSqlSession作为自己的实现。所以executor 这个执行器是CachingExecutor 类型的。那下面的流程就不用探究了,它走的是二级缓存的流程。
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 可以看到
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}