更多的可以参考我的博客,也在陆续更新ing
http://www.hspweb.cn/
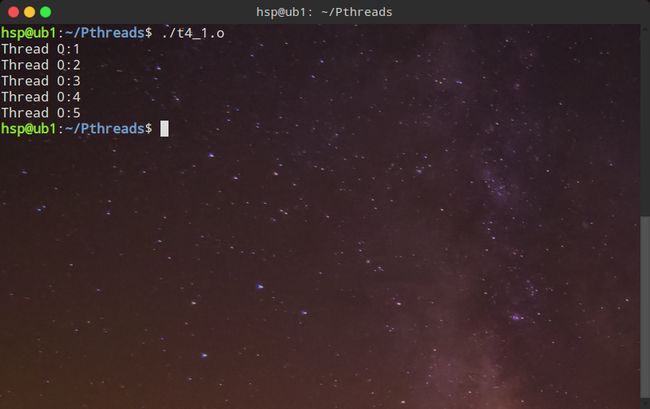
1、用VIM编写创建一个进程的代码,每隔一秒递增输出1-5。
#include
#include
void* fun(void* rank){
int i;
int my_rank=(int)rank;
for(i=1;i<=5;i++){
printf("Thread %d:%d\n",my_rank,i);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(0);
}
int main(){
pthread_t tid1; //the 2 thread identifier
int num1=0;
//create the thread
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,fun,(void *)num1);
//now wait for the thread to exit
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
}
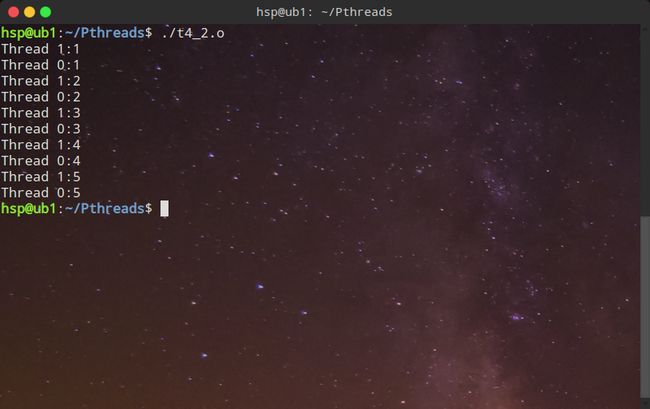
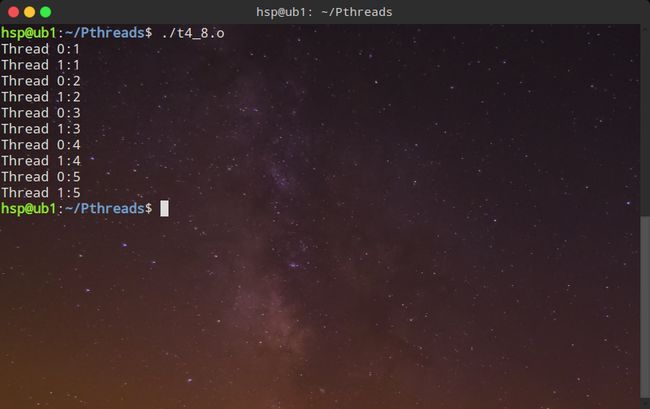
2、用VIM编写创建两个进程的代码,每隔一秒递增输出1-5。
#include
#include
void* fun(void* rank){
int i;
int my_rank=(int)rank;
for(i=1;i<=5;i++){
printf("Thread %d:%d\n",my_rank,i);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(0);
}
int main(){
pthread_t tid1,tid2; //the 2 thread identifier
int num1=0,num2=1;
//create the thread
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,fun,(void *)num1);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,fun,(void *)num2);
//now wait for the thread to exit
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
}
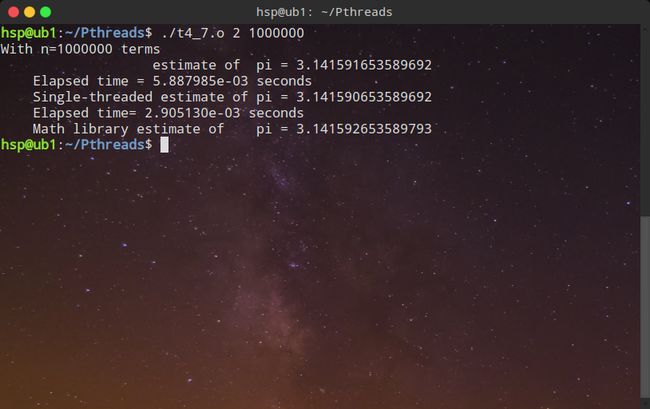
3、用VIM编写创建两个进程计算π的代码,观察竞争条件。
#include
#include
#include
#include
int n,thread_count;
double sum=0.0;
void* Thread_sum(void* rank){
long my_rank=(long)rank;
double factor;
long long i;
long long my_n=n/thread_count;
long long my_first_i=my_n*my_rank;
long long my_last_i=my_first_i+my_n;
if(my_first_i % 2==0 ){
factor=1.0;
}else{
factor=-1.0;
}
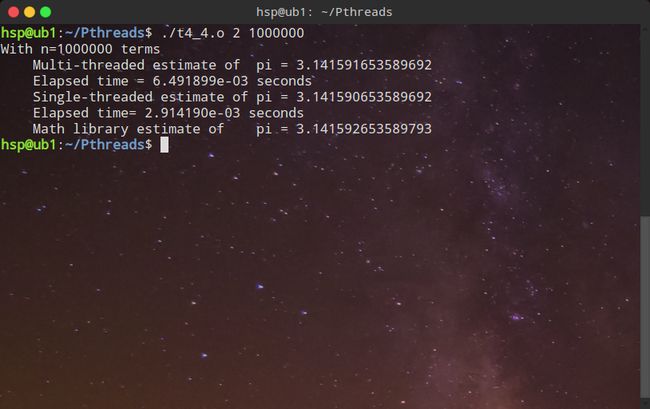
for(i=my_first_i;i 4、用忙等待互斥(严格轮换法)解决计算π的竞争条件。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "timer.h"
int n,thread_count;
double sum=0.0;
int flag=0;
void* Thread_sum(void* rank){
long my_rank=(long)rank;
double factor,my_sum=0.0;
long long i;
long long my_n=n/thread_count;
long long my_first_i=my_n*my_rank;
long long my_last_i=my_first_i+my_n;
if(my_first_i % 2==0 ){
factor=1.0;
}else{
factor=-1.0;
}
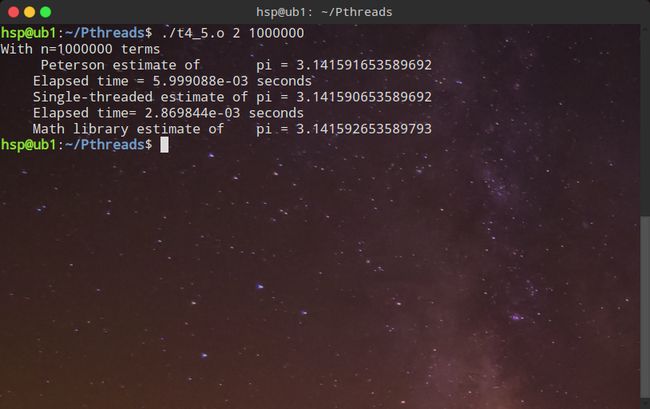
for(i=my_first_i;i 5、用Peterson解法解决计算π的竞争条件。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "timer.h"
int n,thread_count;
double sum=0.0;
int turn;
int interested[2];
void* Thread_sum(void* rank){
long my_rank=(long)rank;
double factor,my_sum=0.0;
long long i;
long long my_n=n/thread_count;
long long my_first_i=my_n*my_rank;
long long my_last_i=my_first_i+my_n;
int other;
other=(my_rank+1)%2;
interested[my_rank]=1;
if(my_first_i % 2==0 ){
factor=1.0;
}else{
factor=-1.0;
}
for(i=my_first_i;i 6、用互斥量解决计算π的竞争条件。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "timer.h"
int n,thread_count;
double sum=0.0;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void* Thread_sum(void* rank){
long my_rank=(long)rank;
double factor,my_sum=0.0;
long long i;
long long my_n=n/thread_count;
long long my_first_i=my_n*my_rank;
long long my_last_i=my_first_i+my_n;
if(my_first_i % 2==0 ){
factor=1.0;
}else{
factor=-1.0;
}
for(i=my_first_i;i 7、用信号量实现互斥解决计算π的竞争条件。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "timer.h"
int n,thread_count;
double sum=0.0;
sem_t sem1,sem2;
void* Thread_sum(void* rank){
long my_rank=(long)rank;
double factor,my_sum=0.0;
long long i;
long long my_n=n/thread_count;
long long my_first_i=my_n*my_rank;
long long my_last_i=my_first_i+my_n;
if(my_first_i % 2==0 ){
factor=1.0;
}else{
factor=-1.0;
}
for(i=my_first_i;i 8、修改信号量的初值,调换上述2中的线程顺序。
#include
#include
#include
sem_t sem1,sem2;
void* fun(void* rank){
int i;
int my_rank=(int)rank;
for(i=1;i<=5;i++){
if(my_rank==0)
sem_wait(&sem1);
else
sem_wait(&sem2);
printf("Thread %d:%d\n",my_rank,i);
sleep(1);
if(my_rank==0)
sem_post(&sem2);
else
sem_post(&sem1);
}
pthread_exit(0);
}
int main(){
pthread_t tid1,tid2; //the 2 thread identifier
int num1=0,num2=1;
sem_init(&sem1,0,1);
sem_init(&sem2,0,0);
//create the thread
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,fun,(void *)num1);
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,fun,(void *)num2);
//now wait for the thread to exit
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
sem_destroy(&sem1);
sem_destroy(&sem2);
}